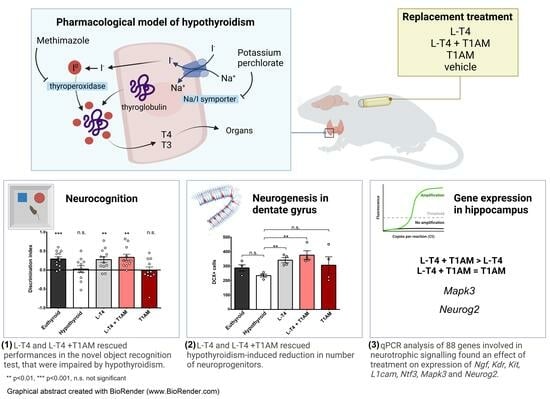
Effect of Combined Levothyroxine (L-T4) and 3-Iodothyronamine (T1AM) Supplementation on Memory and Adult Hippocampal Neurogenesis in a Mouse Model of Hypothyroidism
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Generation of Rodent Model of Hypothyroidism
2.2. Serum Levels of TT4 but Not TT3 Were Different between the Experimental Groups
2.3. Behavioural Correlates of Hypothyroidism and Replacement Treatments
2.4. L-T4 and L-T4+T1AM Restored the Number of DCX+ Cells
2.5. L-T4+T1AM Enhanced the Expression of Genes Involved in Neurogenetic Pathways
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Mouse Model of Pharmacological Hypothyroidism
4.2. HPLC-MS/MS Analysis of Thyroid Hormones
4.3. Behavioural Tests
4.3.1. Elevated Plus Maze Test
4.3.2. Open Field Test
4.3.3. Novel Object Recognition Test
4.3.4. Tail Suspension Test
4.4. Immunofluorescence
4.5. Gene Expression Analysis
4.6. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gothie, J.D.; Demeneix, B.; Remaud, S. Comparative approaches to understanding thyroid hormone regulation of neurogenesis. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2017, 459, 104–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Correia, N.; Mullally, S.; Cooke, G.; Tun, T.K.; Phelan, N.; Feeney, J.; Fitzgibbon, M.; Boran, G.; O’Mara, S.; Gibney, J. Evidence for a specific defect in hippocampal memory in overt and subclinical hypothyroidism. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2009, 94, 3789–3797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gobel, A.; Heldmann, M.; Gottlich, M.; Dirk, A.L.; Brabant, G.; Munte, T.F. Effect of Mild Thyrotoxicosis on Performance and Brain Activations in a Working Memory Task. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0161552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, K.J.; Parsons, T.D.; Whybrow, P.C.; Van Herle, K.; Rasgon, N.; Van Herle, A.; Martinez, D.; Silverman, D.H.; Bauer, M. Verbal memory retrieval deficits associated with untreated hypothyroidism. J. Neuropsychiatry Clin. Neurosci. 2007, 19, 132–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bathla, M.; Singh, M.; Relan, P. Prevalence of anxiety and depressive symptoms among patients with hypothyroidism. Indian J. Endocrinol. Metab. 2016, 20, 468–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bauer, M.; Goetz, T.; Glenn, T.; Whybrow, P.C. The thyroid-brain interaction in thyroid disorders and mood disorders. J. Neuroendocr. 2008, 20, 1101–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montero-Pedrazuela, A.; Venero, C.; Lavado-Autric, R.; Fernandez-Lamo, I.; Garcia-Verdugo, J.M.; Bernal, J.; Guadano-Ferraz, A. Modulation of adult hippocampal neurogenesis by thyroid hormones: Implications in depressive-like behavior. Mol. Psychiatry 2006, 11, 361–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hosseini, M.; Hadjzadeh, M.A.; Derakhshan, M.; Havakhah, S.; Rassouli, F.B.; Rakhshandeh, H.; Saffarzadeh, F. The beneficial effects of olibanum on memory deficit induced by hypothyroidism in adult rats tested in Morris water maze. Arch Pharm. Res. 2010, 33, 463–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alzoubi, K.H.; Gerges, N.Z.; Aleisa, A.M.; Alkadhi, K.A. Levothyroxin restores hypothyroidism-induced impairment of hippocampus-dependent learning and memory: Behavioral, electrophysiological, and molecular studies. Hippocampus 2009, 19, 66–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Artis, A.S.; Bitiktas, S.; Taskin, E.; Dolu, N.; Liman, N.; Suer, C. Experimental hypothyroidism delays field excitatory post-synaptic potentials and disrupts hippocampal long-term potentiation in the dentate gyrus of hippocampal formation and Y-maze performance in adult rats. J. Neuroendocrinol. 2012, 24, 422–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alzoubi, K.H.; Gerges, N.Z.; Alkadhi, K.A. Levothyroxin restores hypothyroidism-induced impairment of LTP of hippocampal CA1: Electrophysiological and molecular studies. Exp. Neurol. 2005, 195, 330–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapoor, R.; Desouza, L.A.; Nanavaty, I.N.; Kernie, S.G.; Vaidya, V.A. Thyroid hormone accelerates the differentiation of adult hippocampal progenitors. J. Neuroendocrinol. 2012, 24, 1259–1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gould, E.; Beylin, A.; Tanapat, P.; Reeves, A.; Shors, T.J. Learning enhances adult neurogenesis in the hippocampal formation. Nat. Neurosci. 1999, 2, 260–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schinder, A.F.; Gage, F.H. A hypothesis about the role of adult neurogenesis in hippocampal function. Physiology 2004, 19, 253–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Migaud, M.; Butruille, L.; Duittoz, A.; Pillon, D.; Batailler, M. Adult neurogenesis and reproductive functions in mammals. Theriogenology 2016, 86, 313–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apple, D.M.; Fonseca, R.S.; Kokovay, E. The role of adult neurogenesis in psychiatric and cognitive disorders. Brain Res. 2017, 1655, 270–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Desouza, L.A.; Ladiwala, U.; Daniel, S.M.; Agashe, S.; Vaidya, R.A.; Vaidya, V.A. Thyroid hormone regulates hippocampal neurogenesis in the adult rat brain. Mol. Cell. Neurosci. 2005, 29, 414–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaker, L.; Bianco, A.C.; Jonklaas, J.; Peeters, R.P. Hypothyroidism. Lancet 2017, 390, 1550–1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biondi, B.; Wartofsky, L. Combination treatment with T4 and T3: Toward personalized replacement therapy in hypothyroidism? J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2012, 97, 2256–2271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gereben, B.; McAninch, E.A.; Ribeiro, M.O.; Bianco, A.C. Scope and limitations of iodothyronine deiodinases in hypothyroidism. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2015, 11, 642–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gullo, D.; Latina, A.; Frasca, F.; Le Moli, R.; Pellegriti, G.; Vigneri, R. Levothyroxine monotherapy cannot guarantee euthyroidism in all athyreotic patients. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e22552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hackenmueller, S.A.; Marchini, M.; Saba, A.; Zucchi, R.; Scanlan, T.S. Biosynthesis of 3-iodothyronamine (T1AM) is dependent on the sodium-iodide symporter and thyroperoxidase but does not involve extrathyroidal metabolism of T4. Endocrinology 2012, 153, 5659–5667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kohrle, J.; Biebermann, H. 3-iodothyronamine—A thyroid hormone metabolite with distinct target profiles and mode of action. Endocr. Rev. 2019, 40, 602–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manni, M.E.; De Siena, G.; Saba, A.; Marchini, M.; Landucci, E.; Gerace, E.; Zazzeri, M.; Musilli, C.; Pellegrini-Giampietro, D.; Matucci, R.; et al. Pharmacological effects of 3-iodothyronamine (T1AM) in mice include facilitation of memory acquisition and retention and reduction of pain threshold. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2013, 168, 354–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landucci, E.; Gencarelli, M.; Mazzantini, C.; Laurino, A.; Pellegrini-Giampietro, D.E.; Raimondi, L. N-(3-Ethoxy-phenyl)-4-pyrrolidin-1-yl-3-trifluoromethyl-benzamide (EPPTB) prevents 3-iodothyronamine (T1AM)-induced neuroprotection against kainic acid toxicity. Neurochem. Int. 2019, 129, 104460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellusci, L.; Laurino, A.; Sabatini, M.; Sestito, S.; Lenzi, P.; Raimondi, L.; Rapposelli, S.; Biagioni, F.; Fornai, F.; Salvetti, A.; et al. New Insights into the Potential Roles of 3-Iodothyronamine (T1AM) and Newly Developed Thyronamine-Like TAAR1 Agonists in Neuroprotection. Front. Pharmacol. 2017, 8, 905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Accorroni, A.; Rutigliano, G.; Sabatini, M.; Frascarelli, S.; Borso, M.; Novelli, E.; Bandini, L.; Ghelardoni, S.; Saba, A.; Zucchi, R.; et al. Exogenous 3-Iodothyronamine Rescues the Entorhinal Cortex from beta-Amyloid Toxicity. Thyroid 2019, 30, 147–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tozzi, F.; Rutigliano, G.; Borsò, M.; Falcicchia, C.; Zucchi, R.; Origlia, N. T1AM-TAAR1 signalling protects against OGD-induced synaptic dysfunction in the entorhinal cortex. Neurobiol. Dis. 2021, 151, 105271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, D.; Zhou, H.; Yang, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Wang, T.; Lv, L.; Zhou, Q.; Yang, Y.; Dong, X.; He, J.; et al. The bidirectional effects of hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism on anxiety- and depression-like behaviors in rats. Horm. Behav. 2015, 69, 106–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buras, A.; Battle, L.; Landers, E.; Nguyen, T.; Vasudevan, N. Thyroid hormones regulate anxiety in the male mouse. Horm. Behav. 2014, 65, 88–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venero, C.; Guadano-Ferraz, A.; Herrero, A.I.; Nordstrom, K.; Manzano, J.; de Escobar, G.M.; Bernal, J.; Vennstrom, B. Anxiety, memory impairment, and locomotor dysfunction caused by a mutant thyroid hormone receptor alpha1 can be ameliorated by T3 treatment. Genes Dev. 2005, 19, 2152–2163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alzoubi, K.H.; Aleisa, A.M.; Alkadhi, K.A. Adult-onset hypothyroidism facilitates and enhances LTD: Reversal by chronic nicotine treatment. Neurobiol. Dis. 2007, 26, 264–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, J.D.; Stern, R.A.; Flashman, L.A. Cognitive and neuropsychiatric aspects of subclinical hypothyroidism: Significance in the elderly. Curr. Psychiatry Rep. 2003, 5, 384–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganguli, M.; Burmeister, L.A.; Seaberg, E.C.; Belle, S.; DeKosky, S.T. Association between dementia and elevated TSH: A community-based study. Biol. Psychiatry 1996, 40, 714–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stern, R.A.; Davis, J.D.; Rogers, B.L.; Smith, K.E.; Harrington, C.J.; Ott, B.R.; Jackson, I.M.; Prange, A.J., Jr. Preliminary study of the relationship between thyroid status and cognitive and neuropsychiatric functioning in euthyroid patients with Alzheimer dementia. Cogn. Behav. Neurol. 2004, 17, 219–223. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- James, T.D.; Moffett, S.X.; Scanlan, T.S.; Martin, J.V. Effects of acute microinjections of the thyroid hormone derivative 3-iodothyronamine to the preoptic region of adult male rats on sleep, thermoregulation and motor activity. Horm. Behav. 2013, 64, 81–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polini, B.; Ricardi, C.; Bertolini, A.; Carnicelli, V.; Rutigliano, G.; Saponaro, F.; Zucchi, R.; Chiellini, G. T1AM/TAAR1 System Reduces Inflammatory Response and beta-Amyloid Toxicity in Human Microglial HMC3 Cell Line. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 11569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiellini, G.; Erba, P.; Carnicelli, V.; Manfredi, C.; Frascarelli, S.; Ghelardoni, S.; Mariani, G.; Zucchi, R. Distribution of exogenous [125I]-3-iodothyronamine in mouse in vivo: Relationship with trace amine-associated receptors. J. Endocrinol. 2012, 213, 223–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, M.; Zhu, P.; Hu, S.; Wang, W.; Su, Z.; Guan, J.; Sun, C.; Zheng, W. Notch1 Signaling Activation Contributes to Adult Hippocampal Neurogenesis Following Traumatic Brain Injury. Med. Sci. Monit. 2017, 23, 5480–5487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samuels, I.S.; Karlo, J.C.; Faruzzi, A.N.; Pickering, K.; Herrup, K.; Sweatt, J.D.; Saitta, S.C.; Landreth, G.E. Deletion of ERK2 mitogen-activated protein kinase identifies its key roles in cortical neurogenesis and cognitive function. J. Neurosci. 2008, 28, 6983–6995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paquin, A.; Barnabe-Heider, F.; Kageyama, R.; Miller, F.D. CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein phosphorylation biases cortical precursors to generate neurons rather than astrocytes in vivo. J. Neurosci. 2005, 25, 10747–10758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoefig, C.S.; Zucchi, R.; Köhrle, J. Thyronamines and derivatives: Physiological relevance, pharmacological actions and future research directions. Thyroid 2016, 26, 1656–1673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Efimova, E.V.; Kuvarzin, S.R.; Mor, M.S.; Katolikova, N.V.; Shemiakova, T.S.; Razenkova, V.; Ptukha, M.; Kozlova, A.A.; Murtazina, R.Z.; Smirnova, D.; et al. Trace Amine-Associated Receptor 2 Is Expressed in the Limbic Brain Areas and Is Involved in Dopamine Regulation and Adult Neurogenesis. Front. Behav. Neurosci. 2022, 16, 847410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dodd, S.; Carvalho, A.F.; Puri, B.K.; Maes, M.; Bortolasci, C.C.; Morris, G.; Berk, M. Trace Amine-Associated Receptor 1 (TAAR1): A new drug target for psychiatry? Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2021, 120, 537–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borowsky, B.; Adham, N.; Jones, K.A.; Raddatz, R.; Artymyshyn, R.; Ogozalek, K.L.; Durkin, M.M.; Lakhlani, P.P.; Bonini, J.A.; Pathirana, S.; et al. Trace amines: Identification of a family of mammalian G protein–coupled receptors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 8966–8971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindemann, L.; Ebeling, M.; Kratochwil, N.A.; Bunzow, J.R.; Grandy, D.K.; Hoener, M.C. Trace amine-associated receptors form structurally and functionally distinct subfamilies of novel G protein-coupled receptors. Genomics 2005, 85, 372–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grandy, D.K. Trace amine-associated receptor 1-Family archetype or iconoclast? In Pharmacology and Therapeutics; NIH Public Access: Bethesda, MD, USA, 2007; Volume 116, pp. 355–390. [Google Scholar]
- Underhill, S.M.; Hullihen, P.D.; Chen, J.; Fenollar-Ferrer, C.; Rizzo, M.A.; Ingram, S.L.; Amara, S.G. Amphetamines signal through intracellular TAAR1 receptors coupled to Galpha13 and GalphaS in discrete subcellular domains. Mol. Psychiatry 2021, 26, 1208–1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bradaia, A.; Trube, G.; Stalder, H.; Norcross, R.D.; Ozmen, L.; Wettstein, J.G.; Pinard, A.; Buchy, D.; Gassmann, M.; Hoener, M.C.; et al. The selective antagonist EPPTB reveals TAAR1-mediated regulatory mechanisms in dopaminergic neurons of the mesolimbic system. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 20081–20086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Munhall, A.C.; Johnson, S.W. Dopamine Evokes a Trace Amine Receptor-dependent Inward Current that is Regulated by AMP Kinase in Substantia Nigra Dopamine Neurons. Neuroscience 2020, 427, 77–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harmeier, A.; Obermueller, S.; Meyer, C.A.; Revel, F.G.; Buchy, D.; Chaboz, S.; Dernick, G.; Wettstein, J.G.; Iglesias, A.; Rolink, A.; et al. Trace amine-associated receptor 1 activation silences GSK3beta signaling of TAAR1 and D2R heteromers. Eur. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2015, 25, 2049–2061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Mantas, I.; Alvarsson, A.; Yoshitake, T.; Shariatgorji, M.; Pereira, M.; Nilsson, A.; Kehr, J.; Andren, P.E.; Millan, M.J.; et al. Striatal Tyrosine Hydroxylase Is Stimulated via TAAR1 by 3-Iodothyronamine, But Not by Tyramine or beta-Phenylethylamine. Front. Pharmacol. 2018, 9, 166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panici, J.A.; Harper, J.M.; Miller, R.A.; Bartke, A.; Spong, A.; Masternak, M.M. Early life growth hormone treatment shortens longevity and decreases cellular stress resistance in long-lived mutant mice. FASEB J. 2010, 24, 5073–5079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saba, A.; Donzelli, R.; Colligiani, D.; Raffaelli, A.; Nannipieri, M.; Kusmic, C.; Dos Remedios, C.G.; Simonides, W.S.; Iervasi, G.; Zucchi, R. Quantification of thyroxine and 3,5,3′-triiodo-thyronine in human and animal hearts by a novel liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry method. Horm. Metab. Res. 2014, 46, 628–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, T.P.; Gullotti, D.M.; Hernandez, P.; O’Brien, W.T.; Capehart, B.P.; Morrison, B., 3rd; Bass, C.; Eberwine, J.E.; Abel, T.; Meaney, D.F. An open-source toolbox for automated phenotyping of mice in behavioral tasks. Front. Behav. Neurosci. 2014, 8, 349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walf, A.A.; Frye, C.A. The use of the elevated plus maze as an assay of anxiety-related behavior in rodents. Nat. Protoc. 2007, 2, 322–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cruz, A.P.; Frei, F.; Graeff, F.G. Ethopharmacological analysis of rat behavior on the elevated plus-maze. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 1994, 49, 171–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, C.; File, S.E. The influence of open arm ledges and maze experience in the elevated plus-maze. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 1996, 54, 31–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodgers, R.J. Animal models of ‘anxiety’: Where next? Behav. Pharmacol. 1997, 8, 477–496, discussion 497–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





| Experiment | Hypothyroid | Euthyroid | L-T4 | L-T4+T1AM | T1AM | F (DFn, DFd), p |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EPM: | ||||||
| % of time spent in open arms | 7.51 ± 0.99 | 9.81 ± 2.85 | 11.83 ± 2.65 | 9.34 ± 1.67 | 7.06 ± 1.77 | 0.79 (4, 57), 0.79 |
| n of entries into open arms | 3.17 ± 0.49 | Mdn = 3 IQR = 2–4 | 4.08 ± 0.73 | 2.92 ± 0.43 | 2.33 ± 0.51 | 3.69, 0.45 a |
| n of entries into closed arms | 7.00 ± 0.73 | 9.67 ± 0.64 | 8.83 ± 0.76 | 7.69 ± 0.87 | 8.58 ± 0.72 | 1.87 (4, 56), 0.13 |
| n of total head dips | 11.67 ± 2.55 | Mdn = 15 IQR = 10–20 | 13.25 ± 2.23 | 11.23 ± 2.09 | 12.25 ± 2.10 | 2.39, 0.66 a |
| n of unprotected head dips | 4.30 ± 0.89 | 5.38 ± 2.40 | 5.50 ± 1.39 | 4.10 ± 1.00 | 3.50 ± 0.98 | 0.29 (4, 48), 0.89 |
| n of protected head dips | 9.70 ± 1.71 | 11.23 ± 1.21 | 10.40 ± 1.17 | 10.50 ± 1.21 | 11.2 ± 0.87 | 0.25 (4, 48), 0.25 |
| n of end arm explorations | 1.10 ± 0.35 | 1.31 ± 0.41 | 1.10 ± 0.50 | 0.45 ± 0.21 | 0.90 ± 0.35 | 0.77 (4, 49), 0.55 |
| n of stretch attend postures | 2.60 ± 0.65 | 6.69 ± 1.07 | 6.40 ± 1.51 | 6.50 ± 1.81 | 4.60 ± 0.87 | 1.96 (4, 48), 0.12 |
| OF: | ||||||
| total distance travelled (m) | 789.1 ± 79.61 | 996.8 ± 65.35 | 846.7 ± 90.59 | 943.6 ± 84.08 | Mdn = 901.9 IQR = 694.8–1025 | 3.77, 0.44 a |
| time spent in open vs. closed arms (s) | Mdn = 0.81 IQR = 0.70–0.86 | 0.79 ± 0.02 | 0.85 ± 0.02 | 0.79 ± 0.04 | 0.83 ± 0.04 | 2.97, 0.56 a |
| ORT: | ||||||
| discrimination index | 0.02 ± 0.09 | 0.29 ± 0.06 | 0.27 ± 0.08 | 0.34 ± 0.08 | −0.01 ± 0.10 | 3.15 (3, 42), 0.03 |
| TST: | ||||||
| % of immobility time | 61.86 ± 1.73 | 59.03 ± 2.52 | 62.13 ± 2.83 | 62.1 ± 2.88 | 60.72 ± 1.84 | 0.32 (4, 43), 0.86 |
| Variable | Behavioural Interpretation |
|---|---|
| Time in open arms (%) | Anxiety-related |
| n of entries into open arms | Anxiety-related |
| n of entries into closed arms | Spontaneous locomotor activity |
| Total n of head dips | Anxiety-related |
| n of unprotected head dips | Anxiety-related |
| n of protected head dips | Decision-making; assessment of height and openness |
| n of end-arm explorations | Anxiety-related |
| n of SAPs | Risk-assessment |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rutigliano, G.; Bertolini, A.; Grittani, N.; Frascarelli, S.; Carnicelli, V.; Ippolito, C.; Moscato, S.; Mattii, L.; Kusmic, C.; Saba, A.; et al. Effect of Combined Levothyroxine (L-T4) and 3-Iodothyronamine (T1AM) Supplementation on Memory and Adult Hippocampal Neurogenesis in a Mouse Model of Hypothyroidism. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 13845. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241813845
Rutigliano G, Bertolini A, Grittani N, Frascarelli S, Carnicelli V, Ippolito C, Moscato S, Mattii L, Kusmic C, Saba A, et al. Effect of Combined Levothyroxine (L-T4) and 3-Iodothyronamine (T1AM) Supplementation on Memory and Adult Hippocampal Neurogenesis in a Mouse Model of Hypothyroidism. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2023; 24(18):13845. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241813845
Chicago/Turabian StyleRutigliano, Grazia, Andrea Bertolini, Nicoletta Grittani, Sabina Frascarelli, Vittoria Carnicelli, Chiara Ippolito, Stefania Moscato, Letizia Mattii, Claudia Kusmic, Alessandro Saba, and et al. 2023. "Effect of Combined Levothyroxine (L-T4) and 3-Iodothyronamine (T1AM) Supplementation on Memory and Adult Hippocampal Neurogenesis in a Mouse Model of Hypothyroidism" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24, no. 18: 13845. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241813845
APA StyleRutigliano, G., Bertolini, A., Grittani, N., Frascarelli, S., Carnicelli, V., Ippolito, C., Moscato, S., Mattii, L., Kusmic, C., Saba, A., Origlia, N., & Zucchi, R. (2023). Effect of Combined Levothyroxine (L-T4) and 3-Iodothyronamine (T1AM) Supplementation on Memory and Adult Hippocampal Neurogenesis in a Mouse Model of Hypothyroidism. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(18), 13845. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241813845