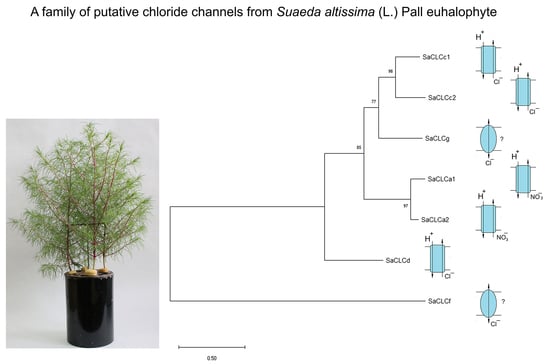
Chloride Channel Family in the Euhalophyte Suaeda altissima (L.) Pall: Cloning of Novel Members SaCLCa2 and SaCLCc2, General Characterization of the Family
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Plant Material
4.2. Extraction of Total RNA from Plant Material and Synthesis of First Strand cDNA
4.3. Cloning of SaCLCa2 and SaCLCc2
4.4. Heterologous Expression of the SaCLCa2 and SaCLCc2 Genes in Δgef1 Yeast Mutant
4.5. Site-Directed Mutagenesis of SaCLCa2(C544T)
4.6. Quantitative Analysis of SaCLCa2 and SaCLCc2 Transcripts in S. altissima Organs
4.7. Primer Design
4.8. Bioinformatic Analysis of Amino Acid Sequences
4.9. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Schütze, P.; Freitag, H.; Weising, K. An integrated molecular and morphological study of the subfamily Suaedoideae Ulbr. (Chenopodiaceae). Plant Syst. Evol. 2003, 239, 257–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Shao, X.; Zhang, W.; Sun, T.; Ding, Y.; Lin, Z.; Li, Y. Genus Suaeda: Advances in Phytology, Chemistry, Pharmacology and Clinical Application (1895–2021). Pharmacol. Res. 2022, 179, 106203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flowers, T.J. Salt Tolerance in the Halophyte Suaeda maritima (L.) Dum: The effect of sodium chloride on growth, respiration, and soluble enzymes in a comparative study with Pisum sativum (L.). J. Exp. Botany. 1972, 23, 310–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lun’kov, R.V.; Andreev, I.M.; Myasoedov, N.A.; Khailova, G.F.; Kurkova, E.B.; Balnokin, Y.V. Functional identification of H+-ATPase and Na+/H + antiporter in the plasma membrane isolated from the root cells of salt-accumulating halophyte Suaeda altissima. Russ. J. Plant Physiol. 2005, 52, 635–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balnokin, Y.V.; Kotov, A.A.; Myasoedov, N.A.; Khailova, G.F.; Kurkova, E.B.; Lun’kov, R.V.; Kotova, L.M. Involvement of long-distance Na+ transport in maintaining water potential gradient in the medium-root-leaf system of a halophyte Suaeda altissima. Russ. J. Plant Physiol. 2005, 52, 489–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balnokin, Y.V.; Kurkova, E.B.; Khalilova, L.A.; Myasoedov, N.A.; Yusufov, A.G. Pinocytosis in the root cells of a salt-accumulating halophyte Suaeda altissima and its possible involvement in chloride transport. Russ. J. Plant Physiol. 2007, 54, 797–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flowers, T.J.; Colmer, T.D. Salinity tolerance in halophytes. New Phytol. 2008, 179, 945–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shuvalov, A.V.; Orlova, J.V.; Khalilova, L.A.; Myasoedov, N.A.; Andreev, I.M.; Belyaev, D.V.; Balnokin, Y.V. Evidence for the functioning of a Cl−/H+ antiporter in the membranes isolated from root cells of the halophyte Suaeda altissima and enriched with Golgi membranes. Russ. J. Plant Physiol. 2015, 62, 45–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, W.; Wu, W.; Zhang, N.; Wang, L.; Wang, Y.; Wang, B.; Lan, Q.; Wang, Y. Research Advances on Molecular Mechanism of Salt Tolerance in Suaeda. Biology 2022, 11, 1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flowers, T.J.; Galal, H.K.; Bromham, L. Evolution of halophytes: Multiple origins of salt tolerance in land plants. Funct. Plant Biol. 2010, 37, 604–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shabala, S. Learning from halophytes: Physiological basis and strategies to improve abiotic stress tolerance in crops. Ann. Bot. 2013, 112, 1209–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flowers, T.J.; Munns, R.; Colmer, T.D. Sodium chloride toxicity and the cellular basis of salt tolerance in halophytes. Ann. Bot. 2015, 115, 419–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tester, M.; Davenport, R. Na+ tolerance and Na+ transport in higher plants. Ann. Bot. 2003, 91, 503–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, B.; Davenport, R.J.; Volkov, V.; Amtmann, A. Low unidirectional sodium influx into root cells restricts net sodium accumulation in Thellungiella halophila, a salt-tolerant relative of Arabidopsis thaliana. J. Exp. Bot. 2006, 57, 1161–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Teakle, N.L.; Tyerman, S.D. Mechanisms of Cl- transport contributing to salt tolerance. Plant Cell Environ. 2010, 33, 566–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamaguchi, T.; Hamamoto, S.; Uozumi, N. Sodium transport system in plant cells. Front. Plant Sci. 2013, 4, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jentsch, T.J.; Friedrich, T.; Schriever, A.; Yamada, H. The CLC chloride channel family. Pflugers Arch. Eur. J. Physiol. 1999, 437, 783–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, C. ClC chloride channels viewed through a transporter lens. Nature 2006, 440, 484–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marmagne, A.; Vinauger-Douard, M.; Monachello, D.; De Longevialle, A.F.; Charon, C.; Allot, M.; Rappaport, F.; Wollman, F.A.; Barbier-Brygoo, H.; Ephritikhine, G. Two members of the Arabidopsis CLC (chloride channel) family, AtCLCe and AtCLCf, are associated with thylakoid and golgi membranes, respectively. J. Exp. Bot. 2007, 58, 3385–3393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Barbier-Brygoo, H.; De Angeli, A.; Filleur, S.; Frachisse, J.-M.; Gambale, F.; Thomine, S.; Wege, S. Anion channels/transporters in plants: From molecular bases to regulatory networks. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2011, 62, 25–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poroca, D.R.; Pelis, R.M.; Chappe, V.M. ClC channels and transporters: Structure, physiological functions, and implications in human chloride channelopathies. Front. Pharmacol. 2017, 8, 151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hodin, J.; Lind, C.; Marmagne, A.; Espagne, C.; Bianchi, M.W.; De Angeli, A.; Abou-Choucha, F.; Bourge, M.; Chardon, F.; Thomine, S.; et al. Proton exchange in the nitrate vacuolar transporter AtCLCa is required for growth and nitrogen use efficiency. The Plant Cell 2022, koac325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nedelyaeva, O.I.; Shuvalov, A.V.; Balnokin, Y.V. Chloride Channels and Transporters of the CLC Family in Plants. Russ. J. Plant Physiol. 2020, 67, 767–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Angeli, A.; Monachello, D.; Ephritikhine, G.; Frachisse, J.M.; Thomine, S.; Gambale, F.; Barbier-Brygoo, H. The nitrate/proton antiporter AtCLCa mediates nitrate accumulation in plant vacuoles. Nature 2006, 442, 939–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- von der Fecht-Bartenbach, J.; Bogner, M.; Dynowski, M.; Ludewig, U. CLC-b-mediated NO3 -/H+ exchange across the tonoplast of Arabidopsis vacuoles. Plant Cell Physiol. 2010, 51, 960–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jentsch, T.J.; Pusch, M. CLC chloride channels and transporters: Structure, function, physiology, and disease. Physiol. Rev. 2018, 98, 1493–1590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wege, S.; De Angeli, A.; Droillard, M.J.; Kroniewicz, L.; Merlot, S.; Cornu, D.; Gambale, F.; Martinoia, E.; Barbier-Brygoo, H.; Thomine, S.; et al. Phosphorylation of the vacuolar anion exchanger AtCLCa is required for the stomatal response to abscisic acid. Sci. Signal. 2014, 7, ra65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demes, E.; Besse, L.; Cubero-Font, P.; Satiat-Jeunemaitre, B.; Thomine, S.; Angeli, A. De Dynamic measurement of cytosolic pH and [NO3] uncovers the role of the vacuolar transporter AtCLCa in cytosolic pH homeostasis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 15343–15353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbier-Brygoo, H.; Vinauger, M.; Colcombet, J.; Ephritikhine, G.; Frachisse, J.M.; Maurel, C. Anion channels in higher plants: Functional characterization, molecular structure and physiological role. Biochim. Biophys. Acta—Biomembr. 2000, 1465, 199–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zifarelli, G.; Pusch, M. CLC transport proteins in plants. FEBS Lett. 2010, 584, 2122–2127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nedelyaeva, O.I.; Shuvalov, A.V.; Mayorova, O.V.; Yurchenko, A.A.; Popova, L.G.; Balnokin, Y.V.; Karpichev, I.V. Cloning and functional analysis of SaCLCc1, a gene belonging to the chloride channel family (CLC), from the halophyte Suaeda altissima (L.) Pall. Dokl. Biochem. Biophys. 2018, 481, 186–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nedelyaeva, O.I.; Shuvalov, A.V.; Karpichev, I.V.; Beliaev, D.V.; Myasoedov, N.A.; Khalilova, L.A.; Khramov, D.E.; Popova, L.G.; Balnokin, Y.V. Molecular cloning and characterisation of SaCLCa1, a novel protein of the chloride channel (CLC) family from the halophyte Suaeda altissima (L.) Pall. J. Plant Physiol. 2019, 240, 152995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nedelyaeva, O.I.; Popova, L.G.; Volkov, V.S.; Balnokin, Y.V. Molecular Cloning and Characterization of SaCLCd, SaCLCf, and SaCLCg, Novel Proteins of the Chloride Channel Family (CLC) from the Halophyte Suaeda altissima (L.) Pall. Plants 2022, 11, 409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- López-Rodríguez, A.; Cárabez Trejo, A.; Coyne, L.; Halliwell, R.F.; Miledi, R.; Martínez-Torres, A. The product of the gene GEF1 of Saccharomyces cerevisiae transports Cl—Across the plasma membrane. FEMS Yeast Res. 2007, 7, 1218–1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shuvalov, A.V.; Yurchenko, A.A.; Nedelyaeva, O.I.; Myasoedov, N.A.; Karpichev, I.V.; Khalilova, L.A.; Popova, L.G.; Balnokin, Y.V. Identification of Some Anion Transporter Genes in the Halophyte Suaeda altissima (L.) Pall. and Their Expression under Nitrate Deficiency and Salinity. Russ. J. Plant Physiol. 2021, 68, 873–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hechenberger, M.; Schwappach, B.; Fischer, W.N.; Frommer, W.B.; Jentsch, T.J.; Steinmeyer, K. A family of putative chloride channels from Arabidopsis and functional complementation of a yeast strain with a CLC gene disruption. J. Biol. Chem. 1996, 271, 33632–33638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dutzler, R. The structural basis of ClC chloride channel function. Trends Neurosci. 2004, 27, 315–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zifarelli, G.; Pusch, M. Conversion of the 2 Cl-/1 H+ antiporter ClC-5 in a NO3-/H+ antiporter by a single point mutation. EMBO J. 2009, 28, 175–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wege, S.; Jossier, M.; Filleur, S.; Thomine, S.; Barbier-Brygoo, H.; Gambale, F.; De Angeli, A. The proline 160 in the selectivity filter of the Arabidopsis NO 3-/H+ exchanger AtCLCa is essential for nitrate accumulation in planta. Plant J. 2010, 63, 861–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcote, M.J.; Sancho-Andrés, G.; Soriano-Ortega, E.; Aniento, F. Sorting signals for PIN1 trafficking and localization. Plant Signal. Behav. 2016, 11, e1212801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishimura, K.; Matsunami, E.; Yoshida, S.; Kohata, S.; Yamauchi, J.; Jisaka, M.; Nagaya, T.; Yokota, K.; Nakagawa, T. The tyrosine-sorting motif of the vacuolar sorting receptor VSR4 from Arabidopsis thaliana, which is involved in the interaction between VSR4 and AP1M2, μ1-adaptin type 2 of clathrin adaptor complex 1 subunits, participates in the post-Golgi sorting of VS. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2016, 80, 694–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Müdsam, C.; Wollschläger, P.; Sauer, N.; Schneider, S. Sorting of Arabidopsis NRAMP3 and NRAMP4 depends on adaptor protein complex AP4 and a dileucine-based motif. Traffic 2018, 19, 503–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yamamoto, M.; Nishio, T.; Nasrallah, J.B. Activation of self-incompatibility signaling in transgenic Arabidopsis thaliana is independent of AP2-based clathrin-mediated endocytosis. G3 Genes Genomes Genet. 2018, 8, 2231–2239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, D.; Kumar, R.; Claus, L.A.N.; Johnson, A.J.; Siao, W.; Vanhoutte, I.; Wang, P.; Bender, K.W.; Yperman, K.; Martins, S.; et al. Endocytosis of brassinosteroid insensitive1 is partly driven by a canonical tyr-based motif. Plant Cell 2020, 32, 3598–3612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arora, D.; van Damme, D. Motif-based endomembrane trafficking. Plant Physiol. 2021, 186, 221–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaxiola, R.A.; Yuan, D.S.; Klausner, R.D.; Fink, G.R. The yeast CLC chloride channel functions in cation homeostasis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 4046–4050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Robinson, S.P.; Downton, W.J.S. Potassium, sodium and chloride ion concentrations in leaves and isolated chloroplasts of the halophyte Suaeda australis R. Br. Aust. J. Plant Physiol. 1985, 12, 471–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greene, J.R.; Brown, N.H.; DiDomenico, B.J.; Kaplan, J.; Eide, D.J. The GEF1 gene of Saccharomyces cerevisiae encodes an integral membrane protein; mutations in which have effects on respiration and iron-limited growth. Mol. Gen. Genet. 1993, 241, 542–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Accardi, A.; Walden, M.; Nguitragool, W.; Jayaram, H.; Williams, C.; Miller, C. Separate ion pathways in a Cl–/H+ exchanger. J. Gen. Physiol. 2005, 126, 563–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Robinson, M.S. Adaptable adaptors for coated vesicles. Trends Cell Biol. 2004, 14, 167–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guzman, R.E.; Miranda-Laferte, E.; Franzen, A.; Fahlke, C. Neuronal ClC-3 splice variants differ in subcellular localizations, but mediate identical transport functions. J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 290, 25851–25862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Scholl, S.; Hillmer, S.; Krebs, M.; Schumacher, K. ClCd and ClCf act redundantly at the trans -Golgi network/early endosome and prevent acidification of the Golgi stack. J. Cell Sci. 2021, 134, jcs258807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rubinigg, M.; Posthumus, F.; Ferschke, M.; Elzenga, J.T.M.; Stulen, I. Effects of NaCl salinity on 15N-nitrate fluxes and specific root length in the halophyte Plantago maritima L. Plant Soil 2003, 250, 201–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.; Ding, X.; Feng, G.; Zhang, F. Nutritional and osmotic roles of nitrate in a euhalophyte and a xerophyte in saline conditions. New Phytol. 2006, 171, 357–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kudo, N.; Fujiyama, H. Responses of halophyte Salicornia bigelovii to different forms of nitrogen source. Pedosphere 2010, 20, 311–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, J.F.; Tian, C.Y.; Feng, G. Effects of sodium on nitrate uptake and osmotic adjustment of Suaeda physophora. J. Arid Land 2010, 2, 190–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, Z.; Li, X.; Hao, J.; Winston, J.H.; Weinman, S.A. The ClC-3 chloride transport protein traffics through the plasma membrane via interaction of an N-terminal dileucine cluster with clathrin. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 29022–29031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yuorieva, N.O.; Voronkov, A.S.; Tereshonok, D.V.; Osipova, E.S.; Platonova, E.V.; Belyaev, D.V. An assay for express screening of potato transformants by GFP fluorescence. Moscow Univ. Biol. Sci. Bull. 2018, 73, 69–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerasimov, A.S.; Zeinalov, O.A.; El’darov, M.A.; Shul’ga, A.A. Biosynthesis of human β2-adrenergic receptor in methylotrophic yeast Pichia pastoris and its purification. Mol. Biol. 2012, 46, 279–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eldarov, M.A.; Baranov, M.V.; Dumina, M.V.; Shgun, A.A.; Andreeva, N.A.; Trilisenko, L.V.; Kulakovskaya, T.V.; Ryasanova, L.P.; Kulaev, I.S. Polyphosphates and exopolyphosphatase activities in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae under overexpression of homologous and heterologous PPN1 genes. Biochem. 2013, 78, 946–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sambrook, J.; Fritsch, E.F.; Maniatis, T. Molecular Cloning: A Laboratory Manual; Cold Spring Harb Lab Press: New York, NY, USA, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Jones, D.T.; Taylor, W.R.; Thornton, J.M. The rapid generation of mutation data matrices from sequences. Bioinformatics 1992, 8, 275–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]








| SaCLCa1 | SaCLCa2 | SaCLCc1 | SaCLCc2 | SaCLCd | SaCLCf | SaCLCg | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| mRNA, complete cds (GenBank ID) | KX013489.1 | OM994378 | MG670589.1 | OM994379 | OK626332.1 | OK626333.1 | OK626334.1 |
| Number of amino acids | 811 | 800 | 791 | 708 | 793 | 587 | 776 |
| Subunit size (kDa) | 89.5 | 88.2 | 87.0 | 77.5 | 87.6 | 62.3 | 85.8 |
| pI * | 8.55 ± 0.09 | 8.48 ± 0.07 | 7.91 ± 0.35 | 7.91 ± 0.11 | 8.15 ± 0.12 | 6.62 ± 0.33 | 8.07 ± 0.13 |
| GRAVY index * | 0.209 | 0.272 | 0.314 | 0.385 | 0.202 | 0.249 | 0.395 |
| Subcellular localization ** | vacuole (p = 0.82 ± 0.1) | vacuole (p = 0.77 ± 0.0) | vacuole (p = 0.82 ± 0.1) | vacuole (p = 0.75 ± 0.1) | vacuole (p = 0.67 ± 0.1) | vacuole/mitochondrion (p = 0.34 ± 0.08/ p = 0.17 ± 0.02) | vacuole (p = 0.64 ± 0.07) |
| The CLC proteins of A. thaliana with highest homology scores | AtCLCb (75.33% Identity) | AtCLCb (77.23% Identity) | AtCLCc (69.60% Identity) | AtCLCc (75.04% Identity) | AtCLCd (79.75% Identity) | AtCLCf (70.44% Identity) | AtCLCg (71.09% Identity) |
| Function | NO3–/H+-exchange | NO3–/H+- exchange | Cl−/H+- exchange | Cl−/H+- exchange? | Cl−/H+- exchange | Cl−-channel? | Cl−-channel? |
| Selectivity filter | GPGIP | GPGIP | GSGIP | GSGIP | GSGIP | SSKSSQ | GSGIP |
| E148 (Eg) *** | E | E | E | E | E | E | A |
| E203 (Ep) *** | E | E | E | E | E | T | E |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nedelyaeva, O.I.; Popova, L.G.; Khramov, D.E.; Volkov, V.S.; Balnokin, Y.V. Chloride Channel Family in the Euhalophyte Suaeda altissima (L.) Pall: Cloning of Novel Members SaCLCa2 and SaCLCc2, General Characterization of the Family. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 941. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24020941
Nedelyaeva OI, Popova LG, Khramov DE, Volkov VS, Balnokin YV. Chloride Channel Family in the Euhalophyte Suaeda altissima (L.) Pall: Cloning of Novel Members SaCLCa2 and SaCLCc2, General Characterization of the Family. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2023; 24(2):941. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24020941
Chicago/Turabian StyleNedelyaeva, Olga I., Larissa G. Popova, Dmitrii E. Khramov, Vadim S. Volkov, and Yurii V. Balnokin. 2023. "Chloride Channel Family in the Euhalophyte Suaeda altissima (L.) Pall: Cloning of Novel Members SaCLCa2 and SaCLCc2, General Characterization of the Family" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24, no. 2: 941. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24020941
APA StyleNedelyaeva, O. I., Popova, L. G., Khramov, D. E., Volkov, V. S., & Balnokin, Y. V. (2023). Chloride Channel Family in the Euhalophyte Suaeda altissima (L.) Pall: Cloning of Novel Members SaCLCa2 and SaCLCc2, General Characterization of the Family. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(2), 941. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24020941