Mixture of Peanut Skin Extract, Geniposide, and Isoquercitrin Improves the Hepatic Lipid Accumulation of Mice via Modification of Gut Microbiota Homeostasis and the TLR4 and AMPK Signaling Pathways
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. MPGI Extends the Replicative Lifespan of K6001 Yeast and Inhibits the Eto-Induced Senescence of PC12 Cells
2.2. MPGI Reduces Body Weight and Improves Hepatic Lipid Accumulation in MASLD Mice
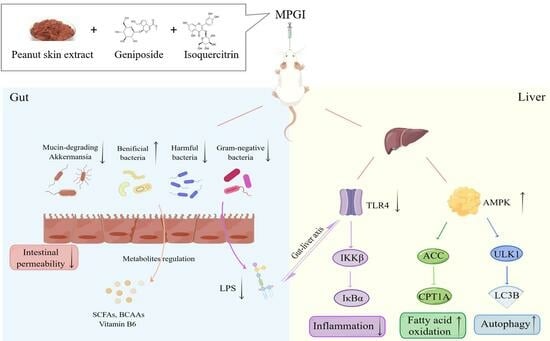
2.3. MPGI Alters the Composition of the Gut Microbiome in Mice with MASLD
2.4. Function and Bacterial Phenotypic Prediction for the Gut Microbiota of Mice with MASLD
2.5. MPGI Mitigates Inflammation of Mice with MASLD
2.6. MPGI Improves Inflammation by Regulating the Gut Microbiota and TLR4/NF-κB Signaling Pathway
2.7. MPGI Regulates AMPK/ACC/CPT1 and Autophagy Signaling Pathways in the Liver of MASLD Mice
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Drugs and Reagents
4.2. Composition Analysis of the PSE
4.3. Replicative Lifespan Assay of K6001 Yeast Strain
4.4. SA β-Gal Assay of PC12 Cells
4.5. Animal and Experimental Design
4.6. Biochemical Analysis and Immunological Staining
4.7. Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA)
4.8. Western Blot Analysis
4.9. Gut Microbiota Analysis
4.10. Biostatistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Younossi, Z.; Tacke, F.; Arrese, M.; Sharma, B.C.; Mostafa, I.; Bugianesi, E.; Wong, V.W.-S.; Yilmaz, Y.; George, J.; Fan, J.; et al. Global perspectives on nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and nonalcoholic steatohepatitis: Hepatology. Hepatology 2019, 69, 2672–2682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loomba, R.; Friedman, S.L.; Shulman, G.I. Mechanisms and disease consequences of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Cell 2021, 184, 2537–2564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rinella, M.E.; Lazarus, J.V.; Ratziu, V.; Francque, S.M.; Sanyal, A.J.; Kanwal, F.; Romero, D.; Abdelmalek, M.F.; Anstee, Q.M.; Arab, J.P.; et al. A multisociety Delphi consensus statement on new fatty liver disease nomenclature. Ann. Hepatol. 2023, 29, 101133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pierantonelli, I.; Svegliati-Baroni, G. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: Basic pathogenetic mechanisms in the progression from NAFLD to NASH. Transplantation 2019, 103, e1–e13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Younossi, Z.M.; Koenig, A.B.; Abdelatif, D.; Fazel, Y.; Henry, L.; Wymer, M. Global epidemiology of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease—Meta-analytic assessment of prevalence, incidence, and outcomes. Hepatology 2016, 64, 73–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yip, T.C.F.; Vilar Gomez, E.; Petta, S.; Yilmaz, Y.; Wong, G.L.H.; Adams, L.A.; de Lédinghen, V.; Sookoian, S.; Wong, V.W.S. Geographical similarity and differences in the burden and genetic predisposition of NAFLD. Hepatology 2023, 77, 1404–1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferguson, D.; Finck, B.N. Emerging therapeutic approaches for the treatment of NAFLD and type 2 diabetes mellitus. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2021, 17, 484–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semmler, G.; Datz, C.; Reiberger, T.; Trauner, M. Diet and exercise in NAFLD/NASH: Beyond the obvious. Liver Int. 2021, 41, 2249–2268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estes, C.; Anstee, Q.M.; Arias-Loste, M.T.; Bantel, H.; Bellentani, S.; Caballeria, J.; Colombo, M.; Craxi, A.; Crespo, J.; Day, C.P.; et al. Modeling NAFLD disease burden in China, France, Germany, Italy, Japan, Spain, United Kingdom, and United States for the period 2016–2030. J. Hepatol. 2018, 69, 896–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mantovani, A.; Scorletti, E.; Mosca, A.; Alisi, A.; Byrne, C.D.; Targher, G. Complications, morbidity and mortality of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Metabolism 2020, 111, 154170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedman, S.L.; Neuschwander-Tetri, B.A.; Rinella, M.; Sanyal, A.J. Mechanisms of NAFLD development and therapeutic strategies. Nat. Med. 2018, 24, 908–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Shen, L.; Li, X.; Zhang, H.; Cui, Y.; Zhang, K.; Li, W.; Chen, W.; Zhao, S.; et al. Diagnostic and therapeutic strategies for non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 973366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, H.; Jiang, Y.; Wang, M.; Melaku, M.; Liu, L.; Zhao, Y.; Everaert, N.; Yi, B.; Zhang, H. Intestinal dysbiosis in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD): Focusing on the gut-liver axis. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. 2023, 63, 1689–1706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kolodziejczyk, A.A.; Zheng, D.; Shibolet, O.; Elinav, E. The role of the microbiome in NAFLD and NASH. EMBO Mol. Med. 2019, 11, e9302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mouries, J.; Brescia, P.; Silvestri, A.; Spadoni, I.; Sorribas, M.; Wiest, R.; Mileti, E.; Galbiati, M.; Invernizzi, P.; Adorini, L.; et al. Microbiota-driven gut vascular barrier disruption is a prerequisite for non-alcoholic steatohepatitis development. J. Hepatol. 2019, 71, 1216–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohammad, S.; Thiemermann, C. Role of metabolic endotoxemia in systemic inflammation and potential interventions. Front. Immunol. 2021, 11, 594150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newman, D.J.; Cragg, G.M. Natural products as sources of new drugs from 1981 to 2014. J. Nat. Prod. 2016, 79, 629–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, L.; Wu, Q.; Cheng, L.; Sun, K.; Li, J.; Yoshida, M.; Qi, J. Leptin and adiponectin signaling pathways are involved in the antiobesity effects of peanut skin extract. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2019, 2019, 2935315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, L.; Wu, Q.; Osada, H.; Yoshida, M.; Pan, W.; Qi, J. Peanut skin extract ameliorates the symptoms of type 2 diabetes mellitus in mice by alleviating inflammation and maintaining gut microbiota homeostasis. Aging 2020, 12, 13991–14018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Zhang, R.; Rahman, K.; Cao, Z.; Zhang, H.; Peng, C. Diverse pharmacological activities and potential medicinal benefits of geniposide. Evid.-Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2019, 2019, 4925682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manzoor, M.; Muroi, M.; Ogawa, N.; Kobayashi, H.; Nishimura, H.; Chen, D.; Fasina, O.B.; Wang, J.; Osada, H.; Yoshida, M.; et al. Isoquercitrin from Apocynum venetum L. produces an anti-obesity effect on obese mice by targeting C-1-tetrahydrofolate synthase, carbonyl reductase, and glutathione S-transferase P and modification of the AMPK/SREBP-1c/FAS/CD36 signaling pathway in mice in vivo. Food Funct. 2022, 13, 10923–10936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campisi, J.; Kapahi, P.; Lithgow, G.J.; Melov, S.; Newman, J.C.; Verdin, E. From discoveries in ageing research to therapeutics for healthy ageing. Nature 2019, 571, 183–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, B.S.; Lee, J. Recognition of lipopolysaccharide pattern by TLR4 complexes. Exp. Mol. Med. 2013, 45, e66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia, D.; Shaw, R.J. AMPK: Mechanisms of cellular energy sensing and restoration of metabolic balance. Mol. Cell 2017, 66, 789–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watt, M.J.; Miotto, P.M.; De Nardo, W.; Montgomery, M.K. The liver as an endocrine organ—Linking NAFLD and insulin resistance. Endocr. Rev. 2019, 40, 1367–1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, F.; Chen, R.; Kong, L.; Wei, P.; Liu, Z.; Wang, X.; Hao, H.; Lu, Y.; Hu, W. Effects of serum branched-chain amino acids on nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and subsequent cardiovascular disease. Hepatol. Int. 2022, 16, 1424–1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, W.; Hua, S.; Li, X.; Shen, L.; Wu, H.; Ji, H. Microbially produced vitamin B12 contributes to the lipid-lowering effect of silymarin. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cani, P.D.; Depommier, C.; Derrien, M.; Everard, A.; de Vos, W.M. Akkermansia muciniphila: Paradigm for next-generation beneficial microorganisms. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2022, 19, 625–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, J.; Li, Y.; Cai, Z.; Li, S.; Zhu, J.; Zhang, F.; Liang, S.; Zhang, W.; Guan, Y.; Shen, D.; et al. A metagenome-wide association study of gut microbiota in type 2 diabetes. Nature 2012, 490, 55–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoyles, L.; Fernández-Real, J.; Federici, M.; Serino, M.; Abbott, J.; Charpentier, J.; Heymes, C.; Luque, J.L.; Anthony, E.; Barton, R.H.; et al. Molecular phenomics and metagenomics of hepatic steatosis in non-diabetic obese women. Nat. Med. 2018, 24, 1070–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshii, K.; Hosomi, K.; Sawane, K.; Kunisawa, J. Metabolism of dietary and microbial vitamin B family in the regulation of host immunity. Front. Nutr. 2019, 6, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Li, X.; Sun, B. Dynamic balancing of intestinal short-chain fatty acids: The crucial role of bacterial metabolism. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 100, 118–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kashiwada, Y.; Iizuka, H.; Yoshioka, K.; Chen, R.; Nonaka, G.; Nishioka, I. Tannins and related compounds. XCIII. Occurrence of enantiomeric proanthocyanidins in the leguminosae plants, Cassia fistula L. and C. javanica L. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1990, 38, 888–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, H.; Yamazaki, Y.; Sasaki, T.; Uchida, M.; Tanaka, H.; Oka, S. A-type proanthocyanidins from peanut skins. Phytochemistry 1999, 51, 297–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fasina, O.B.; Wang, J.; Mo, J.; Osada, H.; Ohno, H.; Pan, W.; Xiang, L.; Qi, J. Gastrodin from Gastrodia elata enhances cognitive function and neuroprotection of ad mice via the regulation of gut microbiota composition and inhibition of neuron inflammation. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 814271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yi, M.; Fasina, O.B.; Li, Y.; Xiang, L.; Qi, J. Mixture of Peanut Skin Extract, Geniposide, and Isoquercitrin Improves the Hepatic Lipid Accumulation of Mice via Modification of Gut Microbiota Homeostasis and the TLR4 and AMPK Signaling Pathways. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 16684. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms242316684
Yi M, Fasina OB, Li Y, Xiang L, Qi J. Mixture of Peanut Skin Extract, Geniposide, and Isoquercitrin Improves the Hepatic Lipid Accumulation of Mice via Modification of Gut Microbiota Homeostasis and the TLR4 and AMPK Signaling Pathways. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2023; 24(23):16684. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms242316684
Chicago/Turabian StyleYi, Meijuan, Opeyemi B. Fasina, Yajing Li, Lan Xiang, and Jianhua Qi. 2023. "Mixture of Peanut Skin Extract, Geniposide, and Isoquercitrin Improves the Hepatic Lipid Accumulation of Mice via Modification of Gut Microbiota Homeostasis and the TLR4 and AMPK Signaling Pathways" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24, no. 23: 16684. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms242316684
APA StyleYi, M., Fasina, O. B., Li, Y., Xiang, L., & Qi, J. (2023). Mixture of Peanut Skin Extract, Geniposide, and Isoquercitrin Improves the Hepatic Lipid Accumulation of Mice via Modification of Gut Microbiota Homeostasis and the TLR4 and AMPK Signaling Pathways. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(23), 16684. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms242316684