Molecular Mechanisms of the Regulation of Liver Cytochrome P450 by Brain NMDA Receptors and via the Neuroendocrine Pathway—A Significance for New Psychotropic Therapies
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
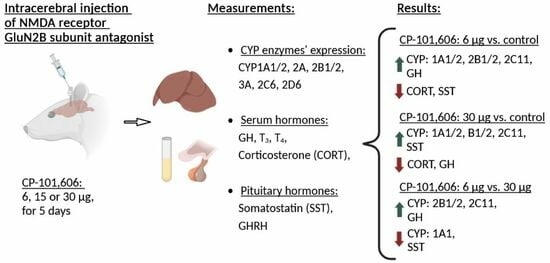
2.1. The Impact of Intracerebral Administration of CP-101,606 on the Hepatic Activity of CYP1A, CYP2A, CYP2B, CYP2C11, CYP3A, CYP2C6, and CYP2D Enzymes
2.2. The Impact of the Intracerebral Administration of CP-101,606 on the Protein Levels of CYP1A, CYP2A, CYP2B, CYP2C11, CYP3A, CYP2C6, and CYP2D in the Liver
2.3. The Impact of Intracerebral Administration of CP-101,606 on the Hepatic mRNA Levels of CYP1A1, CYP1A2, CYP2B1, CYP2B2, and CYP2C11
2.4. The Influence of CP-101,606 Intracerebral Administration on the Levels of Hormones
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Animals
4.2. Drugs and Chemicals
4.3. Animal Treatment and the Preparation of Microsomes
4.4. Assessment of Cytochrome P450 Enzyme Activities in Microsomes Isolated from the Liver
4.5. Assessment of CYP Protein Levels in the Liver Microsomes
4.6. RNA Isolation and Quantitative Real-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction (qRT-PCR)
4.7. Assessment of Hormone Levels
4.8. Data Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hines, R.N.; Luo, Z.; Cresteil, T.; Ding, X.; Prough, R.A.; Fitzpatrick, J.L.; Ripp, S.L.; Falkner, K.C.; Ge, N.-L.; Levine, A.; et al. Molecular Regulation of Genes Encoding Xenobiotic-Metabolizing Enzymes: Mechanisms Involving Endogenous Factors. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2001, 29, 623–633. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Honkakoski, P.; Negishi, M. Regulation of Cytochrome P450 (CYP) Genes by Nuclear Receptors. Biochem. J. 2000, 347, 321–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pascussi, J.-M.; Gerbal-Chaloin, S.; Duret, C.; Daujat-Chavanieu, M.; Vilarem, M.-J.; Maurel, P. The Tangle of Nuclear Receptors That Controls Xenobiotic Metabolism and Transport: Crosstalk and Consequences. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2008, 48, 1–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wójcikowski, J.; Daniel, W.A. The Role of the Nervous System in the Regulation of Liver Cytochrome P450. Curr. Drug Metab. 2011, 12, 124–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMahon, C.D.; Radcliff, R.P.; Lookingland, K.J.; Tucker, H.A. Neuroregulation of Growth Hormone Secretion in Domestic Animals. Domest. Anim. Endocrinol. 2001, 20, 65–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, E.E. Some Aspects of the Neurotransmitter Control of Anterior Pituitary Function. Pharmacol. Res. 1989, 21, 75–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wójcikowski, J.; Daniel, W.A. The Brain Dopaminergic System as an Important Center Regulating Liver Cytochrome P450 in the Rat. Expert Opin. Drug Metab. Toxicol. 2009, 5, 631–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bromek, E.; Wójcikowski, J.; Daniel, W.A. Involvement of the Paraventricular (PVN) and Arcuate (ARC) Nuclei of the Hypothalamus in the Central Noradrenergic Regulation of Liver Cytochrome P450. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2013, 86, 1614–1620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadakierska-Chudy, A.; Haduch, A.; Rysz, M.; Gołembiowska, K.; Daniel, W.A. The Role of Brain Noradrenergic System in the Regulation of Liver Cytochrome P450 Expression. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2013, 86, 800–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bromek, E.; Daniel, W.A. The Regulation of Liver Cytochrome P450 Expression and Activity by the Brain Serotonergic System in Different Experimental Models. Expert Opin. Drug Metab. Toxicol. 2021, 17, 413–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wittmann, G.; Lechan, R.M.; Liposits, Z.; Fekete, C. Glutamatergic Innervation of Corticotropin-Releasing Hormone- and Thyrotropin-Releasing Hormone-Synthesizing Neurons in the Hypothalamic Paraventricular Nucleus of the Rat. Brain Res. 2005, 1039, 53–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiss, J.; Csaba, Z.; Csáki, Á.; Halász, B. Glutamatergic Innervation of Growth Hormone-Releasing Hormone-Containing Neurons in the Hypothalamic Arcuate Nucleus and Somatostatin-Containing Neurons in the Anterior Periventricular Nucleus of the Rat—ScienceDirect. Brain Res. Bull. 2006, 70, 263–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hrabovszky, E.; Deli, L.; Turi, G.F.; Kalló, I.; Liposits, Z. Glutamatergic Innervation of the Hypothalamic Median Eminence and Posterior Pituitary of the Rat. Neuroscience 2007, 144, 1383–1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hrabovszky, E.; Liposits, Z. Novel Aspects of Glutamatergic Signalling in the Neuroendocrine System. J. Neuroendocrinol. 2008, 20, 743–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evanson, N.K.; Van Hooren, D.C.; Herman, J.P. GluR5-Mediated Glutamate Signaling Regulates Hypothalamo–Pituitary–Adrenocortical Stress Responses at the Paraventricular Nucleus and Median Eminence. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2009, 34, 1370–1379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Csáki, A.; Kocsis, K.; Halász, B.; Kiss, J. Localization of Glutamatergic/Aspartatergic Neurons Projecting to the Hypothalamic Paraventricular Nucleus Studied by Retrograde Transport of [3H]D-Aspartate Autoradiography. Neuroscience 2000, 101, 637–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulrich-Lai, Y.M.; Jones, K.R.; Ziegler, D.R.; Cullinan, W.E.; Herman, J.P. Forebrain Origins of Glutamatergic Innervation to the Rat Paraventricular Nucleus of the Hypothalamus: Differential Inputs to the Anterior Versus Posterior Subregions. J. Comp. Neurol. 2011, 519, 1301–1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziegler, D.R.; Edwards, M.R.; Ulrich-Lai, Y.M.; Herman, J.P.; Cullinan, W.E. Brainstem Origins of Glutamatergic Innervation of the Rat Hypothalamic Paraventricular Nucleus. J. Comp. Neurol. 2012, 520, 2369–2394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meeker, R.B.; Greenwood, R.S.; Hayward, J.N. Glutamate Receptors in the Rat Hypothalamus and Pituitary. Endocrinology 1994, 134, 621–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brann, D.W.; Mahesh, V.B. Glutamate: A Major Neuroendocrine Excitatory Signal Mediating Steroid Effects on Gonadotropin Secretion. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 1995, 53, 325–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brann, D.W.; Mahesh, V.B. Excitatory Amino Acids: Evidence for a Role in the Control of Reproduction and Anterior Pituitary Hormone Secretion. Endocr. Rev. 1997, 18, 678–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evanson, N.K.; Herman, J.P. Role of Paraventricular Nucleus Glutamate Signaling in Regulation of HPA Axis Stress Responses. Interdiscip. Inf. Sci. 2015, 21, 253–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aguilar, E.; Tena-Sempere, M.; Pinilla, L. Role of Excitatory Amino Acids in the Control of Growth Hormone Secretion. Endocrine 2005, 28, 295–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alfonso, M.; Durán, R.; Arufe, M.C. Effect of Excitatory Amino Acids on Serum TSH and Thyroid Hormone Levels in Freely Moving Rats. Horm. Res. Paediatr. HRP 2000, 54, 78–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arufe, M.C.; Durán, R.; Perez-Vences, D.; Alfonso, M. Endogenous Excitatory Amino Acid Neurotransmission Regulates Thyroid-Stimulating Hormone and Thyroid Hormone Secretion in Conscious Freely Moving Male Rats. Endocrine 2002, 17, 193–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, X.-T.; Yang, J.-X.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, C.-Y.; Luo, Z.-Q.; Liu, W.; Tang, S.-Y. Activation of N-Methyl-D-Aspartate Receptor Regulates Insulin Sensitivity and Lipid Metabolism. Theranostics 2021, 11, 2247–2262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rischka, L.; Murgaš, M.; Pichler, V.; Vraka, C.; Rausch, I.; Winkler, D.; Nics, L.; Rasul, S.; Silberbauer, L.R.; Reed, M.B.; et al. Biodistribution and Dosimetry of the GluN2B-Specific NMDA Receptor PET Radioligand (R)-[11C]Me-NB1. EJNMMI Res. 2022, 12, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosenko, E.; Tikhonova, L.; Alilova, G.; Montoliu, C. Is NMDA-Receptor-Mediated Oxidative Stress in Mitochondria of Peripheral Tissues the Essential Factor in the Pathogenesis of Hepatic Encephalopathy? J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ugale, V.; Deshmukh, R.; Lokwani, D.; Narayana Reddy, P.; Khadse, S.; Chaudhari, P.; Kulkarni, P.P. GluN2B Subunit Selective N-Methyl-D-Aspartate Receptor Ligands: Democratizing Recent Progress to Assist the Development of Novel Neurotherapeutics. Mol. Divers. 2023, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, S.; Yao, K.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, S. NMDA Receptors as Therapeutic Targets for Depression Treatment: Evidence from Clinical to Basic Research. Neuropharmacology 2023, 225, 109378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seillier, C.; Lesept, F.; Toutirais, O.; Potzeha, F.; Blanc, M.; Vivien, D. Targeting NMDA Receptors at the Neurovascular Unit: Past and Future Treatments for Central Nervous System Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 10336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Ross, P.J.; Ellis, J.; Salter, M.W. Targeting NMDA Receptors in Neuropsychiatric Disorders by Drug Screening on Human Neurons Derived from Pluripotent Stem Cells. Transl. Psychiatry 2022, 12, 243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bromek, E.; Haduch, A.; Rysz, M.; Jastrzębska, J.; Pukło, R.; Wójcikowska, O.; Danek, P.J.; Daniel, W.A. The Selective NMDA Receptor GluN2B Subunit Antagonist CP-101,606 with Antidepressant Properties Modulates Cytochrome P450 Expression in the Liver. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 1643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waxman, D.J.; O’Connor, C. Growth Hormone Regulation of Sex-Dependent Liver Gene Expression. Mol. Endocrinol. 2006, 20, 2613–2629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waxman, D.J.; Holloway, M.G. Sex Differences in the Expression of Hepatic Drug Metabolizing Enzymes. Mol. Pharmacol. 2009, 76, 215–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monostory, K.; Dvorak, Z. Steroid Regulation of Drug-Metabolizing Cytochromes P450. Curr. Drug Metab. 2011, 12, 154–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dvorak, Z.; Pavek, P. Regulation of Drug-Metabolizing Cytochrome P450 Enzymes by Glucocorticoids. Drug Metab. Rev. 2010, 42, 621–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brtko, J.; Dvorak, Z. Role of Retinoids, Rexinoids and Thyroid Hormone in the Expression of Cytochrome P450 Enzymes. Curr. Drug Metab. 2011, 12, 71–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sikora, M.; Tokarski, K.; Bobula, B.; Zajdel, J.; Jastrzębska, K.; Cieślak, P.E.; Zygmunt, M.; Sowa, J.; Smutek, M.; Kamińska, K.; et al. NMDA Receptors on Dopaminoceptive Neurons Are Essential for Drug-Induced Conditioned Place Preference. eNeuro 2016, 3, ENEURO.0084-15.2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cieślak, P.E.; Llamosas, N.; Kos, T.; Ugedo, L.; Jastrzębska, K.; Torrecilla, M.; Rodriguez Parkitna, J. The Role of NMDA Receptor-Dependent Activity of Noradrenergic Neurons in Attention, Impulsivity and Exploratory Behaviors. Genes Brain Behav. 2017, 16, 812–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soiza-Reilly, M.; Commons, K.G. Glutamatergic Drive of the Dorsal Raphe Nucleus. J. Chem. Neuroanat. 2011, 41, 247–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tao, R.; Auerbach, S.B. Regulation of Serotonin Release by GABA and Excitatory Amino Acids. J. Psychopharmacol. 2000, 14, 100–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kretschmer, B.D. Modulation of the Mesolimbic Dopamine System by Glutamate: Role of NMDA Receptors. J. Neurochem. 1999, 73, 839–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pittaluga, A. Presynaptic Release-Regulating NMDA Receptors in Isolated Nerve Terminals: A Narrative Review. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2021, 178, 1001–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forray, M.I.; Gysling, K.; Andrés, M.E.; Bustos, G.; Araneda, S. Medullary Noradrenergic Neurons Projecting to the Bed Nucleus of the Stria Terminalis Express mRNA for the NMDA-NR1 Receptor. Brain Res. Bull. 2000, 52, 163–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gok-Yurtseven, D.; Kafa, I.M.; Minbay, Z.; Eyigor, O. Glutamatergic Activation of A1 and A2 Noradrenergic Neurons in the Rat Brain Stem. Croat. Med. J. 2019, 60, 352–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, R.; Auerbach, S.B. Differential Effect of NMDA on Extracellular Serotonin in Rat Midbrain Raphe and Forebrain Sites. J. Neurochem. 1996, 66, 1067–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haduch, A.; Rysz, M.; Papp, M.; Daniel, W.A. The Activity of Brain and Liver Cytochrome P450 2D (CYP2D) Is Differently Affected by Antidepressants in the Chronic Mild Stress (CMS) Model of Depression in the Rat. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2018, 156, 398–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Route of CP-101,606 Administration | Administered Intracerebrally | Administered Intraperitoneally * | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CYP | 6 µg vs. Control | 30 µg vs. Control | 6 µg vs. 30 µg | 20 mg/kg | ||||||||
| Activity | Protein Level | mRNA Level | Activity | Protein Level | mRNA Level | Activity | Protein Level | mRNA Level | Activity | Protein Level | mRNA Level | |
| 1A1/2 | − | − | ↑ ↑ | − | ↑ | ↑ ↑ | − | − | ↓ − | ↓ | ↓ | ↑ ↑ |
| 2A | − | − | n.t. | − | − | n.t. | ↑ | − | n.t. | ↓ | − | − |
| 2B1/2 | (↑) | (↑) | ↑ ↑ | − | − | ↑ − | (↑) | ↑ | ↑ ↑ | ↓ | − | − |
| 2C11 | ↑ | ↑ | ↑ | − | − | ↑ | ↑ | ↑ | ↑ | ↓ | ↓ | ↓ |
| 3A | − | − | n.t. | − | − | n.t. | − | − | n.t. | ↓ | ↓ | ↓ |
| 2C6 | − | − | n.t. | − | − | n.t. | ↑ | − | n.t. | − | n.t. | n.t. |
| 2D | − | − | n.t. | − | − | n.t. | ↑ | − | n.t. | ↓ | − | − |
| Hormone concentration | 6 µg vs. control | 30 µg vs. control | 6 µg vs. 30 µg | 20 mg/kg | ||||||||
| Triiodothyronine (T3) | − | − | − | − | ||||||||
| Thyroxine (T4) | − | − | − | − | ||||||||
| Corticosterone | ↓ | ↓ | − | ↓ | ||||||||
| Growth hormone | (↑) | (↓) | ↑ | ↓ | ||||||||
| Somatostatin | (↓) | (↑) | ↓ | n.t. | ||||||||
| Growth hormone- releasing hormone | − | − | − | ↓ | ||||||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pukło, R.; Bromek, E.; Haduch, A.; Basińska-Ziobroń, A.; Kuban, W.; Daniel, W.A. Molecular Mechanisms of the Regulation of Liver Cytochrome P450 by Brain NMDA Receptors and via the Neuroendocrine Pathway—A Significance for New Psychotropic Therapies. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 16840. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms242316840
Pukło R, Bromek E, Haduch A, Basińska-Ziobroń A, Kuban W, Daniel WA. Molecular Mechanisms of the Regulation of Liver Cytochrome P450 by Brain NMDA Receptors and via the Neuroendocrine Pathway—A Significance for New Psychotropic Therapies. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2023; 24(23):16840. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms242316840
Chicago/Turabian StylePukło, Renata, Ewa Bromek, Anna Haduch, Agnieszka Basińska-Ziobroń, Wojciech Kuban, and Władysława A. Daniel. 2023. "Molecular Mechanisms of the Regulation of Liver Cytochrome P450 by Brain NMDA Receptors and via the Neuroendocrine Pathway—A Significance for New Psychotropic Therapies" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24, no. 23: 16840. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms242316840
APA StylePukło, R., Bromek, E., Haduch, A., Basińska-Ziobroń, A., Kuban, W., & Daniel, W. A. (2023). Molecular Mechanisms of the Regulation of Liver Cytochrome P450 by Brain NMDA Receptors and via the Neuroendocrine Pathway—A Significance for New Psychotropic Therapies. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(23), 16840. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms242316840