Traffic-Related Air Pollution and Ground-Level Ozone Associated Global DNA Hypomethylation and Bulky DNA Adduct Formation
Abstract
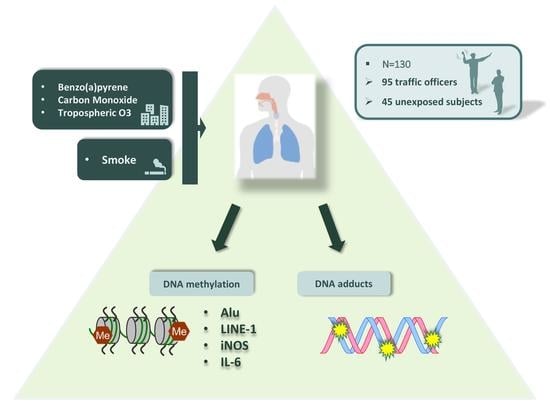
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Demographic Variables
2.2. Air Pollution Biomonitoring
2.3. Air Pollution and Epigenetic Marks
2.4. Air Pollution and Bulky DNA Adducts
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Study Population
4.2. Air Pollution Exposure Analysis
4.3. Bulky DNA Adduct Analysis
4.4. DNA Methylation Analysis
4.5. Statistical Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rider, C.F.; Carlsten, C. Air pollution and DNA methylation: Effects of exposure in humans. Clin. Epigenet. 2019, 11, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Loxham, M.; Davies, D.E.; Holgate, S.T. The health effects of fine particulate air pollution. BMJ 2019, 367, l6609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- IARC. Outdoor Air Pollution; IARC monographs on the evaluation of carcinogenic risks to humans; World Health Organization, International Agency for Research on Cancer: Geneva, Switzerland, 2013; p. 103.
- Finlayson-Pitts, B.J.; Pitts, J.N., Jr. Tropospheric air pollution: Ozone, airborne toxics, polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons, and particles. Science 1997, 276, 1045–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Reed, L.; Mrizova, I.; Barta, F.; Indra, R.; Moserova, M.; Kopka, K.; Schmeiser, H.H.; Wolf, C.R.; Henderson, C.J.; Stiborova, M.; et al. Cytochrome b (5) impacts on cytochrome P450-mediated metabolism of benzo[a]pyrene and its DNA adduct formation: Studies in hepatic cytochrome b (5) /P450 reductase null (HBRN) mice. Arch. Toxicol. 2018, 92, 1625–1638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Munnia, A.; Giese, R.W.; Polvani, S.; Galli, A.; Cellai, F.; Peluso, M.E. Bulky DNA Adducts, Tobacco Smoking, Genetic Susceptibility, and Lung Cancer Risk. Adv. Clin. Chem. 2017, 81, 231–277. [Google Scholar]
- Peluso, M.E.; Munnia, A.; Srivatanakul, P.; Jedpiyawongse, A.; Sangrajrang, S.; Ceppi, M.; Godschalk, R.W.; van Schooten, F.J.; Boffetta, P. DNA adducts and combinations of multiple lung cancer at-risk alleles in environmentally exposed and smoking subjects. Environ. Mol. Mutagen. 2013, 54, 375–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peluso, M.; Srivatanakul, P.; Munnia, A.; Jedpiyawongse, A.; Meunier, A.; Sangrajrang, S.; Piro, S.; Ceppi, M.; Boffetta, P. DNA adduct formation among workers in a Thai industrial estate and nearby residents. Sci. Total Env. 2008, 389, 283–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilberson, T.; Peluso, M.E.; Munia, A.; Lujan-Barroso, L.; Sanchez, M.J.; Navarro, C.; Amiano, P.; Barricarte, A.; Quiros, J.R.; Molina-Montes, E.; et al. Aromatic adducts and lung cancer risk in the European Prospective Investigation into Cancer and Nutrition (EPIC) Spanish cohort. Carcinogenesis 2014, 35, 2047–2054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Peluso, M.; Munnia, A.; Hoek, G.; Krzyzanowski, M.; Veglia, F.; Airoldi, L.; Autrup, H.; Dunning, A.; Garte, S.; Hainaut, P.; et al. DNA adducts and lung cancer risk: A prospective study. Cancer Res. 2005, 65, 8042–8048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brancato, B.; Munnia, A.; Cellai, F.; Ceni, E.; Mello, T.; Bianchi, S.; Catarzi, S.; Risso, G.G.; Galli, A.; Peluso, M.E. 8-Oxo-7, 8-dihydro-2-deoxyguanosine and other lesions along the coding strand of the exon 5 of the tumour suppressor gene P53 in a breast cancer case-control study. DNA Res. Int. J. Rapid Publ. Rep. Genes Genomes 2016, 23, 395–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Galli, A.; Munnia, A.; Cellai, F.; Tarocchi, M.; Ceni, E.; van Schooten, F.J.; Godschalk, R.; Giese, R.W.; Peluso, M. Ligation-Mediated Polymerase Chain Reaction Detection of 8-Oxo-7,8-Dihydro-2’-Deoxyguanosine and 5-Hydroxycytosine at the Codon 176 of the p53 Gene of Hepatitis C-Associated Hepatocellular Carcinoma Patients. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 6753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fessele, K.L.; Wright, F. Primer in Genetics and Genomics, Article 6: Basics of Epigenetic Control. Biol. Res. Nurs. 2018, 20, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Locke, W.J.; Guanzon, D.; Ma, C.; Liew, Y.J.; Duesing, K.R.; Fung, K.Y.; Ross, J.P. DNA Methylation Cancer Biomarkers: Translation to the Clinic. Front. Genet. 2019, 10, 1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prunicki, M.; Cauwenberghs, N.; Lee, J.; Zhou, X.; Movassagh, H.; Noth, E.; Lurmann, F.; Hammond, S.K.; Balmes, J.R.; Desai, M.; et al. Air pollution exposure is linked with methylation of immunoregulatory genes, altered immune cell profiles, and increased blood pressure in children. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 4067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lepeule, J.; Bind Marie-Abele, C.; Baccarelli Andrea, A.; Koutrakis, P.; Tarantini, L.; Litonjua, A.; Sparrow, D.; Vokonas, P.; Schwartz Joel, D. Epigenetic Influences on Associations between Air Pollutants and Lung Function in Elderly Men: The Normative Aging Study. Environ. Health Perspect. 2014, 122, 566–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peluso, M.; Bollati, V.; Munnia, A.; Srivatanakul, P.; Jedpiyawongse, A.; Sangrajrang, S.; Piro, S.; Ceppi, M.; Bertazzi, P.A.; Boffetta, P.; et al. DNA methylation differences in exposed workers and nearby residents of the Ma Ta Phut industrial estate, Rayong, Thailand. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2012, 41, 1753–1760, author response 1761-3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Peluso, M.; Munnia, A.; Russo, V.; Galli, A.; Pala, V.; van der Schouw, Y.T.; Schulze, M.B.; Weiderpass, E.; Tumino, R.; Saieva, C.; et al. Cruciferous Vegetable Intake and Bulky DNA Damage within Non-Smokers and Former Smokers in the Gen-Air Study (EPIC Cohort). Nutrients 2022, 14, 2477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, D.; Castegnaro, M. Standardization and validation of DNA adduct postlabelling methods: Report of interlaboratory trials and production of recommended protocols. Mutagenesis 1999, 14, 301–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munnia, A.; Saletta, F.; Allione, A.; Piro, S.; Confortini, M.; Matullo, G.; Peluso, M. 32P-Post-labelling method improvements for aromatic compound-related molecular epidemiology studies. Mutagenesis 2007, 22, 381–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Smith, M.T.; Hainaut, P.; Perera, F.; Schulte, P.A.; Boffetta, P.; Chanock, S.J.; Rothman, N. Future perspectives on molecular epidemiology. IARC Sci. Publ. 2011, 163, 493–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peluso, M.; Merlo, F.; Munnia, A.; Valerio, F.; Perrotta, A.; Puntoni, R.; Parodi, S. 32P-postlabeling detection of aromatic adducts in the white blood cell DNA of nonsmoking police officers. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 1998, 7, 3–11. [Google Scholar]
- Kutlar Joss, M.; Eeftens, M.; Gintowt, E.; Kappeler, R.; Kunzli, N. Time to harmonize national ambient air quality standards. Int. J. Public Health 2017, 62, 453–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Prins, S.; Koppen, G.; Jacobs, G.; Dons, E.; Van de Mieroop, E.; Nelen, V.; Fierens, F.; Int Panis, L.; De Boever, P.; Cox, B.; et al. Influence of ambient air pollution on global DNA methylation in healthy adults: A seasonal follow-up. Environ. Int. 2013, 59, 418–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yadav, S.; Longkumer, I.; Garg, P.R.; Joshi, S.; Rajkumari, S.; Devi, N.K.; Saraswathy, K.N. Association of air pollution and homocysteine with global DNA methylation: A population-based study from North India. PloS ONE 2021, 16, e0260860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, H.; He, Z.; Ma, J.; Zhang, B.; Sheng, Z.; Bin, P.; Cheng, J.; Niu, Y.; Dong, H.; Lin, H.; et al. Global and MGMT promoter hypomethylation independently associated with genomic instability of lymphocytes in subjects exposed to high-dose polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon. Arch. Toxicol. 2013, 87, 2013–2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tarantini, L.; Bonzini, M.; Apostoli, P.; Pegoraro, V.; Bollati, V.; Marinelli, B.; Cantone, L.; Rizzo, G.; Hou, L.; Schwartz, J.; et al. Effects of Particulate Matter on Genomic DNA Methylation Content and iNOS Promoter Methylation. Environ. Health Perspect. 2009, 117, 217–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Plusquin, M.; Guida, F.; Polidoro, S.; Vermeulen, R.; Raaschou-Nielsen, O.; Campanella, G.; Hoek, G.; Kyrtopoulos, S.A.; Georgiadis, P.; Naccarati, A.; et al. DNA methylation and exposure to ambient air pollution in two prospective cohorts. Environ. Int. 2017, 108, 127–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peluso, M.E.; Munnia, A.; Bollati, V.; Srivatanakul, P.; Jedpiyawongse, A.; Sangrajrang, S.; Ceppi, M.; Giese, R.W.; Boffetta, P.; Baccarelli, A.A. Aberrant methylation of hypermethylated-in-cancer-1 and exocyclic DNA adducts in tobacco smokers. Toxicol. Sci. Off. J. Soc. Toxicol. 2014, 137, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Matullo, G.; Dunning, A.; Guarrera, S.; Baynes, C.; Polidoro, S.; Garte, S.; Autrup, H.; Malaveille, C.; Peluso, M.; Airoldi, L. DNA repair polymorphisms and cancer risk in non-smokers in a cohort study. Carcinogenesis 2006, 27, 997–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ivashkevich, A.; Redon, C.E.; Nakamura, A.J.; Martin, R.F.; Martin, O.A. Use of the γ-H2AX assay to monitor DNA damage and repair in translational cancer research. Cancer Lett. 2012, 327, 123–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Demetriou, C.A.; Vineis, P. Carcinogenicity of ambient air pollution: Use of biomarkers, lessons learnt and future directions. J. Thorac. Dis. 2009, 7, 67–95. [Google Scholar]
- Pedersen, M.; Wichmann, J.; Autrup, H.; Dang, D.A.; Decordier, I.; Hvidberg, M.; Bossi, R.; Jakobsen, J.; Loft, S.; Knudsen, L.E. Increased micronuclei and bulky DNA adducts in cord blood after maternal exposures to traffic-related air pollution. Environ. Res. 2009, 109, 1012–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peluso, M.; Ceppi, M.; Munnia, A.; Puntoni, R.; Parodi, S. Analysis of 13 (32)P-DNA postlabeling studies on occupational cohorts exposed to air pollution. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2001, 153, 546–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pavanello, S.; Bollati, V.; Pesatori, A.C.; Kapka, L.; Bolognesi, C.; Bertazzi, P.A.; Baccarelli, A. Global and gene-specific promoter methylation changes are related to anti-B[a]PDE-DNA adduct levels and influence micronuclei levels in polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon-exposed individuals. Int. J. Cancer 2009, 125, 1692–1697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bukowska, B.; Siciriska, P. Influence of Benzo(a)pyrene on Different Epigenetic Processes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 13453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tekpli, X.; Landvik, N.E.; Anmarkud, K.H.; Skaug, V.; Haugen, A.; Zienolddiny, S. DNA methylation at promoter regions of interleukin 1B, interleukin 6, and interleukin 8 in non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2013, 62, 337–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartwig, A.; Arand, M.; Epe, B.; Guth, S.; Jahnke, G.; Lampen, A.; Martus, H.-J.; Monien, B.; Rietjens, I.M.C.M.; Schmitz-Spanke, S.; et al. Mode of action-based risk assessment of genotoxic carcinogens. Arch. Toxicol. 2020, 94, 1787–1877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krzyzanowski, M.; Cohen, A. Update of WHO air quality guidelines. Air Qual. Atmos. Health 2008, 1, 7–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bell Michelle, L.; Peng Roger, D.; Dominici, F. The Exposure Response Curve for Ozone and Risk of Mortality and the Adequacy of Current Ozone Regulations. Environ. Health Perspect. 2006, 114, 532–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Orru, H.; Astrom, C.; Andersson, C.; Tamm, T.; Ebi, K.L.; Forsberg, B. Ozone and heat-related mortality in Europe in 2050 significantly affected by changes in climate, population and greenhouse gas emission. Environ. Res. Lett. 2019, 14, 074013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekland, J.; Olsson, D.; Forsberg, B.; Andersson, C.; Orru, H. The effect of current and future maternal exposure to near-surface ozone on preterm birth in 30 European countries—An EU-wide health impact assessment. Environ. Res. Lett. 2021, 16, 055005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bind, M.A.C.; Rubin, D.B.; Cardenas, A.; Dhingra, R.; Ward-Caviness, C.; Liu, Z.; Mirowsky, J.; Schwartz, J.D.; Diaz-Sanchez, D.; Devlin, R.B. Heterogeneous ozone effects on the DNA methylome of bronchial cells observed in a crossover study. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 15739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, C.N.; Dye, J.A.; Schladweiler, M.C.; Richards, J.H.; Ledbetter, A.D.; Stewart, E.J.; Kodavanti, U.P. Acute inhalation of ozone induces DNA methylation of apelin in lungs of Long-Evans rats. Inhal. Toxicol. 2018, 30, 178–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ladd-Acosta, C.; Feinberg, J.I.; Brown, S.C.; Lurmann, F.W.; Croen, L.A.; Hertz-Picciotto, I.; Newschaffer, C.J.; Feinberg, A.P.; Fallin, M.D.; Volk, H.E. Epigenetic marks of prenatal air pollution exposure found in multiple tissues relevant for child health. Environ. Int. 2019, 126, 363–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niu, Y.; Chen, R.; Xia, Y.; Cai, J.; Lin, Z.; Liu, C.; Chen, C.; Peng, L.; Zhao, Z.; Zhou, W.; et al. Personal Ozone Exposure and Respiratory Inflammatory Response: The Role of DNA Methylation in the Arginase-Nitric Oxide Synthase Pathway. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 8785–8791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Y.; Niu, Y.; Cai, J.; Lin, Z.; Liu, C.; Li, H.; Chen, C.; Song, W.; Zhao, Z.; Chen, R.; et al. Effects of Personal Short-Term Exposure to Ambient Ozone on Blood Pressure and Vascular Endothelial Function: A Mechanistic Study Based on DNA Methylation and Metabolomics. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 12774–12782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.; Lin, Y.; Wang, X.; Liu, X.; Wang, Y.; Qin, J.; Wang, X.; Day, D.; Xiang, J.; Mo, J.; et al. Associations of ozone exposure with urinary metabolites of arachidonic acid. Environ. Int. 2020, 145, 106154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valacchi, G.; Pambianchi, E.; Coco, S.; Pulliero, A.; Izzotti, A. MicroRNA Alterations Induced in Human Skin by Diesel Fumes, Ozone, and UV Radiation. J. Pers. Med. 2022, 12, 176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palli, D.; Saieva, C.; Grechi, D.; Masala, G.; Zanna, I.; Barbaro, A.; Decarli, A.; Munnia, A.; Peluso, M. DNA bulky adducts in a Mediterranean population correlate with environmental ozone concentration, an indicator of photochemical smog. Int. J. Cancer 2004, 109, 17–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; Yeung, L.W.; Forbes, M.W.; Mabury, S.; Abbatt, J.P.D. Epoxide formation from heterogeneous oxidation of benzo[a]pyrene with gas-phase ozone and indoor air. Environ. Sci. Process. Impacts 2017, 19, 1292–1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, J.R.; Madugundu, G.S.; Cadet, J. Ozone-Induced DNA Damage: A Pandora’s Box of Oxidatively Modified DNA Bases. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2021, 34, 80–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schulz, W.A.; Steinhoff, C.; Florl, A.R. Methylation of Endogenous Human Retroelements in Health and Disease. In DNA Methylation: Development, Genetic Disease and Cancer; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2006; pp. 211–250. [Google Scholar]
- Ceppi, M.; Munnia, A.; Cellai, F.; Bruzzone, M.; Peluso, M.E. Linking the generation of DNA adducts to lung cancer. Toxicology 2017, 390, 160–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, Z.; Tang, S.a.; Ye, G.; Wang, P.; Li, J.; Liu, W.; Li, M.; Wang, S.; Wu, X.; Cen, S.; et al. Interleukin-6/interleukin-6 receptor complex promotes osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2018, 9, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Linnemann, A.K.; Blumer, J.; Marasco, M.R.; Battiola, T.J.; Umhoefer, H.M.; Han, J.Y.; Lamming, D.W.; Davis, D.B. Interleukin 6 protects pancreatic β cells from apoptosis by stimulation of autophagy. FASEB J. 2017, 31, 4140–4152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Joehanes, R.; Just, A.C.; Marioni, R.E.; Pilling, L.C.; Reynolds, L.M.; Mandaviya, P.R.; Guan, W.; Xu, T.; Elks, C.E.; Aslibekyan, S.; et al. Epigenetic Signatures of Cigarette Smoking. Circ. Cardiovasc. Genet. 2016, 9, 436–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Peluso, M.; Neri, M.; Margarino, G.; Mereu, C.; Munnia, A.; Ceppi, M.; Buratti, M.; Felletti, R.; Stea, F.; Quaglia, R.; et al. Comparison of DNA adduct levels in nasal mucosa, lymphocytes and bronchial mucosa of cigarette smokers and interaction with metabolic gene polymorphisms. Carcinogenesis 2004, 25, 2459–2465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Helalat, S.H.; Moradi, M.; Heidari, H.; Rezaei, F.; Yarmohamadi, M.; Sayadi, M.; Dadashkhan, S.; Eydi, F. Investigating the efficacy of UVSE protein at repairing CPD and 6-4PP DNA damages in human cells. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 2020, 205, 111843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karbaschi, M.; Brady, N.J.; Evans, M.D.; Cooke, M.S. Immuno-Slot Blot Assay for Detection of UVR-Mediated DNA Damage. In DNA Repair Protocols; Humana Press: Totowa, NJ, USA, 2012; pp. 163–175. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, H.-C.; Delgado-Cruzata, L.; Flom, J.D.; Kappil, M.; Ferris, J.S.; Liao, Y.; Santella, R.M.; Terry, M.B. Global methylation profiles in DNA from different blood cell types. Epigenetics 2011, 6, 76–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Traffic-Related Air Pollution | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| B(a)P ng/m3 | CO mg/m3 | O3 µg /m3 | |||||
| n | Mean ± SD | Mean ± SD | Mean ± SD | ||||
| Status | |||||||
| Unexposed subjects | 45 | 0.2 ± 0.3 | 1.1 ± 0.4 | - | |||
| Policemen | 95 | 4.2 ± 2.6 | <0.001 | 8.7 ± 4.2 | <0.001 | 44.2 ± 23.5 | |
| Districts | |||||||
| Seaside | 21 | 5.2 ± 2.2 | 8.2 ± 4.5 | 28.2 ± 9.9 | |||
| Hill | 22 | 3.4 ± 3.1 | 0.050 | 8.7 ± 3.4 | 0.704 | 50.5 ± 17.7 | <0.001 |
| Downtown | 52 | 4.3 ± 2.5 | 0.221 | 9.0 ± 4.4 | 0.503 | 47.4 ± 26.7 | 0.003 |
| Epigenetic and DNA Damage Marks | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LINE-1 | ALU | IL-6 | INOs | DNA Adducts | ||
| n | Mean ± SD | Mean ± SD | Mean ± SD | Mean ± SD | Mean ± SD | |
| Smoking habit | ||||||
| Non-smokers | 53 | 73.4 ± 1.0 | 30.1 ± 2.7 | 5.0 ± 1.4 | 64.4 ± 4.2 | 1.2 ± 1.1 |
| Smokers | 97 | 73.4 ± 1.4 | 29.6 ± 3.5 | 5.6 ± 2.4 | 63.6 ± 5.2 | 1.4 ± 1.2 |
| Occupational status | ||||||
| Unexposed subjects | 45 | 73.4 ± 1.1 | 31.1 ± 3.4 | 5.2 ± 2.5 | 64.0 ± 5.2 | 0.9 ± 0.6 |
| Policemen | 95 | 73.4 ± 1.2 | 29.3 ± 3.2 | 5.1 ± 1.4 | 64.4 ± 4.3 | 1.4 ± 1.3 |
| Working districts | ||||||
| Seaside | 21 | 73.2 ± 1.6 | 30.9 ± 3.9 | 5.1 ± 1.4 | 64.2 ± 4.1 | 0.9 ± 0.9 |
| Hill | 22 | 73.4 ± 1.1 | 29.5 ± 2.6 | 4.8 ± 1.4 | 63.9 ± 4.4 | 0.9 ± 0.8 |
| Downtown | 52 | 73.6 ± 1.0 | 28.8 ± 3.0 | 5.3 ± 1.4 | 64.5 ± 4.4 | 1.8 ± 1.5 |
| Epigenetic and DNA Damage Marks | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LINE-1 | ALU | IL-6 | INOs | DNA Adducts | ||||||
| MD 95% C.I. | p | MD 95% C.I. | p | MD 95% C.I. | p | MD 95% C.I. | p | MD 95% C.I. | p | |
| Status | ||||||||||
| Smokers | 0.01 −0.39–0.42 | 0.942 | −0.19 −1.39–1.00 | 0.750 | 0.73 0.07–1.39 | 0.030 | −0.74 −2.46–0.98 | 0.395 | 0.07 −0.35–0.48 | 0.756 |
| Policemen | 0.04 −0.38–0.46 | 0.857 | −1.41 −2.65–−0.17 | 0.026 | −0.26, −0.94–0.42 | 0.447 | 0.50 −1.28–2.28 | 0.578 | 0.45 0.02–0.88 | 0.039 |
| Working districts | ||||||||||
| Seaside | −0.11 −0.74–0.53 | 0.734 | 0.48 −1.36–2.32 | 0.603 | −0.33 −1.36–0.71 | 0.530 | 0.01 −2.69–2.72 | 0.993 | −0.19 −0.81–0.42 | 0.530 |
| Hill | 0.10 −0.52–0.73 | 0.746 | −0.73 −2.54–1.09 | 0.430 | −0.71 −1.71–0.29 | 0.161 | 0.46 −2.15–3.07 | 0.728 | −0.18 −0.78–0.43 | 0.563 |
| Downtown | 0.16 −0.32–0.63 | 0.511 | −1.86 −3.23–−0.49 | 0.008 | −0.13 −0.89–0.63 | 0.735 | 0.39 −1.62–2.39 | 0.704 | 0.84 0.39–1.29 | <0.001 |
| Epigenetic and DNA Damage Marks | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LINE-1 | ALU | IL-6 | INOs | DNA Adducts | ||||||
| MD 95% C.I. | p | MD 95% C.I. | p | MD 95% C.I. | p | MD 95% C.I. | p | MD 95% C.I. | p | |
| External B(a)P levels (ng/m3) | −0.01 −0.11–0.08 | 0.790 | 0.32 0.03–0.60 | 0.032 | 0.07 −0.05–0.19 | 0.282 | −0.13 −0.50–0.24 | 0.485 | −0.10 −0.21–0.01 | 0.052 |
| External CO levels (mg/m3) | 0.04 −0.02–0.10 | 0.186 | 0.06 −0.12–0.25 | 0.510 | 0.01 −0.07–0.08 | 0.856 | −0.06 −0.29–0.18 | 0.626 | −0.02 −0.09–0.04 | 0.488 |
| Ground-level O3 and cut-off value | ||||||||||
| <30 µg/m3 cut-off | −0.11 −0.64–0.43 | 0.694 | −0.96 −2.53–0.60 | 0.226 | −0.27 −1.13–0.58 | 0.530 | 0.71 −1.54–2.96 | 0.532 | 0.26 −0.28–0.80 | 0.342 |
| ≥30 µg/m3 cut-off | 0.12 −0.34–0.58 | 0.609 | −1.65 −3.01–−0.30 | 0.017 | −0.26 −1.00–0.49 | 0.499 | 0.38 −1.56–2.33 | 0.698 | 0.56 0.09–1.03 | 0.019 |
| ID Forward Primer (5′-3′) | Reverse Primer (5′-3′) | Sequencing Primer (5′-3′) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| LINE-1 | TTTTGAGTTAGGTGTGGGATATA | Biotin-AAAATCAAAAAATTCCCTTTC | AGTTAGGTGTGGGATATAGT |
| ALU | biotin-TTTTTATTAAAAATATAAAAATT | CCCAAACTAAAATACAATAA | AATAACTAAAATTACAAAC |
| INOs | AATGAGAGTTGTTGT TGGGAAGTGTTT | Biotin-CCACCAAACCCAACCAAACT | TAAAGGTATTTTTGTTTTAA |
| IL-6 | biotin-TATTTTAGTTTTGAGAAAGGAGGTG | CAATACTCTAAAACCCAACAAAAAC | TCCTAATACAAACAACCCC |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Munnia, A.; Bollati, V.; Russo, V.; Ferrari, L.; Ceppi, M.; Bruzzone, M.; Dugheri, S.; Arcangeli, G.; Merlo, F.; Peluso, M. Traffic-Related Air Pollution and Ground-Level Ozone Associated Global DNA Hypomethylation and Bulky DNA Adduct Formation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 2041. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24032041
Munnia A, Bollati V, Russo V, Ferrari L, Ceppi M, Bruzzone M, Dugheri S, Arcangeli G, Merlo F, Peluso M. Traffic-Related Air Pollution and Ground-Level Ozone Associated Global DNA Hypomethylation and Bulky DNA Adduct Formation. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2023; 24(3):2041. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24032041
Chicago/Turabian StyleMunnia, Armelle, Valentina Bollati, Valentina Russo, Luca Ferrari, Marcello Ceppi, Marco Bruzzone, Stefano Dugheri, Giulio Arcangeli, Franco Merlo, and Marco Peluso. 2023. "Traffic-Related Air Pollution and Ground-Level Ozone Associated Global DNA Hypomethylation and Bulky DNA Adduct Formation" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24, no. 3: 2041. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24032041
APA StyleMunnia, A., Bollati, V., Russo, V., Ferrari, L., Ceppi, M., Bruzzone, M., Dugheri, S., Arcangeli, G., Merlo, F., & Peluso, M. (2023). Traffic-Related Air Pollution and Ground-Level Ozone Associated Global DNA Hypomethylation and Bulky DNA Adduct Formation. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(3), 2041. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24032041