Assessment of Genetic Damage Induced via Glyphosate and Three Commercial Formulations with Adjuvants in Human Blood Cells
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
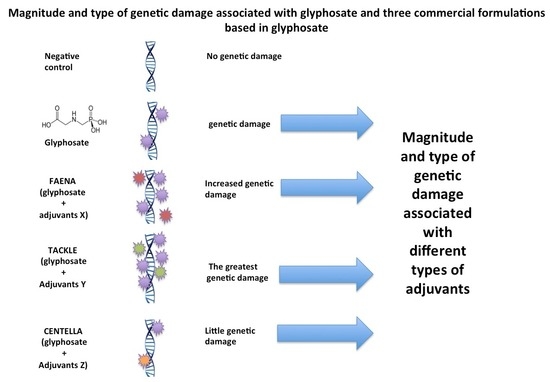
2.1. Genetic Damage Induced via G and GBH Using Tail Length and Tail Moment
2.2. Genetic Damage Induced via G and GBH Using Migration Groups
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Reagents Used
4.2. Obtaining Blood Samples
4.3. Preparation of G and GBH Concentrations
4.4. Comet Assay
4.5. Observation and Quantification of Comets
4.6. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nagy, K.; Tessema, R.A.; Szász, I.; Smeirat, T.; Al Rajo, A.; Ádám, B. Micronucleus formation induced by glyphosate and glyphosate-based herbicides in human peripheral white blood cells. Front. Public Health 2021, 9, 588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andreotti, G.; Koutros, S.; Hofmann, J.N.; Sandler, D.P.; Lubin, J.H.; Lynch, C.F.; Lerro, C.C.; De Roos, A.J.; Parks, C.G.; Alavanja, M.C.; et al. Glyphosate use and cancer incidence in the Agricultural Health Study. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2018, 110, 509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Benbrook, C.M. How did the US EPA and IARC reach diametrically opposed conclusions on the genotoxicity of glyphosate-based herbicides? Environ. Sci. Eur. 2019, 31, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwiatkowska, M.; Reszka, E.; Woźniak, K.; Jabłońska, E.; Michałowicz, J.; Bukowska, B. DNA damage and methylation induced by glyphosate in human peripheral blood mononuclear cells (in vitro study). Food Chem. Toxicol. 2017, 105, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martini, C.N.; Gabrielli, M.; Codesido, M.M.; del Vila, M.C. Glyphosate-based herbicides with different adjuvants are more potent inhibitors of 3T3-L1 fibroblast proliferation and differentiation to adipocytes than glyphosate alone. Comp. Clin. Pathol. 2016, 25, 607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, G.; Mannetje, A.; Keer, S.; Eaglesham, G.; Wang, X.; Lin, C.Y.; Kaserzon, S. Characterization of glyphosate and AMPA concentrations in the urine of Australian and New Zealand populations. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 847, 157585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.; Kumar, V.; Srivastava, A.; Saxena, G.; Verma, P.C. Biomarker-based evaluation of cytogenotoxic potential of glyphosate in Vigna mungo (L.) Hepper genotypes. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2021, 193, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celik, D.A.; Togay, V.A.; Turel, G.Y.; Tuluceoglu, E.E.; Kosar, P.A. DNA damages of widely used pesticides; a comet assay report for chlorothalonil and glyphosate potassium salt. Fresenius. Environ. Bull. 2021, 30, 4170. [Google Scholar]
- Suppa, A.; Kvist, J.; Li, X.; Dhandapani, V.; Almulla, H.; Tian, A.Y.; Orsini, L. Roundup causes embryonic development failure and alters metabolic pathways and gut microbiota functionality in non-target species. Microbiome 2020, 8, 170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez-Moya, C.; Reynoso Silva, M.; Valdez-Ramírez, C.; Gómez-Gallardo, D.; León-Sánchez, R.; Canales-Aguirre, A.; Feria-Velasco, A. Comparison of the in vivo and in vitro genotoxicity of glyphosate isopropylamine salt in three different organisms. Genet. Mol. Biol. 2014, 37, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lara-Rodríguez, A.M.; Páez-Almanza, V.; Manrique-Torres, O.V.; Guevara-Medina, C.J.; Alarcón- Vargas, A.F.; Arenas, N.E.; Cuervo, L.I. Efectos del glifosato en la expresión de algunos genes y sus implicaciones en la salud humana. Rev. Cienc. Agropec. 2020, 6, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woźniak, E.; Reszka, E.; Jabłońska, E.; Balcerczyk, A.; Broncel, M.; Bukowska, B. Glyphosate affects methylation in the promoter regions of selected tumor suppressors as well as expression of major cell cycle and apoptosis drivers in PBMCs (in vitro study). Toxicol. In Vitro 2020, 63, 104736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, S.W.; Gonzalez, P.; Cormier, B.; Mazzella, N.; Bonnaud, B.; Morin, S.; Cachot, J. A glyphosate-based herbicide induces sub-lethal effects in early life stages and liver cell line of rainbow trout, Oncorhynchus mykiss. Aquat. Toxicol. 2019, 216, 105291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Argüello-Rangel, J.; Triana-García, P.A.; Eslava-Mocha, P.R. Eosinophlic granular cells/Mast cells and their relation with the effects of herbicides: Case of glyphosate and accompanying surfactants on fish. Orinoquia 2015, 19, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kier, L.D.; Kirkland, D.J. Review of genotoxicity studies of glyphosate and glyphosate-based formulations. Crit. Rev. Toxicol. 2013, 43, 283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Portier, C.J. A comprehensive analysis of the animal carcinogenicity data for glyphosate from chronic exposure rodent carcinogenicity studies. Environ. Health 2020, 19, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, L.; Deng, Q.; Hu, H.; Liu, M.; Gong, Z.; Zhang, S.; Li, Y. Glyphosate induces benign monoclonal gammopathy and promotes multiple myeloma progression in mice. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2019, 12, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weisenburger, D.D. A review and update with perspective of evidence that the herbicide glyphosate (Roundup) is a Cause of non-Hodgkin lymphoma. Clin. Lymph. Myelom. Leuk. 2021, 21, 621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paumgartten, F.J.R. To be or not to be a carcinogen; delving into the glyphosate classification controversy. Braz. J. Pharm. Sci. 2019, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Székács, A.; Darvas, B. Re-registration challenges of glyphosate in the European Union. Front. Environ. Sci. 2018, 6, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chaufan, G.; Coalova, I.; Molina, M.D.C.R.D. Glyphosate commercial formulation causes cytotoxicity, oxidative effects, and apoptosis on human cells: Differences with its active ingredient. Int. J. Toxicol. 2014, 33, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peillex, C.; Pelletier, M. The impact and toxicity of glyphosate and glyphosate-based herbicides on health and immunity. J. Immunotoxicol. 2020, 17, 163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woźniak, E.; Sicińska, P.; Michałowicz, J.; Woźniak, K.; Reszka, E.; Huras, B.; Bukowska, B. The mechanism of DNA damage induced by Roundup 360 PLUS, glyphosate and AMPA in human peripheral blood mononuclear cells-genotoxic risk assessement. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2018, 120, 510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vera-Candioti, J.; Soloneski, S.; Larramendy, M.L. Evaluation of the genotoxic and cytotoxic effects of glyphosate-based herbicides in the ten spotted live-bearer fish Cnesterodon decemmaculatus (Jenyns, 1842). Ecotox. Environ. Safe 2013, 89, 166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koller, V.J.; Fürhacker, M.; Nersesyan, A.; Mišík, M.; Eisenbauer, M.; Knasmueller, S. Cytotoxic and DNA-damaging properties of glyphosate and Roundup in human-derived buccal epithelial cells. Arch. Toxicol. 2012, 86, 805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vandenberg, L.N.; Blumberg, B.; Antoniou, M.N.; Benbrook, C.M.; Carroll, L.; Colborn, T.; Myers, J.P. Is it time to reassess current safety standards for glyphosate-based herbicides? J. Epidemiol. Community Health 2017, 71, 613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milić, M.; Žunec, S.; Micek, V.; Kašuba, V.; Mikolić, A.; Tariba-Lovaković, B.; Želježić, D. Oxidative stress, cholinesterase activity, and DNA damage in the liver, whole blood, and plasma of Wistar rats following a 28-day exposure to glyphosate. Arh. Za Hig. Rada I Toksikol. 2018, 69, 154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Singh, N.P.; McCoy, M.T.; Tice, R.R.; Schneider, E.L. A simple technique for quantitation of low levels of DNA damage in individual cells. Exp. Cell. Res. 1988, 175, 184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tice, R.R.; Agurell, E.; Anderson, D.; Burlinson, B.; Hartmann, A.; Kobayashi, H.; Sasaki, Y.F. Single cell gel/comet assay: Guidelines for in vitro and in vivo genetic toxicology testing. Environ. Mol. Mutagen. 2000, 35, 206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olive, P.L.; Banáth, J.P. The comet assay: A method to measure DNA damage in individual cells. Nat. Protoc. 2006, 1, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reynoso-Silva, M.; Alvarez-Moya, C.; Ramírez-Velasco, R.; Sámano-León, A.G.; Arvizu-Hernández, E.; Castañeda-Vásquez, H.; Ruíz-Lopez, M.A. Migration Groups: A Poorly Explored Point of View for Genetic Damage Assessment Using Comet Assay in Human Lymphocytes. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 4094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faust, F.; Kassie, F.; Knasmüller, S.; Boedecker, R.H.; Mann, M.; Mersch-Sundermann, V. The use of the alkaline comet assay with lymphocytes in human biomonitoring studies. Mutat. Res. Rev. Mutat. Res. 2004, 566, 209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santovito, A.; Ruberto, S.; Gendusa, C.; Cervella, P. In vitro evaluation of genomic damage induced by glyphosate on human lymphocytes. Environ. Sci. Poll. Res. 2018, 25, 34693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez-Moya, C.; Sámano-León, A.G.; Reynoso-Silva, M.; Ramírez-Velasco, R.; Ruiz-López, M.A.; Villalobos-Arámbula, A.R. Antigenotoxic effect of sscorbic acid and resveratrol in erythrocytes of ambystoma mexicanum, Oreochromis niloticus and human lymphocytes exposed to glyphosate. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2022, 44, 2230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conte, F.M.; Cestonaro, L.V.; Piton, Y.V.; Guimarães, N.; Garcia, S.C.; da Silva, D.D.; Arbo, M.D. Toxicity of pesticides widely applied on soybean cultivation: Synergistic effects of fipronil, glyphosate and imidacloprid in HepG2 cells. Toxicol. In Vitro 2022, 84, 105446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, M.; Ye, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Gillings, M.; Qu, Q.; Xu, N.; Qian, H. Synergistic effects of glyphosate and multiwall carbon nanotubes on Arabidopsis thaliana physiology and metabolism. Sci. Total. Environ. 2021, 769, 145156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zúñiga, G. Sistemas de detección de daño genético. In Genética Ambiente y Salud, 3rd ed.; Alvarez-Moya, C., Ed.; Universidad de Guadalajara: Guadalajara, México, 2013; pp. 127–150. [Google Scholar]
- Kirkland, D.; Uno, Y.; Luijten, M.; Beevers, C.; van Benthem, J.; Burlinson, B.K.; Lovell, D.P. In vivo genotoxicity testing strategies: Report from the 7th International workshop on genotoxicity testing (IWGT). Mutat. Res. Genet. Toxicol. Environ. Mutagen. 2019, 847, 403035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koppen, G.; Azqueta, A.; Pourrut, B.; Brunborg, G.; Collins, A.R.; Langie, S.A.S. The next three decades of the comet assay: A report of the 11th International Comet AssayWorkshop. Mutagenesis 2017, 32, 397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glei, M.; Schneider, T.; Schlörmann, W. Comet assay: An essential tool in toxicological research. Arch. Toxicol. 2016, 90, 2315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uno, Y.; Kojima, H.; Omori, T.; Corvi, R.; Honma, M.; Schechtman, L.; Hayashi, M. JaCVAM-organized international validation study of the in vivo rodent alkaline comet assay for detection of genotoxic carcinogens: II. Summary of definitive validation study results. Res. Genet. Toxicol. Environ. Mutagen. 2015, 45, 786–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kent, C.R.H.; Eady, J.J.; Ross, G.M.; Steel, G.G. The comet moment as a measure of DNA damage in the comet assay. Int. J. Radiat. Biol. 1995, 67, 655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kyoya, T.; Iwamoto, R.; Shimanura, Y.; Terada, M.; Masuda, S. The effect of different methods and image analyzers on the results of the in vivo comet assay. Genes. Environ. 2018, 40, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Møller, P.; Azqueta, A.; Boutet-Robinet, E.; Koppen, G.; Bonassi, S.; Milić, M.; Langie, S.A. Minimum Information for Reporting on the Comet Assay (MIRCA): Recommendations for describing comet assay procedures and results. Nat. Protoc. 2020, 15, 3817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Speit, G.; Hartmann, A. The comet assay (single-cell gel test). In DNA Repair Protocols; Humana Press: Totowa, NJ, USA, 1999; pp. 203–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alvarez-Moya, C.; Reynoso-Silva, M. Assessment of Genetic Damage Induced via Glyphosate and Three Commercial Formulations with Adjuvants in Human Blood Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 4560. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24054560
Alvarez-Moya C, Reynoso-Silva M. Assessment of Genetic Damage Induced via Glyphosate and Three Commercial Formulations with Adjuvants in Human Blood Cells. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2023; 24(5):4560. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24054560
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlvarez-Moya, Carlos, and Mónica Reynoso-Silva. 2023. "Assessment of Genetic Damage Induced via Glyphosate and Three Commercial Formulations with Adjuvants in Human Blood Cells" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24, no. 5: 4560. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24054560
APA StyleAlvarez-Moya, C., & Reynoso-Silva, M. (2023). Assessment of Genetic Damage Induced via Glyphosate and Three Commercial Formulations with Adjuvants in Human Blood Cells. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(5), 4560. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24054560