MicroRNA-423-5p Mediates Cocaine-Induced Smooth Muscle Cell Contraction by Targeting Cacna2d2
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
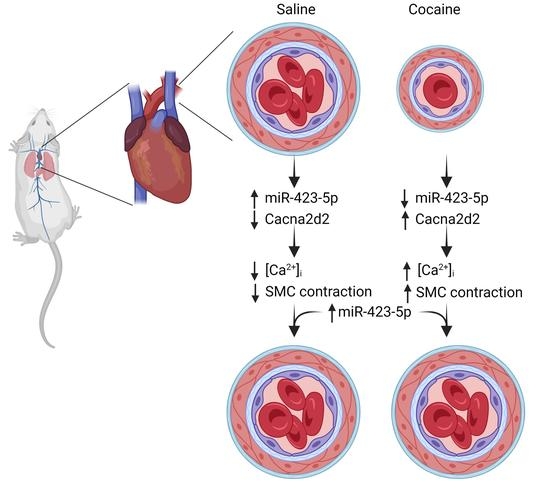
2.1. Cocaine and Cocaine Methiodide (CM) Exposure Increased BP, Aortic Stiffness, and Alters miR-423-5p and Cacna2d2 Expression in the Mouse Aorta
2.2. Cocaine and CM Treatment Increased Intracellular Free Calcium [Ca2+] and Induce Primary Mouse Aortic SMCs Contraction
2.3. Modulation of the miR-423—Cacna2d2 Axis Altered Intracellular Free Calcium [Ca2+]i and Contractility of Mouse Aortic SMCs
2.4. miR-423-5p Ameliorated Cocaine-Induced Increases in BP and Aortic Stiffness In Vivo
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Animals
4.2. Blood Pressure and Pulse Wave Velocity Measurement
4.3. Lentivirus Production and SMC Cell Lines
4.4. Site-Directed Mutagenesis in Cacna2d2 and Luciferase Reporter Assays
4.5. Real-Time Quantitative PCR (RT-PCR) for mRNAs and miRNAs
4.6. Cytosolic Free Calcium Measurement
4.7. Collagen Gel Contraction Assay
4.8. Immunofluorescence Staining
4.9. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Singh, V.; Rodriguez, A.P.; Thakkar, B.; Savani, G.T.; Patel, N.J.; Badheka, A.O.; Cohen, M.G.; Alfonso, C.E.; Mitrani, R.D.; Viles-Gonzalez, J.; et al. Hospital Admissions for Chest Pain Associated with Cocaine Use in the United States. Am. J. Med. 2017, 130, 688–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Secemsky, E.; Lange, D.; Waters, D.D.; Goldschlager, N.F.; Hsue, P.Y. Hemodynamic and arrhythmogenic effects of cocaine in hypertensive individuals. J. Clin. Hypertens. 2011, 13, 744–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bastante, T.; Rivero, F.; Cuesta, J.; Benedicto, A.; Restrepo, J.; Alfonso, F. Nonatherosclerotic causes of acute coronary syndrome: Recognition and management. Curr. Cardiol. Rep. 2014, 16, 543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, R.; Arshed, S.; Jehangir, W.; Sen, S.; Yousif, A. Cocaine-Induced Delayed Myocardial Infarction Complicated by Apical Thrombus. J. Clin. Med. Res. 2016, 8, 59–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schwartz, B.G.; Rezkalla, S.; Kloner, R.A. Cardiovascular effects of cocaine. Circulation. Circulation 2010, 122, 2558–2569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dean, J.H.; Woznicki, E.M.; O’Gara, P.; Montgomery, D.G.; Trimarchi, S.; Myrmel, T.; Pyeritz, R.E.; Harris, K.M.; Suzuki, T.; Braverman, A.C.; et al. Cocaine-related aortic dissection: Lessons from the International Registry of Acute Aortic Dissection. Am. J. Med. 2014, 127, 878–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrio, G.; Molist, G.; de la Fuente, L.; Fernández, F.; Guitart, A.; Bravo, M.J.; Brugal, M.T. Mortality in a cohort of young primary cocaine users: Controlling the effect of the riskiest drug-use behaviors. Addict. Behav. 2013, 38, 1601–1604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Degenhardt, L.; Singleton, J.; Calabria, B.; McLaren, J.; Kerr, T.; Mehta, S.; Kirk, G.; Hall, W.D. Mortality among cocaine users: A systematic review of cohort studies. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2011, 113, 88–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozor, R.; Grieve, S.M.; Buchholz, S.; Kaye, S.; Darke, S.; Bhindi, R.; Figtree, G.A. Regular cocaine use is associated with increased systolic blood pressure, aortic stiffness and left ventricular mass in young otherwise healthy individuals. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e89710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Traub, M.; Aochi, T.; Kawada, T.; Shishido, T.; Sunagawa, K.; Knuepfer, M.M. Contribution of baroreflex sensitivity and vascular reactivity to variable haemodynamic responses to cocaine in conscious rats. CClin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiol. 2005, 32, 911–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumura, K.; Tsuchihashi, T.; Abe, I. Central human cocaine- and amphetamine-regulated transcript peptide 55-102 increases arterial pressure in conscious rabbits. Hypertension 2001, 38, 1096–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vongpatanasin, W.; Mansour, Y.; Chavoshan, B.; Arbique, D.; Victor, R.G. Cocaine stimulates the human cardiovascular system via a central mechanism of action. Circulation 1999, 100, 497–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fandino, J.; Sherman, J.D.; Zuccarello, M.; Rapoport, R.M. Cocaine-induced endothelin-1-dependent spasm in rabbit basilar artery in vivo. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. 2003, 41, 158–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iliff, J.J.; Alkayed, N.J.; Golshani, K.J.; Weinstein, J.; Traystman, R.J.; West, G.A. In vivo cerebrovascular effects of cocaine- and amphetamine-regulated transcript (CART) peptide. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. 2008, 52, 82–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mehta, P.M.; Grainger, T.A.; Lust, R.M.; Movahed, A.; Terry, J.; Gilliland, M.G.; Jolly, S.R. Effect of cocaine on left ventricular function. Relation to increased wall stress and persistence after treatment. Circulation 1995, 91, 3002–3009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egashira, K.; Morgan, K.G.; Morgan, J.P. Effects of cocaine on excitation-contraction coupling of aortic smooth muscle from the ferret. J. Clin. Investig. 1991, 87, 1322–1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liaudet, L.; Calderari, B.; Pacher, P. Pathophysiological mechanisms of catecholamine and cocaine-mediated cardiotoxicity. Heart Fail. Rev. 2014, 19, 815–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Reuter, H. Calcium channel modulation by neurotransmitters, enzymes and drugs. Nature 1983, 301, 569–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDonald, T.F.; Pelzer, S.; Trautwein, W.; Pelzer, D.J. Regulation and modulation of calcium channels in cardiac, skeletal, and smooth muscle cells. Physiol. Rev. 1994, 74, 365–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Leary, M.E.; Hancox, J.C. Role of voltage-gated sodium, potassium and calcium channels in the development of cocaine-associated cardiac arrhythmias. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2010, 69, 427–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, W.; Singh, A.K.; Arruda, J.A.; Dunea, G. Role of nitric oxide in cocaine-induced acute hypertension. Am. J. Hypertens. 1998, 11 Pt 1, 708–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mendoza-Baumgart, M.I.; Pravetoni, M.; Sparber, S.B. Inhibition of nitric oxide synthase enhances cocaine’s developmental toxicity: Vascular and CNS effects. Neuropsychopharmacology 2007, 32, 940–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varga, Z.V.; Ferdinandy, P.; Liaudet, L.; Pacher, P. Drug-induced mitochondrial dysfunction and cardiotoxicity. Am. J. Physiol. Circ. Physiol. 2015, 309, H1453–H1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hale, S.L.; Alker, K.J.; Rezkalla, S.H.; Eisenhauer, A.C.; Kloner, R.A. Nifedipine protects the heart from the acute deleterious effects of cocaine if administered before but not after cocaine. Circulation 1991, 83, 1437–1443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhu, W.; Wang, H.; Sartor, G.; Bao, M.; Griswold, A.J.; Wahlestedt, C.R.; Dong, C. Abstract 14472: RNA Sequencing Analyses Reveal Eight miRNA/mRNA Pairs that may Mediate the Effects of Cocaine in Cardiovascular Diseases. Circulation 2016, 134, A14472. [Google Scholar]
- Bartel, D.P. MicroRNAs: Target recognition and regulatory functions. Cell 2009, 136, 215–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guo, H.; Ingolia, N.T.; Weissman, J.S.; Bartel, D.P. Mammalian microRNAs predominantly act to decrease target mRNA levels. Nature 2010, 466, 835–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dykxhoorn, D.M.; Novina, C.D.; Sharp, P.A. Killing the messenger: Short RNAs that silence gene expression. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2003, 4, 457–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olson, E.N. MicroRNAs as therapeutic targets and biomarkers of cardiovascular disease. Sci. Transl. Med. 2014, 6, 239ps3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xin, M.; Olson, E.N.; Bassel-Duby, R. Mending broken hearts: Cardiac development as a basis for adult heart regeneration and repair. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2013, 14, 529–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mendell, J.T.; Olson, E.N. MicroRNAs in stress signaling and human disease. Cell 2012, 148, 1172–1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nanoudis, S.; Pikilidou, M.; Yavropoulou, M.; Zebekakis, P. The Role of MicroRNAs in Arterial Stiffness and Arterial Calcification. An Update and Review of the Literature. Front. Genet. 2017, 8, 209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhu, W.; Wang, H.; Wei, J.; Sartor, G.C.; Bao, M.M.; Pierce, C.T.; Wahlestedt, C.R.; Dykxhoorn, D.M.; Dong, C. Cocaine Exposure Increases Blood Pressure and Aortic Stiffness via the miR-30c-5p-Malic Enzyme 1-Reactive Oxygen Species Pathway. Hypertension 2018, 71, 752–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hollander, J.A.; Im, H.I.; Amelio, A.L.; Kocerha, J.; Bali, P.; Lu, Q.; Willoughby, D.; Wahlestedt, C.; Conkright, M.D.; Kenny, P.J. Striatal microRNA controls cocaine intake through CREB signallling. Nature 2010, 466, 197–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Im, H.-I.; Hollander, J.A.; Bali, P.; Kenny, P.J. MeCP2 controls BDNF expression and cocaine intake through homeostatic interactions with microRNA-212. Nat. Neurosci. 2010, 13, 1120–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Doura, M.B.; Unterwald, E.M. MicroRNAs Modulate Interactions between Stress and Risk for Cocaine Addiction. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2016, 10, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dewar, K.; Nolan, S. Chronic hypertension, recreational cocaine use and a subsequent acute aortic dissection in a young adult. BMJ Case Rep. 2017, 2017, bcr-2016-218235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richards, J.R. Toxicity, Cocaine; StatPearls Publishing: Tampa, FL, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Lucas, G.M.; Atta, M.G.; Fine, D.M.; McFall, A.M.; Estrella, M.M.; Zook, K.; Stein, J.H. HIV, Cocaine Use, and Hepatitis C Virus: A Triad of Nontraditional Risk Factors for Subclinical Cardiovascular Disease. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2016, 36, 2100–2107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McGeary, S.E.; Lin, K.S.; Shi, C.Y.; Pham, T.M.; Bisaria, N.; Kelley, G.M.; Bartel, D.P. The biochemical basis of microRNA targeting efficacy. Science 2019, 366, eaav1741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Wang, X. miRDB: An online database for prediction of functional microRNA targets. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020, 48, D127–D131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bigi, M.A.B.; Aslani, A.; Mehrpour, M. Effect of chronic cocaine abuse on the elastic properties of aorta. Echocardiography 2008, 25, 308–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Hua, Y.; Park, K.; Volkow, N.D.; Pan, Y.; Du, C. Cocaine’s cerebrovascular vasoconstriction is associated with astrocytic Ca2+ increase in mice. Commun. Biol. 2022, 5, 936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rapoport, R.M.; Yoon, S.; Zuccarello, M. Cocaine Constrictor Mechanisms of the Cerebral Vasculature. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. 2016, 67, 442–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agrawal, P.R.; Scarabelli, T.M.; Saravolatz, L.; Kini, A.; Jalota, A.; Chen-Scarabelli, C.; Fuster, V.; Halperin, J.L. Current strategies in the evaluation and management of cocaine-induced chest pain. Cardiol. Rev. 2015, 23, 303–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoon, S.; Zuccarello, M.; Rapoport, R.M. Cocaine constriction of rat basilar artery in situ: Roles of nitric oxide and endothelin-1. Pharmacology 2014, 93, 151–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, D.; Syed, A.; Prada, M.; Nystoriak, M.; Santana, L.; Nieves-Cintrón, M.; Navedo, M. Calcium Channels in Vascular Smooth Muscle. Adv. Pharmacol. 2017, 78, 49–87. [Google Scholar]
- Amberg, G.C.; Navedo, M.F. Calcium dynamics in vascular smooth muscle. Microcirculation 2013, 20, 281–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Knot, H.J.; Nelson, M.T. Regulation of arterial diameter and wall [Ca2+] in cerebral arteries of rat by membrane potential and intravascular pressure. J. Physiol. 1998, 508 Pt 1, 199–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, M.T.; Patlak, J.B.; Worley, J.F.; Standen, N.B. Calcium channels, potassium channels, and voltage dependence of arterial smooth muscle tone. Am. J. Physiol. 1990, 259 Pt 1, C3–C18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Havakuk, O.; Rezkalla, S.H.; Kloner, R.A. The Cardiovascular Effects of Cocaine. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2017, 70, 101–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qureshi, A.I.; Suri, M.F.K.; Guterman, L.R.; Hopkins, L.N. Cocaine use and the likelihood of nonfatal myocardial infarction and stroke: Data from the Third National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. Circulation 2001, 103, 502–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Stankowski, R.V.; Kloner, R.A.; Rezkalla, S.H. Cardiovascular consequences of cocaine use. Trends Cardiovasc. Med. 2015, 25, 517–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Talarico, G.P.; Crosta, M.L.; Giannico, M.B.; Summaria, F.; Calò, L.; Patrizi, R. Cocaine and coronary artery diseases: A systematic review of the literature. J. Cardiovasc. Med. 2017, 18, 291–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilbert-Lampen, U.; Seliger, C.; Zilker, T.; Arendt, R.M. Cocaine increases the endothelial release of immunoreactive endothelin and its concentrations in human plasma and urine: Reversal by coincubation with sigma-receptor antagonists. Circulation 1998, 98, 385–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Havranek, E.P.; Nademanee, K.; Grayburn, P.A.; Eichhorn, E.J. Endothelium-dependent vasorelaxation is impaired in cocaine arteriopathy. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 1996, 28, 1168–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Perreault, C.L.; US Department of Health and Human Services; National Institute on Drug Abuse; Morgan, K.G.; Morgan, J.P. Effects of cocaine on intracellular calcium handling in cardiac and vascular smooth muscle. NIDA Res. Monogr. 1991, 108, 139–153. [Google Scholar]
- Kenny, P.J. Epigenetics, microRNA, and addiction. Dialogues Clin. Neurosci. 2014, 16, 335–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bali, P.; Kenny, P.J. MicroRNAs and Drug Addiction. Front. Genet. 2013, 4, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jonkman, S.; Kenny, P.J. Molecular, cellular, and structural mechanisms of cocaine addiction: A key role for microRNAs. Neuropsychopharmacology 2013, 38, 198–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dreyer, J.-L. New insights into the roles of microRNAs in drug addiction and neuroplasticity. Genome Med. 2010, 2, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bastle, R.M.; Oliver, R.J.; Gardiner, A.S.; Pentkowski, N.S.; Bolognani, F.; Allan, A.M.; Chaudhury, T.; Peter, M.S.; Galles, N.; Smith, C.; et al. In silico identification and in vivo validation of miR-495 as a novel regulator of motivation for cocaine that targets multiple addiction-related networks in the nucleus accumbens. Mol. Psychiatry 2018, 23, 434–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chandrasekar, V.; Dreyer, J.L. Regulation of MiR-124, Let-7d, and MiR-181a in the accumbens affects the expression, extinction, and reinstatement of cocaine-induced conditioned place preference. Neuropsychopharmacology 2011, 36, 1149–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Luo, P.; He, T.; Jiang, R.; Li, G. MicroRNA-423-5p targets O-GlcNAc transferase to induce apoptosis in cardiomyocytes. Mol. Med. Rep. 2015, 12, 1163–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yuan, X.-P.; Liu, L.-S.; Chen, C.-B.; Zhou, J.; Zheng, Y.-T.; Wang, X.-P.; Han, M.; Wang, C.-X. MicroRNA-423-5p facilitates hypoxia/reoxygenation-induced apoptosis in renal proximal tubular epithelial cells by targeting GSTM1 via endoplasmic reticulum stress. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 82064–82077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Clarkson, C.W.; Xu, Y.Q.; Chang, C.; Follmer, C.H. Analysis of the ionic basis for cocaine’s biphasic effect on action potential duration in guinea-pig ventricular myocytes. J. Mol. Cell Cardiol. 1996, 28, 667–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolphin, A.C. Calcium channel auxiliary α2δ and β subunits: Trafficking and one step beyond. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2012, 13, 542–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Wu, L.; Li, Z.; Fu, G. miR-1231 exacerbates arrhythmia by targeting calciumchannel gene CACNA2D2 in myocardial infarction. Am J Transl Res. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2017, 9, 1822–1833. [Google Scholar]
- Hoppa, M.B.; Lana, B.; Margas, W.; Dolphin, A.C.; Ryan, T.A. α2δ expression sets presynaptic calcium channel abundance and release probability. Nature 2012, 486, 122–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Barclay, J.; Balaguero, N.; Mione, M.; Ackerman, S.L.; Letts, V.A.; Brodbeck, J.; Canti, C.; Meir, A.; Page, K.M.; Kusumi, K.; et al. Ducky mouse phenotype of epilepsy and ataxia is associated with mutations in the Cacna2d2 gene and decreased calcium channel current in cerebellar Purkinje cells. J. Neurosci. 2001, 21, 6095–6104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brodbeck, J.; Davies, A.; Courtney, J.M.; Meir, A.; Balaguero, N.; Canti, C.; Moos, F.J.; Page, K.M.; Pratt, W.S.; Hunt, S.P. The ducky mutation in Cacna2d2 results in altered Purkinje cell morphology and is associated with the expression of a truncated alpha 2 delta-2 protein with abnormal function. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 7684–7693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fell, B.; Eckrich, S.; Blum, K.; Eckrich, T.; Hecker, D.; Obermair, G.J.; Münkner, S.; Flockerzi, V.; Schick, B.; Engel, J. α2δ2 Controls the Function and Trans-Synaptic Coupling of Cav1.3 Channels in Mouse Inner Hair Cells and Is Essential for Normal Hearing. J. Neurosci. 2016, 36, 11024–11036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, H.; Liu, D.; Zhu, S.; Wang, F.; Sun, X.; Yang, S.; Wang, C. Plasma Exosomal Mir-423-5p Is Involved in the Occurrence and Development of Bicuspid Aortopathy via TGF-β/SMAD2 Pathway. Front. Physiol. 2021, 12, 759035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, X.; Lu, X. MiR-423-5p inhibition alleviates cardiomyocyte apoptosis and mitochondrial dysfunction caused by hypoxia/reoxygenation through activation of the wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway via targeting MYBL2. J. Cell. Physiol. 2019, 234, 22034–22043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, D.T.; Reed, R.R. Molecular cloning of five GTP-binding protein cDNA species from rat olfactory neuroepithelium. J. Biol. Chem. 1987, 262, 14241–14249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Periyasamy, P.; Liao, K.; Kook, Y.H.; Niu, F.; Callen, S.E.; Guo, M.L.; Buch, S. Cocaine-Mediated Downregulation of miR-124 Activates Microglia by Targeting KLF4 and TLR4 Signaling. Mol. Neurobiol. 2018, 55, 3196–3210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.P.; Chen, J.; Seok, H.Y.; Zhang, Z.; Kataoka, M.; Hu, X.; Wang, D.Z. MicroRNA-22 regulates cardiac hypertrophy and remodeling in response to stress. Circ. Res. 2013, 112, 1234–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, C.; Calado, D.P.; Galler, G.; Thai, T.H.; Patterson, H.C.; Wang, J.; Rajewsky, N.; Bender, T.P.; Rajewsky, K. MiR-150 controls B cell differentiation by targeting the transcription factor c-Myb. Cell 2007, 131, 146–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]







Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dykxhoorn, D.M.; Wang, H.; Da Fonseca Ferreira, A.; Wei, J.; Dong, C. MicroRNA-423-5p Mediates Cocaine-Induced Smooth Muscle Cell Contraction by Targeting Cacna2d2. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 6584. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24076584
Dykxhoorn DM, Wang H, Da Fonseca Ferreira A, Wei J, Dong C. MicroRNA-423-5p Mediates Cocaine-Induced Smooth Muscle Cell Contraction by Targeting Cacna2d2. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2023; 24(7):6584. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24076584
Chicago/Turabian StyleDykxhoorn, Derek M., Huilan Wang, Andrea Da Fonseca Ferreira, Jianqin Wei, and Chunming Dong. 2023. "MicroRNA-423-5p Mediates Cocaine-Induced Smooth Muscle Cell Contraction by Targeting Cacna2d2" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24, no. 7: 6584. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24076584
APA StyleDykxhoorn, D. M., Wang, H., Da Fonseca Ferreira, A., Wei, J., & Dong, C. (2023). MicroRNA-423-5p Mediates Cocaine-Induced Smooth Muscle Cell Contraction by Targeting Cacna2d2. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(7), 6584. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24076584