The Effect of Epimedium Isopentenyl Flavonoids on the Broiler Gut Health Using Microbiomic and Metabolomic Analyses
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Isopentenyl Flavonols Composition of EM
2.2. Apparent Digestibilities of Nutrients
2.3. Serum Immune Response
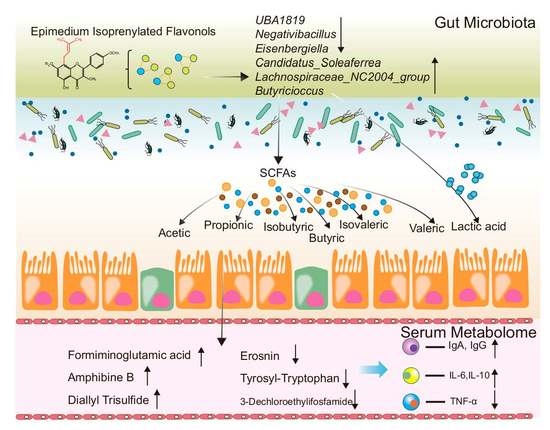
2.4. Cecal Lactic Acid and SCFAs Concentrations
2.5. Cecum Microbiota Analysis
2.6. Blood Serum Metabolome
2.7. Co-Occurrence Network
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Chemicals and Reagents
4.2. Epimedium Extracts for Dietary Supplementation and Analysis
4.3. Birds and Experimental Design
4.4. Sample Collection
4.5. Apparent Digestibilities of Nutrients
4.6. Immune Markers
4.7. Cecal Lactic Acid and SCFAs Analysis
4.8. The 16S rRNA High-Throughput Sequencing
4.9. UHPLC-Q Exactive HF-X Analysis of Serum Metabolites
4.10. Co-Occurrence Network Analysis
4.11. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Ethics Approval
Abbreviations
References
- Thilakarathna, S.H.; Rupasinghe, H.V. Flavonoid bioavailability and attempts for bioavailability enhancement. Nutrients 2013, 5, 3367–3387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivey, K.L.; Croft, K.; Prince, R.L.; Hodgson, J.M. Comparison of flavonoid intake assessment methods. Food Funct. 2016, 7, 3748–3759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maugeri, A.; Calderaro, A.; Patanè, G.T.; Navarra, M.; Barreca, D.; Cirmi, S.; Felice, M.R. Targets Involved in the Anti-Cancer Activity of Quercetin in Breast, Colorectal and Liver Neoplasms. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 2952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martínez-Coria, H.; Arrieta-Cruz, I.; Gutiérrez-Juárez, R.; López-Valdés, H.E. Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Flavonoids in Common Neurological Disorders Associated with Aging. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 4297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Russo, C.; Maugeri, A.; Musumeci, L.; De Sarro, G.; Cirmi, S.; Navarra, M. Inflammation and Obesity: The Pharmacological Role of Flavonoids in the Zebrafish Model. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 2899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teles, Y.C.; Souza, M.S.R.; Souza, M.d.F.V.d. Sulphated flavonoids: Biosynthesis, structures, and biological activities. Molecules 2018, 23, 480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nile, S.H.; Keum, Y.S.; Nile, A.S.; Jalde, S.S.; Patel, R.V. Antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and enzyme inhibitory activity of natural plant flavonoids and their synthesized derivatives. J. Biochem. Mol. Toxicol. 2018, 32, e22002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, J. Dietary flavonoid aglycones and their glycosides: Which show better biological significance? Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2017, 57, 1874–1905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukai, R. Prenylation enhances the biological activity of dietary flavonoids by altering their bioavailability. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2018, 82, 207–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, M.; Liu, Y.; Li, T.; Liu, X.; Hao, Z.; Ding, S.; Panichayupakaranant, P.; Zhu, K.; Shen, J. Plant natural flavonoids against multidrug resistant pathogens. Adv. Nutr. 2021, 8, 2100749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, L.; Jiang, Y.; Yang, J.; Zhao, Y.; Tian, M.; Yang, B. Structure, bioactivity, and synthesis of methylated flavonoids. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2017, 1398, 120–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lippolis, T.; Cofano, M.; Caponio, G.R.; De Nunzio, V.; Notarnicola, M. Bioaccessibility and Bioavailability of Diet Polyphenols and Their Modulation of Gut Microbiota. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 3813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murota, K.; Nakamura, Y.; Uehara, M. Flavonoid metabolism: The interaction of metabolites and gut microbiota. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2018, 82, 600–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, F.; Ding, Y.; Guo, Y.; Liu, B.; Kou, Z.; Xiao, W.; Zhu, J. Anti-osteoporosis effect of Epimedium via an estrogen-like mechanism based on a system-level approach. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2016, 177, 148–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Z.D.; Wang, W.J.; Han, X.L.; Yang, X.L. Three New Hydroxyphenylacetic Acid Derivatives and A New Alkaloid from Endophytic Fungus mortierella sp. in Epimedium acuminatum Franch. and Their Antibacterial Activity. Chem. Biodivers. 2021, 18, e2100741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, Y.; Yang, Z.; Shi, J.; Yang, J.; Zhao, J.; He, Y.; Qi, M. Total flavonoids of Epimedium ameliorates testicular damage in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats by suppressing inflammation and oxidative stress. Environ. Toxicol. 2020, 35, 268–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhou, S.; Liang, Y.; Xie, G.; Zhu, M.; Wang, Z.; Qu, Q.; Long, Y.; Lv, Y.; Peng, J. Effects of Astragalus, Epimedium and Fructus Ligustri Lucidi extractive on antioxidant capacity, production performance and immune mechanism of breeding pigeons under stress. Poult. Sci. 2022, 102, 102350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, C.; Li, Z.; Zhu, J.; Chen, X.; Hao, Y.; Yang, R.; Huang, R.; Zhou, J.; Wang, Z.; Xiao, W. Systems pharmacology dissection of Epimedium targeting tumor microenvironment to enhance cytotoxic T lymphocyte responses in lung cancer. Aging 2021, 13, 2912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, H.; Shan, Y.; Ma, Z.; Yu, M.; Gong, B. A network pharmacology approach to explore active compounds and pharmacological mechanisms of epimedium for treatment of premature ovarian insufficiency. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2019, 13, 2997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.; Zheng, W.; Sun, X.; Yuan, M.; Zhang, J.; Chen, X.; Yu, K.; Guo, B.; Ma, B. Comparative analysis of chemical components in different parts of Epimedium Herb. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2021, 198, 113984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, Y. The discovery of artemisinin (qinghaosu) and gifts from Chinese medicine. Nat. Med. 2011, 17, 1217–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Yu, H.; Zhang, H.; Zhao, Q.; Si, W.; Qin, Y.; Zhang, J. Dietary Epimedium extract supplementation improves intestinal functions and alters gut microbiota in broilers. J. Anim. Sci. Biotechnol. 2023, 14, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peluso, I.; Miglio, C.; Morabito, G.; Ioannone, F.; Serafini, M. Flavonoids and immune function in human: A systematic review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2015, 55, 383–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, K.; Fang, X.; Yang, J.; Yao, Y.; Nandakumar, K.S.; Salem, M.L.; Cheng, K. Recent research on flavonoids and their biomedical applications. Curr. Med. Chem. 2021, 28, 1042–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Wang, J.; Jia, X.; Tan, X.; Hu, M. Role of intestinal hydrolase in the absorption of prenylated flavonoids present in Yinyanghuo. Molecules 2011, 16, 1336–1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukai, R.; Fujikura, Y.; Murota, K.; Uehara, M.; Minekawa, S.; Matsui, N.; Kawamura, T.; Nemoto, H.; Terao, J. Prenylation enhances quercetin uptake and reduces efflux in Caco-2 cells and enhances tissue accumulation in mice fed long-term. J. Nutr. 2013, 143, 1558–1564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhai, Y.; Wang, Q.; Li, Y.; Cui, J.; Feng, K.; Kong, X.; Xian, C.J. The higher osteoprotective activity of psoralidin in vivo than coumestrol is attributed by its presence of an isopentenyl group and through activated PI3K/Akt axis. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 102, 1015–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amevor, F.K.; Cui, Z.; Ning, Z.; Du, X.; Jin, N.; Shu, G.; Deng, X.; Zhu, Q.; Tian, Y.; Li, D. Synergistic effects of quercetin and vitamin E on egg production, egg quality, and immunity in aging breeder hens. Poult. Sci. 2021, 100, 101481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, X.; Liu, S.; Ding, C.; Miao, Y.; Gao, Z.; Li, M.; Fan, W.; Tang, Z.; Mhlambi, N.H.; Yan, L. Comparative effects of genistein and bisphenol A on non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in laying hens. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 288, 117795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Zhong, G.; Gu, W.; Yin, N.; Chen, L.; Shi, S. Dietary supplementation with daidzein and Chinese herbs, independently and combined, improves laying performance, egg quality and plasma hormone levels of post-peak laying hens. Poult. Sci. 2021, 100, 101115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, L.-H.; Qiao, J.-Y.; Huang, H.-Y.; Fang, X.-Y.; Zhang, R.; Miao, M.-S.; Li, X.-M. PI3K–AKT signaling activation and icariin: The potential effects on the perimenopausal depression-like rat model. Molecules 2019, 24, 3700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Liu, Z.; Miao, Y.; Wang, L.; Yin, H. Sex hormone-like Effects of Icariin on T-cells immune modulation in spontaneously hypertensive rats. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2021, 269, 113717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, R.; Liu, X.; Bolling, B. Flavonoids and gut health. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2020, 61, 153–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terao, J.; Mukai, R. Prenylation modulates the bioavailability and bioaccumulation of dietary flavonoids. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2014, 559, 12–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murciano-Brea, J.; Garcia-Montes, M.; Geuna, S.; Herrera-Rincon, C. Gut microbiota and neuroplasticity. Cells 2021, 10, 2084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Järbrink-Sehgal, E.; Andreasson, A. The gut microbiota and mental health in adults. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 2020, 62, 102–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Wang, J.; Yu, L.; Xu, T.; Zhu, N. Microbiota and metabolome responses in the cecum and serum of broiler chickens fed with plant essential oils or virginiamycin. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 5382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miquel, S.; Martin, R.; Rossi, O.; Bermúdez-Humarán, L.; Chatel, J.; Sokol, H.; Thomas, M.; Wells, J.; Langella, P. Faecalibacterium prausnitzii and human intestinal health. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2013, 16, 255–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davinelli, S.; Scapagnini, G. Interactions between dietary polyphenols and aging gut microbiota: A review. BioFactors 2022, 48, 274–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, R.-R.; He, P.; Lei, S.-F. Novel microbiota-related gene set enrichment analysis identified osteoporosis associated gut microbiota from autoimmune diseases. J. Bone Miner. Metab. 2021, 39, 984–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gryp, T.; Huys, G.R.; Joossens, M.; Van Biesen, W.; Glorieux, G.; Vaneechoutte, M. Isolation and quantification of uremic toxin precursor-generating gut bacteria in chronic kidney disease patients. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 1986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Egerton, S.; Donoso, F.; Fitzgerald, P.; Gite, S.; Fouhy, F.; Whooley, J.; Dinan, T.G.; Cryan, J.F.; Culloty, S.C.; Ross, R.P. Investigating the potential of fish oil as a nutraceutical in an animal model of early life stress. Nutr. Neurosci. 2022, 25, 356–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sorbara, M.T.; Littmann, E.R.; Fontana, E.; Moody, T.U.; Kohout, C.E.; Gjonbalaj, M.; Eaton, V.; Seok, R.; Leiner, I.M.; Pamer, E.G. Functional and genomic variation between human-derived isolates of Lachnospiraceae reveals inter-and intra-species diversity. Cell Host Microbe 2020, 28, 134–146.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milton-Laskibar, I.; Cuevas-Sierra, A.; Portillo, M.P.; Martínez, J.A. Effects of resveratrol administration in liver injury prevention as induced by an obesogenic diet: Role of ruminococcaceae. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 1797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gryaznova, M.; Solodskikh, S.; Panevina, A.; Syromyatnikov, M.; Dvoretskaya, Y.D.; Sviridova, T.; Popov, E.; Popov, V. Study of microbiome changes in patients with ulcerative colitis in the Central European part of Russia. Heliyon 2021, 7, e06432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wexler, H.M. Bacteroides: The good, the bad, and the nitty-gritty. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2007, 20, 593–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Filippis, F.; Pasolli, E.; Ercolini, D. The food-gut axis: Lactic acid bacteria and their link to food, the gut microbiome and human health. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2020, 44, 454–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rowland, I.; Gibson, G.; Heinken, A.; Scott, K.; Swann, J.; Thiele, I.; Tuohy, K. Gut microbiota functions: Metabolism of nutrients and other food components. Eur. J. Nutr. 2018, 57, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicholson, J.K.; Holmes, E.; Kinross, J.; Burcelin, R.; Gibson, G.; Jia, W.; Pettersson, S. Host-gut microbiota metabolic interactions. Science 2012, 336, 1262–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dale, N. National research council nutrient requirements of poultry—Ninth revised edition. J. Appl. Poult. Res. 1994, 3, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, B.; Pang, Z.; Luo, Q. Tables of Feed Composition and Nutritive Values in China. Chin Feed 2012, 21, 33–44. [Google Scholar]
- GB5009.268-2016; National food safety standard—Determination of multi-elements in foods. Standardization Administration of China, Standards Press of China: Beijing, China, 2016.
- GB/T 6432-2018; Determination of crude protein in feeds - Kjeldahl method. Standardization Administration of China, Standards Press of China: Beijing, China, 2018.
- T_NAIA 006-2020; Determination of manure urine energy value of livestock and poultry feed. Ningxia Chemical Analysis and Testing Association: Yinchuan, China, 2020.
- Sun, Z.H.; Tan, Z.L.; Liu, S.M.; Tayo, G.O.; Lin, B.; Teng, B.; Tang, S.X.; Wang, W.J.; Liao, Y.P.; Pan, Y.F. Effects of dietary methionine and lysine sources on nutrient digestion, nitrogen utilization, and duodenal amino acid flow in growing goats. J. Anim. Sci. 2007, 85, 3340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]








| No. | Identity | Formula | RT (min) | MS (m/z) | Adduct Ions | Main MS/MS Fragments Detected (Arranged from Large to Small According to Relative Intensity) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Quercetin 3-neohesperidoside | C27H30O16 | 4.70 | 610.1548 | [M−H]− | 300.0275[M-2H-C12H20O9]−; 301.0350[M-H-C12H20O9]− |
| 2 | Lespedin | C27H30O14 | 4.91 | 578.1644 | [M−H]− | 287.0547[M-H-C9H18O8]−; 433.1117[M-H-C6H8O4]− |
| 3 | Rouhuoside | C38H48O20 | 5.41 | 824.2753 | [M−H]− | 661.2147[M-H-C6H10O5]− |
| 4 | Epimedoside D | C37H46O19 | 5.52 | 794.2644 | [M−H]− | 631.2038[M-H-C6H10O5]− |
| 5 | Ikarisoside B | C32H38O15 | 5.68 | 662.2221 | [M−H]− | 353.1030[M-H-C12H22O9]−; 351.0874[M-3H-C12H26O9]−; 514.1484[M-2H-C6H14O4]− |
| 6 | Epimedoside A | C32H38O15 | 5.73 | 662.2200 | [M−H]− | 355.1171[M+H-C12H20O9]+; 517.1693[M+H-C6H10O4]+ |
| 7 | Epimedin A | C38H48O20 | 6.31 | 824.2756 | [M−H]− | 675.2301[M-H-C5H8O5]− |
| 8 | Epimedin C | C39H50O19 | 6.44 | 822.2856 | [M+H]+ | 531.1854[M+H-C12H20O8]+; 677.24327[M+H-C6H10O4]+; 369.1326[M+H-C18H30O13]+ |
| 9 | Epimedin B | C38H48O19 | 6.45 | 809.2856 | [M+H]+ | 369.1324[M+H-C17H28O13]+; 531.1847[M+H-C11H18O8]+; 677.2426[M+H-C5H8O4]+ |
| 10 | Icariin | C33H40O15 | 6.76 | 677.2400 | [M−H]− | 367.1190[M-H-C12H20O9]−; 531.1774[M-H-C6H10O5]−; 529.1724[M-H-C6H10O4]− |
| 11 | Sagittatoside A | C33H40O15 | 6.97 | 677.2400 | [M−H]− | 367.1186[M-H-C12H20O9]−; 513.1774[M-H-C6H10O5]−; 529.1718[M-H-C6H10O4]− |
| 12 | Baohuoside II | C26H28O10 | 8.13 | 500.1695 | [M+H]+ | 352.0954[M-2H-C6H10O4]−; 353.1029[M-H-C6H10O4]− |
| 13 | Sagittatoside B | C32H38O14 | 8.86 | 646.2255 | [M+H]+ | 369.1328[M+2H-C6H6O4]+ |
| 14 | 2″-O-Rhamnosyl ikarisoside A | C32H38O14 | 8.87 | 646.2271 | [M−H]− | 366.1106[M-2H-C12H18O8]−; 351.0872[M-3H-C12H20O8]−; 367.1180[M-H-C11H18O8]− |
| 15 | Anhydroicaritin 3-Rhamnosyl-(1->2)-Rhamnoside | C33H40O14 | 8.95 | 660.2426 | [M−H]− | 366.1108[M-2H-C12H20O8]−; 351.0871[M-3H-C13H22O8]−; 367.1182[M-H-C12H20O8]− |
| 16 | Baohuoside I | C27H30O10 | 9.45 | 515.1906 | [M+H]+ | 369.1327[M+H-C6H9O5]+; 313.0702[M+H-C6H9O5]+ |
| 17 | Icartin | C21H20O6 | 9.46 | 369.1327 | [M+H]+ | 313.0702[M+H-C4H6O6]+ |
| Target Compounds | Ion Mode | RT (min) | Precursor Ion (m/z) | Product Ions (m/z) | DP (V) | CE (V) | Quantification Transition | Compound Concentration (g/kg) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Epimedin A | + | 4.609 | 839.3 | 369.1 | 150 | 45 | 839.3→369.1 | 39.7908 |
| 313.1 | 150 | 77 | ||||||
| Epimedin B | + | 5.211 | 809.3 | 369.1 | 150 | 41 | 809.3→369.1 | 91.9008 |
| 313.1 | 150 | 74 | ||||||
| Epimedin C | + | 5.882 | 823.3 | 369.1 | 150 | 44 | 823.3→369.1 | 110.4184 |
| 313.1 | 150 | 76 | ||||||
| Sagittatoside A | + | 12.761 | 677.7 | 369.5 | 110 | 8 | 677.7→369.1 | 5.758 |
| 313.3 | 110 | 46 | ||||||
| Sagittatoside B | + | 12.963 | 646.5 | 369.1 | 120 | 40 | 646.5→369.1 | ND |
| 325.3 | 120 | 48 | ||||||
| 2′-O-rhamnosyl icariside II | + | 12.999 | 661.3 | 369.4 | 90 | 20 | 661.3→369. 1 | ND |
| 369.1 | 90 | 20 | ||||||
| Icariin | + | 6.727 | 677.2 | 313.3 | 110 | 46 | 677.2→313.1 | 249.3108 |
| 313.1 | 120 | 62 | ||||||
| Baohuoside Ⅰ | + | 12.428 | 515.2 | 369.1 | 150 | 17 | 515.2→369.1 | 14.1668 |
| 313.1 | 150 | 45 | ||||||
| Icartin | + | 13.793 | 387.5 | 369.3 | 120 | 22 | 387.5→369.1 | 8.8632 |
| 313.4 | 120 | 30 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, J.; Zhao, Q.; Qin, Y.; Si, W.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, J. The Effect of Epimedium Isopentenyl Flavonoids on the Broiler Gut Health Using Microbiomic and Metabolomic Analyses. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 7646. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24087646
Zhang J, Zhao Q, Qin Y, Si W, Zhang H, Zhang J. The Effect of Epimedium Isopentenyl Flavonoids on the Broiler Gut Health Using Microbiomic and Metabolomic Analyses. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2023; 24(8):7646. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24087646
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Jiaqi, Qingyu Zhao, Yuchang Qin, Wei Si, Huiyan Zhang, and Junmin Zhang. 2023. "The Effect of Epimedium Isopentenyl Flavonoids on the Broiler Gut Health Using Microbiomic and Metabolomic Analyses" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24, no. 8: 7646. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24087646
APA StyleZhang, J., Zhao, Q., Qin, Y., Si, W., Zhang, H., & Zhang, J. (2023). The Effect of Epimedium Isopentenyl Flavonoids on the Broiler Gut Health Using Microbiomic and Metabolomic Analyses. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(8), 7646. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24087646