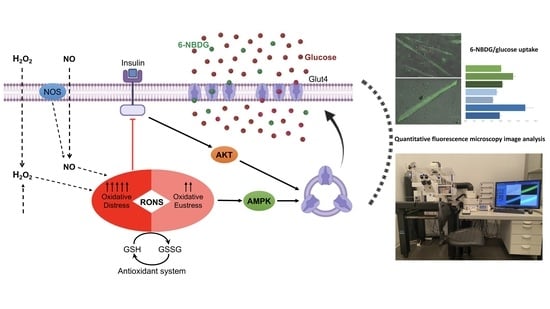
Effect of RONS-Induced Intracellular Redox Homeostasis in 6-NBDG/Glucose Uptake in C2C12 Myotubes and Single Isolated Skeletal Muscle Fibres
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. 6-NBDG/Glucose Uptake in C2C12 Myotubes: Insulin and Hydrogen Peroxide Effects
2.1.1. Bovine Insulin: 6-NBDG Incubation 1 h
2.1.2. Recombinant Human Insulin
Recombinant Human Insulin: 6-NBDG Incubation 1 h
Recombinant Human Insulin: 6-NBDG Incubation Overnight
2.2. 6-NBDG/Glucose Uptake in C2C12 Myotubes: Effects of Insulin Receptor Blocker and Angiotensin II—6-NBDG Incubation Overnight
2.3. 6-NBDG/Glucose Uptake in C2C12 Myotubes: Effect of Antioxidant Glutathione Depletion Induced by Diethyl Maleate and Diamide—6-NBDG Incubation Overnight
2.4. 6-NBDG/Glucose Uptake in C2C12 Myotubes: Effects of Cytochalasin B and Oxidants (Diethyl Maleate and Diamide)—6-NBDG Incubation Overnight
2.5. 6-NBDG/Glucose Uptake in C2C12 Myotubes: Effect of Nitric Oxide—6-NBDG Incubation Overnight
2.6. 6-NBDG/Glucose Uptake in Isolated Skeletal Muscle Fibres: Effects of Insulin and Hydrogen Peroxide—6-NBDG Incubation Overnight
2.7. 6-NBDG/Glucose Uptake in Isolated Skeletal Muscle Fibres: Effects of Insulin, Hydrogen Peroxide, and Angiotensin II—6-NBDG Incubation Overnight
2.8. 6-NBDG/Glucose Uptake in Isolated Skeletal Muscle Fibres from Aged Mice: Effects of Insulin, Hydrogen Peroxide, and Nitric Oxide—6-NBDG Incubation Overnight
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Reagents
4.2. Skeletal Muscle Cell Culture
4.3. Animals
4.4. Skeletal Muscle Fibres Isolation
4.5. Experimental Procedure
4.6. Fluorescence Microscopy and Quantitative Image Analysis
4.7. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Frontera, W.R.; Ochala, J. Skeletal Muscle: A Brief Review of Structure and Function. Calcif. Tissue Int. 2015, 96, 183–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reid, K.F.; Fielding, R.A. Skeletal Muscle Power: A Critical Determinant of Physical Functioning in Older Adults. Exerc. Sport Sci. Rev. 2012, 40, 4–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sylow, L.; Kleinert, M.; Richter, E.A.; Jensen, T.E. Exercise-Stimulated Glucose Uptake—Regulation and Implications for Glycaemic Control. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2016, 13, 133–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richter, E.A.; Hargreaves, M. Exercise, GLUT4, and Skeletal Muscle Glucose Uptake. Physiol. Rev. 2013, 93, 993–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merz, K.E.; Thurmond, D.C. Role of Skeletal Muscle in Insulin Resistance and Glucose Uptake. Compr. Physiol. 2020, 10, 785–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Llanos, P.; Palomero, J. Reactive Oxygen and Nitrogen Species (RONS) and Cytokines—Myokines Involved in Glucose Uptake and Insulin Resistance in Skeletal Muscle. Cells 2022, 11, 4008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dumont, N.A.; Bentzinger, C.F.; Sincennes, M.C.; Rudnicki, M.A. Satellite Cells and Skeletal Muscle Regeneration. Compr. Physiol. 2015, 5, 1027–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gillies, A.R.; Lieber, R.L. Structure and Function of the Skeletal Muscle Extracellular Matrix. Muscle Nerve 2011, 44, 318–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sylow, L.; Møller, L.L.V.; Kleinert, M.; Richter, E.A.; Jensen, T.E. Rac1—A Novel Regulator of Contraction-Stimulated Glucose Uptake in Skeletal Muscle. Exp. Physiol. 2014, 99, 1574–1580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henríquez-Olguin, C.; Knudsen, J.R.; Raun, S.H.; Li, Z.; Dalbram, E.; Treebak, J.T.; Sylow, L.; Holmdahl, R.; Richter, E.A.; Jaimovich, E.; et al. Cytosolic ROS Production by NADPH Oxidase 2 Regulates Muscle Glucose Uptake during Exercise. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 4623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merry, T.L.; McConell, G.K. Skeletal Muscle Glucose Uptake during Exercise: A Focus on Reactive Oxygen Species and Nitric Oxide Signaling. IUBMB Life 2009, 61, 479–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.H.; Park, S.J.; Chae, U.; Seong, J.; Lee, H.S.; Lee, S.R.; Lee, S.; Lee, D.S. Peroxiredoxin 2 Mediates Insulin Sensitivity of Skeletal Muscles through Regulation of Protein Tyrosine Phosphatase Oxidation. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2018, 99, 80–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roden, M.; Williams, L. Non-Invasive Studies of Glycogen Metabolism in Human Skeletal Muscle Using Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy; Lippincott Williams & Wilkins: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2001; Volume 4. [Google Scholar]
- Bernal-Sore, I.; Navarro-Marquez, M.; Osorio-Fuentealba, C.; Díaz-Castro, F.; del Campo, A.; Donoso-Barraza, C.; Porras, O.; Lavandero, S.; Troncoso, R. Mifepristone Enhances Insulin-Stimulated Akt Phosphorylation and Glucose Uptake in Skeletal Muscle Cells. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2018, 461, 277–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sánchez-Aguilera, P.; Diaz-Vegas, A.; Campos, C.; Quinteros-Waltemath, O.; Cerda-Kohler, H.; Barrientos, G.; Contreras-Ferrat, A.; Llanos, P. Role of ABCA1 on Membrane Cholesterol Content, Insulin-Dependent Akt Phosphorylation and Glucose Uptake in Adult Skeletal Muscle Fibers from Mice. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA) Mol. Cell Biol. Lipids 2018, 1863, 1469–1477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jorquera, G.; Meneses-Valdés, R.; Rosales-Soto, G.; Valladares-Ide, D.; Campos, C.; Silva-Monasterio, M.; Llanos, P.; Cruz, G.; Jaimovich, E.; Casas, M. High Extracellular ATP Levels Released through Pannexin-1 Channels Mediate Inflammation and Insulin Resistance in Skeletal Muscle Fibres of Diet-Induced Obese Mice. Diabetologia 2021, 64, 1389–1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llanos, P.; Contreras-Ferrat, A.; Georgiev, T.; Osorio-Fuentealba, C.; Espinosa, A.; Hidalgo, J.; Hidalgo, C.; Jaimovich, E. The Cholesterol-Lowering Agent Methyl-β-Cyclodextrin Promotes Glucose Uptake via GLUT4 in Adult Muscle Fibers and Reduces Insulin Resistance in Obese Mice. Am. J. Physiol. Metab. 2015, 308, E294–E305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, D.-W.; Ha, H.-H.; Zheng, X.; Chang, Y.-T.; Williams, D.R. Novel Use of Fluorescent Glucose Analogues to Identify a New Class of Triazine-Based Insulin Mimetics Possessing Useful Secondary Effects. Mol. BioSyst. 2011, 7, 346–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barros, L.F.; Bittner, C.X.; Loaiza, A.; Ruminot, I.; Larenas, V.; Moldenhauer, H.; Oyarzún, C.; Alvarez, M. Kinetic Validation of 6-NBDG as a Probe for the Glucose Transporter GLUT1 in Astrocytes. J. Neurochem. 2009, 109, 94–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loaiza, A.; Porras, O.H.; Barros, L.F. Glutamate Triggers Rapid Glucose Transport Stimulation in Astrocytes as Evidenced by Real-Time Confocal Microscopy. J. Neurosci. 2003, 23, 7337–7342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimitriadis, G.; Maratou, E.; Boutati, E.; Psarra, K.; Papasteriades, C.; Raptis, S.A. Evaluation of Glucose Transport and Its Regulation by Insulin in Human Monocytes Using Flow Cytometry. Cytom. Part A 2005, 64, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aneesa, N.; Anitha, R.; Varghese, S. Antidiabetic Activity of Ajwain Oil in Different In Vitro Models. J. Pharm. Bioallied Sci. 2019, 11, 142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaudreault, N.; Scriven, D.R.L.; Laher, I.; Moore, E.D.W. Subcellular Characterization of Glucose Uptake in Coronary Endothelial Cells. Microvasc. Res. 2008, 75, 73–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bala, M.; Gupta, P.; Gupta, S.; Dua, A.; Injeti, E.; Mittal, A. Efficient and Modified 2-NBDG Assay to Measure Glucose Uptake in Cultured Myotubes. J. Pharmacol. Toxicol. Methods 2021, 109, 107069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, W.-C.; Li, H.-Y.; Li, T.-T.; Yang, K.; Chen, J.-X.; Wang, S.-J.; Liu, C.-H.; Zhang, W. Pentadecanoic Acid Promotes Basal and Insulin-Stimulated Glucose Uptake in C2C12 Myotubes. Food Nutr. Res. 2021, 65, 4527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Li, H.; Li, T.; Fu, W.; Du, X.; Liu, C.; Zhang, W. Alisol A-24-Acetate Promotes Glucose Uptake via Activation of AMPK in C2C12 Myotubes. BMC Complement. Med. Ther. 2020, 20, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, M.S.; Hur, H.J.; Kwon, D.Y.; Hwang, J.-T. Tangeretin Stimulates Glucose Uptake via Regulation of AMPK Signaling Pathways in C2C12 Myotubes and Improves Glucose Tolerance in High-Fat Diet-Induced Obese Mice. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2012, 358, 127–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.Y.; Kim, M.H.; Ahn, J.H.; Lee, S.J.; Lee, J.H.; Eum, W.S.; Choi, S.Y.; Kwon, H.Y. The Stimulatory Effect of Essential Fatty Acids on Glucose Uptake Involves Both Akt and AMPK Activation in C2C12 Skeletal Muscle Cells. Korean J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2014, 18, 255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geddo, F.; Scandiffio, R.; Antoniotti, S.; Cottone, E.; Querio, G.; Maffei, M.E.; Bovolin, P.; Gallo, M.P. PipeNig®-FL, a Fluid Extract of Black Pepper (Piper nigrum L.) with a High Standardized Content of Trans-β-Caryophyllene, Reduces Lipid Accumulation in 3T3-L1 Preadipocytes and Improves Glucose Uptake in C2C12 Myotubes. Nutrients 2019, 11, 2788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, H.; Heng, B.; He, W.; Shi, L.; Lai, C.; Xiao, L.; Ren, H.; Mo, S.; Su, Z. Chronic Reactive Oxygen Species Exposure Inhibits Glucose Uptake and Causes Insulin Resistance in C2C12 Myotubes. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2016, 478, 798–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osorio-Fuentealba, C.; Contreras-Ferrat, A.E.; Altamirano, F.; Espinosa, A.; Li, Q.; Niu, W.; Lavandero, S.; Klip, A.; Jaimovich, E. Electrical Stimuli Release ATP to Increase GLUT4 Translocation and Glucose Uptake via PI3Kγ-Akt-AS160 in Skeletal Muscle Cells. Diabetes 2013, 62, 1519–1526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sies, H.; Belousov, V.V.; Chandel, N.S.; Davies, M.J.; Jones, D.P.; Mann, G.E.; Murphy, M.P.; Yamamoto, M.; Winterbourn, C. Defining Roles of Specific Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) in Cell Biology and Physiology. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2022, 23, 499–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schäffer, L.; Brand, C.L.; Hansen, B.F.; Ribel, U.; Shaw, A.C.; Slaaby, R.; Sturis, J. A Novel High-Affinity Peptide Antagonist to the Insulin Receptor. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2008, 376, 380–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.-H.; Bauman, W.A.; Cardozo, C.P. Myostatin Inhibits Glucose Uptake via Suppression of Insulin-Dependent and -Independent Signaling Pathways in Myoblasts. Physiol. Rep. 2018, 6, e13837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Powers, S.K.; Morton, A.B.; Hyatt, H.; Hinkley, M.J. The Renin-Angiotensin System and Skeletal Muscle. Exerc. Sport Sci. Rev. 2018, 46, 205–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, Y.; Sowers, J.R.; Nistala, R.; Gong, H.; Uptergrove, G.M.E.; Clark, S.E.; Morris, E.M.; Szary, N.; Manrique, C.; Stump, C.S. Angiotensin II-Induced NADPH Oxidase Activation Impairs Insulin Signaling in Skeletal Muscle Cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 35137–35146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henriksen, E.J.; Prasannarong, M. The Role of the Renin-Angiotensin System in the Development of Insulin Resistance in Skeletal Muscle. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2013, 378, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferreira, L.F.; Laitano, O. Regulation of NADPH Oxidases in Skeletal Muscle. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2016, 98, 18–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katz, A. Modulation of Glucose Transport in Skeletal Muscle by Reactive Oxygen Species. J. Appl. Physiol. 2007, 102, 1671–1676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merry, T.L.; Steinberg, G.R.; Lynch, G.S.; McConell, G.K. Skeletal Muscle Glucose Uptake during Contraction Is Regulated by Nitric Oxide and ROS Independently of AMPK. Am. J. Physiol. Metab. 2010, 298, 577–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, H.S.; Benoit, B.; Brand, M.D. Mitochondrial and Cytosolic Sources of Hydrogen Peroxide in Resting C2C12 Myoblasts. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2019, 130, 140–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strobel, N.A.; Matsumoto, A.; Peake, J.M.; Marsh, S.A.; Peternelj, T.-T.; Briskey, D.; Fassett, R.G.; Coombes, J.S.; Wadley, G.D. Altering the Redox State of Skeletal Muscle by Glutathione Depletion Increases the Exercise-Activation of PGC-1 α. Physiol. Rep. 2014, 2, e12224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palomero, J.; Vasilaki, A.; Pye, D.; McArdle, A.; Jackson, M.J. Aging Increases the Oxidation of Dichlorohydrofluorescein in Single Isolated Skeletal Muscle Fibers at Rest, but Not during Contractions. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2013, 305, R351–R358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palomero, J.; Pye, D.; Kabayo, T.; Spiller, D.G.; Jackson, M.J. In Situ Detection and Measurement of Intracellular Reactive Oxygen Species in Single Isolated Mature Skeletal Muscle Fibers by Real Time Fluorescence Microscopy. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2008, 10, 1463–1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ardite, E.; Barbera, J.A.; Roca, J.; Fernández-Checa, J.C. Glutathione Depletion Impairs Myogenic Differentiation of Murine Skeletal Muscle C2C12 Cells through Sustained NF-ΚB Activation. Am. J. Pathol. 2004, 165, 719–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Somwar, R.; Bilan, P.J.; Liu, Z.; Jin, J.; Woodgett, J.R.; Klip, A. Protein Kinase B/Akt Participates in GLUT4 Translocation by Insulin in L6 Myoblasts. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1999, 19, 4008–4018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruss, M.D.; Arias, E.B.; Lienhard, G.E.; Cartee, G.D. Increased Phosphorylation of Akt Substrate of 160 KDa (AS160) in Rat Skeletal Muscle in Response to Insulin or Contractile Activity. Diabetes 2005, 54, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kojer, K.; Bien, M.; Gangel, H.; Morgan, B.; Dick, T.P.; Riemer, J. Glutathione Redox Potential in the Mitochondrial Intermembrane Space Is Linked to the Cytosol and Impacts the Mia40 Redox State. EMBO J. 2012, 31, 3169–3182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugiura, K.; Tanaka, H.; Kurisu, G.; Wakabayashi, K.-i.; Hisabori, T. Multicolor Redox Sensor Proteins Can Visualize Redox Changes in Various Compartments of the Living Cell. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA) Gen. Subj. 2019, 1863, 1098–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gray, S.R.; Kamolrat, T. The Effect of Exercise Induced Cytokines on Insulin Stimulated Glucose Transport in C2C12 Cells. Cytokine 2011, 55, 221–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-bayati, A.; Lukka, D.; Brown, A.E.; Walker, M. Effects of Thrombin on Insulin Signalling and Glucose Uptake in Cultured Human Myotubes. J. Diabetes Its Complicat. 2016, 30, 1209–1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobayashi, T.; Akiyama, Y.; Akiyama, N.; Katoh, H.; Yamamoto, S.; Funatsuki, K.; Yanagimoto, T.; Notoya, M.; Asakura, K.; Shinosaki, T.; et al. Irbesartan Enhances GLUT4 Translocation and Glucose Transport in Skeletal Muscle Cells. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2010, 649, 23–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deshmukh, A.S.; Murgia, M.; Nagaraj, N.; Treebak, J.T.; Cox, J.; Mann, M. Deep Proteomics of Mouse Skeletal Muscle Enables Quantitation of Protein Isoforms, Metabolic Pathways, and Transcription Factors*. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2015, 14, 841–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pye, D.; Palomero, J.; Kabayo, T.; Jackson, M.J. Real-Time Measurement of Nitric Oxide in Single Mature Mouse Skeletal Muscle Fibres during Contractions. J. Physiol. 2007, 581, 309–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higaki, Y.; Hirshman, M.F.; Fujii, N.; Goodyear, L.J. Nitric Oxide Increases Glucose Uptake through a Mechanism That Is Distinct from the Insulin and Contraction Pathways in Rat Skeletal Muscle. Diabetes 2001, 50, 241–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernández-Puente, E.; Palomero, J. Genetically Encoded Biosensors to Monitor Intracellular Reactive Oxygen and Nitrogen Species and Glutathione Redox Potential in Skeletal Muscle Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 10876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sies, H.; Jones, D.P. Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) as Pleiotropic Physiological Signalling Agents. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2020, 21, 363–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Higaki, Y.; Mikami, T.; Fujii, N.; Hirshman, M.F.; Koyama, K.; Seino, T.; Tanaka, K.; Goodyear, L.J. Oxidative Stress Stimulates Skeletal Muscle Glucose Uptake through a Phosphatidylinositol 3-Kinase-Dependent Pathway. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2008, 294, 889–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakellariou, G.K.; Vasilaki, A.; Palomero, J.; Kayani, A.; Zibrik, L.; McArdle, A.; Jackson, M.J. Studies of Mitochondrial and Nonmitochondrial Sources Implicate Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide Phosphate Oxidase(s) in the Increased Skeletal Muscle Superoxide Generation That Occurs during Contractile Activity. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2013, 18, 603–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakellariou, G.K.; Pye, D.; Vasilaki, A.; Zibrik, L.; Palomero, J.; Kabayo, T.; McArdle, F.; van Remmen, H.; Richardson, A.; Tidball, J.G.; et al. Role of Superoxide-Nitric Oxide Interactions in the Accelerated Age-Related Loss of Muscle Mass in Mice Lacking Cu, Zn Superoxide Dismutase. Aging Cell 2011, 10, 749–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Puente, E.; Sánchez-Martín, M.A.; de Andrés, J.; Rodríguez-Izquierdo, L.; Méndez, L.; Palomero, J. Expression and Functional Analysis of the Hydrogen Peroxide Biosensors HyPer and HyPer2 in C2C12 Myoblasts/Myotubes and Single Skeletal Muscle Fibres. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]










Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fernández-Puente, E.; Martín-Prieto, E.; Márquez, C.M.; Palomero, J. Effect of RONS-Induced Intracellular Redox Homeostasis in 6-NBDG/Glucose Uptake in C2C12 Myotubes and Single Isolated Skeletal Muscle Fibres. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 8082. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24098082
Fernández-Puente E, Martín-Prieto E, Márquez CM, Palomero J. Effect of RONS-Induced Intracellular Redox Homeostasis in 6-NBDG/Glucose Uptake in C2C12 Myotubes and Single Isolated Skeletal Muscle Fibres. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2023; 24(9):8082. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24098082
Chicago/Turabian StyleFernández-Puente, Escarlata, Eva Martín-Prieto, Carlos Manuel Márquez, and Jesús Palomero. 2023. "Effect of RONS-Induced Intracellular Redox Homeostasis in 6-NBDG/Glucose Uptake in C2C12 Myotubes and Single Isolated Skeletal Muscle Fibres" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24, no. 9: 8082. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24098082
APA StyleFernández-Puente, E., Martín-Prieto, E., Márquez, C. M., & Palomero, J. (2023). Effect of RONS-Induced Intracellular Redox Homeostasis in 6-NBDG/Glucose Uptake in C2C12 Myotubes and Single Isolated Skeletal Muscle Fibres. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(9), 8082. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24098082