Protective Effect of the Novel Melatonin Analogue Containing Donepezil Fragment on Memory Impairment via MT/ERK/CREB Signaling in the Hippocampus in a Rat Model of Pinealectomy and Subsequent Aβ1-42 Infusion
Abstract
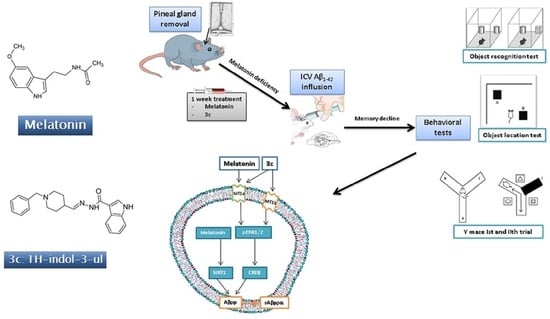
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. The Circadian Pattern of Motor Activity and Effects of Melatonin and 3c Compound in a Rat Model of Pinealectomy and icvAβ1-42 Infusion
2.2. Effects of Melatonin and 3c Compound on Memory Impairment Induced by Pinealectomy and icvAβ1-42 Infusion
2.2.1. Object Recognition Test
2.2.2. Object Location Test
2.2.3. Y-Maze Test
2.3. The Expression of Markers of ADs and Effects of Melatonin and Compound 3c in a Rat Model of Pinealectomy and icvAβ1-42 Infusion
2.4. Neuroprotective Effect of Melatonin and the Hybrid Compound 3c on Aβ1-42 Neurotoxicity via MT Receptors/ERK/CREB Signaling
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Animals
4.2. Experimental Design
4.2.1. Surgery and icv Injection of Aβ1-42
4.2.2. Behavioral Test
Actimeter
Object Recognition Test (ORT)
Object Location Test (OLT)
Y-Maze Test
4.2.3. Detection of Aβ, pTAU, AchE, pERK, pCREB and SIRT1 in the Homogenates from the Hippocampus
Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Selkoe, D.J.; Hardy, J. The Amyloid Hypothesis of Alzheimer’s Disease at 25 Years. EMBO Mol. Med. 2016, 8, 595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benedict, C.; Byberg, L.; Cedernaes, J.; Hogenkamp, P.S.; Giedratis, V.; Kilander, L.; Lind, L.; Lannfelt, L.; Schiöth, H.B. Self-Reported Sleep Disturbance Is Associated with Alzheimer’s Disease Risk in Men. Alzheimers Dement. 2015, 11, 1090–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonanni, E.; Maestri, M.; Tognoni, G.; Fabbrini, M.; Nucciarone, B.; Manca, M.L.; Gori, S.; Iudice, A.; Murri, L. Daytime Sleepiness in Mild and Moderate Alzheimer’s Disease and Its Relationship with Cognitive Impairment. J. Sleep Res. 2005, 14, 311–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Musiek, E.S.; Xiong, D.D.; Holtzman, D.M. Sleep, Circadian Rhythms, and the Pathogenesis of Alzheimer Disease. Exp. Mol. Med. 2015, 47, e148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, G.; Maes, M. Anderson, G.; Maes, M. A Role for the Regulation of the Melatonergic Pathways in Alzheimer’s Disease and Other Neurodegenerative and Psychiatric Conditions. In Serotonin and Melatonin; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2016; pp. 443–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukla, M.; Htoo, H.H.; Wintachai, P.; Hernandez, J.F.; Dubois, C.; Postina, R.; Xu, H.; Checler, F.; Smith, D.R.; Govitrapong, P.; et al. Melatonin Stimulates the Nonamyloidogenic Processing of ΒAPP through the Positive Transcriptional Regulation of ADAM10 and ADAM17. J. Pineal Res. 2015, 58, 151–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukla, M.; Govitrapong, P.; Boontem, P.; Reiter, R.J.; Satayavivad, J. Mechanisms of Melatonin in Alleviating Alzheimer’s Disease. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2017, 15, 1010–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Claustrat, B.; Brun, J.; Borson-Chazot, F. Melatonin and Circadian Rhythms. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2002, 2, 199–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.H.; Feenstra, M.G.P.; Zhou, J.N.; Liu, R.Y.; Toranõ, J.S.; Van Kan, H.J.M.; Fischer, D.F.; Ravid, R.; Swaab, D.F. Molecular Changes Underlying Reduced Pineal Melatonin Levels in Alzheimer Disease: Alterations in Preclinical and Clinical Stages. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2003, 88, 5898–5906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahlberg, R.; Walther, S.; Kalus, P.; Bohner, G.; Haedel, S.; Reischies, F.M.; Kühl, K.P.; Hellweg, R.; Kunz, D. Pineal Calcification in Alzheimer’s Disease: An in Vivo Study Using Computed Tomography. Neurobiol. Aging 2008, 29, 203–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohashi, Y.; Okamoto, N.; Uchida, K.; Iyo, M.; Mori, N.; Morita, Y. Daily Rhythm of Serum Melatonin Levels and Effect of Light Exposure in Patients with Dementia of the Alzheimer’s Type. Biol. Psychiatry 1999, 45, 1646–1652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, J.N.; Liu, R.Y.; Kamphorst, W.; Hofman, M.A.; Swaab, D.F. Early Neuropathological Alzheimer’s Changes in Aged Individuals Are Accompanied by Decreased Cerebrospinal Fluid Melatonin Levels. J. Pineal Res. 2003, 35, 125–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luboshitzky, R.; Shen-Orr, Z.; Tzischichinsky, O.; Maldonado, M.; Herer, P.; Lavie, P. Actigraphic Sleep-Wake Patterns and Urinary 6-Sulfatoxymelatonin Excretion in Patients with Alzheimer’s Disease. Chronobiol. Int. 2001, 18, 513–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beriwal, N.; Namgyal, T.; Sangay, P.; Al Quraan, A.M. Role of Immune-Pineal Axis in Neurodegenerative Diseases, Unraveling Novel Hybrid Dark Hormone Therapies. Heliyon 2019, 5, E01190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tzoneva, R.; Georgieva, I.; Ivanova, N.; Uzunova, V.; Nenchovska, Z.; Apostolova, S.; Stoyanova, T.; Tchekalarova, J. The Role of Melatonin on Behavioral Changes and Concomitant Oxidative Stress in IcvAβ1-42 Rat Model with Pinealectomy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 12763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Angelova, V.T.; Georgiev, B.; Pencheva, T.; Pajeva, I.; Rangelov, M.; Todorova, N.; Zheleva-Dimitrova, D.; Kalcheva-Yovkova, E.; Valkova, I.V.; Vassilev, N.; et al. Design, Synthesis, In Silico Studies and In Vitro Evaluation of New Indole- and/or Donepezil-like Hybrids as Multitarget-Directed Agents for Alzheimer’s Disease. Pharmaceuticals 2023, 16, 1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demir, M.; Yilmaz, U.; Colak, C.; Cigremis, Y.; Ozyalin, F.; Tekedereli, I.; Kilincli, A.; Sandal, S. The Effects of Lack of Melatonin in Experimental Rat Model of Alzheimer’s Disease: Relationship with FEZ1 Gene Expression. Med. Sci. 2016, 6, 217–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, Q.Z.; Shao, H.W.; Zhi, Q.L.; Dan, L.W.; Wang, J.Z. Effect of Inhibiting Melatonin Biosynthesis on Spatial Memory Retention and Tau Phosphorylation in Rat. J. Pineal Res. 2004, 37, 71–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.C.; Hsu, W.L.; Ma, Y.L.; Lee, E.H.Y. Melatonin Induction of APP Intracellular Domain 50 SUMOylation Alleviates AD through Enhanced Transcriptional Activation and Aβ Degradation. Mol. Ther. 2021, 29, 376–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jürgenson, M.; Zharkovskaja, T.; Noortoots, A.; Morozova, M.; Beniashvili, A.; Zapolski, M.; Zharkovsky, A. Effects of the Drug Combination Memantine and Melatonin on Impaired Memory and Brain Neuronal Deficits in an Amyloid-Predominant Mouse Model of Alzheimer’s Disease. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2019, 71, 1695–1705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudnitskaya, E.A.; Muraleva, N.A.; Maksimova, K.Y.; Kiseleva, E.; Kolosova, N.G.; Stefanova, N.A. Melatonin Attenuates Memory Impairment, Amyloid-β Accumulation, and Neurodegeneration in a Rat Model of Sporadic Alzheimer’s Disease. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2015, 47, 103–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.; Qiu, X.; Wang, Y.; Liu, J.; Li, Q.; Jiang, H.; Li, S.; Song, C. Long-Term Oral Melatonin Alleviates Memory Deficits, Reduces Amyloid-β Deposition Associated with Downregulation of BACE1 and Mitophagy in APP/PS1 Transgenic Mice. Neurosci. Lett. 2020, 735, 135192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, K.Y.; Leong, M.K.; Liang, H.; Paxinos, G. Melatonin Receptors: Distribution in Mammalian Brain and Their Respective Putative Functions. Brain Struct. Funct. 2017, 222, 2921–2939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, J.; Tsui, K.C.; Ng, J.; Fung, M.L.; Lim, L.W. Regulation of Melatonin and Neurotransmission in Alzheimer’s Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 6841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, J.; Wan, J.; Liu, A.; Sun, J. Melatonin Regulates Aβ Production/Clearance Balance and Aβ Neurotoxicity: A Potential Therapeutic Molecule for Alzheimer’s Disease. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2020, 132, 110887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Labban, S.; Alshehri, F.S.; Kurdi, M.; Alatawi, Y.; Alghamdi, B.S. Melatonin Improves Short-Term Spatial Memory in a Mouse Model of Alzheimer’s Disease. Degener. Neurol. Neuromuscul. Dis. 2021, 11, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamsrijai, U.; Wongchitrat, P.; Nopparat, C.; Satayavivad, J.; Govitrapong, P. Melatonin Attenuates Streptozotocin-Induced Alzheimer-like Features in Hyperglycemic Rats. Neurochem. Int. 2020, 132, 104601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andrade, M.K.; Souza, L.C.; Azevedo, E.M.; Bail, E.L.; Zanata, S.M.; Andreatini, R.; Vital, M.A.B.F. Melatonin Reduces β-Amyloid Accumulation and Improves Short-Term Memory in Streptozotocin-Induced Sporadic Alzheimer’s Disease Model. IBRO Neurosci. Rep. 2023, 14, 264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keymoradzadeh, A.; Komaki, A.R.; Bakhshi, A.; Faraji, N.; Golipoor, Z.; Shahshahani, P. The Effect of Different Doses of Melatonin on Learning and Memory Deficit in Alzheimer Model of Rats. Casp. J. Neurol. Sci. 2021, 7, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ha, S.; Redmond, L. ERK Mediates Activity Dependent Neuronal Complexity via Sustained Activity and CREB-Mediated Signaling. Dev. Neurobiol. 2008, 68, 1565–1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watson, D.; Castaño, E.; Kokjohn, T.A.; Kuo, Y.M.; Lyubchenko, Y.; Pinsky, D.; Connolly, E.S.; Esh, C.; Luehrs, D.C.; Blaine Stine, W.; et al. Physicochemical Characteristics of Soluble Oligomeric Abeta and Their Pathologic Role in Alzheimer’s Disease. Neurol. Res. 2005, 27, 869–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holcomb, L.; Gordon, M.N.; Mcgowan, E.; Yu, X.; Benkovic, S.; Jantzen, P.; Wright, K.; Saad, I.; Mueller, R.; Morgan, D.; et al. Accelerated Alzheimer-Type Phenotype in Transgenic Mice Carrying Both Mutant Amyloid Precursor Protein and Presenilin 1 Transgenes. Nat. Med. 1998, 4, 97–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cleary, J.P.; Walsh, D.M.; Hofmeister, J.J.; Shankar, G.M.; Kuskowski, M.A.; Selkoe, D.J.; Ashe, K.H. Natural Oligomers of the Amyloid-Beta Protein Specifically Disrupt Cognitive Function. Nat. Neurosci. 2005, 8, 79–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morán, M.A.; Mufson, E.J.; Gómez-Ramos, P. Colocalization of Cholinesterases with Beta Amyloid Protein in Aged and Alzheimer’s Brains. Acta Neuropathol. 1993, 85, 362–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reyes, A.E.; Chacón, M.A.; Dinamarca, M.C.; Cerpa, W.; Morgan, C.; Inestrosa, N.C. Acetylcholinesterase-Aβ Complexes Are More Toxic than Aβ Fibrils in Rat Hippocampus: Effect on Rat β-Amyloid Aggregation, Laminin Expression, Reactive Astrocytosis, and Neuronal Cell Loss. Am. J. Pathol. 2004, 164, 2163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cecon, E.; Chen, M.; Marçola, M.; Fernandes, P.A.C.; Jockers, R.; Markus, R.P. Amyloid β Peptide Directly Impairs Pineal Gland Melatonin Synthesis and Melatonin Receptor Signaling through the ERK Pathway. FASEB J. 2015, 29, 2566–2582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panmanee, J.; Nopparat, C.; Chavanich, N.; Shukla, M.; Mukda, S.; Song, W.; Vincent, B.; Govitrapong, P. Melatonin Regulates the Transcription of ΒAPP-Cleaving Secretases Mediated through Melatonin Receptors in Human Neuroblastoma SH-SY5Y Cells. J. Pineal Res. 2015, 59, 308–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohno, M.; Sametsky, E.A.; Younkin, L.H.; Oakley, H.; Younkin, S.G.; Citron, M.; Vassar, R.; Disterhoft, J.F. BACE1 Deficiency Rescues Memory Deficits and Cholinergic Dysfunction in a Mouse Model of Alzheimer’s Disease. Neuron 2004, 41, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohno, M.; Cole, S.L.; Yasvoina, M.; Zhao, J.; Citron, M.; Berry, R.; Disterhoft, J.F.; Vassar, R. BACE1 Gene Deletion Prevents Neuron Loss and Memory Deficits in 5XFAD APP/PS1 Transgenic Mice. Neurobiol. Dis. 2007, 26, 134–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Fivecoat, H.; Ho, L.; Pan, Y.; Ling, E.; Pasinetti, G.M. The Role of Sirt1: At the Crossroad between Promotion of Longevity and Protection against Alzheimer’s Disease Neuropathology. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2010, 1804, 1690–1694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albani, D.; Polito, L.; Batelli, S.; De Mauro, S.; Fracasso, C.; Martelli, G.; Colombo, L.; Manzoni, C.; Salmona, M.; Caccia, S.; et al. The SIRT1 Activator Resveratrol Protects SK-N-BE Cells from Oxidative Stress and against Toxicity Caused by Alpha-Synuclein or Amyloid-Beta (1-42) Peptide. J. Neurochem. 2009, 110, 1445–1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, W.; Yang, T.; Ho, L.; Zhao, Z.; Wang, J.; Chen, L.; Zhao, W.; Thiyagarajan, M.; MacGrogan, D.; Rodgers, J.T.; et al. Neuronal SIRT1 Activation as a Novel Mechanism Underlying the Prevention of Alzheimer Disease Amyloid Neuropathology by Calorie Restriction. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 21745–21754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cristòfol, R.; Porquet, D.; Corpas, R.; Coto-Montes, A.; Serret, J.; Camins, A.; Pallàs, M.; Sanfeliu, C. Neurons from Senescence-Accelerated SAMP8 Mice Are Protected against Frailty by the Sirtuin 1 Promoting Agents Melatonin and Resveratrol. J. Pineal Res. 2012, 52, 271–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lacoste, B.; Angeloni, D.; Dominguez-Lopez, S.; Calderoni, S.; Mauro, A.; Fraschini, F.; Descarries, L.; Gobbi, G. Anatomical and Cellular Localization of Melatonin MT1 and MT2 Receptors in the Adult Rat Brain. J. Pineal Res. 2015, 58, 397–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shishmanova-Doseva, M.; Peychev, L.; Yoanidu, L.; Uzunova, Y.; Atanasova, M.; Georgieva, K.; Tchekalarova, J.; Shishmanova-Doseva, M.; Peychev, L.; Yoanidu, L.; et al. Anticonvulsant Effects of Topiramate and Lacosamide on Pilocarpine-Induced Status Epilepticus in Rats: A Role of Reactive Oxygen Species and Inflammation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 2264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]











| Mesor | Amplitude | Acrophase (Hours, Decimal) | F-Value | p-Value (Zero Amplitude Test) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| sham-veh-veh | 1887.41 | 1093.94 | 17.45 | 33.89 | <0.00001 |
| pin+Aβ1-42-veh | 2431.16 | 1489.91 | 15.63 | 84.68 | <0.00001 |
| pin+Aβ1-42-veh-mel | 2309.21 | 1320.89 | 17.57 | 34.93 | <0.00001 |
| pin+Aβ1-42-veh-3c | 2179.11 | 1216.88 | 17.64 | 26.26 | <0.00001 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tchekalarova, J.; Ivanova, P.; Krushovlieva, D.; Kortenska, L.; Angelova, V.T. Protective Effect of the Novel Melatonin Analogue Containing Donepezil Fragment on Memory Impairment via MT/ERK/CREB Signaling in the Hippocampus in a Rat Model of Pinealectomy and Subsequent Aβ1-42 Infusion. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 1867. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25031867
Tchekalarova J, Ivanova P, Krushovlieva D, Kortenska L, Angelova VT. Protective Effect of the Novel Melatonin Analogue Containing Donepezil Fragment on Memory Impairment via MT/ERK/CREB Signaling in the Hippocampus in a Rat Model of Pinealectomy and Subsequent Aβ1-42 Infusion. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2024; 25(3):1867. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25031867
Chicago/Turabian StyleTchekalarova, Jana, Petya Ivanova, Desislava Krushovlieva, Lidia Kortenska, and Violina T. Angelova. 2024. "Protective Effect of the Novel Melatonin Analogue Containing Donepezil Fragment on Memory Impairment via MT/ERK/CREB Signaling in the Hippocampus in a Rat Model of Pinealectomy and Subsequent Aβ1-42 Infusion" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 25, no. 3: 1867. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25031867
APA StyleTchekalarova, J., Ivanova, P., Krushovlieva, D., Kortenska, L., & Angelova, V. T. (2024). Protective Effect of the Novel Melatonin Analogue Containing Donepezil Fragment on Memory Impairment via MT/ERK/CREB Signaling in the Hippocampus in a Rat Model of Pinealectomy and Subsequent Aβ1-42 Infusion. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 25(3), 1867. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25031867