TRPV1 Channel in Human Eosinophils: Functional Expression and Inflammatory Modulation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
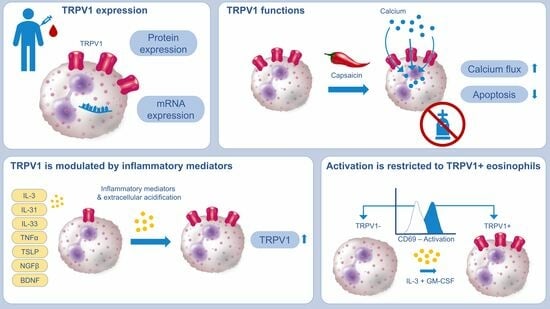
2.1. TRPV1 Is Expressed on RNA and Protein Levels in Human Eosinophils
2.2. Activation of TRPV1 Induces Calcium Influx
2.3. TRPV1 Activation Has an Antiapoptotic Effect on Human Eosinophils
2.4. Eosinophil Surface Expression of TRPV1 Is Linked to Activation Status
2.5. TRPV1 Surface Expression Is Modulated by AD-Related Cytokines and pH
2.6. TRPV1 Expression on Eosinophils in AD Skin
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Patient Materials
4.2. Isolation of Human Peripheral Blood Eosinophils
4.3. Flow Cytometry Analysis of TRPV1 and CD69 Externalization
4.4. RNA Isolation and qPCR
4.5. Immunofluorescence Staining
4.6. Calcium Flux Experiments
4.7. Apoptosis Assay
4.8. Stimulation of Eosinophils with Cytokines and Incubation at Varying pH and Temperatures
4.9. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AD | Atopic dermatitis |
| ATP | Adenosine triphosphate |
| BDNF | Brain-derived neurotrophic factor |
| Ca | Calcium |
| CCR3 | CC chemokine receptor type 3 (CD193) |
| cDNA | Complementary deoxyribonucleic acid |
| CD16 | Cluster of differentiation 16; FcγRIII |
| CD69 | Cluster of differentiation 69 |
| DAPI | 4’,6-diamidino-2-phenylindol |
| ECP | Eosinophil cationic protein |
| EDN | Eosinophil-derived neurotoxin |
| EDTA | Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid |
| EGFR | Epidermal growth factor receptor |
| EPX | Eosinophil peroxidase |
| ER | Endoplasmic reticulum |
| FCS | Fetal calf serum |
| Fig | Figure |
| FMO | Fluorescence minus one |
| GAPDH | Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase |
| GM-CSF | Granulocyte/macrophage-colony-stimulating factor |
| h | Hours |
| IL | Interleukin |
| Iono | Ionomycin |
| MAP | Mitogen-activated protein |
| MBP | Major basic protein |
| MFI | Mean fluorescence intensity |
| NGF | Nerve growth factor |
| OSMR | Oncostatin M receptor |
| PBMC | Peripheral blood mononuclear cells |
| PBS | Phosphate-buffered saline |
| PBS-T | Phosphate-buffered saline with Tween |
| qPCR | Quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction |
| REA | Recombinant antibody |
| (m)RNA | (messenger) ribonucleic acid |
| ROS | Reactive oxygen species |
| RPMI | Roswell park memorial institute |
| Stauro | Staurosporine |
| Th2 | T helper cell type 2 |
| TNF | Tumor necrosis factor |
| TrkA | Tropomyosin receptor kinase A |
| TrkB | Tropomyosin receptor kinase B |
| TRPV1 | Transient receptor potential vanilloid 1 |
| TSLP | Thymic stromal lymphopoietin |
| SEM | Standard error of the mean |
| 7-AAD | 7-aminoactinomycin D |
References
- Meng, J.; Li, Y.; Fischer, M.J.M.; Steinhoff, M.; Chen, W.; Wang, J. Th2 Modulation of Transient Receptor Potential Channels: An Unmet Therapeutic Intervention for Atopic Dermatitis. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 696784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guseva, D.; Rüdrich, U.; Kotnik, N.; Gehring, M.; Patsinakidis, N.; Agelopoulos, K.; Ständer, S.; Homey, B.; Kapp, A.; Gibbs, B.F.; et al. Neuronal branching of sensory neurons is associated with BDNF-positive eosinophils in atopic dermatitis. Clin. Exp. Allergy J. Br. Soc. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2020, 50, 577–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klion, A.D.; Ackerman, S.J.; Bochner, B.S. Contributions of Eosinophils to Human Health and Disease. Annu. Rev. Pathol. 2020, 15, 179–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radonjic-Hoesli, S.; Brüggen, M.-C.; Feldmeyer, L.; Simon, H.-U.; Simon, D. Eosinophils in skin diseases. Semin. Immunopathol. 2021, 43, 393–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Limberg, M.M.; Weihrauch, T.; Gray, N.; Ernst, N.; Hartmann, K.; Raap, U. Eosinophils, Basophils, and Neutrophils in Bullous Pemphigoid. Biomolecules 2023, 13, 1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noga, O.; Englmann, C.; Hanf, G.; Grützkau, A.; Guhl, S.; Kunkel, G. Activation of the specific neurotrophin receptors TrkA, TrkB and TrkC influences the function of eosinophils. Clin. Exp. Allergy J. Br. Soc. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2002, 32, 1348–1354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheung, P.F.-Y.; Wong, C.-K.; Ho, A.W.-Y.; Hu, S.; Chen, D.-P.; Lam, C.W.-K. Activation of human eosinophils and epidermal keratinocytes by Th2 cytokine IL-31: Implication for the immunopathogenesis of atopic dermatitis. Int. Immunol. 2010, 22, 453–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chow, J.Y.S.; Wong, C.K.; Cheung, P.F.Y.; Lam, C.W.K. Intracellular signaling mechanisms regulating the activation of human eosinophils by the novel Th2 cytokine IL-33: Implications for allergic inflammation. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2010, 7, 26–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, C.K.; Hu, S.; Cheung, P.F.Y.; Lam, C.W.K. Thymic stromal lymphopoietin induces chemotactic and prosurvival effects in eosinophils: Implications in allergic inflammation. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2010, 43, 305–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giembycz, M.A.; Lindsay, M.A. Pharmacology of the eosinophil. Pharmacol. Rev. 1999, 51, 213–340. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Esnault, S.; Kelly, E. Essential mechanisms of differential activation of eosinophils by IL-3 compared to GM-CSF and IL-5. Crit. Rev. Immunol. 2016, 36, 429–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weihrauch, T.; Limberg, M.M.; Gray, N.; Schmelz, M.; Raap, U. Neurotrophins: Neuroimmune Interactions in Human Atopic Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 6105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toyoda, M.; Nakamura, M.; Makino, T.; Morohashi, M. Localization and content of nerve growth factor in peripheral blood eosinophils of atopic dermatitis patients. Clin. Exp. Allergy J. Br. Soc. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2003, 33, 950–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamaguchi, J.; Aihara, M.; Kobayashi, Y.; Kambara, T.; Ikezawa, Z. Quantitative analysis of nerve growth factor (NGF) in the atopic dermatitis and psoriasis horny layer and effect of treatment on NGF in atopic dermatitis. J. Dermatol. Sci. 2009, 53, 48–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamagawa-Mineoka, R.; Okuzawa, Y.; Masuda, K.; Katoh, N. Increased serum levels of interleukin 33 in patients with atopic dermatitis. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2014, 70, 882–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Zhu, Z.; Zhai, Y.; Zeng, J.; Li, L.; Wang, D.; Deng, F.; Chang, B.; Zhou, J.; Sun, L. The Role of TSLP in Atopic Dermatitis: From Pathogenetic Molecule to Therapeutical Target. Mediat. Inflamm. 2023, 2023, 7697699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, P.-S.; Rafaels, N.M.; Mu, D.; Hand, T.; Murray, T.; Boguniewicz, M.; Hata, T.; Schneider, L.; Hanifin, J.M.; Gallo, R.L.; et al. Genetic variants in thymic stromal lymphopoietin are associated with atopic dermatitis and eczema herpeticum. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2010, 125, 1403–1407.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunsleben, N.; Rüdrich, U.; Gehring, M.; Novak, N.; Kapp, A.; Raap, U. IL-31 Induces Chemotaxis, Calcium Mobilization, Release of Reactive Oxygen Species, and CCL26 in Eosinophils, Which Are Capable to Release IL-31. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2015, 135, 1908–1911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cevikbas, F.; Wang, X.; Akiyama, T.; Kempkes, C.; Savinko, T.; Antal, A.; Kukova, G.; Buhl, T.; Ikoma, A.; Buddenkotte, J.; et al. A sensory neuron-expressed IL-31 receptor mediates T helper cell-dependent itch: Involvement of TRPV1 and TRPA1. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2014, 133, 448–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Limberg, M.M.; Wiebe, D.; Gray, N.; Weihrauch, T.; Bräuer, A.U.; Kremer, A.E.; Homey, B.; Raap, U. Functional expression of TRPV1 in human peripheral blood basophils and its regulation in atopic dermatitis. Allergy 2024, 79, 225–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juárez-Contreras, R.; Méndez-Reséndiz, K.A.; Rosenbaum, T.; González-Ramírez, R.; Morales-Lázaro, S.L. TRPV1 Channel: A Noxious Signal Transducer That Affects Mitochondrial Function. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 8882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, M.; Cao, E.; Julius, D.; Cheng, Y. Structure of the TRPV1 ion channel determined by electron cryo-microscopy. Nature 2013, 7478, 107–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tominaga, M.; Caterina, M.J.; Malmberg, A.B.; Rosen, T.A.; Gilbert, H.; Skinner, K.; Raumann, B.E.; Basbaum, A.I.; Julius, D. The cloned capsaicin receptor integrates multiple pain-producing stimuli. Neuron 1998, 21, 531–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhaka, A.; Uzzell, V.; Dubin, A.E.; Mathur, J.; Petrus, M.; Bandell, M.; Patapoutian, A. TRPV1 is activated by both acidic and basic pH. J. Neurosci. 2009, 29, 153–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, N.; Inan, S.; Cowan, A.; Sun, R.; Wang, J.M.; Rogers, T.J.; Caterina, M.; Oppenheim, J.J. A proinflammatory chemokine, CCL3, sensitizes the heat- and capsaicin-gated ion channel TRPV1. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 4536–4541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shim, W.-S.; Tak, M.-H.; Lee, M.-H.; Kim, M.; Kim, M.; Koo, J.-Y.; Lee, C.-H.; Kim, M.; Oh, U. TRPV1 mediates histamine-induced itching via the activation of phospholipase A2 and 12-lipoxygenase. J. Neurosci. Off. J. Soc. Neurosci. 2007, 27, 2331–2337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tominaga, M.; Wada, M.; Masu, M. Potentiation of capsaicin receptor activity by metabotropic ATP receptors as a possible mechanism for ATP-evoked pain and hyperalgesia. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 6951–6956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuang, H.H.; Prescott, E.D.; Kong, H.; Shields, S.; Jordt, S.E.; Basbaum, A.I.; Chao, M.V.; Julius, D. Bradykinin and nerve growth factor release the capsaicin receptor from PtdIns(4,5)P2-mediated inhibition. Nature 2001, 411, 957–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moriyama, T.; Higashi, T.; Togashi, K.; Iida, T.; Segi, E.; Sugimoto, Y.; Tominaga, T.; Narumiya, S.; Tominaga, M. Sensitization of TRPV1 by EP1 and IP reveals peripheral nociceptive mechanism of prostaglandins. Mol. Pain 2005, 1, 1744–8069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Huang, J.; McNaughton, P.A. NGF rapidly increases membrane expression of TRPV1 heat-gated ion channels. EMBO J. 2005, 24, 4211–4223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caterina, M.J.; Leffler, A.; Malmberg, A.B.; Martin, W.J.; Trafton, J.; Petersen-Zeitz, K.R.; Koltzenburg, M.; Basbaum, A.I.; Julius, D. Impaired nociception and pain sensation in mice lacking the capsaicin receptor. Science 2000, 288, 306–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waning, J.; Vriens, J.; Owsianik, G.; Stüwe, L.; Mally, S.; Fabian, A.; Frippiat, C.; Nilius, B.; Schwab, A. A novel function of capsaicin-sensitive TRPV1 channels: Involvement in cell migration. Cell Calcium 2007, 42, 17–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalil, M.; Alliger, K.; Weidinger, C.; Yerinde, C.; Wirtz, S.; Becker, C.; Engel, M.A. Functional Role of Transient Receptor Potential Channels in Immune Cells and Epithelia. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, J.B.; Gray, J.; Gunthorpe, M.J.; Hatcher, J.P.; Davey, P.T.; Overend, P.; Harries, M.H.; Latcham, J.; Clapham, C.; Atkinson, K.; et al. Vanilloid receptor-1 is essential for inflammatory thermal hyperalgesia. Nature 2000, 405, 183–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caterina, M.J.; Schumacher, M.A.; Tominaga, M.; Rosen, T.A.; Levine, J.D.; Julius, D. The capsaicin receptor: A heat-activated ion channel in the pain pathway. Nature 1997, 389, 816–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Denda, M.; Fuziwara, S.; Inoue, K.; Denda, S.; Akamatsu, H.; Tomitaka, A.; Matsunaga, K. Immunoreactivity of VR1 on epidermal keratinocyte of human skin. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2001, 285, 1250–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue, K.; Koizumi, S.; Fuziwara, S.; Denda, S.; Inoue, K.; Denda, M. Functional vanilloid receptors in cultured normal human epidermal keratinocytes. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2002, 291, 124–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bodó, E.; Kovács, I.; Telek, A.; Varga, A.; Paus, R.; Kovács, L.; Bíró, T. Vanilloid receptor-1 (VR1) is widely expressed on various epithelial and mesenchymal cell types of human skin. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2004, 123, 410–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Southall, M.D.; Li, T.; Gharibova, L.S.; Pei, Y.; Nicol, G.D.; Travers, J.B. Activation of epidermal vanilloid receptor-1 induces release of proinflammatory mediators in human keratinocytes. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2003, 304, 217–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ständer, S.; Moormann, C.; Schumacher, M.; Buddenkotte, J.; Artuc, M.; Shpacovitch, V.; Brzoska, T.; Lippert, U.; Henz, B.M.; Luger, T.A.; et al. Expression of vanilloid receptor subtype 1 in cutaneous sensory nerve fibers, mast cells, and epithelial cells of appendage structures. Exp. Dermatol. 2004, 13, 129–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tóth, B.I.; Benkő, S.; Szöllősi, A.G.; Kovács, L.; Rajnavölgyi, E.; Bíró, T. Transient receptor potential vanilloid-1 signaling inhibits differentiation and activation of human dendritic cells. FEBS Lett. 2009, 583, 1619–1624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertin, S.; Aoki-Nonaka, Y.; de Jong, P.R.; Nohara, L.L.; Xu, H.; Stanwood, S.R.; Srikanth, S.; Lee, J.; To, K.; Abramson, L.; et al. The ion channel TRPV1 regulates the activation and proinflammatory properties of CD4+ T cells. Nat. Immunol. 2014, 15, 1055–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heiner, I.; Eisfeld, J.; Lückhoff, A. Role and regulation of TRP channels in neutrophil granulocytes. Cell Calcium 2003, 33, 533–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heiner, I.; Eisfeld, J.; Halaszovich, C.R.; Wehage, E.; Jüngling, E.; Zitt, C.; Lückhoff, A. Expression profile of the transient receptor potential (TRP) family in neutrophil granulocytes: Evidence for currents through long TRP channel 2 induced by ADP-ribose and NAD. Biochem. J. 2003, 371, 1045–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parenti, A.; de Logu, F.; Geppetti, P.; Benemei, S. What is the evidence for the role of TRP channels in inflammatory and immune cells. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2016, 173, 953–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Learoyd, J.; Butt, S.; Zhu, L.; Usatyuk, P.V.; Natarajan, V.; Munoz, N.M.; Leff, A.R. Regulation of eosinophil adhesion by lysophosphatidylcholine via a non-store-operated Ca2+ channel. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2007, 36, 585–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramírez-Barrantes, R.; Córdova, C.; Gatica, S.; Rodriguez, B.; Lozano, C.; Marchant, I.; Echeverria, C.; Simon, F.; Olivero, P. Transient Receptor Potential Vanilloid 1 Expression Mediates Capsaicin-Induced Cell Death. Front. Physiol. 2018, 9, 682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, H.; Wang, Z.; Capo-Aponte, J.E.; Zhang, F.; Pan, Z.; Reinach, P.S. Epidermal growth factor receptor transactivation by the cannabinoid receptor (CB1) and transient receptor potential vanilloid 1 (TRPV1) induces differential responses in corneal epithelial cells. Exp. Eye Res. 2010, 91, 462–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.; Zanvit, P.; Hu, L.; Tseng, P.-Y.; Liu, N.; Wang, F.; Liu, O.; Zhang, D.; Jin, W.; Guo, N.; et al. The Cytokine TGF-β Induces Interleukin-31 Expression from Dermal Dendritic Cells to Activate Sensory Neurons and Stimulate Wound Itching. Immunity 2020, 53, 371–383.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehman, R.; Bhat, Y.A.; Panda, L.; Mabalirajan, U. TRPV1 inhibition attenuates IL-13 mediated asthma features in mice by reducing airway epithelial injury. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2013, 15, 597–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.; Diogenes, A.; Jeske, N.; Henry, M.; Akopian, A.; Hargreaves, K. Tumor necrosis factor alpha enhances the sensitivity of rat trigeminal neurons to capsaicin. Neuroscience 2008, 155, 503–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, Z.; Xu, X.; Sun, Z.; Yang, Y.X.; Guo, H.; Shi, D. TRPV1 alleviates osteoarthritis by inhibiting M1 macrophage polarization via Ca2+/CaMKII/Nrf2 signaling pathway. Cell Death Dis. 2021, 12, 504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raap, U.; Wichmann, K.; Bruder, M.; Ständer, S.; Wedi, B.; Kapp, A.; Werfel, T. Correlation of IL-31 serum levels with severity of atopic dermatitis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2008, 122, 421–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duca, E.; Sur, G.; Armat, I.; Samasca, G.; Sur, L. Correlation between Interleukin 31 and clinical manifestations in children with atopic dermatitis: An observational study. Allergol. Immunopathol. 2022, 50, 75–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imai, Y. Interleukin-33 in atopic dermatitis. J. Dermatol. Sci. 2019, 96, 2–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rochman, Y.; Dienger-Stambaugh, K.; Richgels, P.K.; Lewkowich, I.P.; Kartashov, A.V.; Barski, A.; Khurana Hershey, G.K.; Leonard, W.J.; Singh, H. TSLP signaling in CD4+ T cells programs a pathogenic T helper 2 cell state. Sci. Signal. 2018, 11, aam8858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogiatzi, S.I.; Fernandez, I.; Bichet, J.C.; Marloie-Provost, M.A.; Volpe, E.; Sastre, X.; Soumelis, V. Cutting Edge: Proinflammatory and Th2 cytokines synergize to induce thymic stromal lymphopoietin production by human skin keratinocytes. J. Immunol. 2007, 178, 3373–3377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, J.; Wang, J.; Steinhoff, M.; Dolly, J.O. TNFα induces co-trafficking of TRPV1/TRPA1 in VAMP1-containing vesicles to the plasmalemma via Munc18-1/syntaxin1/SNAP-25 mediated fusion. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 21226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lieu, T.M.; Myers, A.C.; Meeker, S.; Undem, B.J. TRPV1 induction in airway vagal low-threshold mechanosensory neurons by allergen challenge and neurotrophic factors. American journal of physiology. Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2012, 302, L941–L948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papoiu, A.D.; Wang, H.; Nattkemper, L.; Tey, H.L.; Ishiuji, Y.; Chan, Y.-H.; Schmelz, M.; Yosipovitch, G. A study of serum concentrations and dermal levels of NGF in atopic dermatitis and healthy subjects. Neuropeptides 2011, 45, 417–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raap, U.; Werfel, T.; Goltz, C.; Deneka, N.; Langer, K.; Bruder, M.; Kapp, A.; Schmid-Ott, G.; Wedi, B. Circulating levels of brain-derived neurotrophic factor correlate with disease severity in the intrinsic type of atopic dermatitis. Allergy 2006, 61, 1416–1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, J.; Altomare, A.; Guarino, M.; Cicala, M.; Rieder, F.; Fiocchi, C.; Li, D.; Cao, W.; Behar, J.; Biancani, P.; et al. HCl-induced and ATP-dependent upregulation of TRPV1 receptor expression and cytokine production by human esophageal epithelial cells. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2012, 303, G635–G645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schicho, R.; Florian, W.; Liebmann, I.; Holzer, P.; Lippe, I.T. Increased expression of TRPV1 receptor in dorsal root ganglia by acid insult of the rat gastric mucosa. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2004, 19, 1811–1818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manosalva, C.; Quiroga, J.; Hidalgo, A.I.; Alarcón, P.; Anseoleaga, N.; Hidalgo, M.A.; Burgos, R.A. Role of Lactate in Inflammatory Processes: Friend or Foe. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 808799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weinkauf, B.; Rukwied, R.; Quiding, H.; Dahllund, L.; Johansson, P.; Schmelz, M. Local gene expression changes after UV-irradiation of human skin. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e39411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greaves, E.; Grieve, K.; Horne, A.W.; Saunders, P.T. Elevated peritoneal expression and estrogen regulation of nociceptive ion channels in endometriosis. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2014, 99, e1738–e1743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gray, N.; Limberg, M.M.; Wiebe, D.; Weihrauch, T.; Langner, A.; Brandt, N.; Bräuer, A.U.; Raap, U. Differential Upregulation and Functional Activity of S1PR1 in Human Peripheral Blood Basophils of Atopic Patients. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 16117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Weihrauch, T.; Gray, N.; Wiebe, D.; Schmelz, M.; Limberg, M.M.; Raap, U. TRPV1 Channel in Human Eosinophils: Functional Expression and Inflammatory Modulation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 1922. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25031922
Weihrauch T, Gray N, Wiebe D, Schmelz M, Limberg MM, Raap U. TRPV1 Channel in Human Eosinophils: Functional Expression and Inflammatory Modulation. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2024; 25(3):1922. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25031922
Chicago/Turabian StyleWeihrauch, Tobias, Natalie Gray, Daniela Wiebe, Martin Schmelz, Maren M. Limberg, and Ulrike Raap. 2024. "TRPV1 Channel in Human Eosinophils: Functional Expression and Inflammatory Modulation" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 25, no. 3: 1922. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25031922
APA StyleWeihrauch, T., Gray, N., Wiebe, D., Schmelz, M., Limberg, M. M., & Raap, U. (2024). TRPV1 Channel in Human Eosinophils: Functional Expression and Inflammatory Modulation. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 25(3), 1922. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25031922