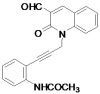
N-{2-[3-(3-Formyl-2-oxoquinolin-1(2H)-yl)prop-1-ynyl]phenyl}acetamide
Abstract
:Preparation of N-{2-[3-(3-formyl-2-oxoquinolin-1(2H)-yl)prop-1-ynyl]phenyl}acetamide
Supplementary materials
Supplementary File 1Supplementary File 2Supplementary File 3Acknowledgements
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Toube, T.P.; Murphy, J.W.; Cross, A.D. The structure of edulitine and edulinine. Tetrahedron 1967, 23, 2061–2065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, H.S.; Woo, W.S. A quinolone alkaloid with antioxidant activity from the aleurone layer of anthocyanin-pigmented rice. J. Nat. Prod. 2001, 64, 1579–1580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, T.-S.; Yeh, J.-H.; Wu, P.-L. The heartwood constituents of tetradium glabrifolium. Phytochemistry 1995, 40, 121–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uchida, M.; Tabusa, F.; Komatsu, M.; Morita, S.; Kanbe, T.; Nakagawa, K. Studies on 2(1H)-quinolinone derivatives as gastric antiulcer active agents. Synthesis and antiulcer activity of the metabolites of 2(4-chlorobenzoylamino)-3-[2(1h)-quinolinon-4-yl]propionic acid. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1986, 34, 4821–4824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michael, J.P. Quinoline, quinazoline and acridone alkaloids. Nat. Prod. Rep. 1997, 14, 595–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alabaster, C.T.; Belli, A.S.; Campbell, S.F.; Ellis, P.; Henderson, C.G.; Roberts, D.A.; Ruddock, K.S.; Samules, G.M.R.; Stefanisk, M.H. 2(1H)-Quinolinones with cardiac stimulant activity. 1. Synthesis and biological activities of (six-membered heteroaryl)-substituted derivatives. J. Med. Chem. 1988, 31, 2048–2056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kimura, N.; Fukui, H.; Takagaki, H.; Yonemochi, E.; Terada, K. Characterization of polymorphs of a novel quinolinone derivative, TA-270 (4-hydroxy-1-methyl-3-octyloxy-7-sinapinoylamino-2(1H)-quinolinone). Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2001, 49, 1321–1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pal, S.; Durgadas, S.; Nallapati, S.B.; Mukkanti, K.; Kapavarapu, R.; Meda, C.L.; Parsa, K.V.; Pal, M. Novel 1-alkynyl substituted 1,2-dihydroquinoline derivatives from nimesulide (and their 2-oxo analogues): A new strategy to identify inhibitors of PDE4B. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2011, 21, 6573–6576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sonogashira, K.; Tohda, Y.; Hagihara, N. A convenient synthesis of acetylenes: Catalytic substitutions of acetylenic hydrogen with bromoalkenes, iodoarenes and bromopyridines. Tetrahedron Lett. 1975, 16, 4467–4470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durgadas, S.; Chatare, V.K.; Mukkanti, K.; Pal, S. Palladium-mediated synthesis of novel nimesulide derivatives. Appl. Organometal. Chem. 2010, 24, 680–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, A.; Singh, R.M. Vilsmeier-Haack reagent: A facile synthesis of 2-chloro-3-formylquinolines from N-arylacetamides and transformation into different functionalities. Indian J. Chem. 2005, 44B, 1868–1875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

© 2013 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Durgadas, S.; Mukkanti, K.; Pal, S. N-{2-[3-(3-Formyl-2-oxoquinolin-1(2H)-yl)prop-1-ynyl]phenyl}acetamide. Molbank 2013, 2013, M807. https://doi.org/10.3390/M807
Durgadas S, Mukkanti K, Pal S. N-{2-[3-(3-Formyl-2-oxoquinolin-1(2H)-yl)prop-1-ynyl]phenyl}acetamide. Molbank. 2013; 2013(3):M807. https://doi.org/10.3390/M807
Chicago/Turabian StyleDurgadas, Shylaprasad, Khagga Mukkanti, and Sarbani Pal. 2013. "N-{2-[3-(3-Formyl-2-oxoquinolin-1(2H)-yl)prop-1-ynyl]phenyl}acetamide" Molbank 2013, no. 3: M807. https://doi.org/10.3390/M807
APA StyleDurgadas, S., Mukkanti, K., & Pal, S. (2013). N-{2-[3-(3-Formyl-2-oxoquinolin-1(2H)-yl)prop-1-ynyl]phenyl}acetamide. Molbank, 2013(3), M807. https://doi.org/10.3390/M807