Spectroscopic and Chromatographic Characterization of Wastewater Organic Matter from a Biological Treatment Plant
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Sample Collection and Preservation
2.2. Analytical Methods
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Changes in Organic Carbon Concentrations, Hydrophobicity and SUVA Values
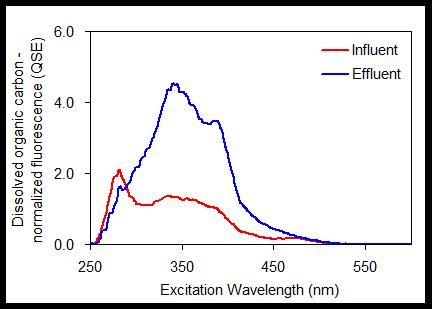
3.2. Changes in Synchronous Fluorescence Spectra
3.3. Changes in the Molecular Weight Distributions
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
References
- Barker, D.J.; Stuckey, D.C. A review of soluble microbial products (SMP) in wastewater treatment systems. Water Res 1999, 33, 3063–3082. [Google Scholar]
- Ang, W.S.; Elimelech, M. Fatty acid fouling of reverse osmosis membranes: Implications for wastewater reclamation. Water Res 2008, 42, 4393–4403. [Google Scholar]
- Holbrook, R.D.; Breidenich, J.; Derose, P.C. Impact of reclaimed water on select organic matter properties of a receiving stream-fluorescence and perylene sorption behavior. Environ. Sci. Technol 2005, 39, 6453–6460. [Google Scholar]
- Imai, A.; Fukushima, T.; Matsushige, K.; Kim, Y.H. Fractionation and characterization of dissolved organic matter in a shallow eutrophic lake, its inflowing rivers, and other organic matter sources. Water Res 2001, 35, 4019–4028. [Google Scholar]
- Hur, J.; Park, M.H.; Schlautman, M.A. Microbial transformation of dissolved leaf litter organic matter (OM) and its effects on selected OM operational descriptors. Environ. Sci. Technol 2009, 43, 2315–2321. [Google Scholar]
- Jarusutthirak, C.; Amy, G. Understanding soluble microbial products (SMP) as a component of effluent organic matter (EfOM). Water Res 2007, 41, 2787–2793. [Google Scholar]
- Volk, C.J.; Volk, C.B.; Kaplan, L.A. Chemical composition of biodegradable dissolved organic matter in streamwater. Limnol. Oceanogr 1997, 42, 39–44. [Google Scholar]
- Imai, A.; Fukushima, T.; Matsushige, K.; Kim, Y.H.; Choi, K.S. Characterization of dissolved organic matter in effluents from wastewater plants. Water Res 2002, 36, 859–870. [Google Scholar]
- Musikavong, C.; Wattanachira, S. Reduction of dissolved organic matter in terms of DOC, UV-254, SUVA and THMFP in industrial estate wastewater treated by stabilization ponds. Environ. Monit. Assess 2007, 134, 489–497. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, Y.S.; Hong, S.W.; Kim, S.J.; Chung, I.H. Development of a biological process for livestock wastewater treatment using a technique for predominant outgrowth of bacillus species. Water Sci. Technol 2000, 45, 71–78. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, J.K.; Park, K.J.; Cho, K.S.; Nam, S.W.; Park, T.J.; Bajpai, R. Aerobic nitrification-denitrification by heterotrophic Bacillus strains. Bioresour. Technol 2005, 96, 1897–1906. [Google Scholar]
- Hur, J.; Hwang, S.J.; Shin, J.K. Using synchronous fluorescence technique as a water quality monitoring tool for an urban river. Water Air Soil Pollut 2008, 191, 231–243. [Google Scholar]
- McKnight, D.M.; Boyer, E.W.; Westerhoff, P.K.; Doran, P.T.; Kulbe, T.; Andersen, D.T. Spectrophotometric characterization of dissolved organic matter for indication of precursor organic material and aromaticity. Limnol. Oceanogr 2001, 46, 38–48. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.; LeBoeuf, E.J.; Dai, S.; Gu, B. Fluorescence spectroscopic studies of natural organic matter fractions. Chemosphere 2003, 50, 639–647. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Z.; Hu, C.; Conmy, R.N.; Muller-Karger, F.; Swarzenski, P. Colored dissolved organic matter in Tampa Bay, Florida. Mar. Chem 2007, 104, 98–109. [Google Scholar]
- Baker, A. Fluorescence excitation-emission matrix characterization of some sewage-impacted rivers. Environ. Sci. Technol 2001, 35, 948–953. [Google Scholar]
- Alberts, J.J.; Takács, M. Total luminescence spectra of IHSS standard and reference fulvic acids, humic acids, natural organic matter: comparison of aquatic and terrestrial source terms. Org. Geochem 2004, 35, 243–256. [Google Scholar]
- Westerhoff, P.; Chen, W.; Esparza, M. Fluorescence analysis of a standard fulvic acid and tertiary treated wastewater. J. Environ. Qual 2001, 30, 2037–2046. [Google Scholar]
- Hur, J.; Schlautman, M.A. Using selected operational descriptors to examine the heterogeneity within a bulk humic substance. Environ. Sci. Technol 2003, 37, 880–887. [Google Scholar]
- Servais, P.; Garnier, J.; Demarteau, N.; Brion, N.; Billen, G. Supply of organic matter and bacteria to aquatic ecosystems through waste water effluents. Water Res 1999, 33, 3521–3531. [Google Scholar]
- Namour, P.; Muller, M.C. Fractionation of organic matter from wastewater treatment plants before and after a 21-day biodegradability test: a physical-chemical method for measurement of the refractory part of effluents. Water Res 1998, 32, 2224–2231. [Google Scholar]
- Hertkorn, N.; Claus, H.; Schmitt-Kopplin, P.H.; Perdue, E.M.; Filip, Z. Utilization and transformation of aquatic humic substances by autochthonous microorganism. Environ. Sci. Technol 2002, 36, 4334–4345. [Google Scholar]
- Laor, Y.; Avnimelech, Y. Fractionation of compost derived dissolved organic matter by flocculation process. Org. Geochem 2002, 33, 257–263. [Google Scholar]
- Li, W.H.; Sheng, G.P.; Liu, X.W.; Yu, H.Q. Characterizing the extracellular and intracellular fluorescent products of activated sludge in a sequencing batch reactor. Water Res 2008, 42, 3173–3181. [Google Scholar]
- Hudson, N.; Baker, A.; Reynolds, D. Fluorescence analysis of dissolved organic matter in natural, waste and polluted waters-a review. River Res. Appl 2007, 23, 631–649. [Google Scholar]
- Ogawa, H.; Amagai, Y.; Koike, I.; Kaiser, K.; Benner, R. Production of refractory dissolved organic matter by bacteria. Science 2001, 292, 917–920. [Google Scholar]
- Chefetz, B.; Iiani, T.; Schulz, E.; Chorover, J. Wastewater dissolved organic matter: characteristics and sorptive capabilities. Water Sci. Technol 2006, 53, 51–57. [Google Scholar]




| Type | BOD (mg/L) | CODCr (mg/L) | DOC (mg C/L) | POC (mg C/L) | TOC (mg C/L) | Ho (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Influent | OM | 109 | 150 | 25.1 (0.30)a | 35.4 (0.08) | 60.5 (0.74) | 34.8 |
| R-OM | 63.0 | 5.24 (0.08) | 21.9 (0.05) | 27.2 (0.41) | 64.1 | ||
| Effluent | OM | 7.60 | 16.1 | 4.50 (0.08) | 2.86 (0.01) | 7.36 (0.13) | 26.9 |
| R-OM | 11.4 | 3.72 (0.03) | 0.92 (0.00) | 4.64 (0.04) | 65.6 |
| Type | SUVA | PLF/DOC | FLF/DOC | HLF/DOC | FLF/PLF | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Influent | DOM | 0.98 (0.02)a | 2.11 (0.03) | 1.33 (0.02) | 0.96 (0.01) | 0.63 (0.01) |
| R-DOMb | 2.10 (0.05) | 1.71 (0.03) | 4.81 (0.09) | 4.05 (0.07) | 2.81 (0.05) | |
| Effluent | DOM | 1.93 (0.05) | 1.63 (0.03) | 4.49 (0.09) | 3.44 (0.07) | 2.75 (0.05) |
| R-DOM | 1.85 (0.04) | 1.29 (0.02) | 5.11 (0.07) | 3.91 (0.05) | 3.95 (0.05) |
| Type | MWw | MWn | Polydispersity | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Influent | OM | 685 | 242 | 2.83 |
| R-OMa | 823 | 504 | 1.63 | |
| Effluent | OM | 849 | 501 | 1.69 |
| R-OM | 871 | 565 | 1.54 |
©2010 by the authors; licensee Molecular Diversity Preservation International, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/)
Share and Cite
Park, M.-H.; Lee, T.-H.; Lee, B.-M.; Hur, J.; Park, D.-H. Spectroscopic and Chromatographic Characterization of Wastewater Organic Matter from a Biological Treatment Plant. Sensors 2010, 10, 254-265. https://doi.org/10.3390/s100100254
Park M-H, Lee T-H, Lee B-M, Hur J, Park D-H. Spectroscopic and Chromatographic Characterization of Wastewater Organic Matter from a Biological Treatment Plant. Sensors. 2010; 10(1):254-265. https://doi.org/10.3390/s100100254
Chicago/Turabian StylePark, Min-Hye, Tae-Hwan Lee, Bo-Mi Lee, Jin Hur, and Dae-Hee Park. 2010. "Spectroscopic and Chromatographic Characterization of Wastewater Organic Matter from a Biological Treatment Plant" Sensors 10, no. 1: 254-265. https://doi.org/10.3390/s100100254
APA StylePark, M. -H., Lee, T. -H., Lee, B. -M., Hur, J., & Park, D. -H. (2010). Spectroscopic and Chromatographic Characterization of Wastewater Organic Matter from a Biological Treatment Plant. Sensors, 10(1), 254-265. https://doi.org/10.3390/s100100254