Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotube-Doped Tungsten Oxide Thin Films for Hydrogen Gas Sensing
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental
2.1. Preparation of Materials
2.2. Fabrication of MWCNTs-doped WO3 Thin Film
2.3. Measurement of Gas Sensing
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characterization of Thin Films
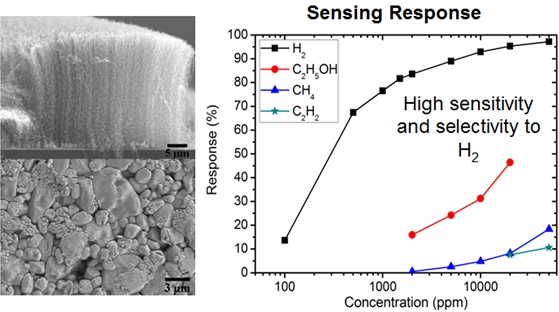
3.2. Sensing Properties of Thin Films
3.3. Sensing Mechanism of MWCNTs-doped WO3 Thin Film
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
References
- Korotcenkov, G; Han, SD; Stetter, JR. Review of electrochemical hydrogen sensors. Chem. Rev 2009, 109, 1402–1433. [Google Scholar]
- Moriarty, P; Honnery, D. Hydrogen's role in an uncertain energy future. Int. J. Hydrogen. Energ 2009, 34, 31–39. [Google Scholar]
- Momirlan, M; Veziroglu, TN. The properties of hydrogen as fuel tomorrow in sustainable energy system for a cleaner planet. Int. J. Hydrogen. Energ 2005, 30, 795–802. [Google Scholar]
- Árnason, B; Sigfússon, TI. Iceland—A future hydrogen economy. Int. J. Hydrogen. Energ 2000, 25, 389–394. [Google Scholar]
- Carcassi, MN; Fineschi, F. Deflagrations of H2-air and CH4-air lean mixtures in a vented multi-compartment environment. Energy 2005, 30, 1439–1451. [Google Scholar]
- Penza, M; Tagliente, MA; Mirenghi, L; Gerardi, C; Martucci, C; Cassano, G. Tungsten trioxide (WO3) sputtered thin films for a NOx gas sensor. Sens. Actuat. B Chem 1998, 50, 9–18. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X; Miura, N; Yamazoe, N. Study of WO3-based sensing materials for NH3 and NO detection. Sens. Actuat. B Chem 2000, 66, 74–76. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, TS; Kim, TB; Yoo, KS; Sung, GS; Jung, HJ. Sensing characteristics of dc reactive sputtered WO3 thin films as an NOx gas sensor. Sens. Actuat. B Chem 2000, 62, 102–108. [Google Scholar]
- Sawicka, KM; Prasad, AK; Gouma, PI. Metal oxide nanowires for use in chemical sensing applications. Sens. Lett 2005, 3, 31–35. [Google Scholar]
- Tao, WH; Tsai, CH. H2S sensing properties of noble metal doped WO3 thin film sensor fabricated by micromachining. Sens. Actuat. B Chem 2002, 81, 237–247. [Google Scholar]
- Frühberger, B; Grunze, M; Dwyer, DJ. Surface chemistry of H2S-sensitive tungsten oxide films. Sens. Actuat. B Chem 1996, 31, 167–174. [Google Scholar]
- Hoel, A; Reyes, LF; Heszler, P; Lantto, V; Granqvist, CG. Nanomaterials for environmental applications: Novel WO3-based gas sensors made by advanced gas deposition. Curr. Appl. Phys 2004, 4, 547–553. [Google Scholar]
- Ionescu, R; Hoel, A; Granqvist, CG; Llobet, E; Heszler, P. Low-level detection of ethanol and H2S with temperature-modulated WO3 nanoparticle gas sensors. Sens. Actuat. B Chem 2005, 104, 132–139. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X; Zhang, G; Cheng, F; Guo, B; Chen, J. Synthesis, characterization, and gas-sensor application of WO3 nanocuboids. J. Electrochem. Soc 2006, 153, 133–137. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Y; Tang, Z; Zhang, Z; Ji, Y; Zhou, Z. Large-scale hydrothermal synthesis of tungsten trioxide nanowires and their gas sensing properties. Sens. Lett 2008, 6, 938–941. [Google Scholar]
- Neri, G; Micali, G; Bonavita, A; Ipsale, S; Rizzo, G; Niederberger, M; Pinna, N. Tungsten oxide nanowires-based ammonia gas sensors. Sens. Lett 2008, 6, 590–595. [Google Scholar]
- Llobet, E; Molas, G; Molinàs, P; Calderer, J; Vilanova, X; Brezmes, J; Sueiras, JE; Correig, X. Fabrication of highly selective tungsten oxide ammonia sensors. J. Electrochem. Soc 2000, 147, 776–779. [Google Scholar]
- Balázsia, C; Wang, L; Zayim, EO; Szilágyid, IM; Sedlackováe, K; Pfeifera, J; Tótha, AL; Goumab, PI. Nanosize hexagonal tungsten oxide for gas sensing applications. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc 2008, 28, 913–917. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, U; Pfeifer, J; Balazsi, C; Gouma, PI. Synthesis and sensing properties to NH3 of hexagonal WO3 metastable nanopowders. Mater. Manuf. Process 2007, 22, 773–776. [Google Scholar]
- Berger, O; Hoffmann, T; Fischer, WJ; Melev, V. Tungsten-oxide thin films as novel materials with high sensitivity and selectivity to NO2, O3, and H2S. Part II: Application as gas sensors. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron 2004, 15, 483–493. [Google Scholar]
- Aroutiounian, V. Metal oxide hydrogen, oxygen, and carbon monoxide sensors for hydrogen setups and cells. Int. J. Hydrogen. Energ 2007, 32, 1145–1158. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmad, A; Walsh, J. Development of WO3-based thick-film hydrogen sensors. ECS Trans 2006, 3, 141–152. [Google Scholar]
- Ippolito, SJ; Kandasamy, S; Kalantar-zadeh, K; Wlodarski, W. Hydrogen sensing characteristics of WO3 thin film conductometric sensors activated by Pt and Au catalysts. Sens. Actuat. B Chem 2005, 108, 154–158. [Google Scholar]
- Hsu, WC; Chan, CC; Peng, CH; Chang, CC. Hydrogen sensing characteristics of an electrodeposited WO3 thin film gasochromic sensor activated by Pt catalyst. Thin Solid Films 2007, 516, 407–411. [Google Scholar]
- Fardindoost, S; Iraji-zad, A; Rahimi, F; Ghasempour, R. Pd doped WO3 films prepared by sol–gel process for hydrogen sensing. Int. J. Hydrogen. Energ 2010, 35, 854–860. [Google Scholar]
- Nakagawa, H; Yamamoto, N; Okazaki, S; Chinzei, T; Asakura, S. A room-temperature operated hydrogen leak sensor. Sens. Actuat. B Chem 2003, 93, 468–474. [Google Scholar]
- Samarasekara, P. Hydrogen and methane gas sensors synthesis of multi-walled carbon nanotubes. Chin. J. Phys 2009, 47, 361–369. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, L; Xiu, Y; Hess, DW; Wong, CP. Aligned carbon nanotube stacks by water-assisted selective etching. Nano Lett 2005, 5, 2641–2645. [Google Scholar]
- Wongchoosuk, C; Wisitsoraat, A; Tuantranont, A; Kerdcharoen, T. Portable electronic nose based on carbon nanotube-SnO2 gas sensors and its application for detection of methanol contamination in whiskeys. Sens. Actuat. B Chem 2010, 147, 392–399. [Google Scholar]
- Ansari, ZA; Ansari, SG; Ko, T; Oh, JH. Effect of MoO3 doping and grain size on SnO2-enhancement of sensitivity and selectivity for CO and H2 gas sensing. Sens. Actuat. B Chem 2002, 87, 105–114. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, DS; Nam, KH; Lee, DD. Effect of substrate on NO2-sensing properties of WO3 thin film gas sensors. Thin Solid Films 2000, 375, 142–146. [Google Scholar]
- Hussain, OM; Swapnasmitha, AS; John, J; Pinto, R. Structure and morphology of laser-ablated WO3 thin films. Appl. Phys. A: Mater. Sci. Process 2005, 81, 1291–1297. [Google Scholar]
- Ashrit, PV. Dry lithiation study of nanocrystalline, polycrystalline and amorphous tungsten trioxide thin-films. Thin Solid Films 2001, 385, 81–88. [Google Scholar]
- Shinde, VR; Gujar, TP; Lokhande, CD. LPG sensing properties of ZnO films prepared by spray pyrolysis method: Effect of molarity of precursor solution. Sens. Actuat. B Chem 2007, 120, 551–559. [Google Scholar]
- Zeng, Y; Zhang, T; Wang, L; Kang, M; Fan, H; Wang, R; He, Y. Enhanced toluene sensing characteristics of TiO2-doped flowerlike ZnO nanostructures. Sens. Actuat. B Chem 2009, 140, 73–78. [Google Scholar]
- Sahay, PP; Nath, RK. Al-doped zinc oxide thin films for liquid petroleum gas (LPG) sensors. Sens. Actuat. B Chem 2008, 133, 222–227. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, YX; Chen, YJ; Wang, TH. Low-resistance gas sensors fabricated from multiwalled carbon nanotubes coated with a thin tin oxide layer. Appl. Phy. Lett 2004, 85, 666–668. [Google Scholar]
- Bittencourt, C; Felten, A; Espinosa, EH; Ionescu, R; Llobet, E; Correig, X; Pireaux, JJ. WO3 films modified with functionalised multi-wall carbon nanotubes: Morphological, compositional and gas response studies. Sens. Actuat. B Chem 2006, 115, 33–41. [Google Scholar]
- Sakai, G; Matsunaga, N; Shimanoe, K; Yamazoe, N. Theory of gas-diffusion controlled sensitivity for thin film semiconductor gas sensor. Sens. Actuat. B Chem 2001, 80, 125–131. [Google Scholar]
- Hieu, NV; Duc, NAP; Trung, T; Tuan, MA; Chien, ND. Gas-sensing properties of tin oxide doped with metal oxides and carbon nanotubes: A competitive sensor for ethanol and liquid petroleum gas. Sens. Actuat. B Chem 2010, 144, 450–456. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, BY; Hsu, MC; Su, PG; Lin, HM; Wu, RJ; Lai, HJ. A novel SnO2 gas sensor doped with carbon nanotubes operating at room temperature. Sens. Actuat. B Chem 2004, 101, 81–89. [Google Scholar]
- Cheong, HW; Lee, MJ. Sensing characteristics and surface reaction mechanism of alcohol sensors based on doped SnO2. J. Ceram. Process. Res 2006, 7, 183–191. [Google Scholar]
- Lupan, O; Ursaki, VV; Chai, G; Chow, L; Emelchenko, GA; Tiginyanu, IM; Gruzintsev, AN; Redkin, AN. Selective hydrogen gas nanosensor using individual ZnO nanowire with fast response at room temperature. Sens. Actuat. B Chem 2010, 144, 56–66. [Google Scholar]







© 2010 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Wongchoosuk, C.; Wisitsoraat, A.; Phokharatkul, D.; Tuantranont, A.; Kerdcharoen, T. Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotube-Doped Tungsten Oxide Thin Films for Hydrogen Gas Sensing. Sensors 2010, 10, 7705-7715. https://doi.org/10.3390/s100807705
Wongchoosuk C, Wisitsoraat A, Phokharatkul D, Tuantranont A, Kerdcharoen T. Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotube-Doped Tungsten Oxide Thin Films for Hydrogen Gas Sensing. Sensors. 2010; 10(8):7705-7715. https://doi.org/10.3390/s100807705
Chicago/Turabian StyleWongchoosuk, Chatchawal, Anurat Wisitsoraat, Ditsayut Phokharatkul, Adisorn Tuantranont, and Teerakiat Kerdcharoen. 2010. "Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotube-Doped Tungsten Oxide Thin Films for Hydrogen Gas Sensing" Sensors 10, no. 8: 7705-7715. https://doi.org/10.3390/s100807705
APA StyleWongchoosuk, C., Wisitsoraat, A., Phokharatkul, D., Tuantranont, A., & Kerdcharoen, T. (2010). Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotube-Doped Tungsten Oxide Thin Films for Hydrogen Gas Sensing. Sensors, 10(8), 7705-7715. https://doi.org/10.3390/s100807705