Low-Cost Photolithographic Fabrication of Nanowires and Microfilters for Advanced Bioassay Devices
Abstract
:1. Introduction

2. Experimental Section
2.1. Materials and Instrumentation
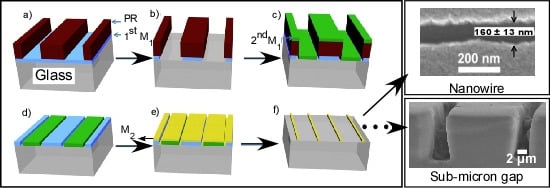
2.2. Nanogap Formation
2.3. Nanowire Fabrication
2.4. Micropillar-Based Microfluidic Photomask Fabrication
2.5. Microfluidics Device Fabrication and Microbead Filtration
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Nanogaps and Nanowires


3.2. Micropillar-Based Filtration within Microfluidic Devices



3.3. Conclusions and Outlook
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Supplemental Information
Supplementary Files
Supplementary File 1Conflict of Interest
References
- Erickson, D.; Li, D. Integrated microfluidic devices. Anal. Chim. Acta 2004, 507, 11–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, K.N.; Li, C.A.; Seong, G.H. Microfluidic chips for immunoassays. Annu. Rev. Anal. Chem. (Palo Alto, Calif.) 2013, 6, 119–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ojeda, I.; Moreno-Guzman, M.; Gonzalez-Cortes, A.; Yanez-Sedeno, P.; Pingarron, J.M. Electrochemical magnetoimmunosensor for the ultrasensitive determination of interleukin-6 in saliva and urine using poly-hrp streptavidin conjugates as labels for signal amplification. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2014, 406, 6363–6371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shamsi, M.H.; Choi, K.; Ng, A.H.C.; Wheeler, A.R. A digital microfluidic electrochemical immunoassay. Lab Chip 2014, 14, 547–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Díaz-González, M.; Baldi, A. Fabrication of biofunctionalized microfluidic structures by low-temperature wax bonding. Anal. Chem. 2012, 84, 7838–7844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Otieno, B.A.; Krause, C.E.; Latus, A.; Chikkaveeraiah, B.V.; Faria, R.C.; Rusling, J.F. On-line protein capture on magnetic beads for ultrasensitive microfluidic immunoassays of cancer biomarkers. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2014, 53, 268–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, C.K.; Vaze, A.; Rusling, J.F. Fabrication of immunosensor microwell arrays from gold compact discs for detection of cancer biomarker proteins. Lab Chip 2012, 12, 281–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rusling, J.F.; Bishop, G.W.; Doan, N.M.; Papadimitrakopoulos, F. Nanomaterials and biomaterials in electrochemical arrays for protein detection. J. Mater. Chem. B 2014, 2, 12–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sardesai, N.; Kadimisetty, K.; Faria, R.; Rusling, J. A microfluidic electrochemiluminescent device for detecting cancer biomarker proteins. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2013, 405, 3831–3838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, F.; Shen, H.; Zhang, G.; Jiang, X.; Kang, X. Chemiluminescence immunoassay based on microfluidic chips for α-fetoprotein. Clin. Chim. Acta 2014, 431, 113–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ge, L.; Yan, J.; Song, X.; Yan, M.; Ge, S.; Yu, J. Three-dimensional paper-based electrochemiluminescence immunodevice for multiplexed measurement of biomarkers and point-of-care testing. Biomaterials 2012, 33, 1024–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venkatanarayanan, A.; Crowley, K.; Lestini, E.; Keyes, T.E.; Rusling, J.F.; Forster, R.J. High sensitivity carbon nanotube based electrochemiluminescence sensor array. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2012, 31, 233–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Justino, C.I.L.; Freitas, A.C.; Amaral, J.P.; Rocha-Santos, T.A.P.; Cardoso, S.; Duarte, A.C. Disposable immunosensors for c-reactive protein based on carbon nanotubes field effect transistors. Talanta 2013, 108, 165–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamahori, M.; Ishige, Y.; Shimoda, M. Enzyme immunoassay using a reusable extended-gate field-effect-transistor sensor with a ferrocenylalkanethiol-modified gold electrode. Anal. Sci. 2008, 24, 1073–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Zhang, Y.; To, S.; You, L.; Sun, Y. Effect of nanowire number, diameter, and doping density on nano-fet biosensor sensitivity. ACS Nano 2011, 5, 6661–6668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Makowski, M.S.; Ivanisevic, A. Molecular analysis of blood with micro-/nanoscale field-effect-transistor biosensors. Small 2011, 7, 1863–1875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patolsky, F.; Zheng, G.; Lieber, C.M. Nanowire-based biosensors. Anal. Chem. 2006, 78, 4260–4269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tkac, J.J.D. Engineering the Bioelectronic Interface; Royal Society of Chemistry: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2009; pp. 193–224. [Google Scholar]
- Ikami, M.; Kawakami, A.; Kakuta, M.; Okamoto, Y.; Kaji, N.; Tokeshi, M.; Baba, Y. Immuno-pillar chip: A new platform for rapid and easy-to-use immunoassay. Lab Chip 2010, 10, 3335–3340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mayer, K.M.; Lee, S.; Liao, H.; Rostro, B.C.; Fuentes, A.; Scully, P.T.; Nehl, C.L.; Hafner, J.H. A label-free immunoassay based upon localized surface plasmon resonance of gold nanorods. ACS Nano 2008, 2, 687–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chin, C.D.; Laksanasopin, T.; Cheung, Y.K.; Steinmiller, D.; Linder, V.; Parsa, H.; Wang, J.; Moore, H.; Rouse, R.; Umviligihozo, G.; et al. Microfluidics-based diagnostics of infectious diseases in the developing world. Nat. Med. 2011, 17, 1015–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andersson, H.; Van Der Wijngaart, W.; Enoksson, P.; Stemme, G. Micromachined flow-through filter-chamber for chemical reactions on beads. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2000, 67, 203–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maeng, J.-H.; Lee, B.-C.; Ko, Y.-J.; Cho, W.; Ahn, Y.; Cho, N.-G.; Lee, S.-H.; Hwang, S.Y. A novel microfluidic biosensor based on an electrical detection system for alpha-fetoprotein. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2008, 23, 1319–1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Cui, D.; Chen, J. Design, fabrication and characterization of nano-filters in silicon microfluidic channels based on mems technology. Electrophoresis 2009, 30, 3168–3173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruffert, C.; Ramadan, Q.; Gijs, M.A.M. Fabrication of a high aspect ratio (har) micropillar filter for a magnetic bead-based immunoassay. Microsyst. Technol. 2014, 20, 1869–1873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Z.; Shao, G.; Wang, J.; Lu, D.; Wang, W.; Lin, Y. Microfabricated renewable beads-trapping/releasing flow cell for rapid antigen-antibody reaction in chemiluminescent immunoassay. Anal. Chem. 2011, 83, 2685–2690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vieu, C.; Carcenac, F.; Pépin, A.; Chen, Y.; Mejias, M.; Lebib, A.; Manin-Ferlazzo, L.; Couraud, L.; Launois, H. Electron beam lithography: Resolution limits and applications. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2000, 164, 111–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandison, M.E.; Cooper, J.M. Nanofabrication of electrode arrays by electron-beam and nanoimprint lithographies. Lab Chip 2006, 6, 1020–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altissimo, M. E-beam lithography for micro-/nanofabrication. Biomicrofluidics 2010, 4, 026503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, X.M.; Kwon, S.; Contreras, A.M.; Bokor, J.; Somorjai, G.A. Fabrication of large number density platinum nanowire arrays by size reduction lithography and nanoimprint lithography. Nano Lett. 2005, 5, 745–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Chung, S.W.; Mirkin, C.A. Fabrication of sub-50-nm solid-state nanostructures on the basis of dip-pen nanolithography. Nano Lett. 2003, 3, 43–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Love, J.C.; Paul, K.E.; Whitesides, G.M. Fabrication of nanometer-scale features by controlled isotropic wet chemical etching. Adv. Mater. 2001, 13, 604–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mani, V.; Chikkaveeraiah, B.V.; Patel, V.; Gutkind, J.S.; Rusling, J.F. Ultrasensitive immunosensor for cancer biomarker proteins using gold nanoparticle film electrodes and multienzyme-particle amplification. ACS Nano 2009, 3, 585–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tennico, Y.H.; Hutanu, D.; Koesdjojo, M.T.; Bartel, C.M.; Remcho, V.T. On-chip aptamer-based sandwich assay for thrombin detection employing magnetic beads and quantum dots. Anal. Chem. 2010, 82, 5591–5597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.N.; Lee, Y.; Koh, W.G. Fabrication of microfluidic devices incorporating bead-based reaction and microarray-based detection system for enzymatic assay. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2009, 137, 305–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mani, V.; Wasalathanthri, D.P.; Joshi, A.A.; Kumar, C.V.; Rusling, J.F. Highly efficient binding of paramagnetic beads bioconjugated with 100,000 or more antibodies to protein-coated surfaces. Anal. Chem. 2012, 84, 10485–10491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menke, E.J.; Thompson, M.A.; Xiang, C.; Yang, L.C.; Penner, R.M. Lithographically patterned nanowire electrodeposition. Nat. Mater. 2006, 5, 914–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henstridge, M.C.; Compton, R.G. Mass transport to micro- and nanoelectrodes and their arrays: A review. Chem. Rec. (New York, N.Y.) 2012, 12, 63–71. [Google Scholar]
- Rusling, J.F. Multiplexed electrochemical protein detection and translation to personalized cancer diagnostics. Anal. Chem. 2013, 85, 5304–5310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiang, C.; Kung, S.-C.; Taggart, D.K.; Yang, F.; Thompson, M.A.; Guell, A.G.; Yang, Y.; Penner, R.M. Lithographically patterned nanowire electrodeposition: A method for patterning electrically continuous metal nanowires on dielectrics. ACS Nano 2008, 2, 1939–1949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ponoth, S.S.; Agarwal, N.T.; Persans, P.D.; Plawsky, J.L. Fabrication of controlled sidewall angles in thin films using isotropic etches. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. B Microelectron. Nanometer Struct. 2003, 21, 1240–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metev, S.M.; Vejko, V.P. Laser Assisted Microtechnology; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, H.; Odom, T.W.; Whitesides, G.M. Generation of chrome masks with micrometer-scale features using microlens lithography. Adv. Mater. 2002, 14, 1213–1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, T.; Okazaki, S. Pushing the limits of lithography. Nature 2000, 406, 1027–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maluf, N.; Williams, K. Introduction to microelectromechanical systems engineering; Artech House, Inc.: Norwood, MA, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Herold, K.E.; Rasooly, A. Lab on a Chip Technology, Volume 1; Caister Academic Press: Norfolk, UK, 2009. [Google Scholar]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Doan, N.M.; Qiang, L.; Li, Z.; Vaddiraju, S.; Bishop, G.W.; Rusling, J.F.; Papadimitrakopoulos, F. Low-Cost Photolithographic Fabrication of Nanowires and Microfilters for Advanced Bioassay Devices. Sensors 2015, 15, 6091-6104. https://doi.org/10.3390/s150306091
Doan NM, Qiang L, Li Z, Vaddiraju S, Bishop GW, Rusling JF, Papadimitrakopoulos F. Low-Cost Photolithographic Fabrication of Nanowires and Microfilters for Advanced Bioassay Devices. Sensors. 2015; 15(3):6091-6104. https://doi.org/10.3390/s150306091
Chicago/Turabian StyleDoan, Nhi M., Liangliang Qiang, Zhe Li, Santhisagar Vaddiraju, Gregory W. Bishop, James F. Rusling, and Fotios Papadimitrakopoulos. 2015. "Low-Cost Photolithographic Fabrication of Nanowires and Microfilters for Advanced Bioassay Devices" Sensors 15, no. 3: 6091-6104. https://doi.org/10.3390/s150306091
APA StyleDoan, N. M., Qiang, L., Li, Z., Vaddiraju, S., Bishop, G. W., Rusling, J. F., & Papadimitrakopoulos, F. (2015). Low-Cost Photolithographic Fabrication of Nanowires and Microfilters for Advanced Bioassay Devices. Sensors, 15(3), 6091-6104. https://doi.org/10.3390/s150306091