Development of Ionic Liquid Modified Disposable Graphite Electrodes for Label-Free Electrochemical Detection of DNA Hybridization Related to Microcystis spp.
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Apparatus
2.2. Chemicals
2.3. Procedure
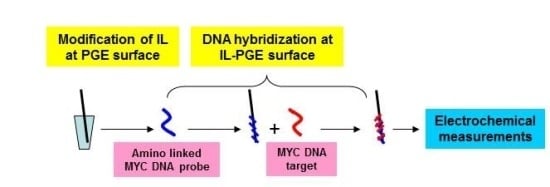
2.3.1. Preparation of IL Modified PGE
2.3.2. Microscopic Characterization of Unmodified and IL Modified PGE by Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
2.3.3. Electrochemical Monitoring of DNA Hybridization
2.3.4. Voltammetric Measurements
2.3.5. Impedimetric Measurements
3. Results and Discussion






4. Conclusions
Supplementary Files
Supplementary File 1Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, J.; Kawde, A.N. Pencil-based renewable biosensor for label-free electrochemical detection of DNA hybridization. Anal. Chim. Acta 2001, 431, 219–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palecek, E.; Bartosik, M. Electrochemistry of nucleic acids. Chem. Rev. 2012, 112, 3427–3481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, C.-H.; Willner, B.; Willner, I. DNA nanotechnology: From sensing and DNA machines to drug-delivery systems. ACS Nano 2013, 7, 8320–8332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ping, J.; Wang, Y.; Fan, K.; Wu, J.; Ying, Y. Direct electrochemical reduction of graphene oxide on ionic liquid doped screen-printed electrode and its electrochemical biosensing applications. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2011, 28, 204–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Espinoza-Castañeda, M.; de la Escosura-Munñiz, A.; Merkoçi, A. Nanoparticle/nanochannels-based electrochemical biosensors. In Electrospinning for High Performance Sensors; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Erdem, A. Nanomaterial based electrochemical DNA sensing strategies. Talanta 2007, 74, 318–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erdem, A.; Muti, M.; Karadeniz, H.; Congur, G.; Canavar, E. Electrochemical biosensors for screening of toxins and pathogens. In Portable Chemical Sensors; Nikolelis, D., Ed.; Springer Netherlands: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Congur, G.; Erdem, A. Micro and nanopatterning for bacteria and virus-based biosensing applications. In Portable Biosensing of Food Toxicants and Environmental Pollutants; Nikolelis, D.P., Varzakas, T., Erdem, A., Nikoleli, G.-P., Eds.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.K.; Zhou, G.Y.; Chang, C.J.; Cheng, C.C. Label-free detection of DNA hybridization using nanopillar arrays based optical biosensor. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2014, 194, 10–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Touahir, L.; Galopin, E.; Boukherroub, R.; Gouget-Laemmel, A.C.; Chazalviel, J.N.; Ozanam, F.; Szunerits, S. Localized surface plasmon-enhanced fluorescence spectroscopy for highly-sensitive real-time detection of DNA hybridization. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2010, 25, 2579–2585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zerrouki, C.; Fourati, N.; Lucas, R.; Vergnaud, J.; Fougnion, J.M.; Zerrouki, Z.; Pernelle, C. Biological investigation using a shear horizontal surface acoustic wave sensor: Small “Click generated” DNA hybridization detection. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2010, 26, 1759–1762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, D.; Chen, G.; Wang, J.; Tang, W.; Pan, W.; Li, N.; Liu, F. A reusable quartz crystal microbalance biosensor for highly specific detection of single-base DNA mutation. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2013, 48, 276–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erdem, A.; Muti, M.; Mese, F.; Eksin, E. Chitosan-ionic liquid modified single-use sensor for electrochemical monitoring of sequence-selective DNA hybridization. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2014, 114, 261–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erdem, A.; Karadeniz, H.; Canavar, P.E.; Congur, G. Single-use sensor platforms based on carbon nanotubes for electrochemical detection of DNA hybridization related to Microcystis spp. Electroanalysis 2012, 24, 502–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismaiel, A.A.; Aroua, M.K.; Yusoff, R. A new electrochemical sensor based on task-specific ionic liquids-modified palm shell activated carbon for the determination of mercury in water samples. Sensors 2014, 14, 13102–13113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahman, M.M.; Li, X.B.; Lopa, N.S.; Ahn, S.J.; Lee, J.J. Electrochemical DNA hybridization sensors based on conducting polymers. Sensors 2015, 15, 3801–3829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Ma, Y.; Chen, D.; Ma, M.; Li, C. Electrochemical fabrication of polymerized imidazole-based ionic liquid bearing pyrrole moiety for sensitive determination of hexestrol in chicken meat. Food Chem. 2015, 180, 142–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kerman, K.; Kobayashi, M.; Tamiya, E. Recent trends in electrochemical DNA biosensor technology. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2004, 15, R1–R11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teles, F.R.R.; Fonseca, L.P. Applications of polymers for biomolecule immobilization in electrochemical biosensors. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2008, 28, 1530–1543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monošík, R.; Šturdík, E. Biosensors—Classification, characterization and new trends. Acta Chim. 2012, 5, 109–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rumbau, V.; Marcilla, R.; Ochoteco, E.; Pomposo, J.A.; Mecerreyes, D. Ionic liquid immobilized enzyme for biocatalytic synthesis of conducting polyaniline. Macromolecules 2006, 39, 8547–8549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, P.; Lin, Y.; Xiang, L.; Su, L.; Zhang, J.; Mao, L. Molecular films of water-miscible ionic liquids formed onto glassy carbon electrode: characterization and electrochemical applications. Langmuir 2005, 21, 9000–9006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, D.; Ivaska, A. Applications of ionic liquids in electrochemical sensors. Anal. Chim. Acta 2008, 607, 126–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, Z.L.; Li, Z.J.; Sun, X.L.; Fang, Y.J.; Liu, J.K. Synergistic contributions of fullerene, ferrocene, chitosan and ionic liquid towards improved performance for a glucose sensor. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2010, 25, 1434–1438. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Chu, Z.; Shi, S.; Jin, W. Amperometric glucose biosensor based on direct assembly of Prussian blue film with ionic liquid-chitosan matrix assisted enzyme immobilization. Sens. Actuator B Chem. 2013, 176, 978–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, F.; Liu, L.; Wu, Q.; Lin, X. One-step construction of biosensor based on chitosan-ionic liquid-horseradish peroxidase biocomposite formed by electrodeposition. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2008, 24, 29–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eksin, E.; Muti, M.; Erdem, A. Chitosan/Ionic liquid composite electrode for electrochemical monitoring of the surface-confined interaction between mitomycin C and DNA. Electroanalysis 2013, 25, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.; Duan, Y.; Li, Y.; Gao, H.; Jiao, K. Electrochemical behaviors of guanosine on carbon ionic liquid electrode and its determination. Talanta 2009, 78, 695–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; He, P.; Li, Z.; Sun, C.; Shi, L.; Liu, Y.; Zhu, G.; Li, J. An ionic liquid-type carbon paste electrode and its polyoxometalate-modified properties. Electrochem. Commun. 2005, 7, 1357–1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, L. An electrochemical fungicide pyrimethanil sensor based on carbon nanotubes/ionic-liquid construction modified electrode. Food Chem. 2015, 187, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- She, Y.; Tang, Y.; Liu, H.; He, P. Electrochemical determination of hydroquinone using hydrophobic ionic liquid-type carbon paste electrodes. Chem. Cent. J. 2010, 4, 17–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, R.; Leng, C.; Zhang, S. A chronocoulometric DNA sensor based on screen-printed electrode doped with ionic liquid and polyaniline nanotubes. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2010, 25, 2089–2094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, W.; Gao, R.F.; Jiao, K. Electrochemistry and electrocatalysis of hemoglobin in nafion/nano-CaCO3 film on a new ionic liquid BPPF6 modified carbon paste electrode. J. Phys. Chem. B 2007, 111, 4560–4567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Palecek, E.; Nielsen, P.E.; Rivas, G.; Cai, X.; Shiraishi, H.; Dontha, N.; Luo, D.; Farias, P.A.M. Peptide nucleic acid probes for sequence-specific DNA biosensors. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1996, 118, 7667–7670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos, A.; Vasconcelos, V. Molecular mechanisms of microcystin toxicity in animal cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2010, 11, 268–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erdem, A.; Meric, B.; Kerman, K.; Ozkan, D.; Kara, P.; Ozsoz, M. DNA biosensor for Microcystis spp. sequence detection by using methylene blue and ruthenium complex as electrochemical hybridization labels. Turk. J. Chem. 2002, 26, 851–862. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, S.; Srivastava, A.; Oh, H.M.; Ahn, C.Y.; Choi, G.G.; Asthana, R.J. Recent trends in development of biosensors for detection of microcystin. Toxicon 2012, 60, 878–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McElhiney, J.; Lawton, L.A. Detection of the cyanobacterial hepatotoxins microcystins. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2005, 203, 219–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, F.; Erdem, A.; Merıc, B.; Kerman, K.; Ozsoz, M.; Sadık, O.A. Electrochemical DNA biosensor for the detection of specific gene related to microcystis species. Electrochem. Commun. 2001, 3, 224–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, P.; Shao, Y.; Chen, J.; He, Y.; Zhang, L. A sensitive electrochemical DNA biosensor for Microcystis spp. sequence detection based on an Ag@Au NP composite film. Anal. Methods 2015, 7, 2993–2999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herranz, S.; Marazuela, M.D.; Moreno-Bondi, M.C. Automated portable array biosensor for multisample microcystin analysis in freshwater samples. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2012, 33, 50–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janek, R.P.; Fawcett, W.R. Impedance spectroscopy of self-assembled monolayers on Au(111): Sodium ferrocyanide charge transfer at modified electrodes. Langmuir 1998, 14, 3011–3018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erdem, A.; Congur, G. Impedimetric detection of in situ interaction between anti-cancer drug bleomycin and DNA. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2013, 61, 295–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, J.N.; Miller, J.C. Statistics and Chemometrics for Analytical Chemistry; Pearson Education: Essex, UK, 2005. [Google Scholar]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sengiz, C.; Congur, G.; Erdem, A. Development of Ionic Liquid Modified Disposable Graphite Electrodes for Label-Free Electrochemical Detection of DNA Hybridization Related to Microcystis spp. Sensors 2015, 15, 22737-22749. https://doi.org/10.3390/s150922737
Sengiz C, Congur G, Erdem A. Development of Ionic Liquid Modified Disposable Graphite Electrodes for Label-Free Electrochemical Detection of DNA Hybridization Related to Microcystis spp. Sensors. 2015; 15(9):22737-22749. https://doi.org/10.3390/s150922737
Chicago/Turabian StyleSengiz, Ceren, Gulsah Congur, and Arzum Erdem. 2015. "Development of Ionic Liquid Modified Disposable Graphite Electrodes for Label-Free Electrochemical Detection of DNA Hybridization Related to Microcystis spp." Sensors 15, no. 9: 22737-22749. https://doi.org/10.3390/s150922737
APA StyleSengiz, C., Congur, G., & Erdem, A. (2015). Development of Ionic Liquid Modified Disposable Graphite Electrodes for Label-Free Electrochemical Detection of DNA Hybridization Related to Microcystis spp. Sensors, 15(9), 22737-22749. https://doi.org/10.3390/s150922737