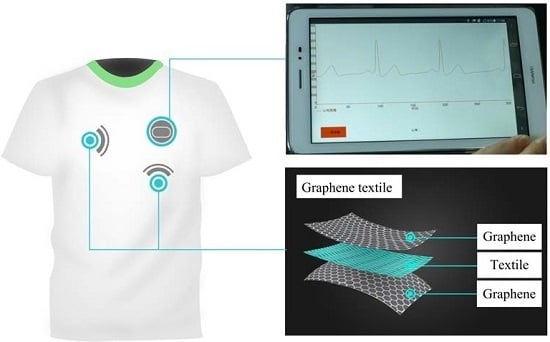
Flexible Graphene Electrodes for Prolonged Dynamic ECG Monitoring
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Wireless ECG Monitoring System
2.2. Construction of the Graphene Electrode
2.3. Characterization of Structural and Electrical Properties
2.4. Motion Artifacts Evaluation and Long-Term ECG Measurement
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ECG | electrocardiography |
| SEM | scanning electron microscope |
| SNR | signal-to-noise ratio |
| CNT | carbon nanotube |
| MWCNTs | multiwall carbon nanotube arrays |
| PDMS | polydimethylsiloxane |
| PET | polyethylene terephthalate |
| CVD | chemical vapor deposition |
| EMG | electromyography |
| EEG | electroencephalography |
References
- Moran, A.; Degennaro, V.; Ferrante, D.; Coxson, P.G.; Palmas, W.; Mejia, R.; Perez-Stable, E.J.; Goldman, L. Coronary heart disease and stroke attributable to major risk factors is similar in argentina and the united states: The coronary heart disease policy model. Int. J. Cardiol. 2011, 150, 332–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Domanski, M.J.; Fuster, V.; Diaz-Mitoma, F.; Grundy, S.; Lloyd-Jones, D.; Mamdani, M.; Roberts, R.; Thorpe, K.; Hall, J.; Udell, J.A. Next steps in primary prevention of coronary heart disease: Rationale for and design of the ECAD trial. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2015, 66, 1828–1836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, S.; Zhu, Y. Nanomaterial-enabled dry electrodes for electrophysiological sensing: A review. J. Miner. Met. Mater. Soc. 2016, 68, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.T.; Chang, K.C.; Lin, C.L.; Chiang, C.C.; Lu, S.W.; Chang, S.S.; Lin, B.S.; Liang, H.Y.; Chen, R.J.; Lee, Y.T.; et al. An intelligent telecardiology system using a wearable and wireless ECG to detect atrial fibrillation. IEEE Trans. Inf. Technol. Biomed. 2010, 14, 726–733. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mathias, D.N.; Kim, S.I.; Park, J.S.; Joung, Y.H.; Choi, W.S. Electrode characteristics of non-contact electrocardiographic measurement. Trans. Electr. Electron. Mater. 2015, 16, 42–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, Y.M.; Cauwenberghs, G. Micropower non-contact EEG electrode with active common-mode noise suppression and input capacitance cancellation. In Proceedings of the 2009 Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, Minneapolis, MN, USA, 3–6 September 2009; pp. 4218–4221.
- Fung, E.; Järvelin, M.R.; Doshi, R.N.; Shinbane, J.S.; Carlson, S.K.; Grazette, L.P.; Chang, P.M.; Sangha, R.S.; Huikuri, H.V.; Peters, N.S. Electrocardiographic patch devices and contemporary wireless cardiac monitoring. Front. Physiol. 2015, 6, 149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, D.; Cheng, T.K.; Xie, K.; Lam, R.H. Microengineered conductive elastomeric electrodes for long-term electrophysiological measurements with consistent impedance under stretch. Sensors 2015, 15, 26906–26920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baek, J.Y.; An, L.H.; Choi, J.M. Flexible polymeric dry electrodes for the long-term monitoring of ECG. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2008, 143, 423–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, H.C.; Moon, J.H.; Baek, D.H.; Lee, J.H.; Choi, Y.Y.; Hong, J.S.; Lee, S.H. CNT/PDMS composite flexible dry electrodes for long-term ECG monitoring. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2012, 59, 1472–1479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weder, M.; Hegemann, D.; Amberg, M.; Hess, M.; Boesel, L.F.; Abächerli, R.; Meyer, V.R.; Rossi, R.M. Embroidered electrode with silver/titanium coating for long-term ECG monitoring. Sensors 2015, 15, 1750–1759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruffini, G.; Dunne, S.; Fuentemilla, L.; Grau, C.; Farres, E.; Marco-Pallarés, J.; Watts, P.C.P.; Silva, S.R.P. First human trials of a dry electrophysiology sensor using a carbon nanotube array interface. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2008, 144, 275–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thap, T.; Yoon, K.H.; Lee, J. Graphite based electrode for ECG monitoring: Evaluation under freshwater and saltwater conditions. Sensors 2016, 542, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, L.M.; Tay, F.E.H.; Guo, D.G.; Xu, L.; Yap, K.L. A microfabricated electrode with hollow microneedles for ECG measurement. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2009, 151, 17–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.S.; Heo, J.; Lee, W.K.; Lim, Y.G.; Kim, Y.H.; Park, K.S. Flexible capacitive electrodes for minimizing motion artifacts in ambulatory electrocardiograms. Sensors 2014, 14, 14732–14743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvo, P.; Raedt, R.; Carrette, E.; Schaubroeck, D.; Vanfleteren, J.; Cardon, L. A 3d printed dry electrode for ECG/EEG recording. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2012, 174, 96–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Wang, R.; Sun, J.; Gao, L. A stretchable and highly sensitive graphene-based fiber for sensing tensile strain, bending, and torsion. Adv. Mater. 2015, 27, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samad, Y.A.; Li, Y.; Alhassan, S.M.; Liao, K. Non-destroyable graphene cladding on a range of textile and other fibers and fiber mats. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 16935–16938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.H.; Lin, C.T.; Hsu, W.L.; Chang, Y.C. A flexible hydrophilic-modified graphene microprobe for neural and cardiac recording. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 2013, 9, 600–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skrzetuska, E.; Puchalski, M.; Krucinska, I. Chemically driven printed textile sensors based on graphene and carbon nanotubes. Sensors 2014, 14, 16816–16828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.H.; Nam, Y.W.; Jung, H.C.; Baek, D.H.; Lee, S.H.; Hong, J.S. Shear induced CNT/PDMS conducting thin film for electrode cardiogram (ECG) electrode. BioChip J. 2012, 6, 91–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yapici, M.K.; Alkhidir, T.; Samad, Y.A.; Liao, K. Graphene-clad textile electrodes for electrocardiogram monitoring. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2015, 221, 1469–1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.; Park, J.; Sohn, J.; Cho, D.; Jeon, S. Bioinspired, highly stretchable, and conductive dry adhesives based on 1D-2D hybrid carbon nanocomposites for all-in-one ECG electrodes. ACS Nano 2016, 10, 4770–4778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Celik, N.; Manivannan, N.; Strudwicuk, A.; Balachandran, W. Graphene-enabled electrodes for electrocardiogram monitoring. Nanomaterials 2016, 6, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, K.; Shao, Z.; Xue, W.; Xi, W.; Jia, L.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, W.; Wang, F. Cellulose nanofibers/reduced graphene oxide flexible transparent conductive paper. Carbohydr. Polym. 2013, 97, 243–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tung, V.C.; Allen, M.J.; Yang, Y.; Kaner, R.B. High-throughput solution processing of large-scale graphene. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2009, 4, 25–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, H.; Hu, C.; Zhao, Y.; Qu, L. Graphene fiber: A new material platform for unique applications. NPG Asia Mater. 2014, 6, e113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, C.N.R.; Biswas, K.; Subrahmanyam, K.S.; Govindaraj, A. Graphene, the new nanocarbon. J. Mater. Chem. 2009, 19, 2457–2469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Englert, J.M.; Dotzer, C.; Yang, G.A.; Schmid, M.; Papp, C.; Gottfried, J.M.; Steinruck, H.P.; Spiecker, E.; Hauke, F.; Hirsch, A. Covalent bulk functionalization of graphene. Nat. Chem. 2011, 3, 279–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zan, X.; Zheng, F.; Jin, W.; Fei, X.; Huo, F.; Duan, H. Freestanding graphene paper decorated with 2d-assembly of Au@Pt nanoparticles as flexible biosensors to monitor live cell secretion of nitric oxide. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2013, 49, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chun, S.; Jung, H.; Choi, Y.; Bae, G.; Kil, J.P.; Park, W. A tactile sensor using a graphene film formed by the reduced graphene oxide flakes and its detection of surface morphology. Carbon 2015, 94, 982–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.E.; Ghatkesar, M.K.; Zhang, C.; Janssen, G.C.A.M. Graphene based piezoresistive pressure sensor. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2013, 102, 161904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, M.; Huang, Y.; Wang, W.; Li, R.; Liu, P.; Liu, C.; Zhang, Y. Temperature-dependent electrical properties of graphene nanoplatelets film dropped on flexible substrates. J. Mater. Res. 2014, 29, 1288–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]










| Motion State | Graphene Textile | Ag–AgCl | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P–P | Heart Rate | SNR | SD | P–P | Heart Rate | SNR | SD | |
| Rest | 1750 | 66 | 31.6 | 116.8 | 1790 | 66 | 31.0 | 104.2 |
| Walking | 1920 | 70 | 31.2 | 243.5 | 2010 | 71 | 30.1 | 233.6 |
| Swimming arms | 1900 | 68 | 29.5 | 166.3 | 1910 | 66 | 28.7 | 164.4 |
| Exercised | 1875 | 150 | 28.3 | 267.8 | 1834 | 147 | 28.5 | 276.3 |
| Day 1 | Day 2 | Day 3 | Day 4 | Day 5 | Day 6 | Day 7 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P–P | 18.3 | 18.0 | 18.2 | 21.3 | 26.7 | 25.7 | 30.1 |
| SNR | 24.1 | 28.6 | 33.7 | 29.4 | 32.6 | 27.5 | 29.2 |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lou, C.; Li, R.; Li, Z.; Liang, T.; Wei, Z.; Run, M.; Yan, X.; Liu, X. Flexible Graphene Electrodes for Prolonged Dynamic ECG Monitoring. Sensors 2016, 16, 1833. https://doi.org/10.3390/s16111833
Lou C, Li R, Li Z, Liang T, Wei Z, Run M, Yan X, Liu X. Flexible Graphene Electrodes for Prolonged Dynamic ECG Monitoring. Sensors. 2016; 16(11):1833. https://doi.org/10.3390/s16111833
Chicago/Turabian StyleLou, Cunguang, Ruikai Li, Zhaopeng Li, Tie Liang, Zihui Wei, Mingtao Run, Xiaobing Yan, and Xiuling Liu. 2016. "Flexible Graphene Electrodes for Prolonged Dynamic ECG Monitoring" Sensors 16, no. 11: 1833. https://doi.org/10.3390/s16111833
APA StyleLou, C., Li, R., Li, Z., Liang, T., Wei, Z., Run, M., Yan, X., & Liu, X. (2016). Flexible Graphene Electrodes for Prolonged Dynamic ECG Monitoring. Sensors, 16(11), 1833. https://doi.org/10.3390/s16111833