Contact Pressure Level Indication Using Stepped Output Tactile Sensors
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Stepped Output Tactile Sensor
2.1. Concepts and Operating Mechanism
2.2. Fabrication Process
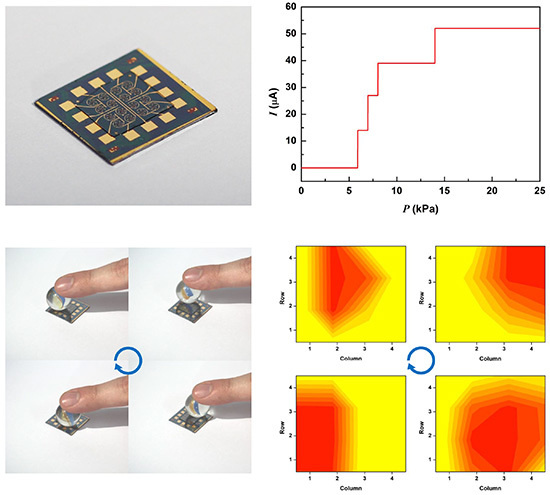
2.3. Pressure Detection Characteristics
2.4. Repeatability Test & Detection of Vibration and Grating
3. SOTS Array
3.1. Concept and Fabrication
3.2. Operating Characteristics
3.3. Read-Out Circuit
3.4. Pressure Mapping Capabilities
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Raspopovic, S.; Capogrosso, M.; Petrini, F.M.; Bonizzato, M.; Rigosa, J.; Di Pino, G.; Carpaneto, J.; Controzzi, M.; Boretius, T.; Fernandez, E.; et al. Restoring natural sensory feedback in real-time bidirectional hand prostheses. Sci. Transl. Med. 2014, 6, 222ra19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.; Lee, M.; Shim, H.J.; Ghaffari, R.; Cho, H.R.; Son, D.; Jung, Y.H.; Soh, M.; Choi, C.; Jung, S.; et al. Stretchable silicon nanoribbon electronics for skin prosthesis. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Odhner, L.U.; Jentoft, L.P.; Claffee, M.R.; Corson, N.; Tenzer, Y.; Ma, R.R.; Buehler, M.; Kohout, R.; Howe, R.D.; Dollar, A.M. A compliant, underactuated hand for robust manipulation. Int. J. Robot. Res. 2014, 33, 736–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westebring-van der Putten, E.P.; Goossens, R.H.M.; Jakimowicz, J.J.; Dankelman, J. Haptics in minimally invasive surgery-A review. Minim. Invasive Ther. Allied Technol. 2008, 17, 3–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Myles, K.; Binseel, M.S. The Tactile Modality: A Review of Tactile Sensitivity and Human Tactile Interfaces; U.S. Army Research Laboratory: Aberdeen, MA, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Bruce, M.F.; Sinclair, D.C. The relationship between tactile thresholds and histology in the human finger. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 1980, 43, 235–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johansson, L.; Kjellberg, A.; Kilbom, A.; Hagg, G.M. Perception of surface pressure applied to the hand. Ergonomics 2010, 42, 1274–1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brennum, J.; Kjeldsen, M.; Kai Jensen, K.; Jensen, T.S. Measurements of human pressure-pain thresholds on fingers and toes. Pain 1989, 38, 211–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallbo, A.B.; Johansson, R.S. Properties of cutaneous mechanoreceptors in the human hand related to touch sensation. Hum. Neurobiol. 1984, 3, 3–14. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Weber, E.H. E.H.Weber on the Tactile Senses, 2nd ed.; Ross, H.E., Murray, D.J., Eds.; Erlbaum (UK) Taylor & Francis: London, UK, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Gu, Y.; Xiong, Z.; Cui, Z.; Zhang, T. Silk-molded flexible, ultrasensitive, and highly stable electronic skin for monitoring human physiological signals. Adv. Mater. 2014, 26, 1336–1342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pang, C.; Lee, G.-Y.; Kim, T.; Kim, S.M.; Kim, H.N.; Ahn, S.-H.; Suh, K.Y. A flexible and highly sensitive strain-gauge sensor using reversible interlocking of nanofibers. Nat. Mater. 2012, 11, 795–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, B.; Niu, Z.; Wang, H.; Leow, W.R.; Wang, H.; Li, Y.; Zheng, L.; Wei, J.; Huo, F.; Chen, X. Microstructured graphene arrays for highly sensitive flexible tactile sensors. Small 2014, 10, 3625–3631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, B.; Gong, S.; Ma, Z.; Yap, L.W.; Cheng, W. Mimosa-inspired design of a flexible pressure sensor with touch sensitivity. Small 2015, 11, 1886–1891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Viry, L.; Levi, A.; Totaro, M.; Mondini, A.; Mattoli, V.; Mazzolai, B.; Beccai, L. Flexible three-axial force sensor for soft and highly sensitive artificial touch. Adv. Mater. 2014, 26, 2659–2664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mannsfeld, S.C.B.; Tee, B.C.-K.; Stoltenberg, R.M.; Chen, C.V.H-H.; Barman, S.; Muir, B.V.O.; Sokolov, A.N.; Reese, C.; Bao, Z. Highly sensitive flexible pressure sensors with microstructured rubber dielectric layers. Nat. Mater. 2010, 9, 859–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.; Kim, H.; Vosgueritchian, M.; Cheon, S.; Kim, H.; Koo, J.H.; Kim, T.R.; Lee, S.; Schwartz, G.; Chang, H.; et al. Stretchable energy-harvesting tactile electronic skin capable of differentiating multiple mechanical stimuli modes. Adv. Mater. 2014, 26, 7324–7332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.Y.; Park, S.; Park, H.W.; Park, D.H.; Jeong, Y.; Kim, D.H. Highly sensitive and multimodal all-carbon skin sensors capable of simultaneously detecting tactile and biological stimuli. Adv. Mater. 2015, 27, 4178–4185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.S.; Shin, K.-Y.; Cheong, O.J.; Kim, J.H.; Jang, J. Highly sensitive and multifunctional tactile sensor using free-standing ZnO/PVDF thin film with graphene electrodes for pressure and temperature monitoring. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 7887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, D.; Pikhitsa1, P.V.; Choi, Y.W.; Lee, C.; Shin, S.S.; Piao, L.; Park, B.; Suh, K.-Y.; Kim, T.; Choi, M. Ultrasensitive mechanical crack-based sensor inspired by the spider sensory system. Nature 2014, 516, 222–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, L.; Yang, T.; Li., X.; Zang, X.; Zhu, M.; Wang, K.; Wu, D.; Zhu, H. Wearable and highly sensitive graphene strain sensors for human motion monitoring. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2014, 24, 4666–4670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Jiu, J.; Nogi, M.; Sugahara, T.; Nagao, S.; Koga, H.; He, P.; Suganuma, K. A highly sensitive and flexible pressure sensor with electrodes and elastomeric interlayer containing silver nanowires. Nanoscale 2015, 7, 2926–2932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jariwala, D.; Sangwan, V.K.; Lauhon, L.J.; Marks, T.J.; Hersma, M.C. Carbon nanomaterials for electronics, optoelectronics, photovoltaics, and sensing. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2013, 42, 2824–2860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.-M.; Kim, J.-H.; Ahn, J.-H. Graphene as a flexible electronic material: Mechanical limitations by defect formation and efforts to overcome. Mater. Today 2015, 18, 336–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terzic, E.; Terzic, J.; Nagarajah, R.; Alamgir, M. A Neural Network Approach to Fluid Quantity Measurement in Dynamic Environments; Springer-Verlag: London, UK, 2012; pp. 11–37. [Google Scholar]
- Yousefa, H.; Boukallel, M.; Althoefer, K. Tactile sensing for dexterous in-hand manipulation in robotics–A review. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2011, 167, 171–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, E.; Sul, O.; Hwang, S.; Cho, J.; Chun, H.; Kim, H.; Lee, S.-B. Spatially digitized tactile pressure sensors with tunable sensitivity and sensing range. Nanotechnology 2014, 25, 425504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scheibert, J.; Leurent, S.; Prevost, A.; Debrégeas, G. The role of fingerprints in the coding of tactile information probed with a biomimetic sensor. Science 2009, 323, 1503–1506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oddo, C.M.; Beccai, L.; Wessberg, J.; Wasling, H.B.; Mattioli, F.; Carrozza, M.C. Roughness encoding in human and biomimetic artificial touch: Spatiotemporal frequency modulation and structural. Sensors 2011, 11, 5596–5615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Timoshenko, S.; Woinowsky-Krieger, S. Theory of Plates and Shells, 2nd ed.; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1959; pp. 51–78. [Google Scholar]
- Johnson, K.O. The roles and functions of cutaneous mechanoreceptors. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 2001, 11, 455–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.-K.; Chang, S.-I.; Yoon, E. A flexible polymer tactile sensor: Fabrication and modular expandability for large area deployment. IEEE J. Microelectromech. Syst. 2006, 15, 1681–1686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, P.; Rajamani, R.; Erdman, A.G. Flexible tactile sensor for tissue elasticity measurements. IEEE J. Microelectromech. Syst. 2009, 18, 1226–1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]












© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons by Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Choi, E.; Sul, O.; Kim, J.; Kim, K.; Kim, J.-S.; Kwon, D.-Y.; Choi, B.-D.; Lee, S.-B. Contact Pressure Level Indication Using Stepped Output Tactile Sensors. Sensors 2016, 16, 511. https://doi.org/10.3390/s16040511
Choi E, Sul O, Kim J, Kim K, Kim J-S, Kwon D-Y, Choi B-D, Lee S-B. Contact Pressure Level Indication Using Stepped Output Tactile Sensors. Sensors. 2016; 16(4):511. https://doi.org/10.3390/s16040511
Chicago/Turabian StyleChoi, Eunsuk, Onejae Sul, Juyoung Kim, Kyumin Kim, Jong-Seok Kim, Dae-Yong Kwon, Byong-Deok Choi, and Seung-Beck Lee. 2016. "Contact Pressure Level Indication Using Stepped Output Tactile Sensors" Sensors 16, no. 4: 511. https://doi.org/10.3390/s16040511
APA StyleChoi, E., Sul, O., Kim, J., Kim, K., Kim, J. -S., Kwon, D. -Y., Choi, B. -D., & Lee, S. -B. (2016). Contact Pressure Level Indication Using Stepped Output Tactile Sensors. Sensors, 16(4), 511. https://doi.org/10.3390/s16040511