Label-Free Fluorescence Assay of S1 Nuclease and Hydroxyl Radicals Based on Water-Soluble Conjugated Polymers and WS2 Nanosheets
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Measurements
2.2. Procedure
2.2.1. Enzyme Assay
2.2.2. Assay for S1 Nuclease as a Function of Incubating Time
2.2.3. Inhibition Assay by ATP
2.2.4. Specificity Assay of S1 Nuclease
2.2.5. ·OH assay and Inhibition Assay by Thiourea
3. Results and Discussion
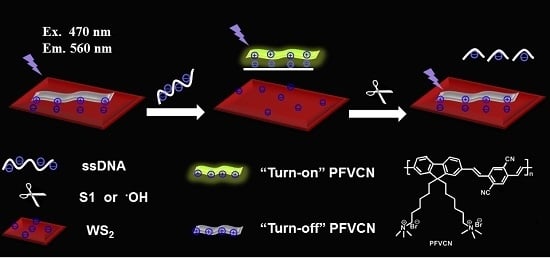
3.1. Array Mechanism
3.2. Optimization of the Experimental Conditions
3.3. Sensing of S1 Nuclease
3.4. Sensing of Hydroxyl Radicals
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, J.J. Using Molecular Beacons as a Sensitive Fluorescence Assay for Enzymatic Cleavage of Single-Stranded DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray, P.C.; Fortner, A.; Darbha, G.K. Gold Nanoparticle Based Fret Assay for the Detection of DNA Cleavage. J. Phys. Chem. B 2006, 110, 20745–20748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J. From DNA Biosensors to Gene Chips. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000, 28, 3011–3016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Butour, J.L.; Mazard, A.M.; Vieussens, C.; Johnson, N.P. Kinetic Studies of the Hydrolysis of Platinum-DNA Complexes by Nuclease S1. Chem. Biol. Interact. 1990, 73, 195–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, R.; Li, B.X.; Zhang, Y.F.; Zhang, Z.N. Naked-Eye Sensitive Detection of Nuclease Activity Using Positively-Charged Gold Nanoparticles as Colorimetric Probes. Chem. Commun. 2011, 47, 12301–12303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, J.W.; Qin, W. Potentiometric Sensing of Nuclease Activities and Oxidative Damage of Single-Stranded DNA Using a Polycation-Sensitive Membrane Electrode. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2013, 47, 559–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, Y.; Feng, F.; He, F.; Wang, S.; Li, Y.; Zhu, D. Direct Visualization of Enzymatic Cleavage and Oxidative Damage by Hydroxyl Radicals of Single-Stranded DNA with a Cationic Polythiophene Derivative. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 14972–14976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.; Pu, F.; Ren, J.; Qu, X. DNA-Templated Ensemble for Label-Free and Real-Time Fluorescence Turn-on Detection of Enzymatic/Oxidative Cleavage of Single-Stranded DNA. Chem. Commun. 2011, 47, 8133–8135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, Q.; Nie, Z.; Guo, M.; Zhong, C.-J.; Lin, B.; Li, W.; Yao, S. Simple and Rapid Colorimetric Sensing of Enzymatic Cleavage and Oxidative Damage of Single-Stranded DNA with Unmodified Gold Nanoparticles as Indicator. Chem. Commun. 2009, 929–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Z.; Zhu, J.; Zhang, L.; Du, Y.; Dong, S.; Wang, E. G-Quadruplex-Based Fluorescent Assay of S1 Nuclease Activity and K. Anal. Chem. 2013, 85, 2431–2435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cleveland, J.L.; Kastan, M.B. Cancer: A Radical Approach to Treatment. Nature 2000, 407, 309–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- White, B.; Smyth, M.R.; Stuart, J.D.; Rusling, J.F. Oscillating Formation of 8-Oxoguanine During DNA Oxidation. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2003, 125, 6604–6605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frenette, M.; Scaiano, J.C. Evidence for Hydroxyl Radical Generation during Lipid (Linoleate) Peroxidation. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 9634–9635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, Y.Q.; Sui, D.D.; Zhou, W.J.; Lu, C. Highly Selective Chemiluminescence Detection of Hydroxyl Radical Via Increased Pi-Electron Densities of Rhodamine B on Montmorillonite Matrix. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2016, 225, 600–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ames, B.N. Dietary Carcinogens and Anticarcinogens. Oxygen Radicals and Degenerative Diseases. Science 1983, 221, 1256–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olinski, R.; Gackowski, D.; Foksinski, M.; Rozalski, R.; Roszkowski, K.; Jaruga, P. Oxidative DNA Damage: Assessment of the Role in Carcinogenesis, Atherosclerosis, and Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2002, 33, 192–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dizdaroglu, M.; Jaruga, P.; Birincioglu, M.; Rodriguez, H. Free Radical-Induced Damage to DNA: Mechanisms and Measurement. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2002, 32, 1102–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aruoma, O.I. Free Radicals, Oxidative Stress, and Antioxidants in Human Health and Disease. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 1998, 75, 199–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Zhao, H.; Lin, Y.; Zhu, N.; Ma, Y.; Mao, L. Colorimetric Detection of Glucose in Rat Brain Using Gold Nanoparticles. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2010, 49, 4800–4804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, W.; Xue, X.; Li, T.; Zeng, H.; Liu, X. Ultrasensitive and Selective Colorimetric DNA Detection by Nicking Endonuclease Assisted Nanoparticle Amplification. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2009, 48, 6849–6852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biggins, J.B.; Prudent, J.R.; Marshall, D.J.; Ruppen, M.; Thorson, J.S. A Continuous Assay for DNA Cleavage: The Application of “Break Lights” to Enediynes, Iron-Dependent Agents, and Nucleases. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 13537–13542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, W.; Ali, M.M.; Aguirre, S.D.; Brook, M.A.; Li, Y. Paper-Based Bioassays Using Gold Nanoparticle Colorimetric Probes. Anal. Chem. 2008, 80, 8431–8437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.H.; Kalantar-Zadeh, K.; Kis, A.; Coleman, J.N.; Strano, M.S. Electronics and Optoelectronics of Two-Dimensional Transition Metal Dichalcogenides. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2012, 7, 699–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, M.; Liang, T.; Shi, M.; Chen, H. Graphene-Like Two-Dimensional Materials. Chem. Rev. 2013, 113, 3766–3798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chhowalla, M.; Shin, H.S.; Eda, G.; Li, L.J.; Loh, K.P.; Zhang, H. The Chemistry of Two-Dimensional Layered Transition Metal Dichalcogenide Nanosheets. Nat. Chem. 2013, 5, 263–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, W.; Ribeiro, R.M.; Toh, M.; Carvalho, A.; Kloc, C.; Castro Neto, A.H.; Eda, G. Origin of Indirect Optical Transitions in Few-Layer MoS2, WS2, and WSe2. Nano Lett. 2013, 13, 5627–5634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ghorbani-Asl, M.; Zibouche, N.; Wahiduzzaman, M.; Oliveira, A.F.; Kuc, A.; Heine, T. Electromechanics in MoS2 and WS2: Nanotubes vs. Monolayers. Sci. Rep. 2013, 3, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, Y.; Ma, Y.; Jin, X.; Zhang, L.; Ye, G.; Zhao, S. A Sensitive Fluorescence Turn-on Assay of Bleomycin and Nuclease Using WS2 Nanosheet as an Effective Sensing Platform. Anal. Chim. Acta 2015, 866, 84–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Zheng, B.; Zhu, C.; Zhang, X.; Tan, C.; Li, H.; Chen, B.; Yang, J.; Chen, J.; Huang, Y.; et al. Single-Layer Transition Metal Dichalcogenide Nanosheet-Based Nanosensors for Rapid, Sensitive, and Multiplexed Detection of DNA. Adv. Mater. 2015, 27, 935–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xi, Q.; Zhou, D.-M.; Kan, Y.-Y.; Ge, J.; Wu, Z.-K.; Yu, R.-Q.; Jiang, J.-H. Highly Sensitive and Selective Strategy for Microrna Detection Based on WS2 nanosheet Mediated Fluorescence Quenching and Duplex-Specific Nuclease Signal Amplification. Anal. Chem. 2014, 86, 1361–1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ge, J.; Tang, L.-J.; Xi, Q.; Li, X.-P.; Yu, R.-Q.; Jiang, J.-H.; Chu, X. A WS2 Nanosheet Based Sensing Platform for Highly Sensitive Detection of T4 Polynucleotide Kinase and Its Inhibitors. Nanoscale 2014, 6, 6866–6872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, Y.; Li, R.; Liu, Z. Establishing Water-Soluble Layered WS2 nanosheet as a Platform for Biosensing. Anal. Chem. 2014, 86, 3610–3615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mulpur, P.; Yadavilli, S.; Rao, A.; Kamisetti, V.; Podila, R. MoS2/WS2/BN-Silver Thin-Film Hybrid Architectures Displaying Enhanced Fluorescence via Surface Plasmon Coupled Emission for Sensing Applications. ACS Sens. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.; Liu, L.; Wang, S.; Zhu, D. Water-Soluble Fluorescent Conjugated Polymers and Their Interactions with Biomacromolecules for Sensitive Biosensors. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2010, 39, 2411–2419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, C.; Liu, L.; Yang, Q.; Lv, F.; Wang, S. Water-Soluble Conjugated Polymers for Imaging, Diagnosis, and Therapy. Chem. Rev. 2012, 112, 4687–4735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Traina, C.A.; Bakus Ii, R.C.; Bazan, G.C. Design and Synthesis of Monofunctionalized, Water-Soluble Conjugated Polymers for Biosensing and Imaging Applications. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 12600–12607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.F.; Fan, Q.L.; Huang, W. DNA Biosensors Based on Water-Soluble Conjugated Polymers. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2011, 26, 2154–2164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, F.; Tang, Y.; Yu, M.; Feng, F.; An, L.; Sun, H.; Wang, S.; Li, Y.; Zhu, D.; Bazan, G.C. Quadruplex-to-Duplex Transition of G-Rich Oligonucleotides Probed by Cationic Water-Soluble Conjugated Polyelectrolytes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 6764–6765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, Y.; Feng, F.; Yu, M.; An, L.; He, F.; Wang, S.; Li, Y.; Zhu, D.; Bazan, G.C. Direct Visualization of Glucose Phosphorylation with a Cationic Polythiophene. Adv. Mater. 2008, 20, 703–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.L.; Liu, Y.; Cao, A. Strategy for Sensor Based on Fluorescence Emission Red Shift of Conjugated Polymers: Applications in Ph Response and Enzyme Activity Detection. Anal. Chem. 2013, 85, 825–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Tang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Guo, Y. Water-Soluble Conjugated Polymer as a Platform for Adenosine Deaminase Sensing Based on Fluorescence Resonance Energy Transfer Technique. Anal. Chem. 2014, 86, 6433–6438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, C.; Yang, Q.; Liu, L.; Wang, S. Rapid, Simple, and High-Throughput Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing and Antibiotics Screening. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2011, 50, 9607–9610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, F.; Tang, Y.; Wang, S.; Li, Y.; Zhu, D. Continuous Fluorometric Assays for Acetylcholinesterase Activity and Inhibition with Conjugated Polyelectrolytes. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2007, 46, 7882–7886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, F.; Tang, Y.; He, F.; Yu, M.; Duan, X.; Wang, S.; Li, Y.; Zhu, D. Cationic Conjugated Polymer/DNA Complexes for Amplified Fluorescence Assays of Nucleases and Methyltransferases. Adv. Mater. 2007, 19, 3490–3495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, X.; Li, L.; Min Chan, A.C.; Gao, N.; Yao, S.Q.; Xu, Q.-H. Water-Soluble Conjugated Polymers for Simultaneous Two-Photon Cell Imaging and Two-Photon Photodynamic Therapy. Adv. Opt. Mater. 2013, 1, 92–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Z.; Yin, Z.; Huang, X.; Li, H.; He, Q.; Lu, G.; Boey, F.; Zhang, H. Single-Layer Semiconducting Nanosheets: High-Yield Preparation and Device Fabrication. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2011, 50, 11093–11097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Dong, X.; Chen, P. Biological and Chemical Sensors Based on Graphene Materials. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2012, 41, 2283–2307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, S.; Dong, S. Graphene Nanosheet: Synthesis, Molecular Engineering, Thin Film, Hybrids, and Energy and Analytical Applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2011, 40, 2644–2672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, H.; Gao, W.; Yan, F.; Ji, H.; Ju, H. Fluorescence Resonance Energy Transfer between Quantum Dots and Graphene Oxide for Sensing Biomolecules. Anal. Chem. 2010, 82, 5511–5517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Ma, K.; Zhang, Y. Label-Free Fluorometric Detection of S1 Nuclease Activity by Using Polycytosine Oligonucleotide-Templated Silver Nanoclusters. Anal. Biochem. 2015, 468, 34–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, P.; Ma, R.; Gao, N.; Garai, M.; Xu, Q.-H. Plasmon Coupling-Enhanced Two-Photon Photoluminescence of Au@Ag Core–Shell Nanoparticles and Applications in the Nuclease Assay. Nanoscale 2015, 7, 10233–10239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.-L.; Kong, X.-J.; Yuan, J.; Yu, R.-Q.; Chu, X. A Dual-Amplification Fluorescent Sensing Platform for Ultrasensitive Assay of Nuclease and ATP Based on Rolling Circle Replication and Exonuclease Iii-Aided Recycling. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 75055–75061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Jiao, B.; Tang, H. Interaction of single-stranded DNA with graphene oxide: Fluorescence study and its application for S1 nuclease detection. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 18294–18300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, J.; Zhao, Q.; Tang, Y. Label-Free Fluorescence Assay of S1 Nuclease and Hydroxyl Radicals Based on Water-Soluble Conjugated Polymers and WS2 Nanosheets. Sensors 2016, 16, 865. https://doi.org/10.3390/s16060865
Li J, Zhao Q, Tang Y. Label-Free Fluorescence Assay of S1 Nuclease and Hydroxyl Radicals Based on Water-Soluble Conjugated Polymers and WS2 Nanosheets. Sensors. 2016; 16(6):865. https://doi.org/10.3390/s16060865
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Junting, Qi Zhao, and Yanli Tang. 2016. "Label-Free Fluorescence Assay of S1 Nuclease and Hydroxyl Radicals Based on Water-Soluble Conjugated Polymers and WS2 Nanosheets" Sensors 16, no. 6: 865. https://doi.org/10.3390/s16060865
APA StyleLi, J., Zhao, Q., & Tang, Y. (2016). Label-Free Fluorescence Assay of S1 Nuclease and Hydroxyl Radicals Based on Water-Soluble Conjugated Polymers and WS2 Nanosheets. Sensors, 16(6), 865. https://doi.org/10.3390/s16060865