A Robust and Multi-Weighted Approach to Estimating Topographically Correlated Tropospheric Delays in Radar Interferograms
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. InSAR Data Set and Interferometric Processing
3. The RMW Tropospheric Correction Method
3.1. Modeling
3.2. Basic Principles of the Least Squares and Robust Estimation Method
- Step 1: Set the initial value of the equivalent weight matrix: .
- Step 2: Calculate the parameter and residual vectors as follows:
- Step 3: Compute standardized residuals as below:
- Step 4: Calculate weight factors by substituting Equations (17) into (10) and then update the equivalent weight: .
- Step 5: Increase k = k + 1, repeat Step 2 to 4 until .
3.3. Expanded Forms of the Involved Matrices and a Test Case
3.4. The Multi-Weighted Phase-Elevation Ratio for PS
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Time Series InSAR Results
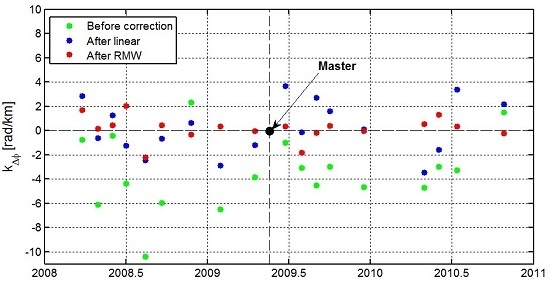
4.2. The Sensitivity of RMW Method to Orbital Ramp
4.3. The Effects of Turbulent Delay
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Thayer, G. An improved equation for the radio refractive index of air. Radio Sci. 1974, 9, 803–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, J.; Herring, T.; Shapiro, I.; Rogers, A.; Elgered, G. Geodesy by radio interferometry: Effects of atmospheric modeling errors on estimates of baseline length. Radio Sci. 1985, 20, 1593–1607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gray, A.L.; Mattar, K.E.; Sofko, G. Influence of ionospheric electron density fluctuations on satellite radar interferometry. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2000, 27, 1451–1454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zebker, H.A.; Rosen, P.; Hensley, S. Atmospheric effects in interferometric synthetic aperture radar surface deformation and topographic maps. J. Geophys. Res. 1997, 102, 7547–7563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.W.; Ding, X.L.; Liu, G.X.; Huang, C. Atmospheric effects on InSAR measurements- A review. Geomat. Res. Australas. 2003, 79, 43–58. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, X.L.; Li, Z.W.; Zhu, J.J.; Feng, G.C.; Long, J.P. Atmospheric effects on InSAR measurements and their mitigation. Sensors 2008, 8, 5426–5448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hooper, A.; Bekaert, D.; Spaans, K.; Arikan, M. Recent advances in SAR interferometry time series analysis for measuring crustal deformation. Tectonophysics 2012, 514–517, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onn, F.; Zebker, H.A. Correction for interferometric synthetic aperture radar atmospheric phase artifacts using time series of zenith wet delay observations from a GPS network. J. Geophy. Res. 2006, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mateus, P.; Nico, G.; Tomé, R.; Catalāo, J.; Miranda, P. Experimental study on the atmospheric delay based on GPS, SAR interferometry, and numerical weather model data. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2013, 51, 6–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wadge, G.; Webley, P.W.; James, I.N.; Bingley, R.; Dodson, A.; Waugh, S.; Veneboer, T.; Puglisi, G.; Mattia, M.; Baker, D.; et al. Atmospheric models, GPS and InSAR measurements of the atmospheric water vapor field over mount Etna. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2002, 29, 11-1–11-4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foster, J.; Brooks, B.; Cherubini, T.; Shacat, C.; Businger, S.; Werner, C.L. Mitigating atmospheric noise for InSAR using a high resolution weather model. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2006, 33, L16304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z. Interferometric synthetic aperture radar (InSAR) atmospheric correction: GPS, Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS), and InSAR integration. J. Geophys. Res. 2005, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Fielding, E.J.; Cross, P.; Muller, J.-P. Interferometric synthetic aperture radar atmospheric correction: Medium Resolution Imaging Spectrometer and Advanced Synthetic Aperture Radar integration. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2006, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doin, M.P.; Lasserre, C.; Peltzer, G.; Cavalié, O.; Doubre, C. Corrections of stratified atmospheric delays in SAR interferometry: Validation with global atmospheric models. J. Appl. Geophys. 2009, 69, 35–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jolivet, R.; Grandin, R.; Lasserre, C.; Doin, M.P.; Peltzer, G. Systematic InSAR atmospheric phase delay corrections from global meteorological reanalysis data. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2011, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delacourt, C.; Briole, P.; Achache, J. Atmospheric corrections of SAR interferograms with strong topography. Application to Etna. Geophys. Res. Lett. 1998, 25, 2849–2852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burgmann, R.; Rosen, P.; Fielding, E. Synthetic aperture radar interferometry to measure Earth’s surface topography and its deformation. Annu. Rev. Earth Planet. Sci. 2000, 28, 169–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Simons, M.; Hetland, E.; Muse, P.; DiCaprio, C. A multiscale approach to estimating topographically correlated propagation delays in radar interferograms. Geochem. Geophys. Geosyst. 2010, 11, Q09002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bekaert, D.; Hooper, A.; Wright, T. A spatially variable powerlaw atmospheric correction technique for InSAR data. J. Geophys. Res. 2015, 120, 1345–1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, P.L. Sign-constrained robust least squares, subjective breakdown point and the effect of weights of observations on robustness. J. Geod. 2005, 79, 146–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.F.; Ou, J.K.; Wang, H.T. Robust estimation for correlated observations: Two local sensitivity-based downweighting strategies. J. Geod. 2010, 84, 243–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kampes, B.; Hanssen, R.; Perski, Z. Radar interferometry with public domain tools. In Proceedings of the Fringe Workshop, Frascati, Italy, 1–5 December 2003; p. 6.
- Hooper, A. Persistent Scatterer Radar Interferometry for Crustal Deformation Studies and Modeling of Volcanic Deformation; Stanford University: Stanford, CA, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Hooper, A.; Zebker, H. Phase unwrapping in three dimensions with application to InSAR time series. J. Opt. Soc. Am. A 2007, 24, 2737–2747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farr, G.T.; Kobrick, M. Shuttle radar topography mission produces a wealth of data. Eos Trans. AGU 2000, 81, 583–585. [Google Scholar]
- Wright, T.; Fielding, E.; Parsons, B. Triggered slip: Observations of the 17 August 1999 Izmit (Turkey) earthquake using radar interferometry. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2001, 28, 1079–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavalie, O.; Pathier, E.; Radiguet, M.; Vergnolle, M.; Cotte, N.; Walpersdorf, A.; Kostoglodov, V.; Cotton, F. Slow slip event in the Mexican subduction zone: Evidence of shallower slip in the Guerrero seismic gap for the 2006 event revealed by the joint inversion of InSAR and GPS data. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2013, 367, 52–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanssen, R.F. Radar Interferometry: Data Interpretation and Error Analysis; Kluwer Academic Publishers: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- DiCaprio, C.; Simons, M. Importance of ocean tidal load corrections for differential InSAR. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2008, 35, L22309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bekaert, D.; Hooper, A.; Wright, T. Reassessing the 2006 Guerrero slow slip event, Mexico: Implications for large earthquakes in the Guerrero Gap. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2015, 120, 1357–1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.; Freymueller, J.T.; Jensen, T. Seasonal hydrological loading in southern Alaska observed by GPS and GRACE. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2012, 39, L15310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y. Robust estimation for dependent observations. Manuscr. Geod. 1994, 19, 10K–17K. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.; Cheng, M.K.; Shum, C.K.; Tapley, B.D. Robust estimation of systematic errors of satellite laser range. J. Geod. 1999, 73, 345–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huber, P.J. Robust Statistics; John Wiley and Sons: New York, NY, USA, 1981. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.W.; Xu, W.B.; Feng, G.C.; Hu, J.; Wang, C.C.; Ding, X.L.; Zhu, J.J. Correcting atmospheric effects on InSAR with MERIS water vapor data and elevation-dependent interpolation model. Geophys. J. Int. 2012, 189, 898–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]













| Ifg Index | Date | Perpendicular Baseline (m) | Temporal Baseline (Days) | Doppler Central Baseline (Hz) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 23 February 2008 | −95 | 420 | 9.6 |
| 2 | 29 March 2008 | 439 | 385 | −1.9 |
| 3 | 3 May 2008 | 91 | 350 | 7.8 |
| 4 | 7 June 2008 | 308 | 315 | 0.1 |
| 5 | 12 July 2008 | 364 | 280 | 0.1 |
| 6 | 16 August 2008 | 284 | 245 | 4.1 |
| 7 | 25 October 2008 | 272 | 175 | −3.4 |
| 8 | 3 January 2009 | 288 | 105 | −0.4 |
| 9 | 14 March 2009 | 692 | 35 | 1.7 |
| 10 | 18 April 2009 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 11 | 23 May 2009 | 203 | −35 | 6.0 |
| 12 | 27 June 2009 | 407 | −70 | −0.7 |
| 13 | 1 August 2009 | 98 | −105 | 0.1 |
| 14 | 5 September 2009 | 432 | −140 | −3.7 |
| 15 | 14 November 2009 | 356 | −210 | −3.0 |
| 16 | 3 April 2010 | 543 | −350 | −7.5 |
| 17 | 8 May 2010 | 369 | −385 | 3.7 |
| 18 | 12 June 2010 | 389 | −420 | −15.7 |
| 19 | 25 September 2010 | 391 | −525 | −10.6 |
| Parameter | Value | Parameter | Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| DEM (SRTM) | 90 m | Gamma convergence | 0.005 |
| Oversample | no | Density random | 20 |
| Dispersion threshold | 0.4 | Weed STD | 1 |
| Patches number | 6 | Weed max noise | Inf |
| Max topography error | 5 | Unwrap method | ‘3D’ |
| Select method | Density | Unwrap grid size | 200 m |
| Ifg Index | Improvement STD (%) | Ifg Index | Improvement STD (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 23.7 | 11 | 6.8 |
| 2 | 5.4 | 12 | 2.4 |
| 3 | 0.2 | 13 | 13.1 |
| 4 | 4.2 | 14 | 3.0 |
| 5 | 3.7 | 15 | 8.4 |
| 6 | 1.6 | 16 | 6.0 |
| 7 | 14.4 | 17 | 14.0 |
| 8 | 2.4 | 18 | 12.8 |
| 9 | 0.1 | 19 | 28.7 |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhu, B.; Li, J.; Chu, Z.; Tang, W.; Wang, B.; Li, D. A Robust and Multi-Weighted Approach to Estimating Topographically Correlated Tropospheric Delays in Radar Interferograms. Sensors 2016, 16, 1078. https://doi.org/10.3390/s16071078
Zhu B, Li J, Chu Z, Tang W, Wang B, Li D. A Robust and Multi-Weighted Approach to Estimating Topographically Correlated Tropospheric Delays in Radar Interferograms. Sensors. 2016; 16(7):1078. https://doi.org/10.3390/s16071078
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhu, Bangyan, Jiancheng Li, Zhengwei Chu, Wei Tang, Bin Wang, and Dawei Li. 2016. "A Robust and Multi-Weighted Approach to Estimating Topographically Correlated Tropospheric Delays in Radar Interferograms" Sensors 16, no. 7: 1078. https://doi.org/10.3390/s16071078
APA StyleZhu, B., Li, J., Chu, Z., Tang, W., Wang, B., & Li, D. (2016). A Robust and Multi-Weighted Approach to Estimating Topographically Correlated Tropospheric Delays in Radar Interferograms. Sensors, 16(7), 1078. https://doi.org/10.3390/s16071078