Identification of Quorum-Sensing Signal Molecules and a Biosynthetic Gene in Alicycliphilus sp. Isolated from Activated Sludge
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Clone Library Analysis
2.2. Screening and Identification of AHL-Producing Bacteria
2.3. Cloning of the AHL-Synthase Gene from Alicycliphilus sp. B1
2.4. Extraction and Identification of AHLs
2.5. Chemical Synthesis of AHL Standards
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Phylogenetic Analysis of the Clone Libraries from Activated Sludge
3.2. Isolation and Identification of AHL-Producing Bacteria from Activated Sludge
3.3. Analytical Identification of AHL Molecules
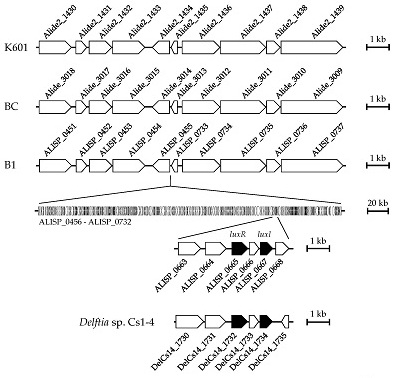
3.4. Comparative Genomic Analysis of Alicycliphilus Strains
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ochiai, S.; Morohoshi, T.; Kurabeishi, A.; Shinozaki, M.; Fujita, H.; Sawada, I.; Ikeda, T. Production and degradation of N-acylhomoserine lactone quorum sensing signal molecules in bacteria isolated from activated sludge. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2013, 77, 2436–2440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waters, C.M.; Bassler, B.L. Quorum sensing: Cell-to-cell communication in bacteria. Annu. Rev. Cell. Dev. Biol. 2005, 21, 319–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parsek, M.R.; Greenberg, E.P. Acyl-homoserine lactone quorum sensing in gram-negative bacteria: A signaling mechanism involved in associations with higher organisms. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 8789–8793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schuster, M.; Sexton, D.J.; Diggle, S.P.; Greenberg, E.P. Acyl-homoserine lactone quorum sensing: From evolution to application. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 2013, 67, 43–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chong, G.; Kimyon, O.; Rice, S.A.; Kjelleberg, S.; Manefield, M. The presence and role of bacterial quorum sensing in activated sludge. Microb. Biotechnol. 2012, 5, 621–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, C.H.; Koh, K.S.; Xie, C.; Tay, M.; Zhou, Y.; Williams, R.; Ng, W.J.; Rice, S.A.; Kjelleberg, S. The role of quorum sensing signalling in EPS production and the assembly of a sludge community into aerobic granules. ISME J. 2014, 8, 1186–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.; Park, S.K.; Kwon, H.; Lee, S.H.; Lee, K.; Nahm, C.H.; Jo, S.J.; Oh, H.S.; Park, P.K.; Choo, K.H.; et al. Crossing the border between laboratory and field: Bacterial quorum quenching for anti-biofouling strategy in an MBR. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 16, 1788–1795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.W.; Lee, J.K.; Min, Y.K.; Hamaguchi, H.O.; Chung, J. Development of an automatic phase-contrast microscopic system capable of determining the microbial density and distribution inside an immobilized carrier. Anal. Sci. 2008, 24, 547–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okutsu, N.; Morohoshi, T.; Ikeda, T. Draft genome sequence of Alicycliphilus sp. B1, an N-acylhomoserine lactone-producing bacterium, isolated from activated sludge. Genome Announc. 2015, 3, e00424-15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mechichi, T.; Stackebrandt, E.; Fuchs, G. Alicycliphilus denitrificans gen. nov., sp. nov., a cyclohexanol-degrading, nitrate-reducing beta-proteobacterium. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2003, 53, 147–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oosterkamp, M.J.; Veuskens, T.; Talarico Saia, F.; Weelink, S.A.; Goodwin, L.A.; Daligault, H.E.; Bruce, D.C.; Detter, J.C.; Tapia, R.; Han, C.S.; et al. Genome analysis and physiological comparison of Alicycliphilus denitrificans strains BC and K601(T.). PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e66971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McClean, K.H.; Winson, M.K.; Fish, L.; Taylor, A.; Chhabra, S.R.; Cámara, M.; Daykin, M.; Lamb, J.H.; Swift, S.; Brcroft, B.W.; et al. Quorum sensing and Chromobacterium violaceum: Exploitation of violacein production and inhibition for the detection of N-acylhomoserine lactones. Microbiology 1997, 143, 3703–3711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morohoshi, T.; Kato, M.; Fukamachi, K.; Kato, N.; Ikeda, T. N-acylhomoserine lactone regulates violacein production in Chromobacterium violaceum type strain ATCC 12472. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2008, 279, 124–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cole, J.R.; Chai, B.; Farris, R.J.; Wang, Q.; Kulam, S.A.; McGarrell, D.M.; Garrity, G.M.; Tiedje, J.M. The Ribosomal Database Project (RDP-II): Sequences and tools for high-throughput rRNA analysis. Nucleic Acids Res. 2005, 33, D294–D296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okutsu, N.; Morohoshi, T.; Xie, X.; Kato, N.; Ikeda, T. Characterization of N-acylhomoserine lactones produced by bacteria isolated from industrial cooling water systems. Sensors 2016, 16, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chhabra, S.R.; Harty, C.; Hooi, D.S.; Daykin, M.; Williams, P.; Telford, G.; Pritchard, D.I.; Bycroft, B.W. Synthetic analogues of the bacterial signal (quorum sensing) molecule N-(3-oxododecanoyl)-l-homoserine lactone as immune modulators. J. Med. Chem. 2003, 46, 97–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pomini, A.M.; Cruz, P.L.; Gai, C.; Araujo, W.L.; Marsaioli, A.J. Long-chain acyl-homoserine lactones from Methylobacterium mesophilicum: Synthesis and absolute configuration. J. Nat. Prod. 2009, 72, 2125–2129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oosterkamp, M.J.; Veuskens, T.; Plugge, C.M.; Langenhoff, A.A.; Gerritse, J.; van Berkel, W.J.; Pieper, D.H.; Junca, H.; Goodwin, L.A.; Daligault, H.E.; et al. Genome sequences of Alicycliphilus denitrificans strains BC and K601T. J. Bacteriol. 2011, 193, 5028–5029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jafra, S.; Przysowa, J.; Czajkowski, R.; Michta, A.; Garbeva, P.; van der Wolf, J.M. Detection and characterization of bacteria from the potato rhizosphere degrading N-acyl-homoserine lactone. Can. J. Microbiol. 2006, 52, 1006–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maisuria, V.B.; Nerurkar, A.S. Interference of quorum sensing by Delftia. sp. VM4 depends on the activity of a novel N-acylhomoserine lactone-acylase. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0138034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shigematsu, T.; Yumihara, K.; Ueda, Y.; Numaguchi, M.; Morimura, S.; Kida, K. Delftia tsuruhatensis sp. nov., a terephthalate-assimilating bacterium isolated from activated sludge. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2003, 53, 1479–1483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Yang, H.; Huang, Z.; Zhou, P.; Liu, S.J. Degradation of aniline by newly isolated, extremely aniline-tolerant Delftia. sp. AN3. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2002, 58, 679–682. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dullius, C.H.; Chen, C.Y.; Schink, B. Nitrate-dependent degradation of acetone by Alicycliphilus and Paracoccus strains and comparison of acetone carboxylase enzymes. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2011, 77, 6821–6825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




| Closest Genera | Clones | % |
|---|---|---|
| Runella | 69 | 72.6 |
| Methylibium | 8 | 8.4 |
| Acidovorax | 5 | 5.3 |
| Alicycliphilus | 3 | 3.2 |
| Leptothrix | 2 | 2.1 |
| Methyloversatilis | 2 | 2.1 |
| Others | 6 | 6.3 |
| Total | 95 | 100 |
| Strains | Related Type Strain | CV026 | VIR07 |
|---|---|---|---|
| B1 | Alicycliphilus denitrificans K601T | - | ++ |
| B3 | Alicycliphilus denitrificans K601T | - | ++ |
| B9 | Alicycliphilus denitrificans K601T | - | ++ |
| B12 | Alicycliphilus denitrificans K601T | - | ++ |
| C3 | Alicycliphilus denitrificans K601T | - | ++ |
| C4 | Alicycliphilus denitrificans K601T | - | ++ |
| C5 | Alicycliphilus denitrificans K601T | - | ++ |
| C10 | Alicycliphilus denitrificans K601T | - | ++ |
| C11 | Alicycliphilus denitrificans K601T | - | ++ |
| D1 | Pseudomonas azotoformans IAM1603T | - | + |
| D2 | Pseudomonas azotoformans IAM1603T | - | + |
| D3 | Alicycliphilus denitrificans K601T | - | ++ |
| D10 | Alicycliphilus denitrificans K601T | - | ++ |
| D11 | Alicycliphilus denitrificans K601T | - | ++ |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Morohoshi, T.; Okutsu, N.; Xie, X.; Ikeda, T. Identification of Quorum-Sensing Signal Molecules and a Biosynthetic Gene in Alicycliphilus sp. Isolated from Activated Sludge. Sensors 2016, 16, 1218. https://doi.org/10.3390/s16081218
Morohoshi T, Okutsu N, Xie X, Ikeda T. Identification of Quorum-Sensing Signal Molecules and a Biosynthetic Gene in Alicycliphilus sp. Isolated from Activated Sludge. Sensors. 2016; 16(8):1218. https://doi.org/10.3390/s16081218
Chicago/Turabian StyleMorohoshi, Tomohiro, Noriya Okutsu, Xiaonan Xie, and Tsukasa Ikeda. 2016. "Identification of Quorum-Sensing Signal Molecules and a Biosynthetic Gene in Alicycliphilus sp. Isolated from Activated Sludge" Sensors 16, no. 8: 1218. https://doi.org/10.3390/s16081218
APA StyleMorohoshi, T., Okutsu, N., Xie, X., & Ikeda, T. (2016). Identification of Quorum-Sensing Signal Molecules and a Biosynthetic Gene in Alicycliphilus sp. Isolated from Activated Sludge. Sensors, 16(8), 1218. https://doi.org/10.3390/s16081218