Recent Advances in Nanoparticle Concentration and Their Application in Viral Detection Using Integrated Sensors
Abstract
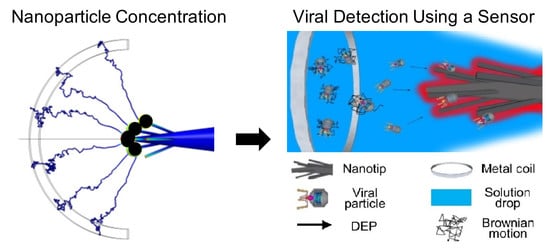
:1. Introduction
2. Review of Concentration Methods and Relevant Theory
2.1. Diffusion
2.2. Centrifugation and Microfiltration
2.3. Electric and Magnetic Fields
2.4. Nano-Microfluidics and Other Emerging Technologies
3. Conclusions and Future Perspectives
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Choi, C.; Choi, M.K.; Hyeon, T.; Kim, D.H. Nanomaterial-based soft electronics for healthcare applications. ChemNanoMat 2016, 2, 1006–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinivasan, B.; Tung, S. Development and applications of portable biosensors. J. Lab. Autom. 2015, 20, 365–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lozano, R.; Naghavi, M.; Foreman, K.; Lim, S.; Shibuya, K.; Aboyans, V.; Abraham, J.; Adair, T.; Aggarwal, R.; Ahn, S.Y.; et al. Global and regional mortality from 235 causes of death for 20 age groups in 1990 and 2010: A systematic analysis for the global burden of disease study 2010. Lancet 2012, 380, 2095–2128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lien, K.Y.; Hung, L.Y.; Huang, T.B.; Tsai, Y.C.; Lei, H.Y.; Lee, G.B. Rapid detection of influenza a virus infection utilizing an immunomagnetic bead-based microfluidic system. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2011, 26, 3900–3907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ammersbach, M.; Bienzle, D. Methods for assessing feline immunodeficiency virus infection, infectivity and purification. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 2011, 143, 202–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lifson, M.A.; Ozen, M.O.; Inci, F.; Wang, S.Q.; Inan, H.; Baday, M.; Henrich, T.J.; Demirci, U. Advances in biosensing strategies for hiv-1 detection, diagnosis, and therapeutic monitoring. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2016, 103, 90–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, J.; Bazant, M.Z. Effects of nanoparticle geometry and size distribution on diffusion impedance of battery electrodes. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2013, 160, A15–A24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agnihotri, S.; Mukherji, S.; Mukherji, S. Size-controlled silver nanoparticles synthesized over the range 5–100 nm using the same protocol and their antibacterial efficacy. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 3974–3983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raeesi, V.; Chan, W.C. Improving nanoparticle diffusion through tumor collagen matrix by photo-thermal gold nanorods. Nanoscale 2016, 8, 12524–12530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eloul, S.; Kätelhön, E.; Batchelor-McAuley, C.; Tschulik, K.; Compton, R.G. Diffusional nanoimpacts: The stochastic limit. J. Phys. Chem. C 2015, 119, 14400–14410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eloul, S.; Kätelhön, E.; Batchelor-McAuley, C.; Tschulik, K.; Compton, R.G. Diffusional impacts of nanoparticles on microdisc and microwire electrodes: The limit of detection and first passage statistics. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2015, 755, 136–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papp, I.; Sieben, C.; Ludwig, K.; Roskamp, M.; Böttcher, C.; Schlecht, S.; Herrmann, A.; Haag, R. Inhibition of influenza virus infection by multivalent sialic-acid-functionalized gold nanoparticles. Small 2010, 6, 2900–2906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Driskell, J.D.; Jones, C.A.; Tompkins, S.M.; Tripp, R.A. One-step assay for detecting influenza virus using dynamic light scattering and gold nanoparticles. Analyst 2011, 136, 3083–3090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, C.; Gaston, M.A.; Weiss, A.A.; Zhang, P. Colorimetric viral detection based on sialic acid stabilized gold nanoparticles. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2013, 42, 236–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.J.; Zhang, L.Q.; Wei, W.; Zhao, H.Y.; Zhou, Z.X.; Zhang, Y.J.; Liu, S.Q. Colorimetric detection of influenza a virus using antibody-functionalized gold nanoparticles. Analyst 2015, 140, 3989–3995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perez-Mendez, A.; Chandler, J.C.; Bisha, B.; Goodridge, L.D. Evaluation of an anion exchange resin-based method for concentration of f-rna coliphages (enteric virus indicators) from water samples. J. Virol. Methods 2014, 204, 109–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perez, J.M.; Simeone, F.J.; Saeki, Y.; Josephson, L.; Weissleder, R. Viral-induced self-assembly of magnetic nanoparticles allows the detection of viral particles in biological media. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2003, 125, 10192–10193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shawky, S.M.; Bald, D.; Azzazy, H.M.E. Direct detection of unamplified hepatitis c virus rna using unmodified gold nanoparticles. Clin. Biochem. 2010, 43, 1163–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, S.Y.; Wang, W.C.; Lan, C.B.; Chen, C.H.; Chieh, J.J.; Horng, H.E.; Hong, C.Y.; Yang, H.C.; Tsai, C.P.; Yang, C.Y.; et al. Magnetically enhanced high-specificity virus detection using magnetic nanoparticles with antibodies as labeling markers. J. Virol. Methods 2010, 164, 14–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alipour, E.; Ghourchian, H.; Boutorabi, S.M. Gold nanoparticle based capacitive immunosensor for detection of hepatitis b surface antigen. Anal. Methods 2013, 5, 4448–4453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooper, M.A.; Dultsev, F.N.; Minson, T.; Ostanin, V.P.; Abell, C.; Klenerman, D. Direct and sensitive detection of a human virus by rupture event scanning. Nat. Biotechnol. 2001, 19, 833–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De la Escosura-Muniz, A.; Maltez-da Costa, M.; Sanchez-Espinel, C.; Diaz-Freitas, B.; Fernandez-Suarez, J.; Gonzalez-Fernandez, A.; Merkoci, A. Gold nanoparticle-based electrochemical magnetoimmunosensor for rapid detection of anti-hepatitis b virus antibodies in human serum. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2010, 26, 1710–1714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agiotis, L.; Theodorakos, I.; Samothrakitis, S.; Papazoglou, S.; Zergioti, I.; Raptis, Y.S. Magnetic manipulation of superparamagnetic nanoparticles in a microfluidic system for drug delivery applications. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2016, 401, 956–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.-H.; Lee, D.; Chew, C.H.C.; Kim, T.; Pak, J.J. A multi-virus detectable microfluidic electrochemical immunosensor for simultaneous detection of h1n1, h5n1, and h7n9 virus using zno nanorods for sensitivity enhancement. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2016, 228, 36–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.P.; Shan, X.N.; Patel, U.; Huang, X.P.; Lu, J.; Li, J.H.; Tao, N.J. Label-free imaging, detection, and mass measurement of single viruses by surface plasmon resonance. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 16028–16032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yanik, A.A.; Huang, M.; Kamohara, O.; Artar, A.; Geisbert, T.W.; Connor, J.H.; Altug, H. An optofluidic nanoplasmonic biosensor for direct detection of live viruses from biological media. Nano Lett. 2010, 10, 4962–4969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agrawal, A.; Tripp, R.A.; Anderson, L.J.; Nie, S.M. Real-time detection of virus particles and viral protein expression with two-color nanoparticle probes. J. Virol. 2005, 79, 8625–8628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tripp, R.A.; Alvarez, R.; Anderson, B.; Jones, L.; Weeks, C.; Chen, W. Bioconjugated nanoparticle detection of respiratory syncytial virus infection. Int. J. Nanomed. 2007, 2, 117–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayashi, Y.; Matsuda, R.; Ito, K.; Nishimura, W.; Imai, K.; Maeda, M. Detection limit estimated from slope of calibration curve: An application to competitive elisa. Anal. Sci. 2005, 21, 167–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.Y.; Garcia-D’Angeli, A.; Brennan, J.P.; Huo, Q. Predicting detection limits of enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (elisa) and bioanalytical techniques in general. Analyst 2014, 139, 439–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, C.F.; Meghrous, J.; Kamen, A. Quantitation of baculovirus particles by flow cytometry. J. Virol. Methods 2002, 105, 321–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez-Hernandez, M.B.; Cunha, J.B.; Wobus, C.E. Plaque assay for murine norovirus. J. Vis. Exp. 2012, 66, 4297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chapagain, M.L.; Nguyen, T.; Bui, T.; Verma, S.; Nerurkar, V.R. Comparison of real-time pcr and hemagglutination assay for quantitation of human polyomavirus jc. Virol. J. 2006, 3, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Welzel, T.M.; Miley, W.J.; Parks, T.L.; Goedert, J.J.; Whitby, D.; Ortiz-Conde, B.A. Real-time pcr assay for detection and quantification of hepatitis b virus genotypes a to g. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2006, 44, 3325–3333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garrett, R.H.; Grisham, C.M. Biochemistry, 5th ed.; Brooks-Cole, Cengage Learning: Belmont, CA, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Ramaswamy, S. Issues in the statistical mechanics of steady sedimentation. Adv. Phys. 2001, 50, 297–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, V.; Park, K.; Srinivasarao, M. Shape separation of gold nanorods using centrifugation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 4981–4985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chandrasekhar, S. Stochastic problems in physics and astronomy. Rev. Mod. Phys. 1943, 15, 1–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhont, J.; Gompper, G.; Richter, D. Soft matter: Complex materials on mesoscopic scales. Forschungszentrum Jülich GmbH, Jülich, Germany 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Dhont, J.K.G. Translational brownian motion. Lect. Manuscr. Spring Sch. Inst. Solid State Res. 2004, 35, A2. [Google Scholar]
- Fujita, H. Foundations of Ultracentrifugal Analysis; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1975. [Google Scholar]
- Piazza, R.; Buzzaccaro, S.; Secchi, E.; Parola, A. What buoyancy really is. A generalized archimedes’ principle for sedimentation and ultracentrifugation. Soft Matter 2012, 8, 7112–7115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutornojs, V.; Niedre-Otomere, B.; Kozlovska, T.; Zajakina, A. Comparison of ultracentrifugation methods for concentration of recombinant alphaviruses: Sucrose and iodixanol cushions. Environ. Exp. Biol. 2012, 2012, 117–123. [Google Scholar]
- Negrete, A.; Pai, A.; Shiloach, J. Use of hollow fiber tangential flow filtration for the recovery and concentration of hiv virus-like particles produced in insect cells. J. Virol. Methods 2014, 195, 240–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dantas-Lima, J.J.; Corteel, M.; Cornelissen, M.; Bossier, P.; Sorgeloos, P.; Nauwynck, H.J. Purification of white spot syndrome virus by iodixanol density gradient centrifugation. J. Fish Dis. 2013, 36, 841–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jungbauer, A. Continuous downstream processing of biopharmaceuticals. Trends Biotechnol. 2013, 31, 479–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wickramasinghe, S.R.; Kalbfuss, B.; Zimmermann, A.; Thom, V.; Reichl, U. Tangential flow microfiltration and ultrafiltration for human influenza a virus concentration and purification. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2005, 92, 199–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pei, L.; Rieger, M.; Lengger, S.; Ott, S.; Zawadsky, C.; Hartmann, N.M.; Selinka, H.C.; Tiehm, A.; Niessner, R.; Seidel, M. Combination of crossflow ultrafiltration, monolithic affinity filtration, and quantitative reverse transcriptase pcr for rapid concentration and quantification of model viruses in water. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 10073–10080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdelzaher, A.M.; Solo-Gabriele, H.M.; Wright, M.E.; Palmer, C.J. Sequential concentration of bacteria and viruses from marine waters using a dual membrane system. J. Environ. Qual. 2008, 37, 1648–1655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evans, O.; Paul-Pont, I.; Hick, P.; Whittington, R.J. A simple centrifugation method for improving the detection of ostreid herpesvirus-1 (oshv-1) in natural seawater samples with an assessment of the potential for particulate attachment. J. Virol. Methods 2014, 210, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ichim, C.V.; Wells, R.A. Generation of high-titer viral preparations by concentration using successive rounds of ultracentrifugation. J. Transl. Med. 2011, 9, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molloy, S.D.; Thomas, E.; Hoyt, K.; Bouchard, D.A. Enhanced detection of infectious salmon anaemia virus using a low-speed centrifugation technique in three fish cell lines. J. Fish Dis. 2013, 36, 35–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pasco, E.V.; Shi, H.; Xagoraraki, I.; Hashsham, S.A.; Parent, K.N.; Bruening, M.L.; Tarabara, V.V. Polyelectrolyte multilayers as anti-adhesive membrane coatings for virus concentration and recovery. J. Membr. Sci. 2014, 469, 140–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.Y.; Riley, L.K.; Lin, M.S.; Purdy, G.A.; Hu, Z.Q. Development of a virus concentration method using lanthanum-based chemical flocculation coupled with modified membrane filtration procedures. J. Virol. Methods 2013, 190, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiles, D. Introduction to Magnetism and Magnetic Materials, 3rd ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Prigiobbe, V.; Ko, S.; Huh, C.; Bryant, S.L. Measuring and modeling the magnetic settling of superparamagnetic nanoparticle dispersions. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2015, 447, 58–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, Y.; Timonen, J.V.; Grzybowski, B.A. A long-lasting concentration cell based on a magnetic electrolyte. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2014, 9, 901–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lien, K.Y.; Lin, J.L.; Liu, C.Y.; Lei, H.Y.; Lee, G.B. Purification and enrichment of virus samples utilizing magnetic beads on a microfluidic system. Lab Chip 2007, 7, 868–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, B.; Salieb-Beugelaar, G.B.; Nigo, M.M.; Weidmann, M.; Hunziker, P. Diagnosing dengue virus infection: Rapid tests and the role of micro/nanotechnologies. Nanomedicine 2015, 11, 1745–1761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hunter, R.J. Foundations of Colloid Science, 2nd ed.; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Dickerson, J.H.; Boccaccini, A.R. Electrophoretic Deposition of Nanomaterials; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Pohl, H.A. Dielectrophoresis: The Behavior of Neutral Matter in Nonuniform Electric Fields; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1978. [Google Scholar]
- Yeo, W.H.; Lee, H.B.; Kim, J.H.; Lee, K.H.; Chung, J.H. Nanotip analysis for dielectrophoretic concentration of nanosized viral particles. Nanotechnology 2013, 24, 185502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, M.M.; Zydney, A.L. Effect of electrostatic, hydrodynamic, and brownian forces on particle trajectories and sieving in normal flow filtration. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2004, 269, 425–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morgan, H.; Green, N.G. AC Electrokinetics: Colloids and Nanoparticles; Research Studies Press: Baldock, UK, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Sonnenberg, A.; Marciniak, J.Y.; McCanna, J.; Krishnan, R.; Rassenti, L.; Kipps, T.J.; Heller, M.J. Dielectrophoretic isolation and detection of cfc-DNA nanoparticulate biomarkers and virus from blood. Electrophoresis 2013, 34, 1076–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalyanasundaram, D.; Inoue, S.; Kim, J.-H.; Lee, H.-B.; Kawabata, Z.; Yeo, W.-H.; Cangelosi, G.A.; Oh, K.; Gao, D.; Lee, K.-H. Electric field-induced concentration and capture of DNA onto microtips. Microfluid. Nanofluid. 2012, 13, 217–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakano, M.; Ding, Z.; Kasahara, H.; Suehiro, J. DNA detection using microbeads-based dielectrophoretic impedance measurement. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE SENSORS, Valencia, Spain, 2–5 November 2014; pp. 1010–1013. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, W.; Wang, C.; Ding, H.; Shao, J.; Ding, Y. Ac electric field induced dielectrophoretic assembly behavior of gold nanoparticles in a wide frequency range. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2016, 370, 184–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeo, W.-H.; Kopacz, A.M.; Kim, J.-H.; Chen, X.; Wu, J.; Gao, D.; Lee, K.-H.; Liu, W.-K.; Chung, J.-H. Dielectrophoretic concentration of low-abundance nanoparticles using a nanostructured tip. Nanotechnology 2012, 23, 485707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teimouri, M. Nanoparticle-Bridge Assay for Amplification-Free Electrical Detection of Oligonucleotides. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Texas at Arlington, Arlington, TX, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Van Tricht, E.; Geurink, L.; Pajic, B.; Nijenhuis, J.; Backus, H.; Germano, M.; Somsen, G.W.; Sanger-van de Griend, C.E. New capillary gel electrophoresis method for fast and accurate identification and quantification of multiple viral proteins in influenza vaccines. Talanta 2015, 144, 1030–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iwata, A.; Satoh, K.; Murata, M.; Hikata, M.; Hayakawa, T.; Yamaguchi, T. Virus concentration using sulfonated magnetic beads to improve sensitivity in nucleic acid amplification tests. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2003, 26, 1065–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uchida, E.; Kogi, M.; Oshizawa, T.; Furuta, B.; Satoh, K.; Iwata, A.; Murata, M.; Hikata, M.; Yamaguchi, T. Optimization of the virus concentration method using polyethyleneimine-conjugated magnetic beads and its application to the detection of human hepatitis a, b and c viruses. J. Virol. Methods 2007, 143, 95–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patolsky, F.; Zheng, G.F.; Hayden, O.; Lakadamyali, M.; Zhuang, X.W.; Lieber, C.M. Electrical detection of single viruses. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 14017–14022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maruyama, H.; Kotani, K.; Masuda, T.; Honda, A.; Takahata, T.; Arai, F. Nanomanipulation of single influenza virus using dielectrophoretic concentration and optical tweezers for single virus infection to a specific cell on a microfluidic chip. Microfluid. Nanofluid. 2011, 10, 1109–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Ostlund, E.N.; Jun, Y.; Nie, F.P.; Li, Y.G.; Johnson, D.J.; Lin, R.; Li, Z.G. Combining reverse-transcription multiplex pcr and microfluidic electrophoresis to simultaneously detect seven mosquito-transmitted zoonotic encephalomyelitis viruses. Vet. J. 2016, 212, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.Y.; Hsiao, T.H.; Chu, L.H.; Lin, Y.L.; Huang, J.L.; Chen, C.H.; Peck, K. Unraveling virus identity by detection of depleted probes with capillary electrophoresis. Anal. Chim. Acta 2012, 734, 88–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, K.; Chen, C.Y.; Liang, C.S.; Liu, C.; Yang, B.; Chen, X.M.; Cai, C.Q. Highly selective recognition and fluorescent detection of jev via virus-imprinted magnetic silicon microspheres. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2016, 233, 607–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubicki, W.; Pajak, B.; Kucharczyk, K.; Walczaka, R.; Dziubana, J.A. Rapid detection of highly pathogenic a(h7n7) avian influenza virus genetic markers in heterogenic samples utilizing on-chip sscp-ce method. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2016, 926–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burns, M.; Valdivia, H. Modelling the limit of detection in real-time quantitative pcr. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2008, 226, 1513–1524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reynisson, E.; Josefsen, M.H.; Krause, A.; Hoorfar, J. Evaluation of probe chemistries and platforms to improve the detection limit of real-time pcr. J. Microbiol. Methods 2006, 66, 206–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pethig, R. Review article-dielectrophoresis: Status of the theory, technology, and applications. Biomicrofluidics 2010, 4, 022811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, J.H.; Gu, H.W.; Xu, B. Multifunctional magnetic nanoparticles: Design, synthesis, and biomedical applications. Acc. Chem. Res. 2009, 42, 1097–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gad-el-Hak, M. Book review. Essentials of micro-and nanofluidics: With applications to the biological and chemical sciences. A. Terrence conlisk. Cambridge University Press, 2013. 537 pages. ISBN 978–0-521-88168-5. J. Fluid Mech. 2015, 779, 859–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edel, J.; Ivanov, A.; Kim, M. Nanofluidics, 2nd ed.; Royal Society of Chemistry: London, UK, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Lopez-Barbosa, N.; Gamarra, J.D.; Osma, J.F. The future point-of-care detection of disease and its data capture and handling. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2016, 408, 2827–2837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamholz, A.E.; Yager, P. Theoretical analysis of molecular diffusion in pressure-driven laminar flow in microfluidic channels. Biophys J. 2001, 80, 155–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Bai, J.H.; Ying, J.Y. A stacking flow immunoassay for the detection of dengue-specific immunoglobulins in salivary fluid. Lab Chip 2015, 15, 1465–1471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaminska, A.; Witkowska, E.; Winkler, K.; Dziecielewski, I.; Weyher, J.L.; Waluk, J. Detection of hepatitis b virus antigen from human blood: Sers immunoassay in a microfluidic system. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2015, 66, 461–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ai, Y.; Qian, S. Direct numerical simulation of electrokinetic translocation of a cylindrical particle through a nanopore using a poisson-boltzmann approach. Electrophoresis 2011, 32, 996–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamblin, M.N.; Xuan, J.; Maynes, D.; Tolley, H.D.; Belnap, D.M.; Woolley, A.T.; Lee, M.L.; Hawkins, A.R. Selective trapping and concentration of nanoparticles and viruses in dual-height nanofluidic channels. Lab Chip 2010, 10, 173–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hagstrom, A.E.V.; Garvey, G.; Paterson, A.S.; Dhamane, S.; Adhikari, M.; Estes, M.K.; Strych, U.; Kourentzi, K.; Atmar, R.L.; Willson, R.C. Sensitive detection of norovirus using phage nanoparticle reporters in lateral-flow assay. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0126571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Xu, T.; Li, C.W.; Yang, M.S. A microfluidic device with microbead array for sensitive virus detection and genotyping using quantum dots as fluorescence labels. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2010, 25, 2402–2407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, Y.K.; Lee, J.G.; Park, J.M.; Lee, B.S.; Lee, Y.; Ko, C. One-step pathogen specific DNA extraction from whole blood on a centrifugal microfluidic device. Lab Chip 2007, 7, 565–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tseng, Y.T.; Wang, C.H.; Chang, C.P.; Lee, G.B. Integrated microfluidic system for rapid detection of influenza h1n1 virus using a sandwich-based aptamer assay. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 82, 105–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heinze, B.C.; Song, J.Y.; Lee, C.H.; Najam, A.; Yoon, J.Y. Microfluidic immunosensor for rapid and sensitive detection of bovine viral diarrhea virus. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2009, 138, 491–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, B.S.; Lee, J.N.; Park, J.M.; Lee, J.G.; Kim, S.; Cho, Y.K.; Ko, C. A fully automated immunoassay from whole blood on a disc. Lab Chip 2009, 9, 1548–1555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, S.Q.; Li, C.Y.; Lin, B.C.; Qin, J.H. Microvalve and micropump controlled shuttle flow microfluidic device for rapid DNA hybridization. Lab Chip 2010, 10, 2925–2931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, G.D.; Alberts, C.J.; Rodriguez, W.; Toner, M. Concentration and purification of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 virions by microfluidic separation of superparamagnetic nanoparticles. Anal. Chem. 2010, 82, 723–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaytseva, N.V.; Goral, V.N.; Montagna, R.A.; Baeumner, A.J. Development of a microfluidic biosensor module for pathogen detection. Lab Chip 2005, 5, 805–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, J.H.; Super, M.; Yung, C.W.; Cooper, R.M.; Domansky, K.; Graveline, A.R.; Mammoto, T.; Berthet, J.B.; Tobin, H.; Cartwright, M.J.; et al. An extracorporeal blood-cleansing device for sepsis therapy. Nat. Med. 2014, 20, 1211–1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shafiee, H.; Asghar, W.; Inci, F.; Yuksekkaya, M.; Jahangir, M.; Zhang, M.H.; Durmus, N.G.; Gurkan, U.A.; Kuritzkes, D.R.; Demirci, U. Paper and flexible substrates as materials for biosensing platforms to detect multiple biotargets. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 8719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, G.G.; Makarov, D.; Melzer, M.; Si, W.P.; Yan, C.L.; Schmidt, O.G. A highly flexible and compact magnetoresistive analytic device. Lab Chip 2014, 14, 4050–4058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, B.K.; Ahn, J.H. Flexible and stretchable oxide electronics. Adv. Electron. Mater. 2016, 2, 1600105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Detection Unit | Target(s) [Ref] | Process Time | Sample Size | Limit of Detection (LOD) | Commercial LOD |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HBsAg [20] | 95 min | 10 μL | 104 fg/μL | 0.7 fg/μL (2) | |
| [mass] | H1N1, H5N1, H7N9 [24] | 120 min | n/a | 1 fg/μL | |
| H1N1 [25] | 30 s (3) | 0.1 mL | 2 × 10−3 fg/μL | ||
| RSV-A2, RSV-dG [27] | 30–60 min | n/a | 1 vp (4) | 102 vp/μL (5) | |
| [viral particles (vp)] | HSV-1 [21] | 45 min | 1 μL | 10 vp/μL | |
| HSV-1, ADV-5 [17] | 120 min | 100 μL | 1 vp/μL (6) | ||
| HCV RNA [18] | 30 min | 7 μL | 7.14 vp/μL | ||
| [plaque forming units (pfu)] | F-RNA coliphages: MS2, QB, GA, HB-P22 [16] | 180 min | 140 μL | 10−3 pfu/μL (MS2, QB) 10−4 pfu/μL (GA, HB-P22) | 10 pfu (7) |
| VSV-pseudotyped Ebola, Vaccinia virus [26] | 90 min | n/a | 104 pfu/μL (8) | ||
| [Hemagglutination Units (HAU)] | H3N2 [15] | 35 min | 200 μL | 0.04 HAU/μL | 0.1 HAU/μL (9) |
| H3N1 [19] | n/a | 60 μL | 2 × 10−4 HAU/μL | ||
| [50% Tissue Culture Infective Dose (TCID)] | H1N1, H3N2 [13] | 40 min | 90 μL | 102 TCID50/mL | 200 TCID50/mL (10) |
| [International Units (IU)] | α-HBsAg IgG antibodies [22] | 5 min | 25 μL | 3 × 10−3 IU/mL | 56 IU/mL (11) |
| n/a | Influenza B/Victoria [14] | 10 min | n/a | 0.09 vol % | n/a |
| Target(s) [Ref] | Sample Size | Sample Type | Volumetric Concentration Factor |
|---|---|---|---|
| somatic coliphage [49] | 400 mL | seawater | 80 |
| white spot syndrome virus [45] | 60 mL | shrimp tissue | 12 |
| Ostreid herpesvirus-1 [50] | 15 mL | seawater | 15 |
| Semliki Forest virus [43] | 29 mL | pure | 4.1 |
| VSV-G [51] | 30 mL | pure | 5 (1) |
| Salmon amaemia virus [52] | 0.2 mL | pure | n/a |
| HIV gag baculovirus [44] | 2 L | pure | 6 |
| P22 Bacteriophage [53] | 1 L | waste water | 4 |
| MS2, human adenovirus, murine norovirus [48] | 10 L | pure | 104 |
| H1N1 [47] | 585 mL (2) | pure | 5.3 |
| MS2, mouse adenovirus [54] | 40 L | spiked tap water | 1.3 × 104 |
| Detection Unit | Target(s) [Ref] | Process Time | Sample Size | Limit of Detection (LOD) | Commercial LOD |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [mass] | hemagglutinin (HA1, HA2) [72] | 22 min | 20 μL | 7 ng/μL (2),(3) | 0.7 fg/μL |
| [viral particles] | porcine parvovirus (PPV), poliovirus [73] | n/a | 1–10 mL | 102 vp/mL | 105 vp/mL |
| SV-40, HSV-1, PPV, poliovirus, HAV, HBV, HCV [74] | 15 min | 1 mL | 103 vp/mL(2) | ||
| T7 bacteriophage [63] | 5 min. (4) | 2 μL | 104 vp/mL | ||
| Influenza A [75] | 10–20 min | n/a | 1 vp | ||
| Influenza virus [76] | 5 min (5) | n/a | 1 vp | ||
| [plaque forming units] | Dengue virus (DENV) [58] | 10.5 min | 25 μL | 10−1 pfu/μL | 10 pfu |
| [genomic copies] | West Nile virus, Saint Louis encephalitis virus, JEV, Western/Eastern equine encephalomyelitis viruses [77] | n/a | 5 μL | 102 RNA copies/μL (2) | 8–12 genomic copies (6) |
| SARS, DENV, JEV, Influenza A, human adenovirus [78] | 20 min | 1 μL | 6 × 102 DNA copies/μL (7) | ||
| [moles] | Japanese encephalitis virus (JEV) [79] | n/a | 2 mL | 0.32 nM | n/a |
| n/a | Influenza A (H7N7) [80] | 320 s | 1 μL | n/a | n/a |
| Detection Unit | Target(s) | Process Time | Sample Size | Sample Type | Limit of Detection (LOD) | Commercial LOD |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [mass] | HBV [90] | 60 min. | n/a | plasma, serum | 0.2 fg/μL (1) | 0.7 fg/μL |
| Dengue Virus [89] | 20 min | 400 μL | saliva | 20 fg/μL | ||
| [viral particles] | Norovirus [93] | n/a | 100 μL | pure | 104 vp/μL | 102 vp/μL |
| HSV-1, HBV [92] | 42 s (2) | 200 μL | pure | 107 vp/μL (3) | ||
| HBV [94] | n/a | 50 μL | serum | 1 vp/μL | ||
| [genomic copies] | HBV, E. coli [95] | 12 min | 100 μL | whole blood | 10 DNA copies/μL | 8–12 genomic copies |
| [Hemagglutination Units] | Influenza A [4] | 15 min | 25 μL | whole blood, serum, saliva | 2 × 10−5 HAU/μL | 0.1 HAU/μL |
| H1N1 [96] | 30 min | 10 μL | pure | 3.2 × 10−3 HAU/μL | ||
| [50% Tissue Culture Infective Dose] | Bovine viral diarrhea virus (BVDB) [97] | <5 min | 20 μL | pure | 10 TCID50/mL | 200 TCID50/mL |
| [International Units] | HBV [98] | <30 min | 150 μL | whole blood | 8.6 × 10−3 IU/mL | 56 IU/mL |
| [moles] | Dengue Virus DNA (serotypes I, II, III, IV) [99] | 90 s | 1 μL | pure | 100 pM | n/a |
| n/a | HIV-1 [100] | 40 min | 1 mL (4) | plasma | n/a | n/a |
| Dengue Virus RNA [101] | 15 min | n/a | pure | n/a | n/a |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dincau, B.M.; Lee, Y.; Kim, J.-H.; Yeo, W.-H. Recent Advances in Nanoparticle Concentration and Their Application in Viral Detection Using Integrated Sensors. Sensors 2017, 17, 2316. https://doi.org/10.3390/s17102316
Dincau BM, Lee Y, Kim J-H, Yeo W-H. Recent Advances in Nanoparticle Concentration and Their Application in Viral Detection Using Integrated Sensors. Sensors. 2017; 17(10):2316. https://doi.org/10.3390/s17102316
Chicago/Turabian StyleDincau, Brian M., Yongkuk Lee, Jong-Hoon Kim, and Woon-Hong Yeo. 2017. "Recent Advances in Nanoparticle Concentration and Their Application in Viral Detection Using Integrated Sensors" Sensors 17, no. 10: 2316. https://doi.org/10.3390/s17102316
APA StyleDincau, B. M., Lee, Y., Kim, J. -H., & Yeo, W. -H. (2017). Recent Advances in Nanoparticle Concentration and Their Application in Viral Detection Using Integrated Sensors. Sensors, 17(10), 2316. https://doi.org/10.3390/s17102316