Verification of Non-Invasive Blood Glucose Measurement Method Based on Pulse Wave Signal Detected by FBG Sensor System
Abstract
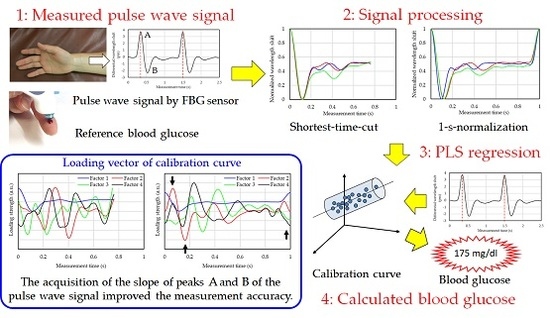
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Design
2.1. FBG Sensor System
2.2. Pulse Wave Signal and Blood Glucose Level Measurement
2.3. Blood Glucose Level Calculation Method
- Division of the measured pulse wave signal at each peak by a 1-pulse pulse wave.
- Averaging of a plurality of divided 1-pulse pulse wave signals.
- Normalization of the vertical axis (wavelength shift) of the 1-pulse pulse wave.
- Normalization of the horizontal axis (measurement time) of the 1-pulse pulse wave.
3. Experimental Results and Discussion
3.1. Reference Blood Glucose Levels and Pulse Wave Signal of Each Subject
3.2. Blood Glucose Level Calculated by Calibration Curve
3.3. Adequacy of Non-Invasive Blood Glucose Measurement
- More glucose was contained in blood after a change in the blood glucose level; consequently, the blood flow changed because of a change in blood viscosity.
- Since glucose is sent into the body, the blood vessels expanded at the time of hyperglycemia, and the blood flow changed.
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Ethical Statement
References
- Ferrante do Amaral, C.E.; Wolf, B. Current development in non-invasive glucose monitoring. Med. Eng. Phys. 2008, 30, 541–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliver, N.S.; Toumazou, C.; Cass, A.E.; Johnston, D.G. Glucose sensors: A review of current and emerging technology. Diabet. Med. 2009, 26, 197–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robinson, M.R.; Eaton, R.P.; Haaland, D.M.; Koepp, G.W.; Thomas, E.V.; Stallard, B.R.; Robinson, P.L. Noninvasive glucose monitoring in diabetic patients: A preliminary evaluation. Clin. Chem. 1992, 38, 1618–1622. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Heise, H.M.; Marbach, R.; Janatsch, G.; Kruse-Jarres, J.D. Multivariate determination of glucose in whole blood by attenuated total reflection infrared spectroscopy. Anal. Chem. 1989, 61, 2009–2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malin, S.F.; Ruchti, T.L.; Blank, T.B.; Thennadil, S.N.; Monfre, S.L. Noninvasive prediction of glucose by near-infrared diffuse reflectance spectroscopy. Clin. Chem. 1999, 45, 1651–1658. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Buford, R.J.; Green, E.C.; McClung, M.J. A microwave frequency sensor for non-invasive blood glucose measurement. In Proceedings of the 2008 IEEE Sensors Applications Symposium (SAS-2008), Atlanta, GA, USA, 12–14 February 2008; pp. 14–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guarin, G.; Hofmann, M.; Weigel, R.; Fischer, G.; Kissinger, D. Determination of sugar concentration in aqueous solutions using ultra-wideband microwave impedance spectroscopy. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE MTT-S International Microwave Symposium Digest (MTT), Seattle, WA, USA, 2–7 June 2013; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savage, M.B.; Kun, S.; Harjunmaa, H.; Peura, R.A. Development of a non-invasive blood glucose monitor: Application of artificial neural networks for signal processing. In Proceedings of the IEEE 26th Annual Northeast Bioengineering Conference, Storrs, CT, USA, 9 April 2000; pp. 29–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujita, K.; Tamura, K.; Kaneko, W.; Morikawa, T.; Nguyen, L.T.; Ishizawa, H.; Toba, E. Noninvasive measurement of blood glucose based on optical sensing and internal standard method. In Proceedings of the 2005 IEEE International and Measurement Technology Conference (IMTC), Ottawa, OT, Canada, 16–19 May 2005; pp. 1433–1437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spegazzini, N.; Barman, I.; Dingori, N.C.; Pandey, R.; Soares, J.S.; Ozaki, Y.; Dasari, R.R. Spectroscopic approach for dynamic bioanalyte tracking with minimal concentration information. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 7013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pandey, R.; Paidi, S.K.; Valdez, T.A.; Zhang, C.; Spegazzini, N.; Dasari, R.R.; Barman, I. Noninvasive monitoring of blood glucose with Raman Spectroscopy. Acc. Chem. Res. 2017, 50, 264–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katsuragawa, Y.; Ishizawa, H. Non-invasive blood pressure measurement by pulse wave analysis using FBG sensor. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Instrumentation and Measurement Technology Conference (I2MTC), Pisa, Italy, 11–14 May 2015; pp. 511–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sano, Y.; Yoshino, T. Fast optical wavelength interrogator employing arrayed waveguide grating for distributed fiber Bragg grating sensors. J. Lightwave Technol. 2003, 21, 132–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martens, H.; Neas, T. Multivariate Calibration; John Wiley & Sons: Montgomery, NY, USA, 1989; pp. 116–165. [Google Scholar]
- Parkes, J.L.; Pardo, S.; Slatin, S.L.; Ginsberg, B.H. A new consensus error grid to evaluate the clinical significance of inaccuracies in the measurement of blood glucose. Diabetes Care 2000, 23, 1143–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clarke, W.L.; Cox, D.; Gonder-Frederick, L.A.; Carter, W.; Pohl, S.L. Evaluating clinical accuracy of systems for self-monitoring of blood glucose. Diabetes Care 1987, 10, 622–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahn, J.M. Wave detection in acceleration plethysmogram. Healthc. Inf. Res. 2015, 21, 111–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elgendi, M.; Norton, I.; Brearley, M.; Abbott, D.; Schuurmans, D. Detection of A and B Waves in the Acceleration Photoplethysmogram. BioMed. Eng. Online 2014, 13, 139–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Funamoto, K.; Hayase, T.; Shirai, A.; Saijo, Y.; Yambe, T. Fundamental study of ultrasonic-measurement-integrated simulation of real blood flow in the aorta. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 2005, 33, 413–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Funamoto, K.; Hayase, T. Reproduction of pressure field in ultrasonic-measurement-integrated simulation of blood flow. Int. J. Numer. Methods Biomed. Eng. 2013, 29, 726–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kadowaki, H.; Hayase, T.; Funamoto, K.; Sone, S.; Shimazaki, T.; Jibiki, T.; Miyama, K. Blood flow analysis in carotid artery bifurcation by two-dimensional ultrasonic-measurement-integrated simulation. J. Biomech. Sci. Eng. 2015, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawamura, M.; Ishizawa, H.; Sato, S.; Koyama, S. Application to vital signs by fiber Bragg grating sensing. In Proceedings of the SICE Annual Conference 2011 Final Program and Papers, Tokyo, Japan, 13–18 September 2011; pp. 2702–2704. [Google Scholar]
- Koyama, S.; Ishizawa, H.; Fujimoto, K.; Chino, S.; Kobayashi, Y. Influence of individual differences on the calculation method for FBG-type blood pressure sensors. Sensors 2017, 17, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koyama, S.; Ishizawa, H.; Sakaguchi, A.; Hosoya, S.; Kawamura, T. Influence on calculated blood pressure of measurement posture for the development of wearable vital sign sensors. J. Sens. 2017, 2017, 8916596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]









| Subject (Gender) | Number of Measurements | Blood Glucose Level (mg/dL) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Maximum | Minimum | Average | ||
| Calibration Data Set | ||||
| A (male) | 50 | 178 | 80 | 119 |
| B (male) | 50 | 232 | 93 | 143 |
| C (male) | 50 | 176 | 89 | 127 |
| D (male) | 50 | 207 | 83 | 138 |
| Validation Data Set | ||||
| A (male) | 10 | 153 | 82 | 113 |
| B (male) | 10 | 188 | 97 | 138 |
| C (male) | 10 | 164 | 89 | 115 |
| D (male) | 10 | 202 | 85 | 129 |
| Subject | A | B | C | D | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Processing Method | Shortest | 1-s | Shortest | 1-s | Shortest | 1-s | Shortest | 1-s | |
| Calibration result | SEC (mg/dL) | 17 | 15 | 34 | 21 | 15 | 14 | 33 | 19 |
| r | 0.67 | 0.77 | 0.58 | 0.86 | 0.84 | 0.87 | 0.44 | 0.86 | |
| factors | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | |
| Validation result | SEP (mg/dL) | 20 | 10 | 23 | 16 | 7 | 12 | 26 | 14 |
| A-zone (%) | 60 | 80 | 80 | 80 | 100 | 100 | 50 | 90 | |
| B-zone (%) | 40 | 20 | 20 | 20 | 0 | 10 | 50 | 10 | |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kurasawa, S.; Koyama, S.; Ishizawa, H.; Fujimoto, K.; Chino, S. Verification of Non-Invasive Blood Glucose Measurement Method Based on Pulse Wave Signal Detected by FBG Sensor System. Sensors 2017, 17, 2702. https://doi.org/10.3390/s17122702
Kurasawa S, Koyama S, Ishizawa H, Fujimoto K, Chino S. Verification of Non-Invasive Blood Glucose Measurement Method Based on Pulse Wave Signal Detected by FBG Sensor System. Sensors. 2017; 17(12):2702. https://doi.org/10.3390/s17122702
Chicago/Turabian StyleKurasawa, Shintaro, Shouhei Koyama, Hiroaki Ishizawa, Keisaku Fujimoto, and Shun Chino. 2017. "Verification of Non-Invasive Blood Glucose Measurement Method Based on Pulse Wave Signal Detected by FBG Sensor System" Sensors 17, no. 12: 2702. https://doi.org/10.3390/s17122702
APA StyleKurasawa, S., Koyama, S., Ishizawa, H., Fujimoto, K., & Chino, S. (2017). Verification of Non-Invasive Blood Glucose Measurement Method Based on Pulse Wave Signal Detected by FBG Sensor System. Sensors, 17(12), 2702. https://doi.org/10.3390/s17122702