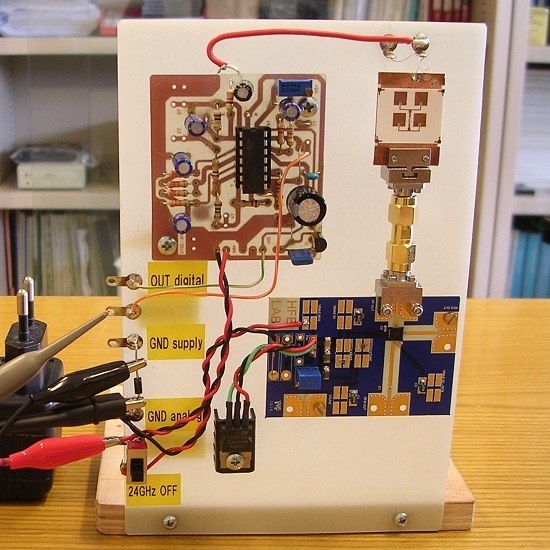
A 24-GHz Front-End Integrated on a Multilayer Cellulose-Based Substrate for Doppler Radar Sensors †
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Basic Theory and Front-End Sensitivity
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Adhesive Copper-Laminate Process
3.2. Fabrication of The Multilayer Cellulose-Based Front-End
3.3. Building-Block Design and Characterization
4. Results
4.1. People Detection
5. Discussion
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A.
Appendix A.1. Via-Through Optimization

Appendix A.2. Branch-Line Coupler

Appendix A.3. Patch Array Antenna
Appendix A.4. Single-Balanced Diode Mixer

References
- Manyika, J.; Chui, M.; Bughin, J.; Dobbs, R.; Bisson, P.; Marrs, A. How the Internet of Things is More Like the Industrial Revolution than the Digital Revolution; MGI Report; McKinsey & Company: New York, NY, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Evans, D. The Internet of Things: How the Next Evolution of the Internet is Changing Everything; CISCO White Papers; Cisco Systems: San Francisco, CA, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Savage, N. All-natural electronics. IEEE Spectr. 2015, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steckl, A.J. Circuits on Cellulose. IEEE Spectr. 2013, 50, 48–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Rida, A.; Vyas, R.; Tentzeris, M.M. RFID Tag and RF Structures on a Paper Substrate Using Inkjet-Printing Technology. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 2007, 55, 2894–2901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Georgiadis, A.; Collado, A.; Tentzeris, M. An Inkjet-Printed Solar-Powered Wireless Beacon on Paper for Identification and Wireless Power Transmission Applications. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 2012, 60, 4178–4186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Cook, B.; Le, T.; Cooper, J.; Lee, H.; Lakafosis, V.; Vyas, R.; Moro, R.; Bozzi, M.; Georgiadis, A.; et al. Inkjet-Printed Antennas, Sensors and Circuits on Paper Substrate. IET Microw. Antennas Propag. 2013, 7, 858–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orecchini, G.; Palazzari, V.; Rida, A.; Alimenti, F.; Tentzeris, M.M.; Roselli, L. Design and Fabrication of Ultra-Low Cost Radio Frequency Identification Antennas and Tags Exploiting Paper Substrates and Inkjet Printing Technology. IET Microw. Antennas Propag. 2011, 5, 993–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, Y.; Chang, T.; Yao, C.; Zheng, Q.; Yang, V.; Mi, H.; Kim, M.; Cho, S.; Park, D.; Jiang, H.; et al. High-performance green flexible electronics based on biodegradable cellulose nanofibril. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Droitcour, A.D.; Boric-Lubecke, O.; Lubecke, V.M.; Lin, J.; Kovacs, G.T.A. Range Correlation and I/Q Performance Benefits in Single-Chip Silicon Doppler Radars for Noncontact Cardiopulmonary Monitoring. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 2004, 52, 838–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ser, W.; Yu, J.; Guo, X.; Zhang, J.; Ong, M.E.H. Noncontact Heart Rate Measurement Using a 24 GHz Doppler Radar. In Proceedings of the IEEE MTT-S International Microwave Workshop Series on RF and Wireless Technologies for Biomedical and Healthcare Applications (IMWS-BIO), Singapore, 9–11 December 2013; pp. 1–3. [Google Scholar]
- Roselli, L.; Alimenti, F.; Comez, M.; Palazzari, V.; Placentino, F.; Porzi, N.; Scarponi, A. A Cost Driven 24 GHz Doppler Radar Sensor Development for Automotive Applications. In Proceedings of the 35th European Microwave Conference, Paris, France, 4–6 October 2005; pp. 2059–2062. [Google Scholar]
- Rohling, H.; Heuel, S.; Ritter, H. Pedestrian Detection Procedure Integrated into an 24 GHz Automotive Radar. In Proceedings of the IEEE Radar Conference, Washington, DC, USA, 10–14 May 2010; pp. 1229–1232. [Google Scholar]
- Gu, C. Short-Range Noncontact Sensors for Healthcare and Other Emerging Applications: A Review. Sensors 2016, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazlouman, S.J.; Tavakolin, K.; Mahanfar, A.; Kaminska, B. Contact-less Assessment of In-Vivo Body Signals Using Microwave Doppler Radar. Biomed. Eng. 2009, 13, 239–260. [Google Scholar]
- Silva Girão, P.; Postolache, O.; Postolache, G.; Ramos, P.M.; Dias Pereira, J.M. Microwave Doppler radar in unobtrusive health monitoring. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2015, 588, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Pfanne, F.; Maier, J.; Allmendinger, T.; Flohr, T.; Kachelriess, M. Monitoring internal organ motion with continuous wave radar in CT. Med. Phys. 2013, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baratchi, M.; Meratnia, N.; Havinga, P.; Skidmore, A.; Toxopeus, B. Sensing Solutions for Collecting Spatio-Temporal Data for Wildlife Monitoring Applications: A Review. Sensors 2013, 13, 6054–6088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pasquali, V.; Scannapieco, E.; Renzi, P. Validation of a Microwave Radar System for the Monitoring of Locomotor Activity in Mice. J. Circadian Rhythm. 2006, 4, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Division, E.M.W. Doppler Radar Front-End Modules at 24 GHz and 94 GHz. Available online: http://www.elva-1.com/products/a40055 (accessed on 10 September 2017).
- Zito, D.; Pepe, D.; Mincica, M.; Zito, F.; Tognetti, A.; Lanatà, A.; Rossi, D.D. SoC CMOS UWB Pulse Radar Sensor for Contactless Respiratory Rate Monitoring. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Circuits Syst. 2011, 5, 503–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ViaSat. Single Chip 24 GHz Radar Transceiver. Available online: https://www.viasat.com/files/assets/24GHz_RADAR_chip_107_web.pdf (accessed on 10 September 2017).
- Lin, C.H.; Wu, Y.S.; Yeh, Y.L.; Weng, S.H.; Chen, G.Y.; Shen, C.H.; Chang, H.Y. A 24-GHz Highly Integrated Transceiver in 0.5-μm E/D-PHEMT Process for FMCW Automotive Radar Applications. In Proceedings of the Asia-Pacific Microwave Conference (APMC), Yokohama, Japan, 7–10 December 2010; pp. 512–515. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, J.G.; Sim, S.H.; Cheon, S.; Hong, S. 24 GHz Circularly Polarized Doppler Radar with a Single Antenna. In Proceedings of the 35th European Microwave Conference, Paris, France, 3–7 October 2005; pp. 1383–1386. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, H.L.; Lim, W.G.; Oh, K.S.; Yu, J.W. 24 GHz Balanced Doppler Radar Front-End With Tx Leakage Canceller for Antenna Impedance Variation and Mutual Coupling. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2011, 59, 4497–4504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, Y.; Kim, S.D.; Lee, J. Design and Implementation of a Hybrid Digital and RF Front-End Module for 24-GHz Intelligent Transport System Pulse-Doppler Radar. Microw. Opt. Technol. Lett. 2013, 55, 1631–1638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.S.; Kim, C.Y. An LTCC Multilayer Packaged 24-GHz Short-Range Radar with an Embedded Tx Leakage Canceller. Microw. Opt. Technol. Lett. 2014, 56, 671–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winkler, V. Range Doppler Detection for automotive FMCW Radars. In Proceedings of the 37th European Microwave Conference, Munich, Germany, 8–12 October 2007; pp. 1445–1448. [Google Scholar]
- IMST GmbH. 24 GHz Radar Sensor. Available online: http://www.imst.de (accessed on 10 September 2017).
- RFbeam Microwave GmbH. K-LC5-High Sensitivity Dual Channel Transceiver. Available online: https://www.rfbeam.ch/files/products/9/downloads/Datasheet_K-LC5.pdf (accessed on 10 September 2017 ).
- Traille, A.; Coustou, A.; Aubert, H.; Kim, S.; Tentzeris, M.M. Monolithic Paper-Based and Inkjet-Printed Technology for Conformal Stepped-FMCW GPR Applications. In Proceedings of the 43rd European Microwave Conference, Nuremberg, Germany, 7–10 October 2013; pp. 13–16. [Google Scholar]
- Alimenti, F.; Palazzi, V.; Mariotti, C.; Virili, M.; Orecchini, G.; Roselli, L.; Mezzanotte, P. 24-GHz CW Radar Front-Ends on Cellulose-Based Substrates: A New Technology for Low-Cost Applications. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Microwave Symposium, Phoenix, AZ, USA, 17–22 May 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Alimenti, F.; Mezzanotte, P.; Dionigi, M.; Virili, M.; Roselli, L. Microwave Circuits in Paper Substrates Exploiting Conductive Adhesive Tapes. IEEE Microw. Wirel. Compon. Lett. 2012, 22, 660–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Battiboia, S.; Caliumi, A.; Catena, S.; Marazzi, E.; Masini, L. Low-Power X-Band Radar for Indoor Burglar Alarms. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 1995, 43, 1710–1714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Droitcour, A.D.; Boric-Lubecke, O.; Kovacs, G.T.A. Signal-to-Noise Ratio in Doppler Radar System for Heart and Respiratory Rate Measurements. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 2009, 57, 2498–2507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, C.; Inoue, T.; Li, C. Analysis and Experiment on the Modulation Sensitivity of Doppler Radar Vibration Measurement. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 2013, 23, 566–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Cattafesta, L.; Li, C.; Lin, J. Analysis of Detection Methods of RF Vibrometer for Complex Motion Measurement. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 2011, 59, 3556–3566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alimenti, F.; Mariotti, C.; Mezzanotte, P.; Dionigi, M.; Virili, M.; Roselli, L. A 1.2 V, 0.9 mW UHF VCO Based on Hairpin Resonator in Paper Substrate and Cu Adhesive Tape. IEEE Microw. Wirel. Compon. Lett. 2013, 23, 214–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mariotti, C.; Alimenti, F.; Mezzanotte, P.; Dionigi, M.; Virili, M.; Giacomucci, S.; Roselli, L. Modeling and Characterization of Copper Tape Microstrips on Paper Substrate and Application to 24 GHz Branch-Line Couplers. In Proceedings of the 43rd European Microwave Conference, Nuremberg, Germany, 7–10 October 2013; pp. 794–797. [Google Scholar]
- Poggiani, M.; Alimenti, F.; Mezzanotte, P.; Virili, M.; Mariotti, C.; Orecchini, G.; Roselli, L. 24-GHz Patch Antenna Array on Cellulose-Based Materials for Green Wireless Internet Applications. IET Sci. Meas. Technol. 2014, 8, 342–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youngwook, K.; Hao, L. Human Activity Classification Based on Micro-Doppler Signatures Using a Support Vector Machine. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2009, 47, 1328–1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dogaru, T.; Le, C. Validation of Xpatch Computer Models for Human Body Radar Signature; Technical Report ARL-TR-4403; Army Research Laboratory: Adelphi, MD, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Fortunity-Guasch, J.; Chareau, J.M. Radar Cross-Section Measurements of Pedestrian Dummies and Humans in the 24/77 GHz Frequency Bands; JCR Scientific and Policy Reports; European Commission: Brussels, Belgium, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Alimenti, F.; Placentino, F.; Battistini, A.; Tasselli, G.; Bernardini, W.; Mezzanotte, P.; Rascio, D.; Palazzari, V.; Leone, S.; Scarponi, A.; et al. A Low-Cost 24 GHz Doppler Radar Sensor for Traffic Monitoring Implemented in Standard Discrete-Component Technology. In Proceedings of the 37th European Microwave Conference, Munich, Germany, 8–12 October 2007; pp. 1441–1444. [Google Scholar]
- Pozar, D.M. Microwave Engineering, 2nd ed.; John Wiley & Sons Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Alimenti, F.; Mezzanotte, P.; Giacomucci, S.; Dionigi, M.; Mariotti, C.; Virili, M.; Roselli, L. 24-GHz Single-Balanced Diode Mixer Exploiting Cellulose-Based Materials. IEEE Microw. Wirel. Compon. Lett. 2013, 23, 596–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






(m) | (Hz) | v (m/s) | (V) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Measurements | Model | |||
| 4 | 195 | 1.2 | 52.6 | 59.7 |
| 6 | 244 | 1.5 | 25.8 | 26.5 |
| 195 | 1.2 | 25.1 | ||
| 8 | 273 | 1.7 | 16.9 | 14.9 |
| Ref. | Technology | (GHz) | Antenna Gain (dBi) | (dBm) | Range (m) | (mm/s) | Size (mm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [10] | 0.25-μm CMOS | 2.4 | 8 | 10 | 0.5 | n.a. | n.a. |
| [25] | RO3003 and FR4 | 24 | 7 | 15 | 2 | 0.5 | |
| [27] | LTCC and FR4 | 24 | n.a. | n.a. | n.a. | 0.8 | |
| [29] | LTCC | 24 | n.a. | 20 (*) | 70 | n.a. | |
| [30] | LTCC | 24 | 8.6 | 15 (*) | 30 | n.a. | |
| [44] | discrete comp. | 24 | 18 | 6 | 300 | n.a. | |
| [32] | cellulose single-layer | 24 | 7 | 3 | n.a. | n.a. | |
| this work | cellulose multilayer | 24 | 7.4 | 7 | 10 | 50 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alimenti, F.; Palazzi, V.; Mariotti, C.; Virili, M.; Orecchini, G.; Bonafoni, S.; Roselli, L.; Mezzanotte, P. A 24-GHz Front-End Integrated on a Multilayer Cellulose-Based Substrate for Doppler Radar Sensors. Sensors 2017, 17, 2090. https://doi.org/10.3390/s17092090
Alimenti F, Palazzi V, Mariotti C, Virili M, Orecchini G, Bonafoni S, Roselli L, Mezzanotte P. A 24-GHz Front-End Integrated on a Multilayer Cellulose-Based Substrate for Doppler Radar Sensors. Sensors. 2017; 17(9):2090. https://doi.org/10.3390/s17092090
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlimenti, Federico, Valentina Palazzi, Chiara Mariotti, Marco Virili, Giulia Orecchini, Stefania Bonafoni, Luca Roselli, and Paolo Mezzanotte. 2017. "A 24-GHz Front-End Integrated on a Multilayer Cellulose-Based Substrate for Doppler Radar Sensors" Sensors 17, no. 9: 2090. https://doi.org/10.3390/s17092090
APA StyleAlimenti, F., Palazzi, V., Mariotti, C., Virili, M., Orecchini, G., Bonafoni, S., Roselli, L., & Mezzanotte, P. (2017). A 24-GHz Front-End Integrated on a Multilayer Cellulose-Based Substrate for Doppler Radar Sensors. Sensors, 17(9), 2090. https://doi.org/10.3390/s17092090