Surface Acoustic Wave Hydrogen Sensors Based on Nanostructured Pd/WO3 Bilayers
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
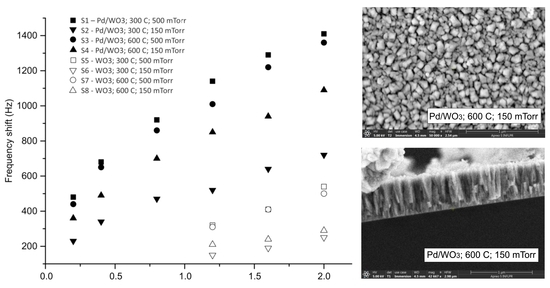
3.1. Film Morphology and Structure
3.2. Sensor Properties
4. Discussion and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hubert, T.; Boon-Brett, L.; Black, G.; Banach, U. Hydrogen sensors—A review. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2011, 157, 329–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kekkonen, V.; Chaudhuri, S.; Clarke, F.; Kaisto, J.; Liimatainen, J.; Kumar Pandian, S.; Piirto, J.; Siltanen, M.; Zolotukhin, A. Picosecond pulsed laser deposition of metal-oxide sensing layers with controllable porosity for gas sensor applications. Appl. Phys. A 2016, 122, 233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.-M.; Chen, Y.-Y.; Felmetsger, V.V.; Senesky, D.G.; Pisano, A.P. AlN/3C-SiC composite plate enabling high-frequency and high-Q micromechanical resonators. Adv. Mater. 2012, 24, 2722–2727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, C.-M.; Yen, T.-T.; Lai, Y.-J.; Felmetsger, V.V.; Hopcroft, M.A.; Kuypers, J.H.; Pisano, A.P. Temperature-compensated aluminum nitride Lamb wave resonators. IEEE Trans. Ultrason. Ferroelectr. Freq. Control 2010, 57, 524–532. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yaacob, M.H.; Breedon, M.; Kalantar-zadeh, K.; Wlodarski, W. Absorption spectral response of nanotextured WO3 thin films with Pt catalyst towards H2. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2009, 137, 115–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaacob, M.H.; Ou, J.Z.; Wlodarski, W.; Kim, C.S.; Lee, J.Y.; Kim, Y.H.; Oh, C.M.; Dhakal, K.P.; Kim, J.Y.; Kang, J.H. Gasochromic Performance of WO3-nanorod Thin Films Fabricated with an ArF Excimer Laser. J. Korean Phys. Soc. 2012, 60, 393–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; Huang, J.; Ong, C.-W. Preparation and structure dependence of H2 sensing properties of palladium-coated tungsten oxide films. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2013, 177, 1062–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garavand, N.T.; Mahdavi, S.M.; Irajizad, A. Pt and Pd as catalyst deposited by hydrogen reduction of metal salts on WO3 films for gasochromic application. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2013, 273, 261–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huotari, j.; Kekkonen, V.; Haapalainen, T.; Leidinger, M.; Sauerwald, T.; Puustinen, J.; Liimatainen, J.; Loppelainen, J. Pulsed laser deposition of metal oxide nanostructures for highly sensitive gas sensor applications. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2016, 236, 978–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakubik, W.P. Investigations of thin film structures of WO3 and WO3 with Pd for hydrogen detection in surface acoustic wave sensor system. Thin Solid Films 2007, 515, 8345–8350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricco, A.J.; Martin, S.J.; Zipperian, T.E. Surface Acoustic Wave gas sensor based on film conductivity changes. Sens. Actuators 1985, 8, 319–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ippolito, S.J.; Kandasamy, S.; Kalentar-Zadeh, K.; Wlodarski, E. Layered SAW hydrogen sensor with modified tungsten trioxide selective layer. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2005, 108, 553–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakubik, W.; Urbanczyk, M.; Maciak, E. SAW hydrogen gas sensor based on WO3 and Pd nanostructures. Procedia Chem. 2009, 1, 200–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hejczyk, T.; Urbanczyk, M. WO3-Pd structure in SAW sensor for Hydrogen Detection. Acta Phys. Pol. A 2011, 120, 616–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viespe, C.; Grigoriu, C. SAW sensor based on highly sensitive nanoporous palladium thin film for hydrogen detection. Microelectron. Eng. 2013, 108, 218–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ou, J.Z.; Yaacob, M.H.; Breedon, M.; Zheng, H.D.; Campbell, J.L.; Latham, K.; du Plessis, J.; Wlodarski, W.; Kalantar-Zadeh, K. In situ Raman spectroscopy of H2 interaction with WO3 films. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2011, 16, 7330–7339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lethy, K.J.; Beena, D.; Vinod Kumar, R.; Mahadevan Pillai, V.P.; Ganesan, V.; Sathe, V.; Phase, D.M. Nanostructured tungsten oxide thin films by the reactive pulsed laser deposition technique. Appl. Phys. A 2008, 91, 637–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lethy, K.J.; Beena, D.; Kumar, R.V.; Pillai, V.P.M.; Ganesan, V.; Sathe, V. Structural, optical and morphological studies on laser ablated nanostructured WO3 thin films. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2008, 254, 2369–2376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buttner, W.J.; Post, M.B.; Burgess, R.; Rivkin, C. An overview of hydrogen safety sensors and requirements. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2011, 36, 2467–2470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viespe, C. Surface Acoustic Wave Sensors based on Nanoporous Films for Hydrogen Detection. Key Eng. Mater. 2014, 605, 331–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakubik, W.; Powroznik, P.; Wrotniak, J.; Krzywiecki, M. Theoretical analysis of acoustoelectrical sensitivity in SAW gas sensors with single and bi-layer structures. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2016, 236, 1069–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viespe, C.; Miu, D. Surface Acoustic Wave Sensor with Pd/ZnO Bilayer Structure for Room Temperature Hydrogen Detection. Sensors 2017, 17, 1529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marcu, A.; Nicolae, I.; Viespe, C. Active surface geometrical control of noise in nanowire-SAW sensors. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2016, 231, 469–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Samples | Unit Cell Parameters | Preferential Orientation | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| a (Å) | b (Å) | c (Å) | β (o) | Vol Å3 | I002/ΣI | I020/ΣI | I200/ΣI | ||
| WO3-Powder | 7.297 | 7.539 | 7.688 | 90.91 | 422.8 | 0.330 | 0.326 | 0.344 | random |
| WO3-Target | 7.290 (4) | 7.537 (6) | 7.682 (6) | 90.88 (1) | 422.03 | 0.280 | 0.450 | 0.270 | random |
| Films | |||||||||
| S1 | 7.25 (2) | 7.52 (1) | 7.69 (2) | 91.17 (4) | 419.04 | 0.371 | 0.298 | 0.330 | random |
| S2 | 7.26 (2) | 7.53 (3) | 7.69 (2) | 91.01 (4) | 420.19 | 0.090 | 0.193 | 0.716 | a-axis |
| S3 | 7.325 (8) | 7.522 (4) | 7.672 (9) | 90.57 (1) | 422.68 | 0.139 | 0.751 | 0.109 | b-axis |
| S4 | 7.359 (5) | 7.541 (6) | 7.733 (6) | 91.42 (2) | 428.44 | 0.792 | 0.155 | 0.052 | c-axis |
| Sensor Type | Sensitivity (Δf/c) (Hz/ppm) | LOD (ppm) |
|---|---|---|
| S1—Pd/WO3; 300 °C; 500 mTorr | 0.13 | 4540 |
| S2—Pd/WO3; 300 °C; 150 mTorr | 0.06 | 9770 |
| S3—Pd/WO3; 600 °C; 500 mTorr | 0.12 | 4710 |
| S4—Pd/WO3; 600 °C; 150 mTorr | 0.1 | 7700 |
| S5—WO3; 300 °C; 500 mTorr | 0.03 | 1120 |
| S6—WO3; 300 °C; 150 mTorr | 0.01 | 2270 |
| S7—WO3; 600 °C; 500 mTorr | 0.03 | 1190 |
| S8—WO3; 600 °C; 150 mTorr | 0.02 | 1490 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Miu, D.; Birjega, R.; Viespe, C. Surface Acoustic Wave Hydrogen Sensors Based on Nanostructured Pd/WO3 Bilayers. Sensors 2018, 18, 3636. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18113636
Miu D, Birjega R, Viespe C. Surface Acoustic Wave Hydrogen Sensors Based on Nanostructured Pd/WO3 Bilayers. Sensors. 2018; 18(11):3636. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18113636
Chicago/Turabian StyleMiu, Dana, Ruxandra Birjega, and Cristian Viespe. 2018. "Surface Acoustic Wave Hydrogen Sensors Based on Nanostructured Pd/WO3 Bilayers" Sensors 18, no. 11: 3636. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18113636
APA StyleMiu, D., Birjega, R., & Viespe, C. (2018). Surface Acoustic Wave Hydrogen Sensors Based on Nanostructured Pd/WO3 Bilayers. Sensors, 18(11), 3636. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18113636