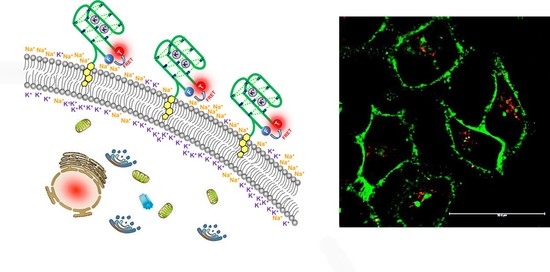
Cholesterol-Bearing Fluorescent G-Quadruplex Potassium Probes for Anchoring at the Langmuir Monolayer and Cell Membrane
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Materials
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. UV-Vis Absorption Studies
2.2.2. Fluorescence Spectra
2.2.3. CD Spectroscopy
2.2.4. Measurements of π-A Isotherms and Fluorescence Spectra at the Monolayer Interface
2.2.5. Introduction of the Probe into Membrane of Living Cell for Fluorescence Imaging Experiment
2.2.6. Fluorescence Imaging Experiments
- (a)
- FAM (fluorescein) channel, ex/em range = 480/510–540 nm.
- (b)
- TAMRA channel, ex/em range = 560/595–630 nm.
- (c)
- FRET channel, ex/em range = 480/595–630 nm.
- (d)
- Hoechst channel, ex/em range = 405/480–500 nm.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Design and Working Principle of Cholesterol-Anchored Fluorescent Oligonucleotide Probes
3.2. Spectral Properties of the Fluorescent Probes in Solution
3.3. Fluorescent Probes at the Water/Monolayer Interface
3.4. Fluorescent Bioimaging of Probes in HeLa Cells
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yeagle, P.L. Cholesterol and the cell membrane. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1985, 822, 267–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maxfield, F.R.; Tabas, I. Role of cholesterol and lipid organization in disease. Nature 2005, 438, 612–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Letsinger, R.L.; Zhang, G.; Sun, D.K.; Ikeuchi, T.; Sarin, P.S. Cholesteryl-conjugated oligonucleotides: Synthesis, properties, and activity as inhibitors of replication of human immunodeficiency virus in cell culture. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1989, 86, 6553–6556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farooqui, F.; Sarin, P.S.; Sun, D.; Letsinger, R.L. Effect of structural variations in cholesteryl-conjugated oligonucleotides on inhibitory activity toward HIV-1. Bioconjug. Chem. 1991, 2, 422–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krieg, A.M.; Tonkinson, J.; Matson, S.; Zhao, Q.; Saxon, M.; Zhang, L.M.; Bhanja, U.; Yakubov, L.; Stein, C.A. Modification of antisense phosphodiester oligodeoxynucleotides by a 5′ cholesteryl moiety increases cellular association and improves efficacy. Proc. Natl. Acid. Sci. USA 1993, 90, 1048–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raouane, M.; Desmaële, D.; Urbinati, G.; Massaad-Massade, L.; Couvreur, P. Lipid Conjugated Oligonucleotides: A Useful Strategy for Delivery. Bioconjug. Chem. 2012, 23, 1091–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, Y.-H.M.; van Lengerich, B.; Boxer, S.G. Effects of linker sequences on vesicle fusion mediated by lipid-anchored DNA oligonucleotides. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 979–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dentinger, P.M.; Simmons, B.A.; Cruz, E.; Sprague, M. DNA-mediated delivery of lipophilic molecules via hybridization to DNA-based vesicular aggregates. Langmuir 2006, 22, 2935–2937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gissot, A.; Camplo, M.; Grinstaff, M.W.; Barthelemy, P. Nucleoside, nucleotide and oligonucleotide based amphiphiles: A successful marriage of nucleic acids with lipids. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2008, 6, 1324–1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- You, M.; Lyu, Y.; Han, D.; Qiu, L.; Liu, Q.; Chen, T.; Sam Wu, C.; Peng, L.; Zhang, L.; Bao, G.; et al. DNA probes for monitoring dynamic and transient molecular encounters on live cell membranes. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2017, 12, 453–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, H.-Y.; Hua, X.-W.; Jia, H.-R.; Liu, P.D.; Gu, N.; Chen, Z.; Wu, F.-G. Enhanced cell membrane enrichment and subsequent cellular internalization of quantum dots via cell surface engineering: Illuminating plasma membranes with quantum dots. J. Mater. Chem. B 2016, 4, 834–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, W.W.; Zhang, L.F. Coating nanoparticles with cell membranes for targeted drug delivery. J. Drug Target. 2015, 23, 619–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, H.; Bai, Y.G.; Wang, J.H.; Deng, Q.R.; Zhu, L.P.; Meng, F.H.; Zhong, Z.Y.; Yin, L.C. Reversibly cross-linked polyplexes enable cancer-targeted gene delivery via self-promoted dna release and self-diminished toxicity. Biomacromolecules 2015, 16, 1390–1400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biffi, G.; Tannahill, D.; McCafferty, J.; Balasubramanian, S. Quantitative visualization of DNA G-quadruplex structures in human cells. Nat. Chem. 2013, 5, 182–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhu, H.; Lewis, F.D. Pyrene excimer fluorescence as a probe for parallel G-quadruplex formation. Bioconjug. Chem. 2017, 18, 1213–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, D.M.; Ma, Y.E.; Guo, J.H.; Yang, W.; Shen, H.X. Fluorescent sensor for monitoring structural changes of G-quadruplexes and detection of potassium ion. Anal. Chem. 2009, 81, 2678–2684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, T.; Wang, E.; Dong, S. G-Quadruplex-based DNAzyme as a sensing platform for ultrasensitive colorimetric potassium detection. Chem. Commun. 2009, 5, 580–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tietz, N.W. Fundamentals of Clinical Chemistry; W.B. Saunders Company: Philadephia, PA, USA, 1976; pp. 875–877. [Google Scholar]
- Nagatoishi, S.; Nojima, T.; Juskowiak, B.; Takenaka, S. A Pyrene-labeled G-quadruplex oligonucleotide as a fluorescence probe for potassium ions detection in biological applications. Angew. Chem. 2005, 44, 5067–5070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagatoishi, S.; Nojima, T.; Galezowska, E.; Gluszynska, A.; Juskowiak, B.; Takenaka, S. Fluorescence energy transfer probes based on the guanine quadruplex formation for the fluorometric detection of potassium ion. Anal. Chim. Acta 2007, 581, 125–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagatoishi, S.; Nojima, T.; Galezowska, E.; Juskowiak, B.; Takenaka, S. G-quadruplex-based FRET probes with the thrombin-binding aptamer (TBA) sequence designed for the efficient fluorometric detection of the potassium ion. ChemBioChem 2006, 7, 1730–1737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, F.; Tang, Y.; Wang, S.; Li, Y.; Zhu, D. Fluorescent amplifying recognition for DNA G-Quadruplex folding with a cationic conjugated polymer: A platform for homogeneous potassium detection. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005, 127, 12343–12346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, D.-M.; Guo, J.-H.; Yang, W.; Ma, Y.-E.; Shen, H.-X. Crystal violet-G-quadruplex complexes as fluorescent sensors for homogeneous detection of potassium ion. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2009, 25, 88–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Świtalska, A.; Juskowiak, B. Effect of Cholesterol Anchoring Group on the Properties of G-Quadruplex-Based FRET Probes for Potassium Ion. Chemosensors 2014, 2, 267–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vance, D.E.; Vance, J.E. Biochemistry of Lipids, Lipoproteins and Membranes, 4th ed.; Elsevier: New York, NY, USA, 2006; ISBN 9780080930169, 9780080574813. [Google Scholar]
- Bock, L.C.; Griffin, L.C.; Latham, J.A.; Vermaas, E.H.; Toole, J.J. Selection of single-stranded DNA molecules that bind and inhibit human thrombin. Nature 1992, 355, 564–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mergny, J.L.; Phan, A.T.; Lacroix, L. Following G-quartet formation by UV-spectroscopy. FEBS Lett. 1998, 435, 74–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kumke, M.U.; Li, G.; McGown, L.B.; Walker, G.T.; Linn, C.P. Hybridization of fluorescein-labeled DNA oligomers detected by fluorescence anisotropy with protein binding enhancement. Anal. Chem. 1995, 67, 3945–3951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fasman, G.D. Handbook of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Nucleic Acids, 3rd ed.; CRC Press: Cleaveland, OH, USA, 1975; p. 589. ISBN 9780849391682. [Google Scholar]
- Viglasky, V.; Bauer, L.; Tluckova, K. Structural features of intra-and intermolecular G-quadruplexes derived from telomeric repeats. Biochemistry 2010, 49, 2110–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clegg, R.M. Fluorescence resonance energy transfer and nucleic acids. Methods Enzymol. 1992, 211, 353–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lakowicz, J.R. Principles of Fluorescence Spectroscopy, 3rd ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2006; pp. 443–453. ISBN 978-0-387-46312-4. [Google Scholar]
- Winnik, F.M. Photophysics of preassociated pyrenes in aqueous polymer solutions and in other organized media. Chem. Rev. 1993, 93, 587–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duhamel, J. New insights in the study of pyrene excimer fluorescence to characterize macromolecules and their supramolecular assemblies in solution. Langmuir 2012, 28, 6527–6538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venner, H. Molekülverbindungen einiger Sterine und Sterinester mit Nitroaromaten. Chem. Ber. 1956, 89, 1634–1641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pagano, B.; Martino, L.; Randazzo, A.; Giancola, C. Stability and binding properties of a modified thrombin binding aptamer. Biophys. J. 2008, 94, 562–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagatoishi, S.; Isono, N.; Tsumoto, K.; Sugimoto, N. Loop residues of thrombin-binding DNA aptamer impact G-quadruplex stability and thrombin binding. Biochimie 2011, 93, 1231–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mergny, J.L.; Maurizot, J.C. Fluorescence resonance energy transfer as a probe for G-quartet formation by a telomeric repeat. ChemBioChem 2001, 2, 124–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swiatkowska, A.; Kosman, J.; Juskowiak, B. FRET study of G-quadruplex forming fluorescent oligonucleotide probes at the lipid monolayer interface. Spectrochim. Acta A 2016, 152, 614–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schultze, P.; Macaya, R.F.; Feigon, J. Three-dimensional solution structure of the thrombin-binding DNA aptamer d(GGTTGGTGTGGTTGG). J. Mol. Biol. 1994, 235, 1532–1547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kankia, B.I.; Marky, L.A. Folding of the thrombin aptamer into a G-quadruplex with Sr2+: Stability, heat, and hydration. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2001, 123, 10799–10804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sastry, M.; Ramakrishnan, V.; Pattarkine, M.; Gole, A.; Ganesh, K.N. Hybridization of DNA by sequential immobilization of oligonucleotides at the air-water interface. Langmuir 2000, 16, 9142–9146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramakrishnan, V.; D’Costa, M.; Ganesh, K.N.; Sastry, M. Effect of salt on the hybridization of DNA by sequential immobilization of oligonucleotides at the air-water interface in the presence of ODA/DOTAP monolayers. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2004, 276, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cardenas, M.; Nylander, T.; Joensson, B.; Lindman, B. The interaction between DNA and cationic lipid films at the air-water interface. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2005, 286, 166–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chatterji, D.; Rajdev, P. Macromolecular recognition at the air-water interface: Application of Langmuir-Blodgett technique. Curr. Sci. 2008, 95, 1226–1236. [Google Scholar]
- Juskowiak, B.; Paczesny, J. The interaction between G-quadruplex-forming oligonucleotide and cationic surfactant monolayer at the air/water interface. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2012, 365, 150–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Juskowiak, B.; Swiatkowska, A. Study of the G-quadruplex–dipalmitoylphosphatidylcholine interactions at the air/water interface. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2013, 417, 250–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, I.; Spence, M. Molecular Probes Handbook: A Guide to Fluorescent Probes and Labeling Technologies, 11st ed.; Life Technologies: Carlsbad, CA, USA, 2010; p. 319. ISBN 0982927916, 978–0982927915. [Google Scholar]








| Abbreviation of Probes | Sequence |
|---|---|
| F-TBA-T | 5′-FAM-GGT TGG TGT GGT TGG ATT T-TAMRA-3′ |
| Ch(F-TBA-T) | 5-Ch-(dT FAM)-TTT AGG TTG GTG TGG TTG GAT TT-TAMRA-3′ |
| py-TBA-py | 5′-py-GGT TGG TGT GGT TGG-py-3′ |
| Ch(py-TBA-py) | 5′-Ch-py-TGG TTG GTG TGG TTG G-py-3′ |
| TBA | 5′-TGG TTG GTG TGG TT GG-3′ |
| Abbreviation of Probes | Tm/K+ (°C) | Tm/Na+ (°C) |
|---|---|---|
| F-TBA-T | 38.0 | 23.0 |
| Ch(F-TBA-T) | 48.0 | 39.0 |
| py-TBA-py | 55.0 | 25.0 |
| Ch(py-TBA-py) | 77.0 | 43.0 |
| TBA | 53.0 | 24.0 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Świtalska, A.; Dembska, A.; Fedoruk-Wyszomirska, A.; Juskowiak, B. Cholesterol-Bearing Fluorescent G-Quadruplex Potassium Probes for Anchoring at the Langmuir Monolayer and Cell Membrane. Sensors 2018, 18, 2201. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18072201
Świtalska A, Dembska A, Fedoruk-Wyszomirska A, Juskowiak B. Cholesterol-Bearing Fluorescent G-Quadruplex Potassium Probes for Anchoring at the Langmuir Monolayer and Cell Membrane. Sensors. 2018; 18(7):2201. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18072201
Chicago/Turabian StyleŚwitalska, Angelika, Anna Dembska, Agnieszka Fedoruk-Wyszomirska, and Bernard Juskowiak. 2018. "Cholesterol-Bearing Fluorescent G-Quadruplex Potassium Probes for Anchoring at the Langmuir Monolayer and Cell Membrane" Sensors 18, no. 7: 2201. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18072201
APA StyleŚwitalska, A., Dembska, A., Fedoruk-Wyszomirska, A., & Juskowiak, B. (2018). Cholesterol-Bearing Fluorescent G-Quadruplex Potassium Probes for Anchoring at the Langmuir Monolayer and Cell Membrane. Sensors, 18(7), 2201. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18072201