Cheeses Made from Raw and Pasteurized Cow’s Milk Analysed by an Electronic Nose and an Electronic Tongue
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Apparatus
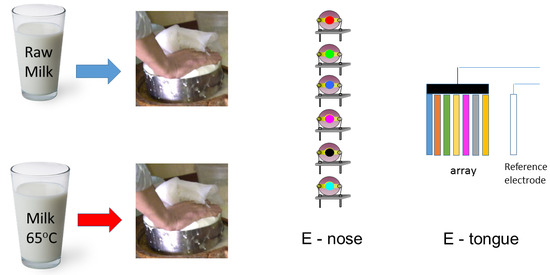
2.1.1. Electronic Nose
2.1.2. Electronic Tongue
2.2. Milk and Rennet
2.3. Cheese Preparation
2.4. Analysis
2.4.1. Electronic Nose Measurements
2.4.2. Electronic Tongue Measurements
2.4.3. Data Processing
2.4.4. Headspace Solid-Phase Micro-Extraction/Gas Chromatography Mass Spectrometry (HS-SPME-GC–MS)
3. Results
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Raynal, K.; Remeuf, F. The effect of heating on physicochemical and renneting properties of milk: A comparison between caprine, ovine and bovine milk. Int. Dairy J. 1998, 8, 695–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schreiber, R.; Hinrichs, J. Rennet coagulation of heated milk concentrates. Le Lait 2000, 80, 33–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noël, Y. Comparison des cinétiques de coagulation enzymatique et mixte du lait. Influence du calcium. Le Lait 1989, 89, 479–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowalchyk, A.W.; Olson, N.F. Milk clotting and curd firmness as affected by type of milk-clotting enzyme, calcium chloride concentration, and season of year. J. Dairy Sci. 1979, 62, 1233–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daviau, C.; Famblard, M.-H.; Pierre, A.; Goudédranche, H.; Maubois, J.-L. Rennet coagulation of skim milk and curd drainage: Effect of pH, casein concentration, ionic strength and heat treatment. Le Lait 2000, 80, 397–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trihaas, J.; Vognsen, L.; Nielsen, P.V. Electronic nose: New tool in modelling the ripening of Danish blue cheese. Int. Dairy J. 2005, 15, 679–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Riordan, P.J.; Delahunty, C.M. Characterisation of commercial Cheddar cheese flavour. 1: Traditional and electronic nose approach to quality assessment and market classification. Int. Dairy J. 2003, 13, 355–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Riordan, P.J.; Delahunty, C.M. Characterisation of commercial Cheddar cheese flavour. 2: Study of Cheddar cheese discrimination by composition, volatile compounds and descriptive flavour assessment. Int. Dairy J. 2003, 13, 371–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cevoli, C.; Cerretani, L.; Gori, A.; Caboni, M.F.; Toschi, T.G.; Fabbri, A. Classification of Pecorino cheeses using electronic nose combined with artificial neural network and comparison with GC-MS analysis of volatile compounds. Food Chem. 2011, 129, 1315–1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haddi, Z.; Annanouch, F.; Amari, A.; Hadoune, A.; Bouchikhi, B. Application of a portable electronic nose device to discriminate and identify cheeses with known percentages of cow’s and goat’s milk. In Proceedings of the IEEE Sensors Conference, Waikoloa, HI, USA, 1–4 November 2010; pp. 771–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bargon, J.; Braschoß, S.; Flörke, J.; Herrmann, U.; Klein, L.; Loergen, J.W.; Lopez, M.; Maric, S.; Parham, A.H.; Piacenza, P.; et al. Determination of the ripening state of Emmental cheese via quartz crystal microbalances. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2003, 95, 6–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pais, V.F.; Oliveira, J.A.B.P.; Gomes, M.T.S.R. An electronic nose based on coated piezoelectric quartz crystals to certify ewes’ cheese and to discriminate between cheese varieties. Sensors 2012, 12, 422–1436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomes, M.T.S.R. Electronic nose in dairy products. In The Electronic Nose and Tongue in Food Science; Rodríguez Méndez, M.L., Ed.; Academic Press: Oxford, UK, 2016; pp. 21–30. ISBN 978-0-12-800243-8. [Google Scholar]
- Winquist, F.; Bjorklund, R.; Krantz-Rulcker, C.; Lundstrom, I.; Ostergren, K.; Skoglund, T. An electronic tongue in the dairy industry. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2005, 111, 299–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciosek, P.; Brudzewski, K.; Wroblewski, W. Milk classification by means of an electronic tongue and Support Vector Machine neural network. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2006, 17, 1379–1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciosek, P.; Wroblewski, W. Miniaturized electronic tongue with an integrated reference microelectrode for the recognition of milk samples. Talanta 2006, 76, 548–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dias, L.A.; Peres, A.M.; Veloso, A.C.A.; Reis, F.S.; Vilas-Boas, M.; Machado, A.A.S.C. An electronic tongue taste evaluation: Identification of goat milk adulteration with bovine milk. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2009, 136, 209–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Paixão, T.R.L.C.; Bertotti, M. Fabrication of disposable voltammetric electronic tongues by using Prussian Blue films electrodeposited onto CD-R gold surfaces and recognition of milk adulteration. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2009, 137, 266–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esbensen, K.; Kirsanov, D.; Legin, A.; Rudnitskaya, A.; Mortensen, J.; Pedersen, J.; Vognsen, L.; Makarychev-Mikhailov, S.; Vlasov, Y. Fermentation monitoring using multisensor systems: Feasibility study of the electronic tongue. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2004, 378, 391–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lipkowitz, J.B.; Ross, C.F.; Diako, C.; Smith, D.M. Discriminating aging and protein-to-fat ratio in Cheddar cheese using sensory analysis and a potentiometric electronic tongue. J. Dairy Sci. 2018, 101, 1990–2004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buratti, S.; Sinelli, N.; Bertone, E.; Venturello, A.; Casiraghi, E.; Geobaldo, F. Discrimination between washed Arabica, natural Arabica and Robusta coffees by using near infrared spectroscopy, electronic nose and electronic tongue analysis. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2015, 95, 2192–2200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ciosek, P.; Brzozka, Z.; Wroblewski, W.; Martinelli, E.; Di Natale, C.; D’Amico, A. Direct and two-stage data analysis procedures based on PCA, PLS-DA and ANN for ISE-based electronic tongue-Effect of supervised feature extraction. Talanta 2005, 67, 590–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, M.; Wang, M.; Wang, J.; Li, D. Comparison of random forest, support vector machine and back propagation neural network for electronic tongue data classification: Application to the recognition of orange beverage and Chinese vinegar. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2013, 177, 970–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Güney, S.; Atasoy, A. Multiclass classification of n-butanol concentrations with k-nearest neighbor algorithm and support vector machine in an electronic nose. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2012, 166–167, 721–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szulczyński, B.; Armiński, K.; Namieśnik, J.; Gębicki, J. Determination of odour interactions in gaseous mixtures using electronic nose methods with artificial neural networks. Sensors 2018, 18, 519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farinha, A.S.F.; Calvete, M.J.F.; Paz, F.A.A.; Tomé, A.C.; Cavaleiro, J.A.S.; Sessler, J.L.; Tomé, J.P.C. Octatosylaminophthalocyanine: A reusable chromogenic anion chemosensor. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2014, 201, 387–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bruckenstein, S.; Shay, M. Experimental aspects of the use of the quartz crystal microbalance in solution. Electrochim. Acta 1985, 30, 1295–1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legin, A.; Rudnitskaya, A.; Vlasov, Y. Electronic tongues: New analytical perspective for chemical sensors. Compr. Anal. Chem. 2003, 39, 437–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawliszyn, J. Theory of Solid-Phase Microextraction. J. Chromatogr. Sci. 2000, 38, 270–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vas, G.; Vékey, K. Solid-phase microextraction: A powerful sample preparation tool prior to mass spectrometric analysis. J. Mass Spectrom. 2004, 3, 233–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Rosa, A.R.; Leone, F.; Cheli, F.; Chiofalo, V. Fusion of electronic nose, electronic tongue and computer vision for animal source food authentication and quality assessment—A review. J. Food Eng. 2017, 210, 62–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Rosa, A.R.; Leone, F.; Scattareggia, C.; Chiofalo, V. Botanical origin identification of Sicilian honeys based on artificial senses and multi-sensor data fusion. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2018, 244, 117–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudnitskaya, A.; Kirsanov, D.; Legin, A.; Beullens, K.; Lammertyn, J.; Nicolai, B.M.; Irudayaraj, J. Analysis of apples varieties—Comparison of electronic tongue with different analytical techniques. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2006, 116, 23–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]













| Peak Number | Compound |
|---|---|
| 1 | Acetaldehyde |
| 2 | Ethanol |
| 3 | Acetone |
| 4 | 2,3-Butanedione |
| 5 | Hexane |
| 6 | Chloroform |
| 7 | 3-Methylbutanal |
| 8 | Branched alkane |
| 9 | 3-Hydroxybutanone-2 |
| 10 | 3-Methylbutanol-1 |
| 11 | Toluene |
| 12 | Acetic acid |
| 13 | Ethyl acetate |
| 14 | Propanoic acid ethyl ester |
| 15 | 2,3-Butanediol |
| 16 | 3-Methylbutanol acetate |
| 17 | 2-Methylpropanol-1 |
| Data | Whey | Fresh Cheese Curd |
|---|---|---|
| Raw correctly classified | 12 | 10 |
| Raw wrongly classified | 0 | 1 |
| Pasteurized correctly classified | 11 | 9 |
| Pasteurized wrongly classified | 1 | 2 |
| Correct classifications, % | 96% | 84% |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Valente, N.I.P.; Rudnitskaya, A.; Oliveira, J.A.B.P.; Gaspar, E.M.M.; Gomes, M.T.S.R. Cheeses Made from Raw and Pasteurized Cow’s Milk Analysed by an Electronic Nose and an Electronic Tongue. Sensors 2018, 18, 2415. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18082415
Valente NIP, Rudnitskaya A, Oliveira JABP, Gaspar EMM, Gomes MTSR. Cheeses Made from Raw and Pasteurized Cow’s Milk Analysed by an Electronic Nose and an Electronic Tongue. Sensors. 2018; 18(8):2415. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18082415
Chicago/Turabian StyleValente, Nuno I. P., Alisa Rudnitskaya, João A. B. P. Oliveira, Elvira M. M. Gaspar, and M. Teresa S. R. Gomes. 2018. "Cheeses Made from Raw and Pasteurized Cow’s Milk Analysed by an Electronic Nose and an Electronic Tongue" Sensors 18, no. 8: 2415. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18082415
APA StyleValente, N. I. P., Rudnitskaya, A., Oliveira, J. A. B. P., Gaspar, E. M. M., & Gomes, M. T. S. R. (2018). Cheeses Made from Raw and Pasteurized Cow’s Milk Analysed by an Electronic Nose and an Electronic Tongue. Sensors, 18(8), 2415. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18082415