Integrated Performance Evaluation of the Smart Body Area Networks Physical Layer for Future Medical and Healthcare IoT †
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- Ultra-low power consumption
- Coexistence with other systems
- Optimum control of QoS.
2. Summary of the SmartBAN PHY
2.1. Frequency Spectrum
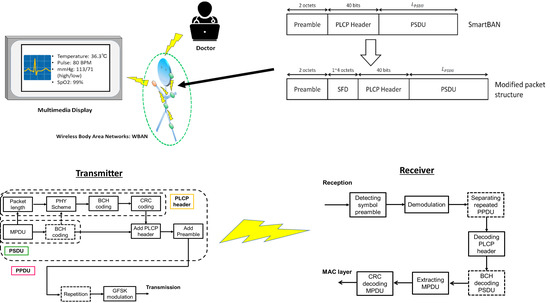
2.2. Packet Structure
2.3. Modulation and Error Controlling
3. Modified Preamble Structure and System Model
3.1. Proposed Packet Structure
3.2. System Model
4. Integrated Performance Evaluation
4.1. Simulation Parameter
4.2. Results of Preamble Detection
4.3. Results of Integrated Performance Evalution
5. Discussion about Optimum LPSDU
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Spinsante, S.; Gambi, E. Remote health monitoring for elderly through interactive television. BioMed. Eng. OnLine 2012, 11, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costa, C.R.; Anido-Rifón, L.E.; Fernández-Iglesias, M.J. An Open Architecture to Support Social and Health Services in a Smart TV Environment. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inform. 2017, 21, 549–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, M.; Gonzalez, S.; Vasilakos, A.V.; Cao, H. VCM Leung, Body Area Networks: A Survey. Mob. Netw. Appl. 2010, 16, 171–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavallari, R.; Martelli, F.; Rosini, R.; Buratti, C.; Verdone, R. A Survey on Wireless Body Area Networks: Technologies and Design Challenges. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2014, 16, 1635–1657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Movassaghi, S.; Abolhasan, M.; Lipman, J.; Smith, D.; Jamalipour, A. Wireless Body Area Networks: A Survey. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2014, 16, 1658–1686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayajneh, T.; Almashaqbeh, G.; Ullah, S.; Vasilakos, A.V. A survey of wireless technologies coexistence in WBAN: Analysis and open research issues. Wirel. Netw. 2014, 20, 2165–2199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fortino, G.; Fatta, G.D.; Pathan, M.; Vasilakos, A.V. Cloud-assisted body area networks: State-of-the-art and future challenges. Wirel. Netw. 2014, 20, 1925–1938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IEEE Standard for Information Technology—Telecommunications and Information Exchange between Systems—Local and Metropolitan Area Networks-Specific Requirements: Part 15.6: Wireless Medium Access Control (MAC) and Physical Layer (PHY) Specifications for Wireless Personal Area Networks (WPANs) Used in or 12 Around a Body. 2012. Available online: https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/6161600 (accessed on 28 September 2018).
- Smart Body Area Network (SmartBAN); Low Complexity Medium Access Control (MAC) for SmartBAN, ETSI TC Smart BAN TS 103 325 V1.1.1 2015. Available online: http://www.etsi.org/deliver/etsi_ts/103300_103399/103325/01.01.01_60/ts_103325v010101p.pdf (accessed on 28 September 2018).
- Smart Body Area Network (SmartBAN); Enhanced Ultra-Low Power Physical Layer. ETSI TC Smart BAN TS 103 326 V1.1.1, 2015. Available online: https://www.etsi.org/deliver/etsi_ts/103300_103399/103326/01.01.01_60/ts_103326v010101p.pdf (accessed on 11 November 2018).
- Paso, T.; Tanaka, H.; Hämäläinen, M.; Chin, W.H.; Matsuo, R.; Subramani, S.; Haapola, J. An overview of ETSI TC SmartBAN MAC protocol. In Proceedings of the 9th International Symposium on Medical Information and Communication Technology (ISMICT 2015), Kamakura, Japan, 24–26 March 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Ruan, L.; Dias, M.P.I.; Wong, E. Towards Ubiquitous E-Health: Modeling of SmartBAN Hybrid MAC under Periodic and Emergency Traffic. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Wireless Communications and Networking Conference (WCNC), San Francisco, CA, USA, 19–22 March 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Ruan, L.; Dias, M.P.I.; Wong, E. Towards Tactile Internet Capable E-Health: A Delay Performance Study of Downlink-Dominated SmartBANs. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Global Communications Conference (GLOBECOM 2017), Singapore, 4–8 December 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Ruan, L.; Dias, M.P.I.; Wong, E. SmartBAN with Periodic Monitoring Traffic: A Performance Study on Low Delay and High Energy Efficiency. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inform. 2018, 22, 471–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramis-Bibiloni, J.; Carrasco-Martorell, L. An energy-efficient and delay-constrained resource allocation scheme for periodical monitoring traffic in SmartBANs. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Biomedical Circuits and Systems Conference (BioCAS), Turin, Italy, 19–21 October 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Takabayashi, K.; Tanaka, H.; Sakakibara, K. Performance Evaluation of Error Control Scheme in ETSI SmartBAN PHY. In Proceedings of the 2018 Global IoT Summit (GIoTS 2018), Bilbao, Spain, 4–7 June 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Yazdandoost, K.Y.; Sayrafian-Pour, K.; Channel Model for Body Area Network (BAN). IEEE P802.15 Working Group for Wireless Personal Area Networks(WPANs), IEEE P802.15-08-0780-10-0006 2009. Available online: https://mentor.ieee.org/802.15/file/08/15-08-0780-10-0006-tg6-channel-model.pdf (accessed on 28 September 2018).
- Khan, R.; Alam, M.M. Joint PHY-MAC Realistic Performance Evaluation of Body-to-Body Communication in IEEE 802.15.6 and SmartBAN. In Proceedings of the 12th International Symposium on Medical Information and Communication Technology (ISMICT 2018), Sydney, Australia, 26–28 March 2018. [Google Scholar]
- D’Souza, A.; Viittala, H.; Hämäläinen, M.; Mucci, L. Performance Comparison Between ETSI SmartBAN and Bluetooth. In Proceedings of the 12th International Symposium on Medical Information and Communication Technology (ISMICT 2018), Sydney, Australia, 26–28 March 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Viittala, H.; Mucchi, L.; Hämäläinen, M.; Paso, T. ETSI SmartBAN System Performance and Coexistence Verification for Healthcare. IEEE Access 2018, 5, 8175–8182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moosavi, H.; Bui, F.M. Delay-Aware Optimization of Physical Layer Security in Multi-Hop Wireless Body Area Networks. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur. 2016, 11, 1928–1939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reusens, E.; Joseph, W.; Latré, B.; Braem, B.; Vermeeren, G.; Tanghe, E.; Martens, L.; Moerman, I.; Blondia, C. Characterization of On-Body Communication Channel and Energy Efficient Topology Design for Wireless Body Area Networks. IEEE Trans. Inf. Technol. Biomed. 2009, 13, 933–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Conway, G.A.; Cotton, S.L.; Scanlon, W.G. An Antennas and Propagation Approach to Improving Physical Layer Performance in Wireless Body Area Networks. IEEE J. Sel. Areas Commun. 2009, 27, 27–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, X.; Shah, S.A.; Ren, A.; Fan, D.; Zhao, N.; Zheng, S.; Zhao, W.; Wang, W.; Soh, P.J.; Abbasi, Q.H. S-Band Sensing-Based Motion Assessment Framework for Cerebellar Dysfunction Patients. IEEE Sens. J. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Shah, S.A.; Ren, A.; Zhao, N.; Fan, D.; Hu, F.; Rehman, M.U.; Tian, J. Wandering Pattern Sensing at S-Band. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inform. 2018, 22, 1863–1870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takabayashi, K.; Tanaka, H.; Sugimoto, C.; Sakakibara, K.; Kohno, R. Cross-layer design and performance analysis of quality of service control scheme for wireless body area networks. IEEE Access 2017, 5, 22462–22470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karvonen, H.; Iinatti, J.; Hämäläinen, M. A cross-layer energy efficiency optimization model for WBAN using IR-UWB transceivers. Telecommun. Syst. 2015, 58, 165–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abughalieh, N.; Steenhaut, K.; Now’e, A.; Anpalagan, A. Turbo codes for multihop wireless sensor networks with decode-and-forward mechanism. EURASIP J. Wirel. Commun. Netw. 2014, 204, 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Ryckaert, J.; Desset, C.; Fort, A.; Badaroglu, M.; De Heyn, V.; Wambacq, P.; Van der Plas, G.; Donnay, S.; Van Poucke, B.; Gyselinckx, B. Ultra-wide-band transmitter for low-power wireless body area networks: Design and evaluation. IEEE Trans. Circuit Syst. I Regul. Pap. 2005, 52, 2515–2525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Z.; Mendoza, D.S.; Wang, P.; Zhou, Q.; Mao, J.; Jonsson, F.; Tenhunen, H.; Zheng, L.R. A Low-Power and Flexible Energy Detection IR-UWB Receiver for RFID and Wireless Sensor Networks. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I Regular Pap. 2011, 58, 1470–1482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindh, J.; Lee, C.; Hernes, M. Measuring Bluetooth Low Energy Power Consumption; Application Report, SWRA478C; Texas Instruments: Dallas, TX, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Seberry, J.; Yamada, M. Hadamard Matrices, Sequences, and Block Designs; John Wiley and Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Habuchi, H. Pseudo-Noise Sequences Based on M-sequence and Its Application for Communications. IEICE Fundam. Rev. 2009, 3, 32–42. (In Japanese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, M.K.; Alouini, M.S. Digital Communication over Fading Channels—A Unified Approach to Performance Analysis, 1st ed.; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
























| Symbol Rate (Mega-Symbol/Sec) | Coding Rate | Data Rate (Mbit/Sec) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1.0 | 1 | 1 | 1.0 |
| 1.0 | 1 | 2 | 0.5 |
| 1.0 | 1 | 4 | 0.25 |
| 1.0 | 113/127 | 1 | 0.89 |
| 1.0 | 113/127 | 2 | 0.44 |
| 1.0 | 113/127 | 4 | 0.22 |
| Channel model | AWGN, IEEE model CM3 |
| Path loss model | IEEE model CM3 (Hospital Room) |
| Frequency spectrum | 2401 MHz–2481 MHz |
| Bandwidth (BW) | 2 MHz |
| Modulation | GFSK |
| Bandwidth-time product (BT) | 0.5 |
| Modulation index (h) | 0.5 |
| FEC (PLCP Header) | (36, 22) shortened BCH code |
| FEC (PSDU) | (127, 113) BCH code |
| FEC (PSDU, proposed option) | (127, 64) BCH code |
| Maximum transmission power () | 0 dBm |
| Thermal noise density () | −174 dBm/Hz |
| Implementation losses () | 5 dB |
| Receiver noise figure () | 10 dB |
| Information bit length () | 678 bits |
| Preamble length () | 2 octets |
| PLCP header length () | 40 bits |
| Symbol rate | 1.0 Mega-symbol/sec |
| Inter-frame spacing duration () | 150 μs |
| Sequence Type | Bit Sequence (Hexadecimal) | |
|---|---|---|
| Additional SFD 1 | “01010101” (0 × 55) | |
| Additional SFD 2 | “10101011” (0 × AB) | |
| Hadamard sequence. [32] | 1 octet | “11001100” (0 × CC) |
| 2 octets | “1100001111000011” (0 × C3C3) | |
| 4 octets | “11000011110000111100001111000011” (0 × C3C3C3C3) | |
| Orthogonal M-sequence. [33] | 1 octet | “11101000” (0 × E8) |
| 2 octets | “1111010110010000” (0 × F590) | |
| 4 octets | “11111001101001000010101110110000” (0 × F9A42BB0) | |
| Manchester- coded Orthogonal M-sequence. [33] | 1 octet | “10100101” (0 × A5) |
| 2 octets | “1010100101100101” (0 × A965) | |
| 4 octets | “10101010011001101001011001010101” (0 × AA669655) | |
| Hospital Room | Anechoic Chamber | |
|---|---|---|
| a | 6.6 | 29.3 |
| b | 36.1 | −16.8 |
| σN | 3.8 | 6.89 |
| [dB] | 30.6 |
| [dB] | 0.43 |
| 3.4 |
| Sequence Type | ||
|---|---|---|
| SmartBAN | 16.6 | |
| Additional SFD 1 | Not satisfied | |
| Additional SFD 2 | Not satisfied | |
| Hadamard sequence | 1 octet | 14 |
| 2 octets | 6.0 | |
| 4 octets | 3.0 | |
| Orthogonal M-sequence | 1 octet | 12.8 |
| 2 octets | 5.8 | |
| 4 octets | Less than 0 | |
| Manchester-coded Orthogonal M-sequence | 1 octet | 6.0 |
| 2 octets | 7.9 | |
| 4 octets | 1.5 | |
| Sequence type | ||
|---|---|---|
| SmartBAN | Not satisfied | |
| Additional SFD 1 | Not satisfied | |
| Additional SFD 2 | Not satisfied | |
| Hadamard sequence | 1 octet | Not satisfied |
| 2 octets | 5.5 | |
| 4 octets | Not satisfied | |
| Orthogonal M-sequence | 1 octet | Not satisfied |
| 2 octets | 4.9 | |
| 4 octets | Less than 0 | |
| Manchester-coded Orthogonal M-sequence | 1 octet | Not satisfied |
| 2 octets | Not satisfied | |
| 4 octets | Not satisfied | |
| Sequence Type | [m] | |
|---|---|---|
| SmartBAN | Not satisfied | |
| Additional SFD 1 | Not satisfied | |
| Additional SFD 2 | Not satisfied | |
| Hadamard sequence | 1 octet | Not satisfied |
| 2 octets | 3.0 | |
| 4 octets | Not satisfied | |
| Orthogonal M-sequence | 1 octet | 0.3 |
| 2 octets | 2.2 | |
| 4 octets | Over than 3 | |
| Manchester-coded Orthogonal M-sequence | 1 octet | Not satisfied |
| 2 octets | Not satisfied | |
| 4 octets | Not satisfied | |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Takabayashi, K.; Tanaka, H.; Sakakibara, K. Integrated Performance Evaluation of the Smart Body Area Networks Physical Layer for Future Medical and Healthcare IoT. Sensors 2019, 19, 30. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19010030
Takabayashi K, Tanaka H, Sakakibara K. Integrated Performance Evaluation of the Smart Body Area Networks Physical Layer for Future Medical and Healthcare IoT. Sensors. 2019; 19(1):30. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19010030
Chicago/Turabian StyleTakabayashi, Kento, Hirokazu Tanaka, and Katsumi Sakakibara. 2019. "Integrated Performance Evaluation of the Smart Body Area Networks Physical Layer for Future Medical and Healthcare IoT" Sensors 19, no. 1: 30. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19010030
APA StyleTakabayashi, K., Tanaka, H., & Sakakibara, K. (2019). Integrated Performance Evaluation of the Smart Body Area Networks Physical Layer for Future Medical and Healthcare IoT. Sensors, 19(1), 30. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19010030