InGaN as a Substrate for AC Photoelectrochemical Imaging
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation and Characterization of Sensor Chip
2.3. Linear Sweep Voltammetry (LSV)
2.4. Cell Culture
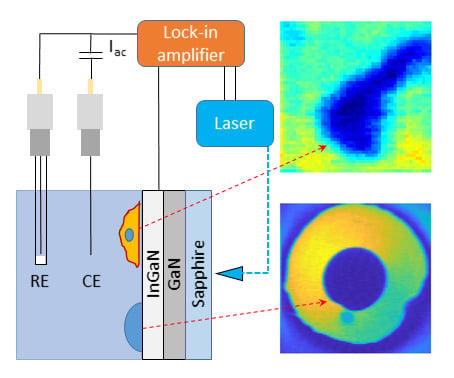
2.5. AC Photocurrent Imaging
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characterization of InGaN/GaN Epilayers on Sapphire
3.2. Photoelectrochemical Imaging Using InGaN
3.3. Cell Imaging on InGaN
3.4. Cell Viability
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hafeman, D.G.; Parce, J.W.; McConnell, H.M. Light-addressable potentiometric sensor for biochemical systems. Science 1988, 240, 1182–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mourzina, Y.; Yoshinobu, T.; Schubert, J.; Lüth, H.; Iwasaki, H.; Schöning, M.J. Ion-selective light-addressable potentiometric sensor (LAPS) with chalcogenide thin film prepared by pulsed laser deposition. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2001, 80, 136–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oba, N.; Yoshinobu, T.; Iwasaki, H. Redox Potential Imaging Sensor. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 1996, 35, 460–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seki, A.; Ikeda, S.; Kubo, I.; Karube, I. Biosensors based on light-addressable potentiometric sensors for urea, penicillin and glucose. Anal. Chim. Acta 1998, 373, 9–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poghossian, A.; Ingebrandt, S.; Offenhäusser, A.; Schöning, M.J. Field-effect devices for detecting cellular signals. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2009, 20, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, N.; Wu, C.; Ha, D.; Wang, T.; Liu, Q.; Wang, P. A novel microphysiometer based on high sensitivity LAPS and microfluidic system for cellular metabolism study and rapid drug screening. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2013, 40, 167–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dantism, S.; Takenaga, S.; Wagner, T.; Wagner, P.; Schöning, M.J. Differential imaging of the metabolism of bacteria and eukaryotic cells based on light-addressable potentiometric sensors. Electrochim. Acta 2017, 246, 234–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owicki, J.C.; Bousse, L.J.; Hafeman, D.G.; Kirk, G.L.; Olson, J.D.; Wada, H.G.; Parce, J.W. The Light-Addressable Potentiometric Sensor: Principles and Biological Applications. Annu. Rev. Biophys. Biomol. Struct. 1994, 23, 87–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, F.; Campos, I.; Zhang, D.W.; Krause, S. Biological imaging using light-addressable potentiometric sensors and scanning photo-induced impedance microscopy. Proc. R. Soc. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 2017, 473, 2201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, Y. High-spatial resolution LAPS. Sens. Actuators B-Chem. 1998, 52, 107–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krause, S.; Talabani, H.; Xu, M.; Moritz, W.; Griffiths, J. Scanning photo-induced impedance microscopy—An impedance based imaging technique. Electrochim. Acta 2002, 47, 2143–2148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Zhou, Y.; Jiang, S.; Kunze, J.; Schmuki, P.; Krause, S. High resolution LAPS and SPIM. Electrochem. commun. 2010, 12, 758–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moritz, W.; Gerhardt, I.; Roden, D.; Xu, M.; Krause, S. Photocurrent measurements for laterally resolved interface characterization. Fresenius J. Anal. Chem. 2000, 367, 329–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, A.; Chang, L.B.; Lai, C.S.; Lin, R.M.; Chu, F.C.; Lin, Y.H.; Chow, L.; Jeng, M.J. GaN Thin Film Based Light Addressable Potentiometric Sensor for pH Sensing Application. Appl. Phys. Express 2013, 6, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzurikawa, J.; Nakao, M.; Jimbo, Y.; Kanzaki, R.; Takahashi, H. A light addressable electrode with a TiO2 nanocrystalline film for localized electrical stimulation of cultured neurons. Sens. Actuators, B Chem. 2014, 192, 393–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Chen, C.; Chang, L.; Lai, C. IGZO Thin-Film Light-Addressable Potentiometric Sensor. IEEE Electron Device Lett. 2016, 37, 1481–1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wu, F.; Watkinson, M.; Zhu, J.; Krause, S. “click” Patterning of Self-Assembled Monolayers on Hydrogen-Terminated Silicon Surfaces and Their Characterization Using Light-Addressable Potentiometric Sensors. Langmuir 2015, 31, 9646–9654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhou, Y.; Watkinson, M.; Gautrot, J.; Krause, S. High-sensitivity light-addressable potentiometric sensors using silicon on sapphire functionalized with self-assembled organic monolayers. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2015, 209, 230–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, F.; Zhang, D.W.; Wang, J.; Watkinson, M.; Krause, S. Copper Contamination of Self-Assembled Organic Monolayer Modified Silicon Surfaces Following a “Click” Reaction Characterized with LAPS and SPIM. Langmuir 2017, 33, 3170–3177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Campos, I.; Wu, F.; Zhu, J.; Sukhorukov, G.B.; Palma, M.; Watkinson, M.; Krause, S. The effect of gold nanoparticles on the impedance of microcapsules visualized by scanning photo-induced impedance microscopy. Electrochim. Acta 2016, 208, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.W.; Wu, F.; Wang, J.; Watkinson, M.; Krause, S. Image detection of yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae by light-addressable potentiometric sensors (LAPS). Electrochem. Commun. 2016, 72, 41–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogel, Y.B.; Gooding, J.J.; Ciampi, S. Light-addressable electrochemistry at semiconductor electrodes: Redox imaging, mask-free lithography and spatially resolved chemical and biological sensing. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2019, 3723–3739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, D.W.; Wu, F.; Krause, S. LAPS and SPIM Imaging Using ITO-Coated Glass as the Substrate Material. Anal. Chem. 2017, 89, 8129–8133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, F.; Zhou, B.; Wang, J.; Zhong, M.; Das, A.; Watkinson, M.; Hing, K.; Zhang, D.W.; Krause, S. Photoelectrochemical Imaging System for the Mapping of Cell Surface Charges. Anal. Chem. 2019, 91, 5896–5903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tu, Y.; Ahmad, N.; Briscoe, J.; Zhang, D.W.; Krause, S. Light-Addressable Potentiometric Sensors Using ZnO Nanorods as the Sensor Substrate for Bioanalytical Applications. Anal. Chem. 2018, 90, 8708–8715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nakamura, S.; Senoh, M.; Mukai, T. P-GaN/N-InGaN/N-GaN Double-Heterostructure Blue-Light-Emitting Diodes. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 1993, 32, 8–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.W.; Lu, Y.J.; Chen, H.Y.; Lee, H.M.; Gwo, S. InGaN/GaN nanorod array white light-emitting diode. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2010, 97, 98–101. [Google Scholar]
- Matioli, E.; Neufeld, C.; Iza, M.; Cruz, S.C.; Al-Heji, A.A.; Chen, X.; Farrell, R.M.; Keller, S.; DenBaars, S.; Mishra, U.; et al. High internal and external quantum efficiency InGaN/GaN solar cells. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2011, 98, 2009–2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kibria, M.G.; Chowdhury, F.A.; Zhao, S.; AlOtaibi, B.; Trudeau, M.L.; Guo, H.; Mi, Z. Visible light-driven efficient overall water splitting using p-type metal-nitride nanowire arrays. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallys, J.; Teubert, J.; Furtmayr, F.; Hofmann, D.M.; Eickhoff, M. Bias-enhanced optical ph response of group III-nitride nanowires. Nano Lett. 2012, 12, 6180–6186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maier, K.; Helwig, A.; Müller, G.; Becker, P.; Hille, P.; Schörmann, J.; Teubert, J.; Eickhoff, M. Detection of oxidising gases using an optochemical sensor system based on GaN/InGaN nanowires. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2014, 197, 87–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riedel, M.; Hölzel, S.; Hille, P.; Schörmann, J.; Eickhoff, M.; Lisdat, F. InGaN/GaN nanowires as a new platform for photoelectrochemical sensors—Detection of NADH. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 94, 298–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, E.; Fang, F.; Oehler, F.; Edwards, P.R.; Kappers, M.J.; Lorenz, K.; Alves, E.; McAleese, C.; Humphreys, C.J.; Martin, R.W. Composition and luminescence studies of InGaN epilayers grown at different hydrogen flow rates. Semicond. Sci. Technol. 2013, 28, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, R.W.; Edwards, P.R.; O’Donnell, K.P.; Mackay, E.G.; Watson, I.M. Microcomposition and Luminescence of InGaN Emitters. Phys. Status Solidi 2002, 192, 117–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tauc, J.; Grigorovici, R.; Vancu, A. Optical Properties and Electronic Structure of Amorphous Germanium. Phys. Status Solidi 1966, 15, 627–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viezbicke, B.D.; Patel, S.; Davis, B.E.; Birnie III, D.P. Evaluation of the Tauc method for optical absorption edge determination: ZnO thin films as a model system. Phys. Status Solidi 2015, 252, 1700–1710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, G.F.; Iii, J.W.A.; Walukiewicz, W.; Wu, J. Solar Energy Materials & Solar Cells Finite element simulations of compositionally graded InGaN solar cells. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2010, 94, 478–483. [Google Scholar]
- Can, M.; Havare, A.K.; Aydın, H.; Yagmurcukardes, N.; Demic, S.; Icli, S.; Okur, S. Electrical properties of SAM-modified ITO surface using aromatic small molecules with double bond carboxylic acid groups for OLED applications. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2014, 314, 1082–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hammer, M.S.; Deibel, C.; Pflaum, J.; Dyakonov, V. Effect of doping of zinc oxide on the hole mobility of poly (3-hexylthiophene) in hybrid transistors. Org. Electron. 2010, 11, 1569–1577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebaid, M.; Kang, J.H.; Lim, S.H.; Ha, J.S.; Lee, J.K.; Cho, Y.H.; Ryu, S.W. Enhanced solar hydrogen generation of high density, high aspect ratio, coaxial InGaN/GaN multi-quantum well nanowires. Nano Energy 2015, 12, 215–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, N.; Morita, R.; Narumi, T.; Yamamoto, J.; Ban, Y.; Wakao, K. Flat-band potentials of GaN and InGaN/GaN QWs by bias-dependent photoluminescence in electrolyte solution. J. Cryst. Growth 2007, 298, 515–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyamoto, K.; Sugawara, Y.; Kanoh, S.; Yoshinobu, T.; Wagner, T.; Schöning, M.J. Image correction method for the chemical imaging sensor. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2010, 144, 344–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- George, M.; Parak, W.J.; Gerhardt, I.; Moritz, W.; Kaesen, F.; Geiger, H.; Eisele, I.; Gaub, H.E. Investigation of the spatial resolution of the light-addressable potentiometric sensor. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2000, 86, 187–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumakura, K.; Makimoto, T.; Kobayashi, N.; Hashizume, T.; Fukui, T.; Hasegawa, H. Minority carrier diffusion lengths in MOVPE-grown n- and p-InGaN and performance of AlGaN/InGaN/GaN double heterojunction bipolar transistors. J. Cryst. Growth 2007, 298, 787–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhou, B.; Das, A.; Kappers, M.J.; Oliver, R.A.; Humphreys, C.J.; Krause, S. InGaN as a Substrate for AC Photoelectrochemical Imaging. Sensors 2019, 19, 4386. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19204386
Zhou B, Das A, Kappers MJ, Oliver RA, Humphreys CJ, Krause S. InGaN as a Substrate for AC Photoelectrochemical Imaging. Sensors. 2019; 19(20):4386. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19204386
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhou, Bo, Anirban Das, Menno J. Kappers, Rachel A. Oliver, Colin J. Humphreys, and Steffi Krause. 2019. "InGaN as a Substrate for AC Photoelectrochemical Imaging" Sensors 19, no. 20: 4386. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19204386
APA StyleZhou, B., Das, A., Kappers, M. J., Oliver, R. A., Humphreys, C. J., & Krause, S. (2019). InGaN as a Substrate for AC Photoelectrochemical Imaging. Sensors, 19(20), 4386. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19204386