A Pilot Study for Estimating the Cardiopulmonary Signals of Diverse Exotic Animals Using a Digital Camera
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods and Procedures
2.1. Animals and Ethical Considerations
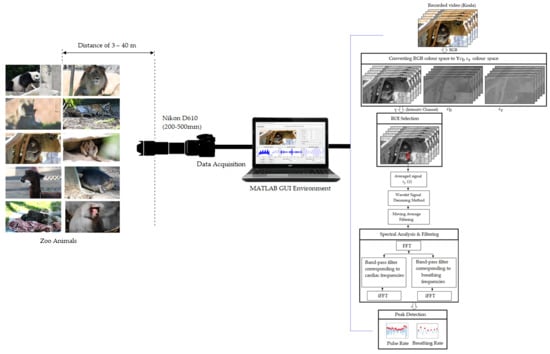
2.2. Data Acquisition and Experimental Setup
2.3. System Framework and Data Analysis
2.4. Data MATLAB Graphical User Interface (GUI)
3. Experimentation and Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Noble, D.J.; MacDowell, C.J.; McKinnon, M.L.; Neblett, T.I.; Goolsby, W.N.; Hochman, S. Use of electric field sensors for recording respiration, heart rate, and stereotyped motor behaviors in the rodent home cage. J. Neurosci. Methods 2017, 277, 88–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Warriss, P.; Pope, S.; Brown, S.; Wilkins, L.; Knowles, T. Estimating the body temperature of groups of pigs by thermal imaging. Vet. Rec. 2006, 158, 331–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stewart, M.; Webster, J.; Stafford, K.; Schaefer, A.; Verkerk, G. Effects of an epinephrine infusion on eye temperature and heart rate variability in bull calves. J. Dairy Sci. 2010, 93, 5252–5257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soerensen, D.D.; Pedersen, L.J. Infrared skin temperature measurements for monitoring health in pigs: A review. Acta. Vet. Scand. 2015, 57, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Magnani, D.; Gatto, M.; Cafazzo, S.; Stelletta, C.; Morgante, M.; Costa, L. Difference of surface body temperature in piglets due to the backtest and environmental condition. In Animal Hygiene and Sustainable Livestock Production, Proceedings of the XVth International Congress of the International Society for Animal Hygiene, Vienna, Austria, 3–7 July 2011; Köfer, J., Schobesberger, H., Eds.; Tribun EU: Brno, Czech Republic, 2011; pp. 1029–1032. [Google Scholar]
- Ludwig, N.; Gargano, M.; Luzi, F.; Carenzi, C.; Verga, M. Applicability of infrared thermography as a non invasive measurements of stress in rabbit. World Rabbit. Sci. 2010, 15, 199–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brivio, F.; Grignolio, S.; Sica, N.; Cerise, S.; Bassano, B. Assessing the impact of capture on wild animals: The case study of chemical immobilisation on alpine ibex. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0130957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, S.; Matsui, T. Remote sensing for medical and health care applications. In Remote Sensing-Applications; Boris, E., Ed.; BoD–Books on Demand: Norderstedt, Deutschland, 2012; pp. 479–492. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, L.; Gu, C.; Li, C.; Lin, J. Doppler radar noncontact vital sign monitoring. In Neural Computation, Neural Devices, and Neural Prosthesis; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2014; pp. 41–62. [Google Scholar]
- Zachariah, U.; Goel, A.; Balasubramanian, K.; Eapen, C. The hibernating bear—A good analogy to explain why acute fatty liver of pregnancy manifests in late pregnancy. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2018, 113, 307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsui, T.; Ishizuka, T.; Takase, B.; Ishihara, M.; Kikuchi, M. Non-contact determination of vital sign alterations in hypovolaemic states induced by massive haemorrhage: An experimental attempt to monitor the condition of injured persons behind barriers or under disaster rubble. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 2004, 42, 807–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsui, T.; Hagisawa, K.; Ishizuka, T.; Takase, B.; Ishihara, M.; Kikuchi, M. A novel method to prevent secondary exposure of medical and rescue personnel to toxic materials under biochemical hazard conditions using microwave radar and infrared thermography. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2004, 51, 2184–2188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, S.; Matsui, T.; Kawahara, H.; Gotoh, S. Development of a noncontact and long–term respiration monitoring system using microwave radar for hibernating black bear. Zoo Biol. 2009, 28, 259–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, T.; Mott, C.; Mollicone, D.; Sanford, L.D. Automated determination of wakefulness and sleep in rats based on non-invasively acquired measures of movement and respiratory activity. J. Neurosci. Methods 2012, 204, 276–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Huang, T.-Y.; Lin, J.; Hayward, L. Non-invasive measurement of laboratory rat’s cardiorespiratory movement using a 60-GHz radar and nonlinear Doppler phase modulation. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE MTT–S 2015 International Microwave Workshop Series on RF and Wireless Technologies for Biomedical and Healthcare Applications (IMWS-BIO), Taipei, Taiwan, 21–23 September 2015; pp. 83–84. [Google Scholar]
- Kranjec, J.; Beguš, S.; Geršak, G.; Drnovšek, J. Non-contact heart rate and heart rate variability measurements: A review. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2014, 13, 102–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-naji, A.; Gibson, K.; Lee, S.H.; Chahl, J. Monitoring of cardiorespiratory signal: Principles of remote measurements and review of methods. IEEE Access 2017, 5, 15776–15790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montanholi, Y.R.; Lim, M.; Macdonald, A.; Smith, B.A.; Goldhawk, C.; Schwartzkopf-Genswein, K.; Miller, S.P. Technological, environmental and biological factors: Referent variance values for infrared imaging of the bovine. J. Anim. Sci. Biotechno. 2015, 6, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maia, A.P.D.A.; Oliveira, S.R.d.M.; Moura, D.J.d.; Sarubbi, J.; Vercellino, R.d.A.; Medeiros, B.B.L.; Griska, P.R. A decision-tree-based model for evaluating the thermal comfort of horses. Sci. Agric. 2013, 70, 377–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lavers, C.; Franks, K.; Floyd, M.; Plowman, A. Application of remote thermal imaging and night vision technology to improve endangered wildlife resource management with minimal animal distress and hazard to humans. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2005, 15, 207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hristov, N.I.; Betke, M.; Kunz, T.H. Applications of thermal infrared imaging for research in aeroecology. Integr. Comp. Biol. 2008, 48, 50–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Herborn, K.A.; Graves, J.L.; Jerem, P.; Evans, N.P.; Nager, R.; McCafferty, D.J.; McKeegan, D.E. Skin temperature reveals the intensity of acute stress. Physiol. Behav. 2015, 152, 225–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Foster, S.; Ijichi, C. The association between infrared thermal imagery of core eye temperature, personality, age and housing in cats. Appl. Anim. Behav. Sci. 2017, 189, 79–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dunbar, M.R.; MacCarthy, K.A. Use of infrared thermography to detect signs of rabies infection in raccoons (Procyon lotor). J. Zoo Wildl. Med. 2006, 37, 518–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dunbar, M.R.; Johnson, S.R.; Rhyan, J.C.; McCollum, M. Use of infrared thermography to detect thermographic changes in mule deer (Odocoileus hemionus) experimentally infected with foot-and-mouth disease. J. Zoo Wildl. Med. 2009, 40, 296–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cilulko, J.; Janiszewski, P.; Bogdaszewski, M.; Szczygielska, E. Infrared thermal imaging in studies of wild animals. Eur. J. Wildlife Res. 2013, 59, 17–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Al-naji, A.; Gibson, K.; Chahl, J. Remote sensing of physiological signs using a machine vision system. J. Med. Eng. Technol. 2017, 41, 396–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, F.; Li, M.; Qian, Y.; Tsien, J.Z. Remote measurements of heart and respiration rates for telemedicine. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e71384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Blanik, N.; Pereira, C.; Czaplik, M.; Blazek, V.; Leonhardt, S. Remote photopletysmographic imaging of dermal Perfusion in a porcine animal model. In Proceedings of the 15th International Conference on Biomedical Engineering, Singapore, 4–7 December 2013; pp. 92–95. [Google Scholar]
- Unakafov, A.M.; Möller, S.; Kagan, I.; Gail, A.; Treue, S.; Wolf, F. Using imaging photoplethysmography for heart rate estimation in non-human primates. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0202581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Adelaide Zoo. Available online: https://www.adelaidezoo.com.au (accessed on 1 April 2019).
- Obeid, D.; Sadek, S.; Zaharia, G.; El Zein, G. Multitunable microwave system for touchless heartbeat detection and heart rate variability extraction. Microwave Opt. Technol. Lett. 2010, 52, 192–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-naji, A.; Perera, A.G.; Mohammed, S.L.; Chahl, J. Life signs detector using a drone in disaster zones. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 2441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wee, A.; Grayden, D.B.; Zhu, Y.; Petkovic-Duran, K.; Smith, D. A continuous wavelet transform algorithm for peak detection. Electrophoresis 2008, 29, 4215–4225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panda facts, II. Available online: http://www.chinadaily.com.cn/regional/2012-09/21/content_15774766.htm (accessed on 5 May 2019).
- Larsson, M.H.M.; Coelho, F.M.; Oliveira, V.M.; Yamaki, F.L.; Pereira, G.G.; Soares, E.C.; Fedullo, J.D.L.; Pereira, R.C.; Ito, F.H. Electrocardiographic parameters of captive lions (Panthera leo) and tigers (Panthera tigris) immobilized with ketamine plus xylazine. J. Zoo Wildlife Med. 2008, 39, 314–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wenger, S.; Buss, P.; Joubert, J.; Steenkamp, J.; Shikwambana, P.; Hatt, J.-M. Evaluation of butorphanol, medetomidine and midazolam as a reversible narcotic combination in free-ranging African lions (Panthera leo). Vet. Anaesth. Analg. 2010, 37, 491–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cassie, T.J.T. Study of Respiratory Rate on Sumatran Tiger (Panthera Tigris Sumaterae) in Gembira Loka Zoo, Yogyakarta. Ph.D. Thesis, Universitas Gadjah Mada, Yogyakarta, Indonesia, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Vogelnest, L.; Woods, R. (Eds.) Medicine of Australian Mammals; Csiro Publishing: Clayton South, VIC, Australia, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Green-Barber, J.M.; Ong, O.T.; Kanuri, A.; Stannard, H.J.; Old, J.M. Blood constituents of free-ranging eastern grey kangaroos (Macropus giganteus). Aust. Mammal. 2018, 40, 136–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holtgrew, B.; Kristin, J. Large Animal Clinical Procedures for Veterinary Technicians-E-Book, 4th ed.; Elsevier Health Sciences: Kidlington, UK, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Green, J.A.; Frappell, P.B.; Clark, T.; Butler, P.J. Predicting rate of oxygen consumption from heart rate while little penguins work, rest and play. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. A: Mol. Integr. Physiol. 2008, 150, 222–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salina, A.; Salim, N.B.; Rasedee, A.; Senthilvel, K.S.S.N. A field study on social behaviour, feeding regime and health status in semi-captive and free-ranging orang utans (Pongo pygmaeus) undergoing rehabilitation programme. In Proceedings of the 11th International Conference of the Association of Institutions for Tropical Veterinary Medicine, Petaling Jaya, Malaysia, 23–27 August 2004; pp. 378–380. [Google Scholar]
- Husbandry Guidelines for Hamadryas Baboon, Papio Hamadryas (Mammalia: Cercopithecidae). Available online: https://nswfmpa.com.au/wp-content/uploads/2017/11/Mammals.-Hamadryas-Baboon-2010LT.pdf (accessed on 9 December 2019).
- Gabriel, I.V.; Anghelescu, P. Vibration monitoring system for human activity detection. In Proceedings of the 2015 7th International Conference on Electronics, Computers and Artificial Intelligence (ECAI), Bucharest, Romania, 25–27 June 2015; pp. 41–44. [Google Scholar]
- Al-naji, A.; Chahl, J.; Lee, S.H. Cardiopulmonary signal acquisition from different regions using video imaging analysis. Comput. Methods Biomech. Biomed. Engin. 2019, 7, 117–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alinovi, D.; Ferrari, G.; Pisani, F.; Raheli, R. Respiratory rate monitoring by video processing using local motion magnification. In Proceedings of the 2018 26th European Signal Processing Conference (EUSIPCO), Roma, Italy, 3–7 September 2018; pp. 1780–1784. [Google Scholar]
- Aubakir, B.; Nurimbetov, B.; Tursynbek, I.; Varol, H.A. Vital sign monitoring utilizing Eulerian video magnification and thermography. In Proceedings of the 2016 38th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC), Orlando, FL, USA, 16–20 August 2016; pp. 3527–3530. [Google Scholar]
- Al-naji, A.; Chahl, J. Remote optical cardiopulmonary signal extraction with noise artifact removal, multiple subject detection & long-distance. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 11573–11595. [Google Scholar]
- Ordóñez, C.; Cabo, C.; Menéndez, A.; Bello, A. Detection of human vital signs in hazardous environments by means of video magnification. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0195290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gibson, K.; Al-naji, A.; Fleet, J.; Steen, M.; Esterman, A.; Chahl, J.; Huynh, J.; Morris, S. Non-contact heart and respiratory rate monitoring of preterm infants based on a computer vision system: A method comparison study. Pediatr. Res. 2019, 86, 738–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Animals | Normal Cardiopulmonary Range | Cardiopulmonary Signal pulse rate (PR b/m) and Breathing Rate (BR r/m) (the Average from 3 Points) |
|---|---|---|
| Giant panda (Ailuropoda melanoleuca) | 70–120 b/m [35] 20–40 r/m | 87.51± 14 b/m 43.59 ± 3 r/m |
| African lion (Panthera leo) | 42–76 b/m [36] 14–32 r/m [37] | 54.04 ± 11 b/m 22.33 ± 4 r/m |
| African lioness (Panthera leo) | 42–76 b/m [36] 14–32 r/m [37] | 55.82 ± 11 b/m 21.92 ± 2 r/m |
| Sumatran tiger (Panthera tigris sumatrae) | 56–97 b/m [36] 7–40 r/m [38] | 76.67 ± 12 b/m 21.79 ± 3 r/m |
| Koala (Phascolarctos cinereus) | 65–90 b/m [39] 10–15 r/m | 75.92 ± 13 b/m 11.89 ± 1 r/m |
| Red kangaroo (Macropus rufus) | 79–100 b/m [40] 26–59 r/m | 92.85 ± 12 b/m 45.59 ± 3 r/m |
| Alpaca (Vicugna pacos) | 60–90 b/m [41] 10–30 r/m | 68.66 ± 12 b/m 25.65 ± 7 r/m |
| Little blue penguin (Eudyptula minor) | 113–280 b/m [42] 7–25 r/m | 219.29 ± 20 b/m 11.05 ± 7 r/m |
| Sumatran Orangutan (Pongo abelii) | 115–121 b/m [43] 24–28 r/m | 120.61 ± 15 b/m 32.89 ± 6 r/m |
| Hamadryas baboon (Papio hamadryas) | 100–154 b/m [44] 12–40 r/m | 119.08 ± 16 b/m 30.33 ± 8 b/m |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Al-Naji, A.; Tao, Y.; Smith, I.; Chahl, J. A Pilot Study for Estimating the Cardiopulmonary Signals of Diverse Exotic Animals Using a Digital Camera. Sensors 2019, 19, 5445. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19245445
Al-Naji A, Tao Y, Smith I, Chahl J. A Pilot Study for Estimating the Cardiopulmonary Signals of Diverse Exotic Animals Using a Digital Camera. Sensors. 2019; 19(24):5445. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19245445
Chicago/Turabian StyleAl-Naji, Ali, Yiting Tao, Ian Smith, and Javaan Chahl. 2019. "A Pilot Study for Estimating the Cardiopulmonary Signals of Diverse Exotic Animals Using a Digital Camera" Sensors 19, no. 24: 5445. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19245445
APA StyleAl-Naji, A., Tao, Y., Smith, I., & Chahl, J. (2019). A Pilot Study for Estimating the Cardiopulmonary Signals of Diverse Exotic Animals Using a Digital Camera. Sensors, 19(24), 5445. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19245445