Multi-GPU Based Parallel Design of the Ant Colony Optimization Algorithm for Endmember Extraction from Hyperspectral Images
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Ant Colony Optimization Algorithm for Endmember Extraction
3. Multi-GPUs-Based Parallel Design of ACOEE
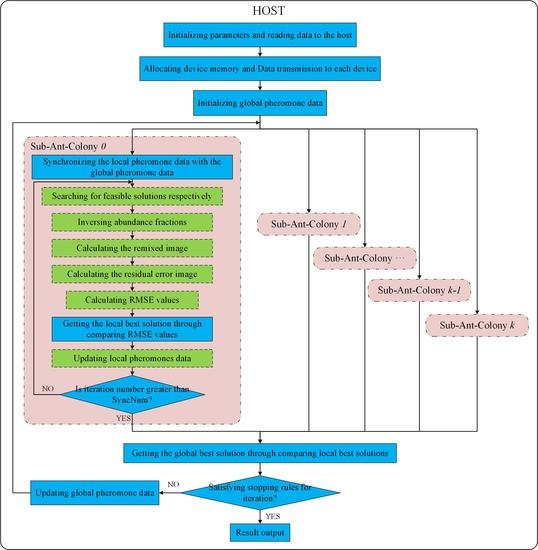
3.1. Parallel Design Based on Multiple Sub-Ant-Colonies
- (1)
- There are two kinds of pheromones in the graph, i.e., global pheromone and local pheromone. The global pheromone is visible for all ants and can be updated by all ants. Each ant can utilize and update the local pheromone in a sub-ant-colony. The global pheromone and local pheromone are both initialized with the same value.
- (2)
- Ants search for routes according to the local pheromone. At the end of each iteration, the local pheromone is updated on the basis of Equation (5) and (6). and in Equation (6) respectively indicate the optimal objective function value of all selected routes searched in this sub-ant-colony and its corresponding route.
- (3)
- After SyncNum iterations, the local pheromone data of all sub-ant-colonies are copied to the host. The global pheromone data are updated to the mean value of the local pheromone data of different sub-ant-colonies. Then, the latest global pheromone data are copied back to each device to update the local pheromone data of all sub-ant-colonies.
- (4)
- If the stopping condition is not satisfied, the host will control the devices to execute the next SyncNum iterations.
| Pseudocode 1: |
| Step 0: Initializing parameters, allocating device memory, and transferring data to devices in the host. The parameters: IterationMax (the preset iteration maximum number), ConverMax (the convergence synchronous cycle number), and SyncNum are initialized. TotalIterNum = 0; ContiConverTimes = 0. |
| Step 1: For each sub-ant-colony, the local pheromone data are synchronized with the global pheromone data. IterNum = 0. |
| Step 2: For each sub-ant-colony, feasible solutions are obtained by ants. The local best solution is updated through comparing the RMSE values of feasible solutions, and then local pheromone data are updated. IterNum = IterNum+1. TotalIterNum=TotalIterNum+1. |
| Step 3: For each sub-ant-colony, if IterNum > SyncNum, copy the local best solution and local pheromone data to the host, and then, go to Step 4; else, go to Step 2. |
| Step 4: For the host, the best solution in this synchronous cycle is obtained through comparing the local best solutions. If this solution is the same as the global best solution, ContiConverTimes=ContiConverTimes + 1; else ContiConverTimes = 0, and update the global best solution. |
| Step 5: For the host, if ContiConverTimes = ConverMax or TotalIterNum = IterationMax, the algorithm stops, and the best solution in the last synchronous cycle is recognized as the final global optimal solution; else, update the global pheromone data, and go to Step 1. |
3.2. Parallel Implementation of ACOEE on the Multi-GPU System
4. Experiments and Discussion
4.1. Computing Facilities and Dataset
4.2. Endmember Extraction Accuracy and Parallel Computing Performance
4.3. Influence of Key Parameters
4.4. Discussions
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Song, C. Spectral mixture analysis for subpixel vegetation fractions in the urban environment: How to incorporate endmember variability? Remote Sens. Environ. 2005, 2, 248–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bioucas-Dias, J.M.; Plaza, A.; Dobigeon, N.; Parente, M.; Du, Q.; Gader, P.; Chanussot, J. Hyperspectral unmixing overview: Geometrical, statistical, and sparse regression-based approaches. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Observ. Remote Sens. 2012, 2, 354–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keshava, N.; Mustard, J.F. Spectral unmixing. IEEE Signal Process. Mag. 2002, 1, 44–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heinz, D.C.; Chang, C.-I. Fully constrained least squares linear spectral mixture analysis method for material quantification in hyperspectral imagery. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2001, 3, 529–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winter, M.E. N-FINDR: An algorithm for fast autonomous spectral endmember determination in hyperspectral data. Proc. SPIE 1999, 3753, 266–275. [Google Scholar]
- Boardman, J.W.; Kruse, F.A.; Green, R.O. Mapping target signatures via partial unmixing of aviris data. In Proceedings of the Fifth Annual JPL Airborne Earth Science Workshop, Pasadena, CA, USA, 23–26 January 1995; pp. 23–26. [Google Scholar]
- Nascimento, J.M.P.; Dias, J.M.B. Vertex component analysis: A fast algorithm to unmix hyperspectral data. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2005, 4, 898–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plaza, A.; Martinez, P.; Perez, R.; Plaza, J. Spatial/spectral endmember extraction by multidimensional morphological operations. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2002, 9, 2025–2041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Bioucas-Dias, J.M. Minimum volume simplex analysis: A fast algorithm to unmix hyperspectral data. In Proceedings of the 2007 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Boston, MA, USA, 8–11 July 2008; pp. III-250–III-253. [Google Scholar]
- Somers, B.; Zortea, M.; Plaza, A.; Asner, G.P. Automated extraction of image-based endmember bundles for improved spectral unmixing. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2012, 2, 396–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, W.; Chang, C.-I.; Wu, C.-C.; Kalpakis, K.; Chen, H.M. Fast algorithms to implement N-FINDR for hyperspectral endmember extraction. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2011, 3, 545–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Bioucas-Dias, J.M.; Zhang, X.; Liu, Y.; Plaza, A. A new classification-oriented endmember extraction and sparse unmixing approach for hyperspectral data. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Fort Worth, TX, USA, 23–28 July 2017; pp. 3644–3647. [Google Scholar]
- Palsson, B.; Sigurdsson, J.; Sveinsson, J.R.; Ulfarsson, M.O. Hyperspectral Unmixing Using a Neural Network Autoencoder. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 25646–25656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Sun, X.; Gao, L.R.; Yang, L. Endmember extraction of hyperspectral remote sensing images based on the ant colony optimization (ACO) algorithm. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2011, 7, 2635–2646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Gao, J.; Gao, L.; Sun, X. Improvements in the Ant Colony Optimization Algorithm for Endmember Extraction From Hyperspectral Images. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2013, 2, 522–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Sun, X.; Gao, L.R.; Yang, L. Endmember extraction of hyperspectral remote sensing images based on the discrete particle swarm optimization algorithm. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2011, 11, 4173–4176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Du, B.; Zhang, L. Multiobjective endmember extraction for hyperspectral image. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Fort Worth, TX, USA, 23–28 July 2017; pp. 1161–1164. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, X.; Yang, L.; Zhang, B.; Gao, L.; Gao, J. An Endmember Extraction Method Based on Artificial Bee Colony Algorithms for Hyperspectral Remote Sensing Images. Remote Sens. 2015, 12, 16363–16383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plaza, A.; Valencia, D.; Plaza, J.; Chang, C.-I. Parallel implementation of endmember extraction algorithms from hyperspectral data. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2006, 3, 334–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plaza, A.; Du, Q.; Chang, Y.-L.; King, R.L. High performance computing for hyperspectral remote sensing. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2011, 3, 528–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.A.; Gasster, S.D.; Plaza, A.; Chang, C.-I.; Huang, B. Recent developments in high performance computing for remote sensing: A review. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2011, 3, 508–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Huang, B.; Plaza, A.; Li, Y.; Wu, C. Real-Time Implementation of the Pixel Purity Index Algorithm for Endmember Identification on GPUs. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2014, 5, 955–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agathos, A.; Li, J.; Petcu, D.; Plaza, A. Multi-GPU Implementation of the Minimum Volume Simplex Analysis Algorithm for Hyperspectral Unmixin. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 2281–2296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jimenez, L.I.; Sanchez, S.; Martin, G.; Plaza, J.; Plaza, A.J. Parallel Implementation of Spatial-Spectral Endmember Extraction on Graphic Processing Units. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2017, 4, 1247–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Chen, S.; Li, D.; Wang, C.; Yang, J. Papaya Tree Detection with UAV Images Using a GPU-Accelerated Scale-Space Filtering Method. Remote Sens. 2017, 7, 721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martel, E.; Lazcano, R.; Lopez, J.; Madronal, D.; Salvador, R.; Lopez, S.; Juarez, E.; Guerra, R.; Sanz, C.; Sarmiento, R. Implementation of the Principal Component Analysis onto High-Performance Computer Facilities for Hyperspectral Dimensionality Reduction: Results and Comparisons. Remote Sens. 2018, 6, 864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; He, F.; Hou, N.; Qiu, Y. Parallel ant colony optimization on multi-core SIMD CPUs. Future Gener. Comput. Syst. 2018, 79, 473–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; He, F.; Qiu, Y. Dynamic strategy based parallel ant colony optimization on GPUs for TSPs. Sci. China Inf. Sci. 2017, 6, 068102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rey, A.; Prieto, M.; Gomez, J.I.; Tenllado, C.; Hidalgo, J. A CPU-GPU Parallel Ant Colony Optimization Solver for the Vehicle Routing Problem. In Proceedings of the International Conference on the Applications of Evolutionary Computation, Parma, Italy, 3–7 April 2018; pp. 653–667. [Google Scholar]
- Cekmez, U.; Ozsiginan, M.; Sahingoz, O.K. Multi-UAV Path Planning with Multi Colony Ant Optimization. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Intelligent Systems Design and Applications, Delhi, India, 14–16 December 2017; pp. 407–417. [Google Scholar]
- Colorni, A.; Dorigo, M.; Maniezzo, V. Distributed optimization by ant colonies. In Proceedings of the Advances in Artificial Life: 5th European Conference, ECAL’99, Lausanne, Switzerland, 13–17 September 1991; pp. 134–142. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, L.; Gao, J.; Li, J.; Plaza, A.; Zhuang, L.; Sun, X.; Zhang, B. Multiple Algorithm Integration Based on Ant Colony Optimization for Endmember Extraction From Hyperspectral Imagery. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2015, 6, 2569–2581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dennison, P.E.; Roberts, D.A. Endmember selection for multiple endmember spectral mixture analysis using endmember average RMSE. Remote Sens. Environ. 2003, 2, 123–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martel, E.; Guerra, R.; Lopez, S.; Sarmiento, R. A GPU-Based Processing Chain for Linearly Unmixing Hyperspectral Images. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2017, 3, 818–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, L.; Du, B. GPU Parallel Implementation of Isometric Mapping for Hyperspectral Classification. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2017, 9, 1532–1536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossam, M.A.; Ebied, H.M.; Abdel-Aziz, M.H.; Tolba, M.F. Accelerated hyperspectral image recursive hierarchical segmentation using GPUs, multicore CPUs, and hybrid CPU/GPU cluster. J. Real-Time Image Process. 2018, 2, 413–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Shi, L.; Li, J.; Wang, Q.; Sun, L.; Wei, Z.; Plaza, J.; Plaza, A. GPU Parallel Implementation of Spatially Adaptive Hyperspectral Image Classification. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2018, 4, 1131–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torti, E.; Fontanella, A.; Plaza, A. Parallel real-time virtual dimensionality estimation for hyperspectral images. J. Real-Time Image Process. 2018, 4, 753–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, L.; Li, H.C.; Ni, J.; Chen, C.; Chen, X.D.; Du, Q. GPU-based fast hyperspectral image classification using joint sparse representation with spectral consistency constraint. J. Real-Time Image Process. 2018, 15, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, R.O.; Eastwood, M.L.; Sarture, C.M.; Chrien, T.G.; Aronsson, M.; Chippendale, B.J.; Faust, J.A.; Pavri, B.E.; Chovit, C.J.; Solis, M.; et al. Imaging spectroscopy and the Airborne Vsible/Infrared Imaging Spectrometer (AVIRIS). Remote Sens. Environ. 1998, 3, 227–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Xia, W.; Wang, B.; Zhang, L. An Approach Based on Constrained Nonnegative Matrix Factorization to Unmix Hyperspectral Data. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2011, 2, 757–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, Y.; Jia, S.; Zhou, J.; Robles-Kelly, A. Hyperspectral Unmixing via L1/2 Sparsity-Constrained Nonnegative Matrix Factorization. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2011, 11, 4282–4297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, F.; Wang, Y.; Xiang, S.; Fan, B.; Pan, C. Structured Sparse Method for Hyperspectral Unmixing. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2014, 2, 101–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bioucas-Dias, J.M.; Nascimento, J.M.P. Hyperspectral subspace identification. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2008, 8, 2435–2445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| NVIDIA TITAN Xp | |
|---|---|
| CUDA core | 3840 |
| Boost Clock (MHz) | 1582 |
| Memory Amount (GB) | 12 |
| Memory Speed (Gbps) | 11.4 |
| Memory Interface width (bit) | 384 |
| Memory Bandwidth (GB/S) | 547.7 |
| Algorithms | Spectral Angle Distance (×10−2) | RMSE | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alunite GDS84 | Calcite WS272 | Kaolinite KGa-1 | Muscovite GDS107 | Mean | ||
| O-ACOEE | 9.20 ± 1.95 | 10.03 ± 0.34 | 9.40 ± 0.77 | 9.82 ± 1.15 | 9.61 ± 1.05 | 3.030 ± 0.016 |
| G-ACOEE | 7.97 ± 1.74 | 10.13 ± 0.26 | 9.05 ± 0.95 | 9.56 ± 0.69 | 9.18 ± 0.91 | 3.024 ± 0.012 |
| MG-ACOEE | 7.19 ± 0 | 9.89 ± 0.31 | 9.79 ± 0.11 | 9.56 ± 0.69 | 9.11 ± 0.28 | 3.018 ± 0.007 |
| Algorithms | Spectral Angle Distance (×10−2) | RMSE | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alunite GDS84 | Calcite WS272 | Kaolinite KGa-1 | Muscovite GDS107 | Mean | ||
| O-ACOEE | 7.27 ± 0.18 | 10.12 ± 0.25 | 9.92 ± 0.13 | 10.13 ± 0.60 | 9.36 ± 0.29 | 3.300 ± 0.020 |
| G-ACOEE | 7.42 ± 0.41 | 10.35 ± 0.25 | 9.53 ± 0.52 | 10.45 ± 0.12 | 9.43 ± 0.33 | 3.295 ± 0.020 |
| MG-ACOEE | 7.19 ± 0 | 10.36 ± 0.30 | 9.71 ± 0.48 | 10.46 ± 0.13 | 9.43 ± 0.23 | 3.295 ± 0.021 |
| Algorithms | Spectral Angle Distance (×10−2) | RMSE | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Asphalt Road | Grass | Tree | Roof | Mean | ||
| O-ACOEE | 19.10 ± 0 | 8.70 ± 0 | 6.92 ± 1.73 | 5.61 ± 0 | 10.08 ± 0.43 | 8.155 ± 0.018 |
| G-ACOEE | 19.10 ± 0 | 8.70 ± 0 | 7.54 ± 2.79 | 5.61 ± 0 | 10.20 ± 0.70 | 8.156 ± 0.018 |
| MG-ACOEE | 19.10 ± 0 | 8.70 ± 0 | 8.19 ± 1.41 | 5.61 ± 0 | 10.40 ± 0.35 | 8.142 ± 0.014 |
| Algorithms | Spectral Angle Distance (×10−2) | RMSE | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Asphalt Road | Grass | Tree | Roof | Mean | ||
| O-ACOEE | 18.83 ± 0 | 8.70 ± 0 | 5.66 ± 0 | 23.70 ± 0 | 14.22 ± 0 | 10.173 ± 0.652 |
| G-ACOEE | 18.83 ± 0 | 8.70 ± 0 | 5.66 ± 0 | 23.70 ± 0 | 14.22 ± 0 | 10.168 ± 0.007 |
| MG-ACOEE | 18.83 ± 0 | 8.70 ± 0 | 5.66 ± 0 | 23.70 ± 0 | 14.22 ± 0 | 10.165 ± 0.007 |
| Algorithms | Iteration Numbers | Total Time | TPI (Time per Iteration) |
|---|---|---|---|
| O-ACOEE | 284.0 ± 35.49 | 9259.83 ± 1468.86 | 32.605 ± 1.140 |
| G-ACOEE | 324.6 ± 50.07 | 154.64 ± 24.12 | 0.476 ± 0.011 |
| MG-ACOEE | 424.8 ± 25.35 | 29.87 ± 1.68 | 0.070 ± 0.001 |
| Algorithms | Iteration Numbers | Total Time | TPI (Time per Iteration) |
|---|---|---|---|
| O-ACOEE | 299.0 ± 28.45 | 67,868.65 ± 9388.48 | 226.500 ± 14.280 |
| G-ACOEE | 370.0 ± 53.58 | 1991.81 ± 304.16 | 5.379 ± 0.059 |
| MG-ACOEE | 444.8 ± 49.10 | 323.73 ± 40.58 | 0.727 ± 0.012 |
| Algorithms | Iteration Numbers | Total Time | TPI (Time per Iteration) |
|---|---|---|---|
| O-ACOEE | 264.6 ± 49.35 | 18,155.67 ± 3244.98 | 68.616 ± 0.898 |
| G-ACOEE | 271.0 ± 35.43 | 226.07 ± 27.56 | 0.834 ± 0.008 |
| MG-ACOEE | 368.0 ± 22.05 | 41.58 ± 2.41 | 0.113 ± 0.001 |
| Algorithms | Iteration Numbers | Total Time | TPI (Time per Iteration) |
|---|---|---|---|
| O-ACOEE | 219.0 ± 17.26 | 44,685.95 ± 4504.05 | 204.142 ± 13.994 |
| G-ACOEE | 226.4 ± 20.40 | 1221.10 ± 115.46 | 5.392 ± 0.034 |
| MG-ACOEE | 285.6 ± 30.93 | 225.89 ± 54.34 | 0.785 ± 0.127 |
| GPUsNum | 1 | 2 | 4 | 8 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| RMSE | 3.024 ± 0.012 | 3.026 ± 0.009 | 3.022 ± 0.009 | 3.018 ± 0.007 |
| IN | 324.6 ± 50.07 | 316.8 ± 30.51 | 368.8 ± 48.69 | 424.8 ± 25.35 |
| TT | 154.64 ± 24.13 | 82.02 ± 7.37 | 49.10 ± 5.59 | 29.87 ± 1.68 |
| TPI | 0.476 ± 0.011 | 0.259 ± 0.011 | 0.133 ± 0.004 | 0.070 ± 0.001 |
| GPUsNum | 1 | 2 | 4 | 8 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| RMSE | 8.170 ± 0.021 | 8.149 ± 0.018 | 8.149 ± 0.017 | 8.142 ± 0.014 |
| IN | 271.0 ± 35.43 | 284.8 ± 11.43 | 312.8 ± 20.61 | 368.0 ± 22.05 |
| TT | 226.07 ± 27.56 | 119.85 ± 5.43 | 66.92 ± 4.29 | 41.58 ± 2.41 |
| TPI | 0.834 ± 0.008 | 0.421 ± 0.003 | 0.214 ± 0.001 | 0.113 ± 0.001 |
| AntsNum | 4 | 12 | 20 | 28 | 32 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RMSE | 3.052 ± 0.016 | 3.035 ± 0.025 | 3.025 ± 0.008 | 3.021 ± 0.007 | 3.018 ± 0.007 |
| IN | 594.4 ± 57.28 | 477.6 ± 75.92 | 411.2 ± 52.24 | 414.4 ± 61.43 | 424.8 ± 25.35 |
| TT | 8.62 ± 0.48 | 15.29 ± 2.28 | 25.33 ± 3.49 | 27.13 ± 4.33 | 29.87 ± 1.68 |
| TPI | 0.014 ± 0.001 | 0.032 ± 0.002 | 0.056 ± 0.003 | 0.065 ± 0.002 | 0.070 ± 0.001 |
| AntsNum | 4 | 12 | 20 | 28 | 32 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RMSE | 8.255 ± 0.117 | 8.163 ± 0.014 | 8.156 ± 0.017 | 8.149 ± 0.018 | 8.142 ± 0.014 |
| IN | 665.6 ± 51.64 | 524.0 ± 57.24 | 452.0 ± 11.03 | 390.4 ± 37.57 | 368.0 ± 22.05 |
| TT | 11.86 ± 0.96 | 23.85 ± 2.30 | 32.88 ± 0.74 | 39.14 ± 3.60 | 41.58 ± 2.41 |
| TPI | 0.018 ± 0 | 0.046 ± 0.001 | 0.073 ± 0 | 0.100 ± 0.001 | 0.113 ± 0.001 |
| SyncNum | 4 | 8 | 16 | 32 | 64 | 96 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RMSE | 3.018 ± 0.007 | 3.020 ± 0.009 | 3.015 ± 0.008 | 3.012 ± 0.004 | 3.012 ± 0.002 | 3.012 ± 0.004 |
| IN | 424.8 ± 25.35 | 420.8 ± 53.69 | 454.4 ± 21.70 | 588.8 ± 15.68 | 652.8 ± 74.64 | 806.4 ± 97.9 |
| TT | 29.87 ± 1.68 | 29.61 ± 3.48 | 31.77 ± 1.81 | 38.68 ± 1.02 | 43.69 ± 4.99 | 52.84 ± 6.21 |
| TPI | 0.070 ± 0.001 | 0.070 ± 0.001 | 0.070 ± 0.002 | 0.066 ± 0 | 0.067 ± 0.001 | 0.066 ± 0 |
| SyncNum | 4 | 8 | 16 | 32 | 64 | 96 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RMSE | 8.142 ± 0.014 | 8.142 ± 0.014 | 8.142 ± 0.014 | 8.141 ± 0.013 | 8.135 ± 0 | 8.135 ± 0 |
| IN | 368.0 ± 22.05 | 411.2 ± 33.79 | 432.0 ± 44.11 | 499.2 ± 47.89 | 576.0 ± 40.48 | 672.0 ± 60.72 |
| TT | 41.58 ± 2.41 | 45.86 ± 3.45 | 47.39 ± 4.80 | 54.16 ± 4.84 | 62.01 ± 4.53 | 71.95 ± 6.27 |
| TPI | 0.113 ± 0.001 | 0.112 ± 0.001 | 0.110 ± 0.001 | 0.108 ± 0.001 | 0.108 ± 0.001 | 0.107 ± 0.001 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gao, J.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, B.; Chen, Z.; Gao, L.; Zhang, W. Multi-GPU Based Parallel Design of the Ant Colony Optimization Algorithm for Endmember Extraction from Hyperspectral Images. Sensors 2019, 19, 598. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19030598
Gao J, Sun Y, Zhang B, Chen Z, Gao L, Zhang W. Multi-GPU Based Parallel Design of the Ant Colony Optimization Algorithm for Endmember Extraction from Hyperspectral Images. Sensors. 2019; 19(3):598. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19030598
Chicago/Turabian StyleGao, Jianwei, Yi Sun, Bing Zhang, Zhengchao Chen, Lianru Gao, and Wenjuan Zhang. 2019. "Multi-GPU Based Parallel Design of the Ant Colony Optimization Algorithm for Endmember Extraction from Hyperspectral Images" Sensors 19, no. 3: 598. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19030598
APA StyleGao, J., Sun, Y., Zhang, B., Chen, Z., Gao, L., & Zhang, W. (2019). Multi-GPU Based Parallel Design of the Ant Colony Optimization Algorithm for Endmember Extraction from Hyperspectral Images. Sensors, 19(3), 598. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19030598