Development of a Portable, Ultra-Rapid and Ultra-Sensitive Cell-Based Biosensor for the Direct Detection of the SARS-CoV-2 S1 Spike Protein Antigen
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Green Monkey Kidney Cell Culture Conditions
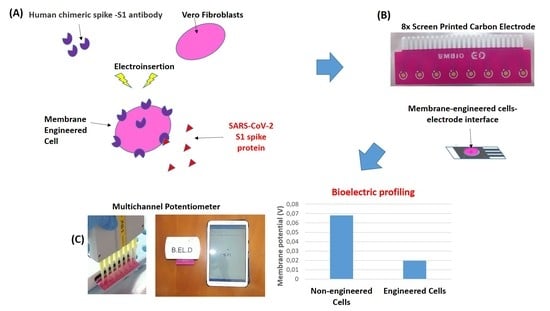
2.2. Sensor Fabrication from Membrane-Engineered Vero Cells (Vero/Anti-S1)
2.3. Vero/Anti-S1 Cell Membrane Potential Measurements: Biosensor Set-Up
2.4. Viability Monitoring of Membrane-Engineered Cells
2.5. Data Analysis and Experimental Design
3. Results
3.1. Membrane-Engineered Vero/anti-S1 Cells have a Distinct Response Against the SARS-CoV-2 Spike S1 Protein
3.2. The Biosensor Response is Dependent on the Concentration of the SARS-CoV-2 Spike S1 Protein
3.3. The Biosensor Response is Selective for the SARS-CoV-2 Spike S1 Protein
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, H.; Liu, S.M.; Yu, X.H.; Tang, S.L.; Tang, C.K. Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): Current status and future perspectives. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2020, 29, 105951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheridan, C. Fast, portable tests come online to curb coronavirus pandemic. Nat. Biotech. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Broughton, J.P.; Deng, X.; Yu, G.; Fasching, C.L.; Singh, J.; Streithorst, J.; Granados, A.; Gonzalez, A.S.; Zorn, K.; Gopez, A.; et al. Rapid Detection of 2019 Novel Coronavirus SARS-CoV-2 Using a CRISPR-based DETECTR Lateral Flow Assay. medRxiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, M.; Shi, Y.; Guo, Z.; Chen, Z.; He, R.; Chen, R.; Zhou, D.; Dai, E.; Wang, X.; Si, B.; et al. Antibody responses to individual proteins of SARS coronavirus and their neutralization activities. Microbes Infect. 2005, 5–6, 882–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tortorici, M.A.; Veesler, D. Structural insights into coronavirus entry. Adv. Virus Res. 2019, 105, 93–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walls, A.C.; Park, Y.J.; Tortorici, M.A.; Wall, A.; McGuire, A.T.; Veesler, D. Structure, function, and antigenicity of the SARS-CoV-2 spike glycoprotein. Cell 2020, 180, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonino, F.; Chiaberge, E.; Maran, E.; Piantino, P. Serological markers of HBV infectivity. Ann. Ist. Super. Sanita 1987, 24, 217–223. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, Y.J.; Goh, P.Y.; Fielding, B.C.; Shen, S.; Chou, C.F.; Fu, J.L.; Leong, H.N.; Leo, Y.S.; Ooi, E.E.; Ling, A.E.; et al. Profiles of antibody responses against severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus recombinant proteins and their potential use as diagnostic markers. Clin. Diagn. Lab. Immunol. 2004, 11, 362–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lu, L.; Manopo, I.; Leung, B.P.; Chng, H.H.; Ling, A.E.; Chee, L.L.; Ooi, E.E.; Chan, S.W.; Kwang, J. Immunological characterization of the spike protein of the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2004, 42, 1570–1576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kwon, J.A.; Yoon, S.Y.; Lee, C.K.; Lima, C.S.; Lee, K.N.; Sung, H.J.; Brennan, C.A.; Devare, S.G. Performance evaluation of three automated human immunodeficiency virus antigen–antibody combination immunoassays. J. Virol. Met. 2006, 133, 20–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berry, J.D.; Hay, K.; Rini, J.M.; Yu, M.; Want, L.; Plummer, F.A.; Corbett, C.R.; Andonov, A. Neutralizing epitopes of the SARS-CoV S-protein cluster independent of repertoire, antigen structure or mAb technology. MAbs 2010, 2, 53–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wu, H.S.; Chiu, S.C.; Tseng, T.C.; Lin, S.F.; Lin, J.H.; Hsu, Y.H.; Wang, M.C.; Lin, T.L.; Yang, W.Z.; Ferng, T.L.; et al. Serologic and molecular biologicmethods for SARS-associated coronavirus infection, Taiwan. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2004, 10, 304–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meyer, B.; Drosten, C.; Müller, M.A. Serological assays for emerging coronaviruses: Challenges and pitfalls. Virus Res. 2014, 194, 175–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moschopoulou, G.; Kintzios, S. Application of “membrane-engineering” to bioelectric recognition cell sensors for the detection of picomole concentrations of superoxide radical: A novel biosensor principle. Anal. Chimica Acta 2006, 573–574, 90–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kintzios, S. Molecular Identification through Membrane Engineered Cells. EPO Patent 1974211, 26 July 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Kokla, A.; Blouchos, P.; Livaniou, E.; Zikos, C.; Kakabakos, S.E.; Petrou, P.S.; Kintzios, S. Visualization of the membrane-engineering concept: Evidence for the specific orientation of electroinserted antibodies and selective binding of target analytes. J. Mol. Rec. 2013, 26, 627–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kintzios, S.; Pistola, E.; Panagiotopoulos, P.; Bomsel, M.; Alexandropoulos, N.; Bem, F.; Biselis, I.; Levin, R. Bioelectric recognition assay (BERA). Biosens. Bioelectron. 2001, 16, 325–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kintzios, S.; Pistola, E.; Konstas, J.; Bem, F.; Matakiadis, T.; Alexandropoulos, N.; Biselis, I.; Levin, R. Application of the Bioelectric recognition assay (BERA) for the detection of human and plant viruses: Definition of operational parameters. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2001, 16, 467–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moschopoulou, G.; Vitsa, K.; Bem, F.; Vassilakos, N.; Perdikaris, A.; Blouhos, P.; Yialouris, C.; Frossiniotis, D.; Anthopoulos, I.; Maggana, O.; et al. Engineering of the membrane of fibroblast cells with virus-specific antibodies: A novel biosensor tool for virus detection. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2008, 24, 1033–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mavrikou, S.; Flampouri, E.; Iconomou, D.; Kintzios, S. Development of a cellular biosensor for the detection of aflatoxin B1, based on the interaction of membrane engineered Vero cells with anti-AFB1 antibodies on the surface of gold nanoparticle screen printed electrodes. Food Control. 2017, 73, 64–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeira, M.; Tosi, P.F.; Mouneimne, Y.; Lazarte, J.; Sneed, L.; Volsky, D.L.; Nikolau, C. Full-length CD4 electroinserted in the erythrocyte membrane as a long-lived inhibitor of infection by human immunodeficiency virus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1991, 88, 4409–4413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Weisman, J.A.; Nicholson, J.C.; Tappa, K.; Jammalamadaka, U.; Wilson, C.G.; Mills, D.K. Antibiotic and chemotherapeutic enhanced three-dimensional printer filaments and constructs for biomedical applications. Int. J. Nanomed. 2015, 10, 357–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Apostolou, T.; Loizou, K.; Hadjilouka, A.; Inglezakis, A.; Kintzios, S. Newly developed system for acetamiprid residue screening in the lettuce samples based on a bioelectric cell biosensor. Biosensors 2020, 10, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Backer, J.A.; Klinkenberg, D.; Wallinga, J. Incubation period of 2019 novel coro- navirus (2019-nCoV) infections among travellers from Wuhan, China, 20–28 January 2020. Euro. Surveill. 2020, 25, 2000062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rothe, C.; Schunk, M.; Sothmann, P.; Bretzel, G.; Froeschl, G.; Wallrauch, C.; Zimmer, T.; Thiel, V.; Janke, C.; Guggemos, W.; et al. Transmission of 2019-nCoV infection from an asymptomatic contact in Germany. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 970–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Murphy, K.; Travers, P.; Walport, M. The Distribution and Functions of Immunoglobulin Classes, 5th ed.; Garland Science: New York, NY, USA, 2001; pp. 400–401. [Google Scholar]
- Li, F.; Li, W.; Farzan, M.; Harrison, S.C. Structure of SARS coronavirus spike receptor-binding domain complexed with receptor. Science 2005, 309, 1864–1868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giménez, L.G.; Rojas, J.; Rojas, A.; Mendoza, J.; Camacho, A.G. Development of an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay-based test with a cocktail of nucleocapsid and spike proteins for detection of severe acute respiratory syndrome-associated coronavirus-specific antibody. Clin. Vac. Immun. 2009, 16, 241–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wrapp, D.; Wang, N.; Corbett, K.S.; Goldsmith, J.A.; Hsieh, C.L.; Abiona, O.; Graham, B.S.; McLellan, J.S. Cryo- EM structure of the 2019-nCoV spike in the prefusion conformation. Science 2020, 367, 1260–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sunwoo, H.H.; Palaniyappan, A.; Ganguly, A.; Bhatnagar, P.K.; Das, D.; El-Kadi, A.O.; Suresh, M.R. Quantitative and sensitive detection of the SARS-CoV spike protein using bispecific monoclonal antibody-based enzyme-linked immunoassay. J. Virol. Meth. 2013, 187, 72–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, G.; Lee, G.; Kim, M.J.; Baek, S.H.; Choi, M.; Ku, K.B.; Lee, C.S.; Jun, S.; Park, D.; Kim, H.G.; et al. Rapid Detection of COVID-19 Causative Virus (SARS-CoV-2) in Human Nasopharyngeal Swab Specimens Using Field-Effect Transistor-Based Biosensor. ACS Nano 2020, 14, 5135–5142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qiu, G.; Gai, Z.; Tao, Y.; Schmitt, J.; Kullak-Ublick, G.A.; Wang, J. Dual-Functional Plasmonic Photothermal Biosensors for Highly Accurate Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 Detection. ACS Nano 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Perdikaris, A.; Alexandropoulos, N.; Kintzios, S. Development of a novel, ultra-rapid biosensor for the qualitative detection of hepatitis b virus-associated antigens and anti-HBV, based on “membrane-engineered” fibroblast cells with virus-specific antibodies and antigens. Sensors 2009, 9, 2176–2186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Perdikaris, A.; Vassilakos, N.; Yiakoumettis, I.; Kektsidou, O.; Kintzios, S. Development of a portable, high throughput biosensor system for rapid plant virus detection. J. Virol. Methods 2011, 177, 94–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gramberg, B.; Kintzios, S.; Schmidt, U.; Mewis, I.; Ulrichs, C. A basic approach towards the development of bioelectric bacterial biosensors for the detection of plant viruses. J. Phytopathol. 2012, 160, 106–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- To, K.K.; Tsang, O.T.; Chik-Yan Yip, C.; Chan, K.H.; Wu, T.C.; Chan, J.M.C.; Leung, W.S.; Hong Chik, T.S.; Chung Choi, C.Y.; Kandamby, D.H.; et al. Consistent detection of 2019 novel coronavirus in saliva. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kirchdoerfer, R.N.; Wang, N.; Pallesen, J.; Wrapp, D.; Turner, H.L.; Cottrell, C.A.; Corbett, K.S.; Graham, B.S.; McLellan, J.S.; Ward, A.B. Stabilized coronavirus spikes are resistant to conformational changes induced by receptor recognition or proteolysis. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 15701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Song, W.; Gui, M.; Wang, X.; Xiang, Y. Cryo-EM structure of the SARS coronavirus spike glycoprotein in complex with its host cell receptor ACE2. PLoS Pathog. 2018, 14, e1007236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hulswit, R.J.G.; Lang, Y.; Bakkers, M.J.G.; Li, W.; Li, Z.; Schouten, A.; Ophorst, B.; van Kuppeveld, F.J.M.; Boons, G.J.; Bosch, B.J.; et al. Human coronaviruses OC43 and HKU1 bind to 9-O-acetylated sialic acids via a conserved receptor-binding site in spike protein domain A. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 2681–2690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Park, Y.J.; Walls, A.C.; Wang, Z.; Sauer, M.M.; Li, W.; Tortorici, M.A.; Bosch, B.J.; DiMaio, F.; Veesler, D. Structures of MERS-CoV spike glycoprotein in complex with sialoside attachment receptors. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2019, 26, 1151–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Walls, A.C.; Xiong, X.; Park, Y.J.; Tortorici, M.A.; Snijder, J.; Quispe, J.; Cameroni, E.; Gopal, R.; Dai, M.; Lanzavecchia, A.; et al. Unexpected receptor functional mimicry elucidates activation of coronavirus fusion. Cell 2019, 176, 1026–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Katsanakis, N.; Katsivelis, A.; Kintzios, S. Immobilization of Electroporated Cells for Fabrication of Cellular Biosensors: Physiological Effects of the Shape of Calcium Alginate Matrices and Foetal Calf Serum. Sensors 2009, 9, 378–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]





© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mavrikou, S.; Moschopoulou, G.; Tsekouras, V.; Kintzios, S. Development of a Portable, Ultra-Rapid and Ultra-Sensitive Cell-Based Biosensor for the Direct Detection of the SARS-CoV-2 S1 Spike Protein Antigen. Sensors 2020, 20, 3121. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20113121
Mavrikou S, Moschopoulou G, Tsekouras V, Kintzios S. Development of a Portable, Ultra-Rapid and Ultra-Sensitive Cell-Based Biosensor for the Direct Detection of the SARS-CoV-2 S1 Spike Protein Antigen. Sensors. 2020; 20(11):3121. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20113121
Chicago/Turabian StyleMavrikou, Sophie, Georgia Moschopoulou, Vasileios Tsekouras, and Spyridon Kintzios. 2020. "Development of a Portable, Ultra-Rapid and Ultra-Sensitive Cell-Based Biosensor for the Direct Detection of the SARS-CoV-2 S1 Spike Protein Antigen" Sensors 20, no. 11: 3121. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20113121
APA StyleMavrikou, S., Moschopoulou, G., Tsekouras, V., & Kintzios, S. (2020). Development of a Portable, Ultra-Rapid and Ultra-Sensitive Cell-Based Biosensor for the Direct Detection of the SARS-CoV-2 S1 Spike Protein Antigen. Sensors, 20(11), 3121. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20113121