A “Global–Local” Visual Servo System for Picking Manipulators
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Principle of “Global–Local” Visual Servo Picking
3. Materials and Methods
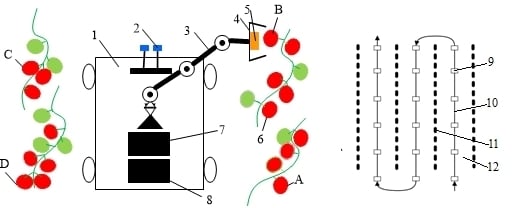
3.1. Prototype of the Picking Robot
3.2. Analysis of the Manipulator’s Operation Space
3.3. Binocular Identification of Mature Fruits and its Range
3.4. Monocular Visual Servo
3.5. Experimental Methods
4. Experimental Results and Analysis
4.1. Efficiency of Discrimination of Fruit Maturity
4.2. Binocular Ranging Accuracy
4.3. Feasibility of Monocular Visual Servo Picking
4.4. Success Rate of Fruit Picking
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhao, Y.S.; Gong, L.; Huang, Y.X.; Liu, C.L. A review of key techniques of vision-based control for harvesting robot. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2016, 127, 311–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaguchi, H.; Nagahama, K.; Hasegawa, T.; Inaba, M. Development of an autonomous tomato harvesting robot with rotational plucking gripper. In Proceedings of the IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Daejeon, South Korea, 9–14 October 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, Q.; Zou, W.; Fan, P.; Zhang, C.; Wang, X. Design and test of robotic harvesting system for cherry tomato. Int. J. Agric. Biol. Eng. 2018, 11, 96–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Q.C.; Wang, X.N.; Wang, G.H.; Zhen, L. Design and test of tomatoes harvesting robot. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Information and Automation, Lijiang, China, 8–10 August 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Barth, R.; Hemming, J.; van Henten, E.J. Design of an eye-in-hand sensing and servo control framework for harvesting robotics in dense vegetation. Biosyst. Eng. 2016, 146, 71–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Henten, E.J.V.; Hemming, J.; Tuijl, B.A.J.V.; Kornet, J.G.; Meuleman, J.; Bontsema, J.; Os, E.A.V. An autonomous robot for harvesting cucumbers in greenhouses. Auton. Robot 2002, 13, 241–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, H.W.; Zhou, H.Y.; Chen, C. Visual perception and modeling for autonomous apple harvesting. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 62151–62163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashimoto, K. A review on vision-based control of robot manipulators. Adv. Robot. 2003, 17, 969–991. [Google Scholar]
- Tabb, A.; Yousef, K.M. Solving the robot-world hand–eye(s) calibration problem with iterative methods. Mach. Vis. Appl. 2017, 28, 569–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, H.; Wang, N.L.; Qin, Y.S. A closed-form solution to eye-to-hand calibration towards visual grasping. Ind. Robot 2014, 41, 567–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, G.; Zhu, Z.H. Incremental visual servo control of robotic manipulator for autonomous capture of non-cooperative target. Adv. Robot. 2016, 30, 1458–1465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehnert, C.; English, A.; McCool, C.; Tow, A.W.; Perez, T. Autonomous sweet pepper harvesting for protected cropping systems. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2017, 2, 872–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mehta, S.S.; Burks, T.F. Vision-based control of robotic manipulator for citrus harvesting. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2014, 102, 146–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, S.; Chan, S.H.G. Wi-Fi fingerprint-based indoor positioning: Recent advances and comparisons. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2016, 18, 466–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.Y.; Chen, X.W.; Jing, G.F.; Wang, Y.; Cao, Y.F.; Li, F.; Zhang, X.L.; Xiao, H. An Indoor Continuous Positioning Algorithm on the Move by Fusing Sensors and Wi-Fi on Smartphones. Sensors 2015, 15, 31244–31267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munguía, R.; Nuño, E.; Aldana, C.; Urzua, S. A visual-aided inertial navigation and mapping system. Int. J. Adv. Robot. Syst. 2016, 13, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohnishi, N.; Imiya, A. Appearance-based navigation and homing for autonomous mobile robot. Image Vis. Comput. 2013, 31, 511–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khorashadizadeh, S.; Fateh, M.M. Robust task-space control of robot manipulators using Legendre polynomials for uncertainty estimation. Nonlinear Dyn. 2015, 79, 1151–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Yan, X.; Zhang, Q. Design and analysis of 3-DOF cylindrical-coordinate-based manipulator. Robot. Comput. Integr. Manuf. 2018, 52, 35–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, T.F.; Zhang, L.B.; Du, M.Y.; Bao, G.J.; Yang, Q.H. Fruit harvesting continuum manipulator inspired by elephant trunk. Int. J. Agric. Biol. Eng. 2015, 8, 57–63. [Google Scholar]
- Hong, S.; Cho, C.; Lee, H.; Kang, S.; Lee, W. Joint configuration for physically safe human–robot interaction of serial-chain manipulators. Mech. Mach. Theory 2017, 107, 246–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crooks, W.; Vukasin, G.; O’Sullivan, M. Fin ray effect inspired soft robotic gripper: From the RoboSoft Grand Challenge toward optimization. Front. Robot. AI 2016, 70, 70–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, B.; Han, L.Z.; Wang, Y.G.; Huang, S.; Liu, L.L. Kinematics analysis and numerical simulation of a manipulator based on virtual prototyping. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2014, 71, 943–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Gu, J.S.; Zang, Y.; Wu, X.; Zhang, S.J.; Guo, M.S. Path planning-oriented obstacle avoiding workspace modeling for robot manipulator. Int. J. Robot. Autom. 2019, 34, 1–16. [Google Scholar]
- Song, J.X.; Liu, L.; Huang, W.; Li, Y.F.; Chen, X.; Zhang, Z. Target detection via HSV color model and edge gradient information in infrared and visible image sequences under complicated background. Opt. Quantum Electron. 2018, 50, 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Junhua, C.; Jing, L. Research on color image classification based on HSV color space. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Instrumentation, Harbin, China, 8–10 December 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Ji, W.; Meng, X.L.; Qian, Z.J.; Xu, B.; Zhao, D.A. Branch localization method based on the skeleton feature extraction and stereo matching for apple harvesting robot. Int. J. Adv. Robot. Syst. 2017, 14, 1729881417705276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, Y.F.; Wang, H.; Dong, C.Y.; Chen, Q. A Car-Following Data Collecting Method Based on Binocular Stereo Vision. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 25350–25363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, L.J.; Li, D.J.; Lin, M.W.; Lin, R.; Yang, C.J. A Fast Binocular Localisation Method for AUV Docking. Sensors 2019, 19, 1735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]

























| Rod | ai | αi/ (°) | di | θi/ (°) | Range of Variables |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0 | 90 | d1 | θ1 | −80~80 |
| 2 | a2 | 0 | 0 | θ2 | 50~130 |
| 3 | a3 | 0 | 0 | θ3 | −60~−130 |
| 4 | a4 | 0 | 0 | θ4 | −80~80 |
| Parameter | Left Camera | Right Camera |
|---|---|---|
| fx | 1198.9821 | 1201.4563 |
| fy | 1197.5947 | 1200.3621 |
| P1 | 0.1021 | 0.1176 |
| P2 | −0.2750 | −0.3068 |
| K1 | 0.0016 | 0.0020 |
| K2 | 0.0016 | 0.0034 |
| K3 | 0 | 0 |
| Time | Ripe Tomatoes | Immature Tomatoes | Errors | Accuracy |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 80 | 32 | 8 | 93.3% |
| 2 | 78 | 33 | 9 | 92.5% |
| 3 | 77 | 34 | 9 | 92.5% |
| Number | Position (cm) | Successes | Average Time (s) | Average Success Rate |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | (30, 20, 45) | 46 | 23.19 | 91.5% |
| 2 | (30, −20, 45) | 45 | 18.71 | |
| 3 | (30, 20, 15) | 47 | 23.34 | |
| 4 | (30, 20, 15) | 44 | 22.49 | |
| 5 | (50, −20, 45) | 45 | 21.28 | |
| 6 | (50, −20, 45) | 46 | 22.30 | |
| 7 | (50, 20, 15) | 47 | 25.63 | |
| 8 | (50, −20, 15) | 46 | 25.07 |
| Number | Color | Successes | Average Time (s) | Average Success Rate | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| a | 1 | red | 47 | 18.10 | 94.5% |
| 2 | red | 48 | 15.15 | ||
| 3 | green | 0 | |||
| 4 | red | 49 | 19.36 | ||
| 5 | red | 45 | 23.11 | ||
| b | 1 | red | 48 | 18.10 | 93.0% |
| 2 | green | 0 | |||
| 3 | red | 47 | 15.15 | ||
| 4 | red | 47 | 19.36 | ||
| 5 | red | 44 | 23.11 | ||
| c | 1 | red | 42 | 18.10 | 90.0% |
| 2 | red | 47 | 15.15 | ||
| 3 | red | 48 | 23.11 | ||
| 4 | red | 43 | 19.36 | ||
| 5 | green | 0 | |||
| d | 1 | green | 0 | 92.5% | |
| 2 | red | 47 | 15.15 | ||
| 3 | red | 49 | 18.10 | ||
| 4 | red | 43 | 19.36 | ||
| 5 | red | 46 | 23.11 | ||
| e | 1 | red | 47 | 22.14 | 92.4% |
| 2 | red | 44 | 20.47 | ||
| 3 | red | 48 | 23.46 | ||
| 4 | red | 47 | 18.65 | ||
| 5 | red | 45 | 21.22 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shi, Y.; Zhang, W.; Li, Z.; Wang, Y.; Liu, L.; Cui, Y. A “Global–Local” Visual Servo System for Picking Manipulators. Sensors 2020, 20, 3366. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20123366
Shi Y, Zhang W, Li Z, Wang Y, Liu L, Cui Y. A “Global–Local” Visual Servo System for Picking Manipulators. Sensors. 2020; 20(12):3366. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20123366
Chicago/Turabian StyleShi, Yinggang, Wei Zhang, Zhiwen Li, Yong Wang, Li Liu, and Yongjie Cui. 2020. "A “Global–Local” Visual Servo System for Picking Manipulators" Sensors 20, no. 12: 3366. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20123366
APA StyleShi, Y., Zhang, W., Li, Z., Wang, Y., Liu, L., & Cui, Y. (2020). A “Global–Local” Visual Servo System for Picking Manipulators. Sensors, 20(12), 3366. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20123366