Real-Time Loosely Coupled 3DMA GNSS/Doppler Measurements Integration Using a Graph Optimization and Its Performance Assessments in Urban Canyons of New York
Abstract
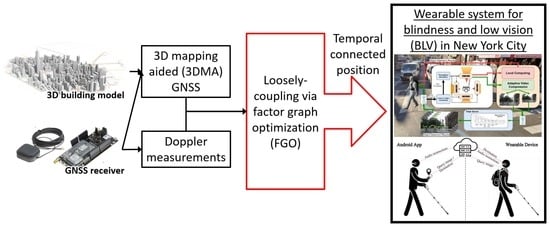
:1. Introduction
2. Navigation System for Visually Impaired Pedestrians
2.1. Overview of Navigation System for Visually Impaired Pedestrians
2.2. Importance of GNSS Positioning
2.3. Related Works on 3DMA GNSS
3. Proposed Real-Time 3D Mapping-Aided (3DMA) GNSS-Positioning System
3.1. Open-Sourced 3D City Models
3.2. Offline Stage Skymasks Generation
3.3. 3DMA GNSS Positioning Algorithm
3.3.1. Skymask Context-Based Candidates Sampling
3.3.2. Integrated Solution of 3DMA GNSS
3.4. Loosely-Coupled Factor Graph Optimization (LC-FGO)
4. Experiments and Results
4.1. Experiment Setup
4.2. Experiment Results
- NMEA: receiver output solution.
- WLS: weighted least squares method [52]; uses pseudorange to estimate receiver location.
- 3DMA GNSS: snapshot state-of-the-art 3DMA GNSS with positioning hypothesis candidates [35].
- LC-FGO (proposed): real-time forward (instantaneous) processed loosely-coupled FGO solution with integrated 3DMA GNSS and velocity.
- LC-FGO-PP (proposed): combined (forward and backward) processed loosely-coupled FGO solution with integrated 3DMA GNSS and velocity.
4.3. Computational Load and Storage Requirements
5. Conclusions and Future Work
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A

Appendix B

References
- Rizzo, J.-R.; Feng, C.; Riewpaiboon, W.; Mongkolwat, P. A Low-Vision Navigation Platform for Economies in Transition Countries. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE World Congress on Services (SERVICES), Beijing, China, 18–23 October 2020; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2020; pp. 1–3. [Google Scholar]
- Niu, L.; Qian, C.; Rizzo, J.-R.; Hudson, T.; Li, Z.; Enright, S.; Sperling, E.; Conti, K.; Wong, E.; Fang, Y. A Wearable Assistive Technology for the Visually Impaired with Door Knob Detection and Real-Time Feedback for Hand-to-Handle Manipulation. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision Workshops, Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 1500–1508. [Google Scholar]
- Gui, W.; Li, B.; Yuan, S.; Rizzo, J.-R.; Sharma, L.; Feng, C.; Tzes, A.; Fang, Y. An Assistive Low-Vision Platform that Augments Spatial Cognition Through Proprioceptive Guidance: Point-to-Tell-and-Touch. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Macau, China, 4–8 November 2019; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2019; pp. 3817–3822. [Google Scholar]
- Boldini, A.; Garcia, A.L.; Sorrentino, M.; Beheshti, M.; Ogedegbe, O.; Fang, Y.; Porfiri, M.; Rizzo, J.-R. An inconspicuous, integrated electronic travel aid for visual impairment. ASME Lett. Dyn. Syst. Control. 2021, 1, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Cui, H.; Rizzo, J.-R.; Wong, E.; Fang, Y. Cross-Safe: A Computer Vision-Based Approach to Make All Intersection-Related Pedestrian Signals Accessible for the Visually Impaired. In Proceedings of the Science and Information Conference, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 25–26 April 2019; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2019; pp. 132–146. [Google Scholar]
- Rizzo, J.-R.; Pan, Y.; Hudson, T.; Wong, E.K.; Fang, Y. Sensor Fusion for Ecologically Valid Obstacle Identification: Bu ilding A Comprehensive Assistive Technology Platform for the Visually Impaired. In Proceedings of the 2017 7th International Conference on Modeling, Simulation, and Applied Optimization (ICMSAO), Sharjah, United Arab Emirates, 4–6 April 2017; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2017; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Shoureshi, R.A.; Rizzo, J.R.; Hudson, T.E. Smart Wearable Systems for Enhanced Monitoring and Mobility. Advances in Science and Technology; Trans Tech Publications: Bach, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 172–178. [Google Scholar]
- Phamduy, P.; Rizzo, J.-R.; Hudson, T.E.; Torre, M.; Levon, K.; Porfiri, M. Communicating through touch: Macro fiber composites for tactile stimulation on the abdomen. IEEE Trans. Haptics 2017, 11, 174–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Groves, P.D. Multipath vs. NLOS signals. Inside GNSS 2013, 8, 40–42. [Google Scholar]
- Asano, S.; Wakuda, Y.; Koshizuka, N.; Sakamura, K. A Robust Pedestrian Dead-Reckoning Positioning Based on Pedestrian Behavior and Sensor Validity. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE/ION Position, Location and Navigation Symposium, Myrtle Beach, SC, USA, 23–26 April 2012; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2012; pp. 328–333. [Google Scholar]
- Steinbrücker, F.; Sturm, J.; Cremers, D. Real-Time Visual Odometry from Dense RGB-D Images. In Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision Workshops (ICCV Workshops), Barcelona, Spain, 6–13 November 2011; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2011; pp. 719–722. [Google Scholar]
- Qin, T.; Li, P.; Shen, S. VINS-Mono: A Robust and Versatile Monocular Visual-Inertial State Estimator. IEEE Trans. Robot. 2018, 34, 1004–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, T.; Kubo, N. N-LOS GNSS signal detection using fish-eye camera for vehicle navigation in urban environments. In Proceedings of the 27th International Technical Meeting of the Satellite Division of the Institute of Navigation, ION GNSS 2014, Tampa, FL, USA, 8–12 September 2014; pp. 1897–1906. [Google Scholar]
- Moreau, J.; Ambellouis, S.; Ruichek, Y. Fisheye-Based Method for GPS Localization Improvement in Unknown Semi-Obstructed Areas. Sensors 2017, 17, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groves, P.D.; Jiang, Z. Height Aiding, C/N0 Weighting and Consistency Checking for GNSS NLOS and Multipath Mitigation in Urban Areas. J. Navig. 2013, 66, 653–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, L.-T.; Tokura, H.; Kubo, N.; Gu, Y.; Kamijo, S. Multiple Faulty GNSS Measurement Exclusion Based on Consistency Check in Urban Canyons. IEEE Sens. J. 2017, 17, 1909–1917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, H.-F.; Zhang, G.; Yang, K.-Y.; Yang, S.-X.; Hsu, L.-T. Improved weighting scheme using consumer-level GNSS L5/E5a/B2a pseudorange measurements in the urban area. Adv. Space Res. 2020, 66, 1647–1658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradbury, J.; Ziebart, M.; Cross, P.A.; Boulton, P.; Read, A. Code Multipath Modelling in the Urban Environment Using Large Virtual Reality City Models: Determining the Local Environment. J. Navig. 2007, 60, 95–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, L.; Cross, P. Development and testing of a new ray-tracing approach to GNSS carrier-phase multipath modelling. J. Geod. 2007, 81, 713–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradbury, J. Prediction of Urban GNSS Availability and Signal Degradation Using Virtual Reality City Models. In Proceedings of the 20th International Technical Meeting of the Satellite Division of The Institute of Navigation (ION GNSS 2007), Fort Worth, TX, USA, 25–28 September 2007; 2007; pp. 2696–2706. [Google Scholar]
- Groves, P.D. It’s Time for 3D Mapping–Aided GNSS. Inside GNSS Magazine, July 2016; pp. 50–56. [Google Scholar]
- Diggelen, F.V. End Game for Urban GNSS: Google’s Use of 3D Building Models. Inside GNSS Magazine, 21 March 2021; pp. 42–49. [Google Scholar]
- Obst, M.; Bauer, S.; Wanielik, G. Urban Multipath Detection and Mitigation with Dynamic 3D Maps for Reliable Land Vehicle Localization. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE/ION Position, Location and Navigation Symposium, Myrtle Beach, SC, USA, 23–26 April 2012; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2012; pp. 685–691. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Groves, P.D.; Ziebart, M.K. GNSS Shadow Matching: Improving Urban Positioning Accuracy Using a 3D City Model with Optimized Visibility Scoring Scheme. NAVIGATION J. Inst. Navig. 2013, 60, 195–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Groves, P.D.; Ziebart, M.K. Smartphone Shadow Matching for Better Cross-street GNSS Positioning in Urban Environments. J. Navig. 2015, 68, 411–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yozevitch, R.; Moshe, B.B. A Robust Shadow Matching Algorithm for GNSS Positioning. Navig. J. Inst. Navig. 2015, 62, 95–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, L.-T.; Gu, Y.; Kamijo, S. 3D building model-based pedestrian positioning method using GPS/GLONASS/QZSS and its reliability calculation. GPS Solut. 2016, 20, 413–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miura, S.; Hsu, L.-T.; Chen, F.; Kamijo, S. GPS Error Correction with Pseudorange Evaluation Using Three-Dimensional Maps. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2015, 16, 3104–3115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziedan, N.I. Urban Positioning Accuracy Enhancement Utilizing 3D Buildings Model and Accelerated Ray Tracing Algorithm. In Proceedings of the 30th International Technical Meeting of The Satellite Division of the Institute of Navigation (ION GNSS+ 2017), Portland, OR, USA, 25–29 September 2017; Oregon Convention Center: Portland, OR, USA, 2017; pp. 3253–3268. [Google Scholar]
- Ng, H.-F.; Zhang, G.; Hsu, L.-T. A Computation Effective Range-based 3D Mapping Aided GNSS with NLOS Correction Method. J. Navig. 2020, 73, 1202–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, T.; Kubo, N. Correcting GNSS Multipath Errors Using a 3D Surface Model and Particle Filter. In Proceedings of the 26th International Technical Meeting of the Satellite Division of The Institute of Navigation (ION GNSS+ 2013), Nashville, TN, USA, 16–20 September 2013; pp. 1583–1595. [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki, T.; Kubo, N. GNSS Positioning with Multipath Simulation Using 3D Surface Model in Urban Canyon. In Proceedings of the 25th International Technical Meeting of the Satellite Division of The Institute of Navigation (ION GNSS 2012), Nashville, TN, USA, 17–21 September 2012; pp. 438–447. [Google Scholar]
- Schön, S.; Baasch, K.-N.; Icking, L.; KarimiDoona, A.; Lin, Q.; Ruwisch, F.; Schaper, A.; Su, J. Towards Integrity for GNSS-Based Urban Navigation—Challenges And Lessons Learned. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE Intelligent Vehicles Symposium (IV); Aachen, Germany, 4–9 June 2022, IEEE Press: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2022; pp. 1774–1781. [Google Scholar]
- Zhong, Q.; Groves, P.D. Multi-Epoch 3D-Mapping-Aided Positioning using Bayesian Filtering Techniques. NAVIGATION 2022, 69, navi.515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, H.-F.; Zhang, G.; Luo, Y.; Hsu, L.-T. Urban positioning: 3D mapping-aided GNSS using dual-frequency pseudorange measurements from smartphones. NAVIGATION J. Inst. Navig. 2021, 68, 727–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groves, P.D. Principles of GNSS, Inertial, and Multisensor Integrated Navigation Systems, 2nd ed.; Artech House: Norwood, MA, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, G.; Wen, W.; Xu, B.; Hsu, L.-T. Extending Shadow Matching to Tightly-Coupled GNSS/INS Integration System. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2020, 69, 4979–4991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, T. Integration of GNSS Positioning and 3D Map using Particle Filter. In Proceedings of the 29th International Technical Meeting of the Satellite Division of The Institute of Navigation (ION GNSS+ 2016), Portland, OR, USA, 12–16 September 2016; Oregon Convention Center: Portland, OR, USA, 2016; pp. 1296–1304. [Google Scholar]
- Ziedan, N.I. Optimized Position Estimation in Multipath Environments using Machine Learning. In Proceedings of the 34th International Technical Meeting of the Satellite Division of The Institute of Navigation (ION GNSS+ 2021), St. Louis, MI, USA, 20–24 September 2021; Union Station Hotel: St. Louis, MI, USA, 2021; pp. 3437–3451. [Google Scholar]
- Sünderhauf, N.; Protzel, P. Towards Robust Graphical Models for GNSS-Based Localization in Urban Environments. In Proceedings of the International Multi-Conference on Systems, Signals & Devices, Chemnitz, Germany, 20–23 March 2012; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2012; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Wen, W.; Hsu, L.-T. Towards Robust GNSS Positioning and Real-time Kinematic Using Factor Graph Optimization. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Xi’an, China, 30 May–5 June 2021; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2021; pp. 5884–5890. [Google Scholar]
- Watson, R.M.; Gross, J.N. Evaluation of Kinematic Precise Point Positioning Convergence with an Incremental Graph Optimizer. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE/ION Position, Location and Navigation Symposium (PLANS), Monterey, CA, USA, 23 April 2018; pp. 589–596. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, G.; Ng, H.-F.; Wen, W.; Hsu, L.-T. 3D Mapping Database Aided GNSS Based Collaborative Positioning Using Factor Graph Optimization. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2021, 22, 6175–6187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Department of City Planning NYC 3D Model by Community District. Available online: https://www1.nyc.gov/site/planning/data-maps/open-data/dwn-nyc-3d-model-download.page (accessed on 11 May 2021).
- Robert McNeel Rhinoceros. Available online: https://www.rhino3d.com/ (accessed on 11 May 2021).
- Epic Games Unreal Engine. Available online: https://www.unrealengine.com/en-US (accessed on 11 May 2021).
- van Diggelen, F. A-GPS: Assisted GPS, GNSS, and SBAS; Artech: Morristown, NJ, USA, 2009; Volume 33. [Google Scholar]
- van Diggelen, F. Assisted GNSS. In Position, Navigation, and Timing Technologies in the 21st Century; Wiley-IEEE Press: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2020; pp. 419–444. [Google Scholar]
- Groves, P.D. Shadow Matching: A New GNSS Positioning Technique for Urban Canyons. J. Navig. 2011, 64, 417–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, L.-T.; Kubo, N.; Wen, W.; Chen, W.; Liu, Z.; Suzuki, T.; Meguro, J. UrbanNav:An Open-Sourced Multisensory Dataset for Benchmarking Positioning Algorithms Designed for Urban Areas. In Proceedings of the 34th International Technical Meeting of the Satellite Division of The Institute of Navigation (ION GNSS+ 2021), St. Louis, MI, USA, 20–24 September 2021; Institute of Navigation: Manassas, VA, USA, 2021; pp. 226–256. [Google Scholar]
- Li, W.; Cui, X.; Lu, M. A robust graph optimization realization of tightly coupled GNSS/INS integrated navigation system for urban vehicles. Tsinghua Sci. Technol. 2018, 23, 724–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takasu, T. RTKLIB: Open Source Program Package for RTK-GPS. In Proceedings of the FOSS4G 2009, Sydney, Australia, 20–23 October 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Agarwal, S.; Mierle, K. Ceres solver: Tutorial & reference. Google Inc. 2012, 2, 8. [Google Scholar]
- Kennedy, S.; Hamilton, J.; Martell, H. Architecture and System Performance of SPAN-NovAtel’s GPS/INS Solution. In Proceedings of the IEEE/ION PLANS 2006, San Diego, CA, USA, 25–27 April 2006; pp. 266–274. [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki, T.; Matsuo, K.; Amano, Y. Rotating GNSS Antennas: Simultaneous LOS and NLOS Multipath Mitigation. GPS Solut. 2020, 24, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, B.; Jia, Q.; Luo, Y.; Hsu, L.T. Intelligent GPS L1 LOS/multipath/NLOS classifiers based on correlator-, RINEX- and NMEA-level measurements. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, P.; Petovello, M.G. Measuring GNSS Multipath Distributions in Urban Canyon Environments. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2015, 64, 366–377. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, L.; Ziedan, N.I.; Niu, X.; Guo, W. Correlation acceleration in GNSS software receivers using a CUDA-enabled GPU. GPS Solut. 2017, 21, 225–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]











| Navigation Trips | Epochs (s) | Algorithm | RMSE (m) | STD (m) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 952 | 1. NMEA | 31.09 | 14.47 |
| 2. WLS | 38.30 | 20.00 | ||
| 2. 3DMA GNSS | 19.70 | 15.51 | ||
| 3. LC-FGO | 24.66 | 14.95 | ||
| 4. LC-FGO-PP | 15.54 | 12.25 | ||
| 2 | 979 | 1. NMEA | 74.81 | 31.57 |
| 2. WLS | 59.15 | 26.94 | ||
| 2. 3DMA GNSS | 29.14 | 16.75 | ||
| 3. LC-FGO | 33.56 | 17.13 | ||
| 4. LC-FGO-PP | 24.66 | 13.08 | ||
| 3 | 574 | 1. NMEA | 19.87 | 7.35 |
| 2. WLS | 62.66 | 38.62 | ||
| 2. 3DMA GNSS | 27.62 | 16.40 | ||
| 3. LC-FGO | 22.98 | 11.04 | ||
| 4. LC-FGO-PP | 21.38 | 9.51 | ||
| 4 | 607 | 1. NMEA | 17.20 | 11.08 |
| 2. WLS | 91.98 | 54.99 | ||
| 2. 3DMA GNSS | 21.08 | 12.26 | ||
| 3. LC-FGO | 13.01 | 6.48 | ||
| 4. LC-FGO-PP | 14.09 | 6.85 | ||
| 5 | 599 | 1. NMEA | 29.01 | 7.43 |
| 2. WLS | 30.34 | 10.46 | ||
| 2. 3DMA GNSS | 22.64 | 13.21 | ||
| 3. LC-FGO | 20.38 | 10.25 | ||
| 4. LC-FGO-PP | 18.90 | 11.18 | ||
| 6 | 934 | 1. NMEA | 36.89 | 18.01 |
| 2. WLS | 39.17 | 19.54 | ||
| 2. 3DMA GNSS | 18.27 | 11.28 | ||
| 3. LC-FGO | 15.32 | 10.44 | ||
| 4. LC-FGO-PP | 14.56 | 8.73 | ||
| 7 | 885 | 1. NMEA | 33.36 | 15.61 |
| 2. WLS | 44.25 | 25.89 | ||
| 2. 3DMA GNSS | 18.64 | 11.27 | ||
| 3. LC-FGO | 25.17 | 11.03 | ||
| 4. LC-FGO-PP | 12.17 | 6.08 | ||
| 8 | 513 | 1. NMEA | 39.09 | 11.05 |
| 2. WLS | 36.43 | 15.94 | ||
| 2. 3DMA GNSS | 16.55 | 9.46 | ||
| 3. LC-FGO | 21.30 | 8.36 | ||
| 4. LC-FGO-PP | 14.22 | 7.47 | ||
| 9 | 878 | 1. NMEA | 24.17 | 10.38 |
| 2. WLS | 40.86 | 21.21 | ||
| 2. 3DMA GNSS | 41.50 | 26.91 | ||
| 3. LC-FGO | 44.62 | 29.99 | ||
| 4. LC-FGO-PP | 37.67 | 24.91 | ||
| 10 | 742 | 1. NMEA | 36.01 | 16.88 |
| 2. WLS | 49.43 | 31.11 | ||
| 2. 3DMA GNSS | 26.72 | 15.29 | ||
| 3. LC-FGO | 25.49 | 13.08 | ||
| 4. LC-FGO-PP | 20.46 | 11.15 | ||
| 11 | 733 | 1. NMEA | 46.78 | 18.12 |
| 2. WLS | 62.33 | 37.96 | ||
| 2. 3DMA GNSS | 36.85 | 28.13 | ||
| 3. LC-FGO | 37.82 | 27.85 | ||
| 4. LC-FGO-PP | 32.13 | 26.08 |
| Algorithm | RMSE (m) | STD (m) |
|---|---|---|
| 1. WLS | 14.92 | 9.20 |
| 2. 3DMA GNSS | 7.94 | 4.85 |
| 3. LC-FGO | 8.09 | 4.55 |
| 4. LC-FGO-PP | 5.80 | 2.95 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ng, H.-F.; Hsu, L.-T.; Lee, M.J.L.; Feng, J.; Naeimi, T.; Beheshti, M.; Rizzo, J.-R. Real-Time Loosely Coupled 3DMA GNSS/Doppler Measurements Integration Using a Graph Optimization and Its Performance Assessments in Urban Canyons of New York. Sensors 2022, 22, 6533. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22176533
Ng H-F, Hsu L-T, Lee MJL, Feng J, Naeimi T, Beheshti M, Rizzo J-R. Real-Time Loosely Coupled 3DMA GNSS/Doppler Measurements Integration Using a Graph Optimization and Its Performance Assessments in Urban Canyons of New York. Sensors. 2022; 22(17):6533. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22176533
Chicago/Turabian StyleNg, Hoi-Fung, Li-Ta Hsu, Max Jwo Lem Lee, Junchi Feng, Tahereh Naeimi, Mahya Beheshti, and John-Ross Rizzo. 2022. "Real-Time Loosely Coupled 3DMA GNSS/Doppler Measurements Integration Using a Graph Optimization and Its Performance Assessments in Urban Canyons of New York" Sensors 22, no. 17: 6533. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22176533
APA StyleNg, H. -F., Hsu, L. -T., Lee, M. J. L., Feng, J., Naeimi, T., Beheshti, M., & Rizzo, J. -R. (2022). Real-Time Loosely Coupled 3DMA GNSS/Doppler Measurements Integration Using a Graph Optimization and Its Performance Assessments in Urban Canyons of New York. Sensors, 22(17), 6533. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22176533