Micromeria fruticosa Induces Cell Cycle Arrest and Apoptosis in Breast and Colorectal Cancer Cells
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Cytotoxic Activity
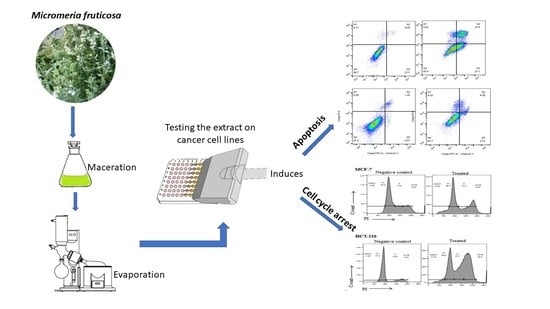
2.2. Apoptotic Activity
2.3. Caspase Activity
2.4. Cell Cycle Analysis
2.5. qRT-PCR and Western Blot
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Chemicals
4.2. Plant Material and Extraction
4.3. Cell Lines
4.4. Cytotoxicity Assay
4.5. Annexin V/PI
4.6. Caspase 8/9 Assay
4.7. Cell Cycle Analysis
4.8. RNA Isolation, cDNA and qRT-PCR
4.9. Western Blotting Analysis
4.10. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- World Health Organization. Cancer registration and statistics. J. Am. Med. Womens Assoc. 1951, 6, 142. [Google Scholar]
- MacDonald, V. Chemotherapy: Managing side effects and safe handling. Can. Vet. J. 2009, 50, 665–668. [Google Scholar]
- Zi, X.; Zhang, R. Anti-cancer molecular targets of natural products. Curr. Cancer Drug Targets 2013, 13, 485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salameh, N.; Shraim, N.; Jaradat, N. Chemical Composition and Enzymatic Screening of Micromeria fruticosa serpyllifolia Volatile Oils Collected from Three Different Regions of West Bank, Palestine. Biomed. Res. Int. 2018, 2018, 6536919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yaniv, Z.; Dudai, N. Medicinal and Aromatic Plants of the Middle-East; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2014; Volume 2. [Google Scholar]
- Dafni, A.; Yaniv, Z.; Palevitch, D. Ethnobotanical survey of medicinal plants in northern Israel. J. Ethnopharmacol. 1984, 10, 295–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu-Gharbieh, E.; Shehab, N.G.; Khan, S.A. Anti-inflammatory and gastroprotective activities of the aqueous extract of Micromeria fruticosa (L.) Druce ssp Serpyllifolia in mice. Pak. J. Pharm. Sci. 2013, 26, 799–803. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Abu-Gharbieh, E.; Bustanji, Y.; Mohammad, M. In vitro effects of Micromeria fruticosa on human leukocyte myeloperoxidase activity. J. Pharm. Res. 2010, 3, 2492–2493. [Google Scholar]
- Abu-Gharbieh, E.; Ahmed, N.G. Bioactive content, hepatoprotective and antioxidant activities of whole plant extract of Micromeria fruticosa (L) Druce ssp Serpyllifolia F Lamiaceae against Carbon tetrachloride-induced hepatotoxicity in mice. Trop. J. Pharm. Res. 2016, 15, 2099–2106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shehab, N.G.; Abu-Gharbieh, E. Constituents and biological activity of the essential oil and the aqueous extract of Micromeria fruticosa (L.) Druce subsp. serpyllifolia. Pak. J. Pharm. Sci. 2012, 25, 687–692. [Google Scholar]
- Koc, K.; Ozdemir, O.; Kizilkaya, O.F.; Sengul, M.; Turkez, H. Cytotoxic activity of the aqueous extract of Micromeria fruticosa (L.) Druce subsp. serpyllifolia on human U-87 MG cell lines. Arch. Biol. Sci. 2017, 69, 449–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, T.; Zhu, W.; Yang, X.; Chen, L.; Yang, R.; Hua, Z.; Li, G. Detection of apoptosis based on the interaction between annexin V and phosphatidylserine. Anal. Chem. 2009, 81, 2410–2413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baskic, D.; Popovic, S.; Ristic, P.; Arsenijevic, N.N. Analysis of cycloheximide-induced apoptosis in human leukocytes: Fluorescence microscopy using annexin V/propidium iodide versus acridin orange/ethidium bromide. Cell Biol. Int. 2006, 30, 924–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Julien, O.; Wells, J.A. Caspases and their substrates. Cell Death Differ. 2017, 24, 1380–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janicke, R.U.; Sprengart, M.L.; Wati, M.R.; Porter, A.G. Caspase-3 is required for DNA fragmentation and morphological changes associated with apoptosis. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 9357–9360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Srinivasula, S.M.; Ahmad, M.; Fernandes-Alnemri, T.; Litwack, G.; Alnemri, E.S. Molecular ordering of the Fas-apoptotic pathway: The Fas/APO-1 protease Mch5 is a CrmA-inhibitable protease that activates multiple Ced-3/ICE-like cysteine proteases. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1996, 93, 14486–14491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ashkenazi, A. Targeting the extrinsic apoptosis pathway in cancer. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2008, 19, 325–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jelinek, M.; Balusikova, K.; Schmiedlova, M.; Nemcova-Furstova, V.; Sramek, J.; Stancikova, J.; Zanardi, I.; Ojima, I.; Kovar, J. The role of individual caspases in cell death induction by taxanes in breast cancer cells. Cancer Cell Int. 2015, 15, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dai, J.; Mumper, R.J. Plant phenolics: Extraction, analysis and their antioxidant and anticancer properties. Molecules 2010, 15, 7313–7352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ElKhazendar, M.; Chalak, J.; El-Huneidi, W.; Vinod, A.; Abdel-Rahman, W.M.; Abu-Gharbieh, E. Antiproliferative and proapoptotic activities of ferulic acid in breast and liver cancer cell lines. Trop. J. Pharm. Res. 2019, 18, 2571–2576. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.D.; Wu, Q.; Yang, S.H. Ferulic acid promoting apoptosis in human osteosarcoma cell lines. Pak. J. Med. Sci. 2017, 33, 127–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.H.; Kee, J.Y.; Hong, S.H. Rosmarinic Acid Activates AMPK to Inhibit Metastasis of Colorectal Cancer. Front. Pharmacol. 2018, 9, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Hu, M.; Liu, L.; Cheng, X.L.; Cai, J.; Zhou, J.; Wang, T. Anticancer effects of Rosmarinic acid in OVCAR-3 ovarian cancer cells are mediated via induction of apoptosis, suppression of cell migration and modulation of lncRNA MALAT-1 expression. J. BUON 2018, 23, 763–768. [Google Scholar]
- Jang, Y.G.; Hwang, K.A.; Choi, K.C. Rosmarinic Acid, a Component of Rosemary Tea, Induced the Cell Cycle Arrest and Apoptosis through Modulation of HDAC2 Expression in Prostate Cancer Cell Lines. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lee, K.H.; Ho, W.Y.; Wu, S.J.; Cheng, T.L.; Huang, P.J.; Wang, C.C.; Hung, J.H. Behavior-selective apoptotic capacity of 4-(3,4,5-Trimethoxyphenoxy) benzoic acid and its methyl derivatives on two breast cancer cell lines. Anticancer Res. 2014, 34, 1801–1809. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, L.T.; Lee, Y.H.; Sharma, A.R.; Park, J.B.; Jagga, S.; Sharma, G.; Lee, S.S.; Nam, J.S. Quercetin induces apoptosis and cell cycle arrest in triple-negative breast cancer cells through modulation of Foxo3a activity. Korean J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2017, 21, 205–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bishayee, K.; Ghosh, S.; Mukherjee, A.; Sadhukhan, R.; Mondal, J.; Khuda-Bukhsh, A.R. Quercetin induces cytochrome-c release and ROS accumulation to promote apoptosis and arrest the cell cycle in G2/M, in cervical carcinoma: Signal cascade and drug-DNA interaction. Cell Prolif. 2013, 46, 153–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, G.T.; Lee, S.H.; Kim, J.I.; Kim, Y.M. Quercetin regulates the sestrin 2-AMPK-p38 MAPK signaling pathway and induces apoptosis by increasing the generation of intracellular ROS in a p53-independent manner. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2014, 33, 863–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maurya, A.K.; Vinayak, M. Anticarcinogenic action of quercetin by downregulation of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K) and protein kinase C (PKC) via induction of p53 in hepatocellular carcinoma (HepG2) cell line. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2015, 42, 1419–1429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidya Priyadarsini, R.; Senthil Murugan, R.; Maitreyi, S.; Ramalingam, K.; Karunagaran, D.; Nagini, S. The flavonoid quercetin induces cell cycle arrest and mitochondria-mediated apoptosis in human cervical cancer (HeLa) cells through p53 induction and NF-kappaB inhibition. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2010, 649, 84–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, W.R.; Stark, G.R. Regulation of the G2/M transition by p53. Oncogene 2001, 20, 1803–1815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Garg, H.; Suri, P.; Gupta, J.C.; Talwar, G.P.; Dubey, S. Survivin: A unique target for tumor therapy. Cancer Cell Int. 2016, 16, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nestal de Moraes, G.; Silva, K.L.; Vasconcelos, F.C.; Maia, R.C. Survivin overexpression correlates with an apoptosis-resistant phenotype in chronic myeloid leukemia cells. Oncol. Rep. 2011, 25, 1613–1619. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, F.; Ambrosini, G.; Chu, E.Y.; Plescia, J.; Tognin, S.; Marchisio, P.C.; Altieri, D.C. Control of apoptosis and mitotic spindle checkpoint by survivin. Nature 1998, 396, 580–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Norbury, C.; Nurse, P. Animal cell cycles and their control. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 1992, 61, 441–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Genes | Forward (5′→3′) | Reverse (5′→3′) |
|---|---|---|
| Survivin | 5’ACCGCATCTCTACATTCAAG3’ | 5’CAAGTCTGGCTCGTTCTC3′ |
| CDK1 Cyclin B1 | 5’CAGACTAGAAAGTGAAGAGGAAGG3’ 5’AAGAGCTTTAAACTTTGGTCTGGG3’ | 5’ACTGACCAGGAGGGATAGAA3′ 5’GTTTGTAAGTCCTTGATTTACCATG3′ |
| 18S rRNA | 5’TCAGATACCGTCGTAGTTCCG3’ | 5’CAGCTTTGCAACCATACTCCC3′ |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
El-Huneidi, W.; Shehab, N.G.; Bajbouj, K.; Vinod, A.; El-Serafi, A.; Shafarin, J.; Bou Malhab, L.J.; Abdel-Rahman, W.M.; Abu-Gharbieh, E. Micromeria fruticosa Induces Cell Cycle Arrest and Apoptosis in Breast and Colorectal Cancer Cells. Pharmaceuticals 2020, 13, 115. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph13060115
El-Huneidi W, Shehab NG, Bajbouj K, Vinod A, El-Serafi A, Shafarin J, Bou Malhab LJ, Abdel-Rahman WM, Abu-Gharbieh E. Micromeria fruticosa Induces Cell Cycle Arrest and Apoptosis in Breast and Colorectal Cancer Cells. Pharmaceuticals. 2020; 13(6):115. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph13060115
Chicago/Turabian StyleEl-Huneidi, Waseem, Naglaa G. Shehab, Khuloud Bajbouj, Arya Vinod, Ahmed El-Serafi, Jasmin Shafarin, Lara J. Bou Malhab, Wael M. Abdel-Rahman, and Eman Abu-Gharbieh. 2020. "Micromeria fruticosa Induces Cell Cycle Arrest and Apoptosis in Breast and Colorectal Cancer Cells" Pharmaceuticals 13, no. 6: 115. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph13060115
APA StyleEl-Huneidi, W., Shehab, N. G., Bajbouj, K., Vinod, A., El-Serafi, A., Shafarin, J., Bou Malhab, L. J., Abdel-Rahman, W. M., & Abu-Gharbieh, E. (2020). Micromeria fruticosa Induces Cell Cycle Arrest and Apoptosis in Breast and Colorectal Cancer Cells. Pharmaceuticals, 13(6), 115. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph13060115