L-Asparaginase from Penicillium sizovae Produced by a Recombinant Komagataella phaffii Strain
Abstract
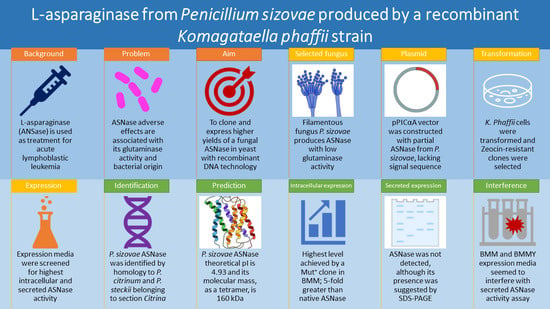
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Identification of L-Asparaginase Gene Sequence from P. sizovae
2.2. Prediction of the Molecular Structure and Active Site Insights of L-Asparaginase from P. sizovae
2.3. Expression of L-Asparaginase from P. sizovae in Recombinant K. phaffii X-33
2.4. Evaluation of the Interference of Expression Media in the Quantification of L-Asparaginase Activity
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Microorganisms and Plasmids
4.2. Culture Media
4.3. Identification of L-Asparaginase Gene Sequence from P. sizovae
4.4. Prediction of the Molecular Structure and Active Site Insights of L-Asparaginase from P. sizovae
4.5. Preparation of Recombinant Plasmid
4.6. K. phaffii X-33 Transformation and Phenotypic Screening
4.7. Screening of Transformants and Expression of L-Asparaginase
4.8. L-Asparaginase Activity Assay
4.9. Evaluation of the Interference of Expression Media in the Quantification of L-Asparaginase Activity
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Demain, A.L.; Vaishnav, P. Production of recombinant proteins by microbes and higher organisms. Biotechnol. Adv. 2009, 27, 297–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khow, O.; Suntrarachun, S. Strategies for production of active eukaryotic proteins in bacterial expression system. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Biomed. 2012, 2, 159–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yin, J.; Li, G.; Ren, X.; Herrler, G. Select what you need: A comparative evaluation of the advantages and limitations of frequently used expression systems for foreign genes. J. Biotechnol. 2007, 127, 335–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cereghino, J.L.; Cregg, J.M. Heterologous protein expression in the methylotrophic yeast Pichia pastoris. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2000, 24, 45–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- WHO. World Health Organization Model List of Essential Medicines for Children—8th List; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- WHO. World Health Organization Model List of Essential Medicines—22nd List; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- NCI. Childhood Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia Treatment (PDQ®)—Health Professional Version. Availabe online: https://www.cancer.gov/types/leukemia/hp/child-all-treatment-pdq (accessed on 29 January 2022).
- Asthana, N.; Azmi, W. Microbial L-Asparaginase: A Potent Antitumour Enzyme. Indian J. Biotechnol. 2003, 2, 184–194. [Google Scholar]
- Cedar, H.; Schwartz, J.H. Localization of the two-L-asparaginases in anaerobically grown Escherichia coli. J. Biol. Chem. 1967, 242, 3753–3755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwartz, J.H.; Reeves, J.Y.; Broome, J.D. Two L-asparaginases from E. coli and their action against tumors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1966, 56, 1516–1519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brumano, L.P.; da Silva, F.V.S.; Costa-Silva, T.A.; Apolinário, A.C.; Santos, J.H.P.M.; Kleingesinds, E.K.; Monteiro, G.; Rangel-Yagui, C.d.O.; Benyahia, B.; Junior, A.P. Development of L-asparaginase Biobetters: Current Research Status and Review of the Desirable Quality Profiles. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2019, 6, 212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Van Trimpont, M.; Peeters, E.; De Visser, Y.; Schalk, A.M.; Mondelaers, V.; De Moerloose, B.; Lavie, A.; Lammens, T.; Goossens, S.; Van Vlierberghe, P. Novel Insights on the Use of L-asparaginase as an Efficient and Safe Anti-Cancer Therapy. Cancers 2022, 14, 902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrivastava, A.; Khan, A.A.; Khurshid, M.; Kalam, M.A.; Jain, S.K.; Singhal, P.K. Recent developments in L-asparaginase discovery and its potential as anticancer agent. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 2016, 100, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, H.A.; Su, Y.; Lavie, A. Design and characterization of Erwinia chrysanthemi L-asparaginase variants with diminished L-glutaminase activity. J. Biol. Chem. 2016, 291, 17664–17676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fonseca, M.H.G.; Fiúza, T.D.S.; Morais, S.B.D.; Souza, T.D.A.C.B.D.; Trevizani, R. Circumventing the side effects of L-asparaginase. Biomed. Pharm. 2021, 139, 111616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarquis, M.I.; Oliveira, E.M.; Santos, A.S.; Costa, G.L. Production of L-asparaginase by filamentous fungi. Mem. Inst. Oswaldo Cruz 2004, 99, 489–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shrivastava, A.; Khan, A.A.; Shrivastav, A.; Jain, S.K.; Singhal, P.K. Kinetic studies of L-asparaginase from Penicillium digitatum. Prep. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2012, 42, 574–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadeem, M.S.; Khan, J.A.; Al-Ghamdi, M.A.; Khan, M.I.; Zeyadi, M.A. Studies on the recombinant production and anticancer activity of thermostable L-asparaginase I from Pyrococcus abyssi. Braz. J. Biol. 2021, 82, e244735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahreini, E.; Aghaiypour, K.; Abbasalipourkabir, R.; Goodarzi, M.T.; Saidijam, M.; Safavieh, S.S. An optimized protocol for overproduction of recombinant protein expression in Escherichia coli. Prep. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2014, 44, 510–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chityala, S.; Venkata Dasu, V.; Ahmad, J.; Prakasham, R.S. High yield expression of novel glutaminase free L-asparaginase II of Pectobacterium carotovorum MTCC 1428 in Bacillus subtilis WB800N. Bioprocess Biosyst. Eng. 2015, 38, 2271–2284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, I.M.; Schultz, L.; de Araujo Bianchi Pedra, B.; Leite, M.S.; Farsky, S.H.; de Oliveira, M.A.; Pessoa, A.; Monteiro, G. Recombinant L-asparaginase 1 from Saccharomyces cerevisiae: An allosteric enzyme with antineoplastic activity. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 36239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Credali, A.; Garcia-Calderon, M.; Dam, S.; Perry, J.; Diaz-Quintana, A.; Parniske, M.; Wang, T.L.; Stougaard, J.; Vega, J.M.; Marquez, A.J. The K+-dependent asparaginase, NSE1, is crucial for plant growth and seed production in Lotus japonicus. Plant Cell Physiol. 2013, 54, 107–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dieterich, D.C.; Landwehr, M.; Reissner, C.; Smalla, K.H.; Richter, K.; Wolf, G.; Bockers, T.M.; Gundelfinger, E.D.; Kreutz, M.R. Gliap—A novel untypical L-asparaginase localized to rat brain astrocytes. J. Neurochem. 2003, 85, 1117–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Sharkawy, A.S.; Farag, A.M.; Embaby, A.M.; Saeed, H.; El-Shenawy, M. Cloning, expression and characterization of aeruginosa EGYII L-Asparaginase from Pseudomonas aeruginosa strain EGYII DSM 101801 in E.coli BL21(DE3) pLysS. J. Mol. Catal. B Enzym. 2016, 132, 16–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erenler, S.O.; Geckil, H. Effect of vitreoscilla hemoglobin and culture conditions on production of bacterial L-asparaginase, an oncolytic enzyme. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2014, 173, 2140–2151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, Y.; Liu, S.; Jiao, Y.; Gao, H.; Wang, M.; Du, G.; Chen, J. Enhanced extracellular production of L-asparaginase from Bacillus subtilis 168 by B. subtilis WB600 through a combined strategy. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2017, 101, 1509–1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrara, M.A.; Severino, N.M.B.; Mansure, J.J.; Martins, A.S.; Oliveira, E.M.M.; Siani, A.C.; Pereira, N.; Torres, F.A.G.; Bon, E.P.S. Asparaginase production by a recombinant Pichia pastoris strain harbouring Saccharomyces cerevisiae ASP3 gene. Enzym. Microb. Technol. 2006, 39, 1457–1463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gervais, D.; Foote, N. Recombinant deamidated mutants of Erwinia chrysanthemi L-asparaginase have similar or increased activity compared to wild-type enzyme. Mol. Biotechnol. 2014, 56, 865–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ghoshoon, M.B.; Berenjian, A.; Hemmati, S.; Dabbagh, F.; Karimi, Z.; Negahdaripour, M.; Ghasemi, Y. Extracellular Production of Recombinant L-Asparaginase II in Escherichia coli: Medium Optimization Using Response Surface Methodology. Int. J. Pept. Res. Ther. 2015, 21, 487–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilbert, H.J.; Blazek, R.; Bullman, H.M.; Minton, N.P. Cloning and expression of the Erwinia chrysanthemi asparaginase gene in Escherichia coli and Erwinia carotovora. J. Gen. Microbiol. 1986, 132, 151–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hatanaka, T.; Usuki, H.; Arima, J.; Uesugi, Y.; Yamamoto, Y.; Kumagai, Y.; Yamasato, A.; Mukaihara, T. Extracellular production and characterization of two streptomyces L-asparaginases. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2011, 163, 836–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hendriksen, H.V.; Kornbrust, B.A.; Ostergaard, P.R.; Stringer, M.A. Evaluating the potential for enzymatic acrylamide mitigation in a range of food products using an asparaginase from Aspergillus oryzae. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2009, 57, 4168–4176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oza, V.P.; Parmar, P.P.; Patel, D.H.; Subramanian, R.B. Cloning, expression and characterization of l-asparaginase from Withania somnifera L. for large scale production. 3 Biotech 2011, 1, 21–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pourhossein, M.; Korbekandi, H. Cloning, expression, purification and characterisation of Erwinia carotovora L-asparaginase in Escherichia coli. Adv. Biomed. Res. 2014, 3, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roth, G.; Nunes, J.E.S.; Rosado, L.A.; Bizarro, C.V.; Volpato, G.; Nunes, C.P.; Renard, G.; Basso, L.A.; Santos, D.S.; Chies, J.M. Recombinant Erwinia carotovora L-asparaginase II production IN Escherichia coli fed-batch cultures. Braz. J. Chem. Eng. 2013, 30, 245–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Saeed, H.; Ali, H.; Soudan, H.; Embaby, A.; El-Sharkawy, A.; Farag, A.; Hussein, A.; Ataya, F. Molecular cloning, structural modeling and production of recombinant Aspergillus terreusl. asparaginase in Escherichia coli. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 106, 1041–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sannikova, E.P.; Bulushova, N.V.; Cheperegin, S.E.; Gubaydullin, I.I.; Chestukhina, G.G.; Ryabichenko, V.V.; Zalunin, I.A.; Kotlova, E.K.; Konstantinova, G.E.; Kubasova, T.S.; et al. The Modified Heparin-Binding L-asparaginase of Wolinella succinogenes. Mol. Biotechnol. 2016, 58, 528–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bon, E.P.S.; Carvajal, E.; Stanbrough, M.; Rowen, D.; Magasanik, B. Asparaginase II of Saccharomyces cerevisiae—GLN3/URE2 regulation of a periplasmic enzyme. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 1997, 63, 203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cachumba, J.J.M.; Antunes, F.A.F.; Peres, G.F.D.; Brumano, L.P.; Santos, J.C.D.; Da Silva, S.S. Current applications and different approaches for microbial L-asparaginase production. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2016, 47, 77–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, F.; Oruna-Concha, M.J.; Elmore, J.S. The use of asparaginase to reduce acrylamide levels in cooked food. Food Chem. 2016, 210, 163–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freitas, M.; Souza, P.; Cardoso, S.; Cruvinel, K.; Abrunhosa, L.S.; Ferreira Filho, E.X.; Inácio, J.; Pinho, D.B.; Pessoa, A.; Magalhães, P.O. Filamentous Fungi Producing l-Asparaginase with Low Glutaminase Activity Isolated from Brazilian Savanna Soil. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lubkowski, J.; Vanegas, J.; Chan, W.-K.; Lorenzi, P.L.; Weinstein, J.N.; Sukharev, S.; Fushman, D.; Rempe, S.; Anishkin, A.; Wlodawer, A. Mechanism of Catalysis by L-Asparaginase. Biochemistry 2020, 59, 1927–1945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, H.A.; Durden, D.L.; Lavie, A. The differential ability of asparagine and glutamine in promoting the closed/active enzyme conformation rationalizes the Wolinella succinogenes L-asparaginase substrate specificity. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 41643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Strzelczyk, P.; Zhang, D.; Dyba, M.; Wlodawer, A.; Lubkowski, J. Generalized enzymatic mechanism of catalysis by tetrameric l-asparaginases from mesophilic bacteria. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 17516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andrade, K.C.R.; Fernandes, R.A.; Pinho, D.B.; de Freitas, M.M.; Filho, E.X.F.; Pessoa, A.; Silva, J.I.; Magalhães, P.O. Sequencing and characterization of an L-asparaginase gene from a new species of Penicillium section Citrina isolated from Cerrado. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 17861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bascomb, S.; Banks, G.T.; Skarstedt, M.T.; Fleming, A.; Bettelheim, K.A. The properties and large-scale production of L-asparaginase from Citrobacter. J. Gen. Microbiol. 1975, 91, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Devi, S.; Azmi, W. One step purification of glutaminase free L-asparaginase from Erwinia carotovora with anticancerous activty. Int. J. Life Sci. Pharma Res. 2012, 2, 36–45. [Google Scholar]
- Scheetz, R.W.; Whelan, H.A.; Wriston, J.C. Purification and properties of an L-asparaginase from Fusarium tricinctum. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 1971, 142, 184–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrara, M.A.; Severino, N.M.B.; Valente, R.H.; Perales, J.; Bon, E.P.S. High-yield extraction of periplasmic asparaginase produced by recombinant Pichia pastoris harbouring the Saccharomyces cerevisiae ASP3 gene. Enzym. Microb. Technol. 2010, 47, 71–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, D.; Pillaca-Pullo, O.; Torres-Obreque, K.; Flores-Santos, J.; Sánchez-Moguel, I.; Pimenta, M.V.; Basi, T.; Converti, A.; Lopes, A.M.; Monteiro, G.; et al. Fed-Batch Production of Saccharomyces cerevisiae L-asparaginase II by Recombinant Pichia pastoris MUT (s) Strain. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2019, 7, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Allen, W.J.; Phan, G.; Waksman, G. Structural Biology of Periplasmic Chaperones. In Advances in Protein Chemistry and Structural Biology; McPherson, A., Ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2009; Volume 78, pp. 51–97. [Google Scholar]
- Roldán, B.; Lima, G.; Cabarca, S.; Pessoa, A.; Farias, J.; Monteiro, G. L-asparaginase from E. chrysanthemi expressed in glycoswitch ® : Effect of His-Tag fusion on the extracellular expression. Prep. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2019, 49, 679–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sturmberger, L.; Chappell, T.; Geier, M.; Krainer, F.; Day, K.J.; Vide, U.; Trstenjak, S.; Schiefer, A.; Richardson, T.; Soriaga, L.; et al. Refined Pichia pastoris reference genome sequence. J. Biotechnol. 2016, 235, 121–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gardes, M.; Bruns, T.D. ITS primers with enhanced specificity for basidiomycetes--application to the identification of mycorrhizae and rusts. Mol. Ecol. 1993, 2, 113–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, T.J.; Bruns, T.; Lee, S.; Taylor, J.W. Amplification and direct sequencing of fungal ribosomal RNA genes for phylogenetics. In PCR Protocols: A Guide to Methods and Applications; Innis, M.A., Gelfand, D.H., Sninsky, J.J., White, T.J., Eds.; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Houbraken, J.; Samson, R.A. Phylogeny of Penicillium and the segregation of Trichocomaceae into three families. Stud. Mycol. 2011, 70, 1–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laemmli, U.K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 1970, 227, 680–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blum, H.; Beier, H.; Gross, H.J. Improved silver staining of plant proteins, RNA and DNA in polyacrylamide gels. Electrophoresis 1987, 8, 93–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drainas, C.; Kinghorn, J.R.; Pateman, J.A. Aspartic hydroxamate resistance and asparaginase regulation in the fungus Aspergillus nidulans. J. Gen. Microbiol. 1977, 98, 493–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Studer, G.; Rempfer, C.; Waterhouse, A.M.; Gumienny, R.; Haas, J.; Schwede, T. QMEANDisCo—Distance constraints applied on model quality estimation. Bioinformatics 2019, 36, 1765–1771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Primers | Sequence (5′–3′) |
|---|---|
| F1.2 | AACAARGCGGAACCAACG |
| F2 | GACARTCGRTACGATAAGC |
| FASP2 | TGAGGGTTCAAGTATCCAC |
| FASP3 | AGGAATCCCATTTCCATTGC |
| RASP2.1 | TGCYAGTGGATACTTGAACC |
| RASP6 | CAGGCTCAGATTCAAGCTC |
| R2 | GAAGYAGTACGATAAGATCAC |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Freitas, M.; Souza, P.; Homem-de-Mello, M.; Fonseca-Bazzo, Y.M.; Silveira, D.; Ferreira Filho, E.X.; Pessoa Junior, A.; Sarker, D.; Timson, D.; Inácio, J.; et al. L-Asparaginase from Penicillium sizovae Produced by a Recombinant Komagataella phaffii Strain. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 746. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph15060746
Freitas M, Souza P, Homem-de-Mello M, Fonseca-Bazzo YM, Silveira D, Ferreira Filho EX, Pessoa Junior A, Sarker D, Timson D, Inácio J, et al. L-Asparaginase from Penicillium sizovae Produced by a Recombinant Komagataella phaffii Strain. Pharmaceuticals. 2022; 15(6):746. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph15060746
Chicago/Turabian StyleFreitas, Marcela, Paula Souza, Mauricio Homem-de-Mello, Yris M. Fonseca-Bazzo, Damaris Silveira, Edivaldo X. Ferreira Filho, Adalberto Pessoa Junior, Dipak Sarker, David Timson, João Inácio, and et al. 2022. "L-Asparaginase from Penicillium sizovae Produced by a Recombinant Komagataella phaffii Strain" Pharmaceuticals 15, no. 6: 746. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph15060746
APA StyleFreitas, M., Souza, P., Homem-de-Mello, M., Fonseca-Bazzo, Y. M., Silveira, D., Ferreira Filho, E. X., Pessoa Junior, A., Sarker, D., Timson, D., Inácio, J., & Magalhães, P. O. (2022). L-Asparaginase from Penicillium sizovae Produced by a Recombinant Komagataella phaffii Strain. Pharmaceuticals, 15(6), 746. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph15060746