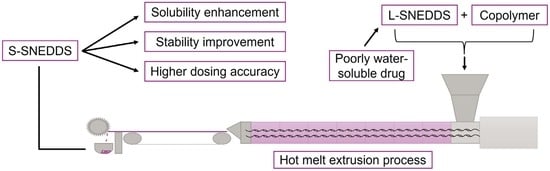
Preparation of Solid Self-Nanoemulsifying Drug Delivery Systems (S-SNEDDS) by Co-Extrusion of Liquid SNEDDS and Polymeric Carriers—A New and Promising Formulation Approach to Improve the Solubility of Poorly Water-Soluble Drugs
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. L-SNEDDS Composition
2.2. S-SNEDDS Composition and Manufacture
2.3. Thermal Characterization of the Pure Drugs, (Co)Polymers, and S-SNEDDS via DSC Analysis
2.4. Saturation Solubility Studies
2.5. Dissolution Studies
2.6. Stability Studies
2.6.1. Appearance (After Three and Six Months of Storage)
2.6.2. Thermal Characterization of S-SNEDDS via DSC Analysis (After Six Months of Storage)
2.6.3. Dissolution Studies after Three and Six Months of Storage
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Methods
3.2.1. Development and Preparation of L-SNEDDS
3.2.2. Preparation of S-SNEDDS via HME
3.2.3. Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC) Analysis
3.2.4. Saturation Solubility Assessments
3.2.5. Dissolution Studies
3.2.6. HPLC Analysis
HPLC Method for Celecoxib
HPLC Method for Efavirenz
HPLC Method for Fenofibrate
3.2.7. Stability Studies
3.2.8. Data Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kalepu, S.; Nekkanti, V. Insoluble drug delivery strategies: Review of recent advances and business prospects. Acta Pharm. Sin. B. 2015, 5, 442–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanada, M.; Jermain, S.V.; Williams, R.O., III. Enhanced dissolution of a porous carrier-containing ternary amorphous solid dispersion system prepared by a hot melt method. J. Pharm. Sci. 2018, 107, 362–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, H.D.; Trevaskis, N.L.; Charman, S.A.; Shanker, R.M.; Charman, W.N.; Pouton, C.W.; Porter, C.J. Strategies to address low drug solubility in discovery and development. Pharmacol. Rev. 2013, 65, 315–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dokania, S.; Joshi, A.K. Self-microemulsifying drug delivery system (SMEDDS)—Challenges and road ahead. Drug Deliv. 2015, 22, 675–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porter, C.J.H.; Pouton, C.W.; Cuine, J.F.; Charman, W.N. Enhancing intestinal drug solubilisation using lipid-based delivery systems. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2008, 60, 673–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pouton, C.W. Lipid formulations for oral administration of drugs: Non-emulsifying, self-emulsifying and ‘self-microemulsifying’ drug delivery systems. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2000, 11, 93–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, N.; Holm, R.; Mullertz, A.; Rades, T. In vitro and in vivo performance of novel supersaturated self-nanoemulsifying drug delivery systems (super-SNEDDS). J. Control. Release. 2012, 160, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vithani, K.; Hawley, A.; Jannin, V.; Pouton, C.; Boyd, B.J. Inclusion of digestible surfactants in solid SMEDDS formulation removes lag time and influences the formation of structured particles during digestion. AAPS J. 2017, 19, 754–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, B.; Almurisi, S.H.; Dukhan, A.A.M.; Mandal, U.K.; Sengupta, P. Controversies with self-emulsifying drug delivery system from pharmacokinetic point of view. Drug Deliv. 2016, 23, 3639–3652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, L.A.D.; Almeida, S.L.; Alonso, E.C.; Rocha, P.B.; Martins, F.T.; Freitas, L.A.; Taveira, S.F.; Cunha-Filho, M.S.; Marreto, R.N. Preparation of a solid self-microemulsifying drug delivery system by hot-melt extrusion. Int. J. Pharm. 2018, 541, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vithani, K.; Hawley, A.; Jannin, V.; Pouton, C.; Boyd, B.J. Solubilisation behaviour of poorly water-soluble drugs during digestion of solid SMEDDS. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2018, 130, 236–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yetukuri, K.; Sudheer, P. Approaches to development of solid-self micron emulsifying drug delivery system: Formulation techniques and dosage forms: A review. Int. J. Pharm. Sci. Res. 2012, 3, 3550–3558. [Google Scholar]
- Sander, C.; Holm, P. Porous magnesium aluminometasilicate tablets as carrier of a cyclosporine self-emulsifying formulation. AAPS PharmSciTech 2009, 10, 1388–1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.S.; Yang, E.S.; Yong, C.S.; Youn, Y.S.; Oh, K.T.; Li, D.X.; Kim, J.O.; Jin, S.G.; Choi, H.G. Effect of inorganic mesoporous carriers on 1-palmitoyl-2-linoleoyl-3-acetyl-rac-glycerol-loaded solid self-emulsifying drug delivery system: Physicochemical characterization and bioavailability in rats. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces. 2017, 160, 331–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawar, J.; Tayade, A.; Gangurde, A.; Moravkar, K.; Amin, P. Solubility and dissolution enhancement of efavirenz hot melt extruded amorphous solid dispersions using combination of polymeric blends: A QbD approach. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2016, 88, 37–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, T.; Niu, B.; Wu, Q.; Zhou, Y.; Pan, X.; Quan, G.; Wu, C. Fenofibrate solid dispersion processed by hot-melt extrusion: Elevated bioavailability and its cell transport mechanism. Curr. Drug Deliv. 2019, 16, 538–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rumondor, A.C.F.; Dhareshwar, S.S.; Kesisoglou, F. Amorphous solid dispersions or prodrugs: Complementary strategies to increase drug absorption. J. Pharm. Sci. 2016, 105, 2498–2508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wegiel, L.A.; Mauer, L.J.; Edgar, K.J.; Taylor, L.S. Crystallization of amorphous solid dispersions of resveratrol during preparation and storage-Impact of different polymers. J. Pharm. Sci. 2013, 102, 171–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wyttenbach, N.; Janas, C.; Siam, M.; Lauer, M.E.; Jacob, L.; Scheubel, E.; Page, S. Miniaturized screening of polymers for amorphous drug stabilization (SPADS): Rapid assessment of solid dispersion systems. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2013, 84, 583–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, S.; Patel, N.; Lin, S. Solubility and dissolution enhancement strategies: Current understanding and recent trends. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2015, 41, 875–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmied, F.P.; Bernhardt, A.; Engel, A.; Klein, S. A customized screening tool approach for the development of a self-nanoemulsifying drug delivery system (SNEDDS). AAPS PharmSciTech 2022, 23, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmied, F.P.; Bernhardt, A.; Moers, C.; Meier, C.; Endres, T.; Klein, S. A novel aminomethacrylate-based copolymer for solubility enhancement—From radical polymer synthesis to manufacture and characterization of amorphous solid dispersions. Polymers 2022, 14, 1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pawar, J.; Suryawanshi, D.; Moravkar, K.; Aware, R.; Shetty, V.; Maniruzzaman, M. Study the influence of formulation process parameters on solubility and dissolution enhancement of efavirenz solid solutions prepared by hot-melt extrusion: A QbD methodology. Drug Deliv. Transl. Res. 2018, 8, 1644–1657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cristofoletti, R.; Nair, A.; Abrahamsson, B.; Groot, D.W.; Kopp, S.; Langguth, P.; Polli, J.E.; Shah, V.P.; Dressman, J.B. Biowaiver monographs for immediate release solid oral dosage forms: Efavirenz. J. Pharm. Sci. 2013, 102, 318–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knopp, M.M.; Nguyen, J.H.; Becker, C.; Francke, N.M.; Jørgensen, E.B.; Holm, P.; Holm, R.; Mu, H.; Rades, T.; Langguth, P. Influence of polymer molecular weight on in vitro dissolution behavior and in vivo performance of celecoxib: PVP amorphous solid dispersions. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2016, 101, 145–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Homayouni, A.; Sadeghi, F.; Nokhodchi, A.; Varshosaz, J.; Garekani, H.A. Preparation and characterization of celecoxib solid dispersions; Comparison of poloxamer-188 and PVP-K30 as carriers. Iran. J. Basic Med. Sci. 2014, 17, 322–331. [Google Scholar]
- Kawakami, K.; Sato, K.; Fukushima, M.; Miyazaki, A.; Yamamura, Y.; Sakuma, S. Phase separation of supersaturated solution created from amorphous solid dispersions: Relevance to oral absorption. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2018, 132, 146–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, C.N.; Pham, C.V.; Le Thien, G.; Ngoc, B.T.; Le Thi, H.; Huyen, C.P.T.; Thi, T.N. Immediate-released pelletized solid dispersion containing fenofibrate: Formulation, in vitro characterization, and bioequivalence studies in experimental beagle dogs. Int. J. Pharm. 2019, 570, 118661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Drug Substance | Miglyol® 812 (%) | Tween® 80 (%) | Gelucire® 44/14 (%) | d-TPGS (%) | IPM-100(%) | Transcutol® HP (%) | Brij® 35 (%) | Drug (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Celecoxib | 27.64 | 45.52 | 4.15 | 5.69 | - | - | - | 17.00 |
| Efavirenz | - | 23.94 | - | 2.99 | 19.45 | 28.42 | - | 25.20 |
| Fenofibrate | 17.20 | 50.16 | - | 10.04 | - | - | 8.60 | 14.00 |
| Polymer | L-SNEDDS Load (%) | Drug Load (%) | Extrusion Temperature (°C) | Screw Speed (rpm) | Torque (Ncm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Soluplus® | 20/16.67/20 | 3.4/4.2/2.8 | 130/130/130 | 200 | 50/40/45 |
| Kollidon® VA 64 | 30/25/30 | 5.1/6.3/4.2 | 150/150/150 | 200 | 45/45/35 |
| Kollidon® 17 PF | 30/25/30 | 5.1/6.3/4.2 | 170/170/170 | 200 | 40/40/35 |
| E-173 kDa | 30/25/30 | 5.1/6.3/4.2 | 150/150/150 | 200 | 75/65/50 |
| E-254 kDa | 30/25/30 | 5.1/6.3/4.2 | 150/150/155 | 200 | 75/70/70 |
| E-281 kDa | 30/25/30 | 5.1/6.3/4.2 | 155/155/150 | 200 | 70/65/75 |
| E-305 kDa | 30/25/30 | 5.1/6.3/4.2 | 155/155/155 | 200 | 60/90/85 |
| Affinisol® HPMC 100 LV | 30/25/30 | 5.1/6.3/4.2 | 160/160/160 | 100 | 85/120/95 |
| Tg (°C) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Polymer | Celecoxib S-SNEDDS | Efavirenz S-SNEDDS | Fenofibrate S-SNEDDS | |
| Soluplus® | 70 ± 0 | 39 ± 2 | 42 ± 2 | 31 ± 2 |
| Kollidon® VA 64 | 107 ± 1 | 67 ± 3 | 43 ± 0 | 47 ± 1 |
| Kollidon® 17 PF | 136 ± 3 | 88 ± 1 | 60 ± 1 | 74 ± 2 |
| E-173 kDa | 77 ± 1 | 43 ± 0 | 38 ± 1 | 48 ± 0 |
| E-254 kDa | 85 ± 2 | 44 ± 1 | 37 ± 1 | 41 ± 0 |
| E-281 kDa | 89 ± 0 | 45 ± 2 | 38 ± 0 | 48 ± 1 |
| E-305 kDa | 91 ± 1 | 42 ± 0 | 42 ± 2 | 44 ± 1 |
| Affinisol® HPMC 100 LV | 103 ± 2 | 45 ± 1 | 43 ± 2 | 36 ± 0 |
| Saturation Solubility (µg/mL) | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Celecoxib | Efavirenz | Fenofibrate | |
| Drug substance | 0.6 ± 0.1 | 0.7 ± 0 | 0.1 ± 0 |
| L-SNEDDS | 31.3 ± 1.2 | 34.7 ± 2.4 | 17.4 ± 1.8 |
| Soluplus® S-SNEDDS | 140 ± 0.9 | 347 ± 2.3 | 70 ± 0.4 |
| Kollidon® VA 64 S-SNEDDS | 252 ± 1.3 | 99 ± 0.9 | 144 ± 1.1 |
| Kollidon® 17 PF S-SNEDDS | 197 ± 0.6 | 226 ± 1.4 | 125 ± 0.4 |
| E-173 kDa S-SNEDDS | 87 ± 0.8 | 46 ± 0.2 | 60 ± 0.5 |
| E-254 kDa S-SNEDDS | 50 ± 0.1 | 18 ± 1.0 | 47 ± 0.3 |
| E-281 kDa S-SNEDDS | 26 ± 0.2 | 16 ± 0.5 | 43 ± 0.4 |
| E-305 kDa S-SNEDDS | 21 ± 0.1 | 8 ± 0.4 | 50 ± 0.2 |
| Affinisol® HPMC 100 LV S-SNEDDS | 423 ± 6.1 | 281 ± 3.1 | 314 ± 3.6 |
| Tg (°C) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Polymer | Celecoxib S-SNEDDS | Efavirenz S-SNEDDS | Fenofibrate S-SNEDDS | |
| Soluplus® | 69 ± 1 | 39 ± 2 | 32 ± 2 | 29 ± 1 |
| Kollidon® VA 64 | 105 ± 1 | 60 ± 2 | 38 ± 1 | 47 ± 0 |
| Kollidon® 17 PF | 135 ± 0 | 88 ± 1 | 59 ± 2 | 75 ± 1 |
| E-173 kDa | 77 ± 1 | 45 ± 1 | 36 ± 0 | 38 ± 1 |
| E-254 kDa | 83 ± 0 | 39 ± 1 | 35 ± 1 | 33 ± 0 |
| E-281 kDa | 88 ± 1 | 44 ± 0 | 33 ± 1 | 32 ± 1 |
| E-305 kDa | 91 ± 1 | 46 ± 2 | 35 ± 0 | 30 ± 0 |
| Affinisol® HPMC 100 LV | 69 ± 1 | 39 ± 2 | 32 ± 2 | 29 ± 1 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Schmied, F.-P.; Bernhardt, A.; Klein, S. Preparation of Solid Self-Nanoemulsifying Drug Delivery Systems (S-SNEDDS) by Co-Extrusion of Liquid SNEDDS and Polymeric Carriers—A New and Promising Formulation Approach to Improve the Solubility of Poorly Water-Soluble Drugs. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 1135. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph15091135
Schmied F-P, Bernhardt A, Klein S. Preparation of Solid Self-Nanoemulsifying Drug Delivery Systems (S-SNEDDS) by Co-Extrusion of Liquid SNEDDS and Polymeric Carriers—A New and Promising Formulation Approach to Improve the Solubility of Poorly Water-Soluble Drugs. Pharmaceuticals. 2022; 15(9):1135. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph15091135
Chicago/Turabian StyleSchmied, Fabian-Pascal, Alexander Bernhardt, and Sandra Klein. 2022. "Preparation of Solid Self-Nanoemulsifying Drug Delivery Systems (S-SNEDDS) by Co-Extrusion of Liquid SNEDDS and Polymeric Carriers—A New and Promising Formulation Approach to Improve the Solubility of Poorly Water-Soluble Drugs" Pharmaceuticals 15, no. 9: 1135. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph15091135
APA StyleSchmied, F. -P., Bernhardt, A., & Klein, S. (2022). Preparation of Solid Self-Nanoemulsifying Drug Delivery Systems (S-SNEDDS) by Co-Extrusion of Liquid SNEDDS and Polymeric Carriers—A New and Promising Formulation Approach to Improve the Solubility of Poorly Water-Soluble Drugs. Pharmaceuticals, 15(9), 1135. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph15091135