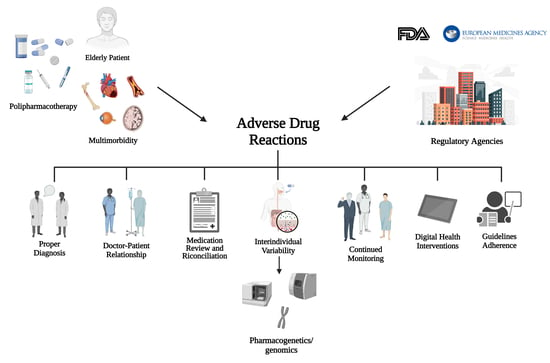
Insight into Risk Factors, Pharmacogenetics/Genomics, and Management of Adverse Drug Reactions in Elderly: A Narrative Review
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Objectives
3. Methods
4. Adverse Drug Reactions
4.1. Definition and Classification
4.2. Epidemiology
5. Adverse Drug Reactions in the Elderly Population: Risk Factors
5.1. Polypharmacy
5.2. Multimorbidity
5.3. Changes in Drug Metabolism
5.4. Geriatric Syndromes
5.5. Pharmacogenetics/Genomics Variability
5.5.1. Drug–Drug Interactions (DDIs), Drug–Gene Interactions (DGIs), and Drug–Drug–Gene Interactions (DDGIs)
Induction, Inhibitory, and Phenoconversion Interactions
5.5.2. Drug–Drug-Transporters–Genes Interactions (DDTGIs)
6. Strategies Supporting the Appropriateness of Drug Use and Prevention of ADRs in Elderly Patients
6.1. Tools to Identify Inappropriate Prescriptions
6.2. Medication Review and Medication Reconciliation
6.3. Drug Label Annotation Based on Pharmacogenetics
- “Required genetic testing” refers to situations where labels indicate or imply that gene, protein, or chromosomal testing, including genetic testing, functional protein assays, or cytogenetic studies, should be carried out before initiating the treatment. Of note, testing may be necessary only for a specific subset of patients.
- “Recommended genetic testing” concerning conditions in which labels indicate or imply that gene, protein, or chromosomal testing, including genetic testing, functional protein assays, or cytogenetic studies, is recommended prior the drug use. It is important to note that the recommendation may be applied only to a specific subset of patients.
- “Actionable genetic testing” refers to labels that provide information about the influence of gene/protein/chromosomal variants or phenotypes on changes in drug efficacy, dosage, metabolism, or toxicity. These labels may also include specific contraindications of the drug for a subset of patients based on particular variants/genotypes/phenotypes.
- “Informative genetic testing” is assigned to labels which yield information stating that specific gene/protein/chromosomal variants or metabolizer phenotypes have no impact on a drug’s efficacy, dosage, metabolism, or toxicity. Alternatively, these labels may indicate that although variants or phenotypes do affect a drug’s efficacy, dosage, metabolism, or toxicity, the effect is not clinically significant. This level is also assigned to all other labels that have been listed in the FDA Table but do not currently meet the criteria for all other PharmGKB annotations mentioned above.
6.4. Digital Tools Supporting Appropriate Prescription
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lenzi, J.; Avaldi, V.M.; Rucci, P.; Pieri, G.; Fantini, M.P. Burden of Multimorbidity in Relation to Age, Gender and Immigrant Status: A Cross-Sectional Study Based on Administrative Data. BMJ Open 2016, 6, e012812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sirois, C.; Domingues, N.S.; Laroche, M.-L.; Zongo, A.; Lunghi, C.; Guénette, L.; Kröger, E.; Émond, V. Polypharmacy Definitions for Multimorbid Older Adults Need Stronger Foundations to Guide Research, Clinical Practice and Public Health. Pharmacy 2019, 7, 126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Midão, L.; Giardini, A.; Menditto, E.; Kardas, P.; Costa, E. Polypharmacy Prevalence among Older Adults Based on the Survey of Health, Ageing and Retirement in Europe. Arch. Gerontol. Geriatr. 2018, 78, 213–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Onder, G.; Bonassi, S.; Abbatecola, A.M.; Folino-Gallo, P.; Lapi, F.; Marchionni, N.; Pani, L.; Pecorelli, S.; Sancarlo, D.; Scuteri, A.; et al. High Prevalence of Poor Quality Drug Prescribing in Older Individuals: A Nationwide Report From the Italian Medicines Agency (AIFA). J. Gerontol. Ser. A 2014, 69, 430–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guerriero, F.; Orlando, V.; Tari, D.U.; Di Giorgio, A.; Cittadini, A.; Trifirò, G.; Menditto, E. How Healthy Is Community-Dwelling Elderly Population? Results from Southern Italy. Transl. Med. UniSa 2016, 13, 59–64. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Valent, F. Polypharmacy in the General Population of a Northern Italian Area: Analysis of Administrative Data. Ann. Dell’istituto Super. Di Sanità 2019, 55, 233–239. [Google Scholar]
- Fickweiler, F.; Fickweiler, W.; Urbach, E. Interactions between Physicians and the Pharmaceutical Industry Generally and Sales Representatives Specifically and Their Association with Physicians’ Attitudes and Prescribing Habits: A Systematic Review. BMJ Open 2017, 7, e016408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, S.E.; Figert, A.E. Medicalization and Pharmaceuticalization at the Intersections: Looking Backward, Sideways and Forward. Soc. Sci. Med. 2012, 75, 775–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abraham, J. Pharmaceuticalization of Society in Context: Theoretical, Empirical and Health Dimensions. Sociology 2010, 44, 603–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fried, T.R.; O’Leary, J.; Towle, V.; Goldstein, M.K.; Trentalange, M.; Martin, D.K. Health Outcomes Associated with Polypharmacy in Community-Dwelling Older Adults: A Systematic Review. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2014, 62, 2261–2272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinman, M.A.; Seth Landefeld, C.; Rosenthal, G.E.; Berthenthal, D.; Sen, S.; Kaboli, P.J. Polypharmacy and Prescribing Quality in Older People. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2006, 54, 1516–1523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rankin, A.; Cadogan, C.A.; Patterson, S.M.; Kerse, N.; Cardwell, C.R.; Bradley, M.C.; Ryan, C.; Hughes, C. Interventions to Improve the Appropriate Use of Polypharmacy for Older People. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2018, 9, CD008165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sönnichsen, A.; Trampisch, U.S.; Rieckert, A.; Piccoliori, G.; Vögele, A.; Flamm, M.; Johansson, T.; Esmail, A.; Reeves, D.; Löffler, C.; et al. Polypharmacy in Chronic Diseases-Reduction of Inappropriate Medication and Adverse Drug Events in Older Populations by Electronic Decision Support (PRIMA-eDS): Study Protocol for a Randomized Controlled Trial. Trials 2016, 17, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, E.A.; O’Mahony, M.S. Adverse Drug Reactions in Special Populations—The Elderly. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2015, 80, 796–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, S.L.; Carr, D.F.; Pirmohamed, M. Advances in the Pharmacogenomics of Adverse Drug Reactions. Drug Saf. 2016, 39, 15–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cacabelos, R.; Torrellas, C. Epigenetics of Aging and Alzheimer’s Disease: Implications for Pharmacogenomics and Drug Response. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 30483–30543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDonough, C.W. Pharmacogenomics in Cardiovascular Diseases. Curr. Protoc. 2021, 1, e189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osanlou, O.; Pirmohamed, M.; Daly, A.K. Pharmacogenetics of Adverse Drug Reactions. Adv. Pharmacol. 2018, 83, 155–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moyer, A.M.; Caraballo, P.J. The Challenges of Implementing Pharmacogenomic Testing in the Clinic. Expert. Rev. Pharmacoecon. Outcomes Res. 2017, 17, 567–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cacabelos, R.; Cacabelos, N.; Carril, J.C. The Role of Pharmacogenomics in Adverse Drug Reactions. Expert. Rev. Clin. Pharmacol. 2019, 12, 407–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bloomfield, H.E.; Greer, N.; Linsky, A.M.; Bolduc, J.; Naidl, T.; Vardeny, O.; MacDonald, R.; McKenzie, L.; Wilt, T.J. Deprescribing for Community-Dwelling Older Adults: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Gen. Intern. Med. 2020, 35, 3323–3332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kua, C.-H.; Yeo, C.Y.Y.; Tan, P.C.; Char, C.W.T.; Tan, C.W.Y.; Mak, V.; Leong, I.Y.-O.; Lee, S.W.H. Association of Deprescribing With Reduction in Mortality and Hospitalization: A Pragmatic Stepped-Wedge Cluster-Randomized Controlled Trial. J. Am. Med. Dir. Assoc. 2021, 22, 82–89.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lunghi, C.; Trevisan, C.; Fusaroli, M.; Giunchi, V.; Raschi, E.; Sangiorgi, E.; Domenicali, M.; Volpato, S.; De Ponti, F.; Poluzzi, E. Strategies and Tools for Supporting the Appropriateness of Drug Use in Older People. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EMA. Adverse Drug Reaction. Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/glossary/adverse-drug-reaction (accessed on 5 July 2023).
- Pharmaceutical Management Plus Program. Rational Pharmaceutical Plus Program Final Report; U.S. Agency for International Development by the Rational Pharmaceutical Management Plus Program. Management Sciences for Health: Arlington, VA, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Rawlins, M.D. Clinical Pharmacology. Adverse Reactions to Drugs. Br. Med. J. (Clin. Res. Ed.) 1981, 282, 974–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwards, I.R.; Aronson, J.K. Adverse Drug Reactions: Definitions, Diagnosis, and Management. Lancet 2000, 356, 1255–1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aronson, J.K.; Ferner, R.E. Joining the DoTS: New Approach to Classifying Adverse Drug Reactions. BMJ 2003, 327, 1222–1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferner, R.E.; Aronson, J.K. EIDOS: A Mechanistic Classification of Adverse Drug Effects. Drug Saf. 2010, 33, 15–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnaswami, A.; Steinman, M.A.; Goyal, P.; Zullo, A.R.; Anderson, T.S.; Birtcher, K.K.; Goodlin, S.J.; Maurer, M.S.; Alexander, K.P.; Rich, M.W.; et al. Deprescribing in Older Adults with Cardiovascular Disease. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2019, 73, 2584–2595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naranjo, C.A.; Busto, U.; Sellers, E.M.; Sandor, P.; Ruiz, I.; Roberts, E.A.; Janecek, E.; Domecq, C.; Greenblatt, D.J. A Method for Estimating the Probability of Adverse Drug Reactions. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 1981, 30, 239–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zazzara, M.B.; Palmer, K.; Vetrano, D.L.; Carfì, A.; Onder, G. Adverse Drug Reactions in Older Adults: A Narrative Review of the Literature. Eur. Geriatr. Med. 2021, 12, 463–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Regulation (EC) No. 726/2004; Proposal for a Regulation Amending, as Regards Pharmacovigilance of Medicinal Products for Human Use. European Commission: Brussels, Belgium, 2008.
- Chisaki, Y.; Aoji, S.; Yano, Y. Analysis of Adverse Drug Reaction Risk in Elderly Patients Using the Japanese Adverse Drug Event Report (JADER) Database. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2017, 40, 824–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oscanoa, T.J.; Lizaraso, F.; Carvajal, A. Hospital Admissions Due to Adverse Drug Reactions in the Elderly. A Meta-Analysis. Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2017, 73, 759–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouvy, J.C.; De Bruin, M.L.; Koopmanschap, M.A. Epidemiology of Adverse Drug Reactions in Europe: A Review of Recent Observational Studies. Drug Saf. 2015, 38, 437–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Field, T.S.; Gurwitz, J.H.; Avorn, J.; McCormick, D.; Jain, S.; Eckler, M.; Benser, M.; Bates, D.W. Risk Factors for Adverse Drug Events among Nursing Home Residents. Arch. Intern. Med. 2001, 161, 1629–1634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooper, J.W. Adverse Drug Reaction-Related Hospitalizations of Nursing Facility Patients: A 4-Year Study. South. Med. J. 1999, 92, 485–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gurwitz, J.H.; Field, T.S.; Judge, J.; Rochon, P.; Harrold, L.R.; Cadoret, C.; Lee, M.; White, K.; LaPrino, J.; Erramuspe-Mainard, J.; et al. The Incidence of Adverse Drug Events in Two Large Academic Long-Term Care Facilities. Am. J. Med. 2005, 118, 251–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wierenga, P.C.; Buurman, B.M.; Parlevliet, J.L.; van Munster, B.C.; Smorenburg, S.M.; Inouye, S.K.; de Rooij, S.E. Association between Acute Geriatric Syndromes and Medication-Related Hospital Admissions. Drugs Aging 2012, 29, 691–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beijer, H.J.M.; de Blaey, C.J. Hospitalisations Caused by Adverse Drug Reactions (ADR): A Meta-Analysis of Observational Studies. Pharm. World Sci. 2002, 24, 46–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dilles, T.; Vander Stichele, R.H.; Van Bortel, L.M.; Elseviers, M.M. The Development and Test of an Intervention to Improve ADR Screening in Nursing Homes. J. Am. Med. Dir. Assoc. 2013, 14, e1–e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hazell, L.; Shakir, S.A.W. Under-Reporting of Adverse Drug Reactions: A Systematic Review. Drug Saf. 2006, 29, 385–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EMA. ICH E7 Studies in Support of Special Populations: Geriatrics-Scientific Guideline. Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/ich-e7-studies-support-special-populations-geriatrics-scientific-guideline (accessed on 28 September 2023).
- McLean, A.J.; Le Couteur, D.G. Aging Biology and Geriatric Clinical Pharmacology. Pharmacol. Rev. 2004, 56, 163–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atkin, P.A.; Veitch, P.C.; Veitch, E.M.; Ogle, S.J. The Epidemiology of Serious Adverse Drug Reactions among the Elderly. Drugs Aging 1999, 14, 141–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onder, G.; Vetrano, D.L.; Palmer, K.; Trevisan, C.; Amato, L.; Berti, F.; Campomori, A.; Catalano, L.; Corsonello, A.; Kruger, P.; et al. Italian Guidelines on Management of Persons with Multimorbidity and Polypharmacy. Aging Clin. Exp. Res. 2022, 34, 989–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muth, C.; Blom, J.W.; Smith, S.M.; Johnell, K.; Gonzalez-Gonzalez, A.I.; Nguyen, T.S.; Brueckle, M.-S.; Cesari, M.; Tinetti, M.E.; Valderas, J.M. Evidence Supporting the Best Clinical Management of Patients with Multimorbidity and Polypharmacy: A Systematic Guideline Review and Expert Consensus. J. Intern. Med. 2019, 285, 272–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Obreli Neto, P.R.; Nobili, A.; de Lyra, D.P.; Pilger, D.; Guidoni, C.M.; de Oliveira Baldoni, A.; Cruciol-Souza, J.M.; de Carvalho Freitas, A.L.; Tettamanti, M.; Gaeti, W.P.; et al. Incidence and Predictors of Adverse Drug Reactions Caused by Drug-Drug Interactions in Elderly Outpatients: A Prospective Cohort Study. J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci. 2012, 15, 332–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevenson, J.M.; Davies, J.G.; Martin, F.C. Medication-Related Harm: A Geriatric Syndrome. Age Ageing 2019, 49, 7–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conforti, A.; Costantini, D.; Zanetti, F.; Moretti, U.; Grezzana, M.; Leone, R. Adverse Drug Reactions in Older Patients: An Italian Observational Prospective Hospital Study. Drug Healthc. Patient Saf. 2012, 4, 75–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardelli, M.; Marchegiani, F.; Corsonello, A.; Lattanzio, F.; Provinciali, M. A Review of Pharmacogenetics of Adverse Drug Reactions in Elderly People. Drug Saf. 2012, 35 (Suppl. S1), 3–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gutiérrez-Valencia, M.; Izquierdo, M.; Cesari, M.; Casas-Herrero, Á.; Inzitari, M.; Martínez-Velilla, N. The Relationship between Frailty and Polypharmacy in Older People: A Systematic Review. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2018, 84, 1432–1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duerden, M.; Avery, T.; Payne, R. Polypharmacy and Medicines Optimisation: Making It Safe and Sound; The King’s Fund: London, UK, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Onder, G.; Pedone, C.; Landi, F.; Cesari, M.; Della Vedova, C.; Bernabei, R.; Gambassi, G. Adverse Drug Reactions as Cause of Hospital Admissions: Results from the Italian Group of Pharmacoepidemiology in the Elderly (GIFA). J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2002, 50, 1962–1968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coleman, J.J.; Pontefract, S.K. Adverse Drug Reactions. Clin. Med. 2016, 16, 481–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ventura, M.T.; Laddaga, R.; Cavallera, P.; Pugliese, P.; Tummolo, R.A.; Buquicchio, R.; Pierucci, P.; Passalacqua, G. Adverse Drug Reactions as the Cause of Emergency Department Admission: Focus on the Elderly. Immunopharmacol. Immunotoxicol. 2010, 32, 426–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Routledge, P.A.; O’Mahony, M.S.; Woodhouse, K.W. Adverse Drug Reactions in Elderly Patients. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2004, 57, 121–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lattanzio, F.; Landi, F.; Bustacchini, S.; Abbatecola, A.M.; Corica, F.; Pranno, L.; Corsonello, A. Geriatric Conditions and the Risk of Adverse Drug Reactions in Older Adults: A Review. Drug Saf. 2012, 35 (Suppl. S1), 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calderón-Larrañaga, A.; Vetrano, D.L.; Onder, G.; Gimeno-Feliu, L.A.; Coscollar-Santaliestra, C.; Carfí, A.; Pisciotta, M.S.; Angleman, S.; Melis, R.J.F.; Santoni, G.; et al. Assessing and Measuring Chronic Multimorbidity in the Older Population: A Proposal for Its Operationalization. J. Gerontol. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2017, 72, 1417–1423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Onder, G.; Lattanzio, F.; Battaglia, M.; Cerullo, F.; Sportiello, R.; Bernabei, R.; Landi, F. The Risk of Adverse Drug Reactions in Older Patients: Beyond Drug Metabolism. Curr. Drug Metab. 2011, 12, 647–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mangoni, A.A.; Jackson, S.H.D. Age-Related Changes in Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics: Basic Principles and Practical Applications. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2004, 57, 6–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Budnitz, D.S.; Pollock, D.A.; Weidenbach, K.N.; Mendelsohn, A.B.; Schroeder, T.J.; Annest, J.L. National Surveillance of Emergency Department Visits for Outpatient Adverse Drug Events. JAMA 2006, 296, 1858–1866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Budnitz, D.S.; Lovegrove, M.C.; Shehab, N.; Richards, C.L. Emergency Hospitalizations for Adverse Drug Events in Older Americans. N. Engl. J. Med. 2011, 365, 2002–2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klotz, U. Pharmacokinetics and Drug Metabolism in the Elderly. Drug Metab. Rev. 2009, 41, 67–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verde, Z.; García de Diego, L.; Chicharro, L.M.; Bandrés, F.; Velasco, V.; Mingo, T.; Fernández-Araque, A. Physical Performance and Quality of Life in Older Adults: Is There Any Association between Them and Potential Drug Interactions in Polymedicated Octogenarians. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 4190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Y.; Chen, J.; Li, D.; Wang, L.; Wang, W.; Liu, H. Systematic Analysis of Adverse Event Reports for Sex Differences in Adverse Drug Events. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 24955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moyer, A.M.; Matey, E.T.; Miller, V.M. Individualized Medicine: Sex, Hormones, Genetics, and Adverse Drug Reactions. Pharmacol. Res. Perspect. 2019, 7, e00541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, C.; Knowles, S.R.; Liu, B.A.; Shear, N.H. Gender Differences in Adverse Drug Reactions. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 1998, 38, 1003–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franconi, F.; Brunelleschi, S.; Steardo, L.; Cuomo, V. Gender Differences in Drug Responses. Pharmacol. Res. 2007, 55, 81–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saraf, A.A.; Petersen, A.W.; Simmons, S.F.; Schnelle, J.F.; Bell, S.P.; Kripalani, S.; Myers, A.P.; Mixon, A.S.; Long, E.A.; Jacobsen, J.M.L.; et al. Medications Associated with Geriatric Syndromes and Their Prevalence in Older Hospitalized Adults Discharged to Skilled Nursing Facilities. J. Hosp. Med. 2016, 11, 694–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vetrano, D.L.; Palmer, K.; Marengoni, A.; Marzetti, E.; Lattanzio, F.; Roller-Wirnsberger, R.; Lopez Samaniego, L.; Rodríguez-Mañas, L.; Bernabei, R.; Onder, G.; et al. Frailty and Multimorbidity: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Gerontol. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2019, 74, 659–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muhlack, D.C.; Hoppe, L.K.; Stock, C.; Haefeli, W.E.; Brenner, H.; Schöttker, B. The Associations of Geriatric Syndromes and Other Patient Characteristics with the Current and Future Use of Potentially Inappropriate Medications in a Large Cohort Study. Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2018, 74, 1633–1644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gage, B.F.; Birman-Deych, E.; Kerzner, R.; Radford, M.J.; Nilasena, D.S.; Rich, M.W. Incidence of Intracranial Hemorrhage in Patients with Atrial Fibrillation Who Are Prone to Fall. Am. J. Med. 2005, 118, 612–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Food and Drug Administration, HHS. International Conference on Harmonisation. Guidance on E15 Pharmacogenomics Definitions and Sample Coding; Availability. Notice. Fed. Regist. 2008, 73, 19074–19076. [Google Scholar]
- Evans, W.E.; Relling, M.V. Pharmacogenomics: Translating Functional Genomics into Rational Therapeutics. Science 1999, 286, 487–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- PharmGKB. Available online: https://www.pharmgkb.org/ (accessed on 6 July 2023).
- Pirazzoli, A.; Recchia, G. Pharmacogenetics and Pharmacogenomics: Are They Still Promising? Pharmacol. Res. 2004, 49, 357–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, K.C.; Ma, J.D.; Kuo, G.M. Pharmacogenomics: Bridging the Gap between Science and Practice. J. Am. Pharm. Assoc. 2010, 50, e1–e17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinto, N.; Dolan, M.E. Clinically Relevant Genetic Variations in Drug Metabolizing Enzymes. Curr. Drug Metab. 2011, 12, 487–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, D.; Kashyap, A.; Pandey, R.V.; Saini, K.S. Novel Advances in Cytochrome P450 Research. Drug Discov. Today 2011, 16, 793–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, S.-M.; Strong, J.M.; Zhang, L.; Reynolds, K.S.; Nallani, S.; Temple, R.; Abraham, S.; Habet, S.A.; Baweja, R.K.; Burckart, G.J.; et al. New Era in Drug Interaction Evaluation: US Food and Drug Administration Update on CYP Enzymes, Transporters, and the Guidance Process. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2008, 48, 662–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, D.R.; Zeldin, D.C.; Hoffman, S.M.G.; Maltais, L.J.; Wain, H.M.; Nebert, D.W. Comparison of Cytochrome P450 (CYP) Genes from the Mouse and Human Genomes, Including Nomenclature Recommendations for Genes, Pseudogenes and Alternative-Splice Variants. Pharmacogenetics 2004, 14, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ingelman-Sundberg, M.; Sim, S.C.; Gomez, A.; Rodriguez-Antona, C. Influence of Cytochrome P450 Polymorphisms on Drug Therapies: Pharmacogenetic, Pharmacoepigenetic and Clinical Aspects. Pharmacol Ther. 2007, 116, 496–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swen, J.J.; van der Wouden, C.H.; Manson, L.E.; Abdullah-Koolmees, H.; Blagec, K.; Blagus, T.; Böhringer, S.; Cambon-Thomsen, A.; Cecchin, E.; Cheung, K.-C.; et al. A 12-Gene Pharmacogenetic Panel to Prevent Adverse Drug Reactions: An Open-Label, Multicentre, Controlled, Cluster-Randomised Crossover Implementation Study. Lancet 2023, 401, 347–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shorr, R.I.; Ray, W.A.; Daugherty, J.R.; Griffin, M.R. Concurrent Use of Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs and Oral Anticoagulants Places Elderly Persons at High Risk for Hemorrhagic Peptic Ulcer Disease. Arch. Intern. Med. 1993, 153, 1665–1670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westervelt, P.; Cho, K.; Bright, D.R.; Kisor, D.F. Drug-Gene Interactions: Inherent Variability in Drug Maintenance Dose Requirements. Pharm. Ther. 2014, 39, 630–637. [Google Scholar]
- Hahn, M.; Roll, S.C. The Influence of Pharmacogenetics on the Clinical Relevance of Pharmacokinetic Drug-Drug Interactions: Drug-Gene, Drug-Gene-Gene and Drug-Drug-Gene Interactions. Pharmaceuticals 2021, 14, 487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peñas-LLedó, E.; LLerena, A. Clinical Use of Pre-Emptive Pharmacogenetic Programmes. Lancet 2023, 401, 320–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malki, M.A.; Pearson, E.R. Drug–Drug–Gene Interactions and Adverse Drug Reactions. Pharmacogen. J. 2020, 20, 355–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joint Formulary Committee. British National Formulary (Online); BMJ and Pharmaceutical Press: London, UK, 2023; Available online: http://www.medicinescomplete.com (accessed on 27 September 2023).
- DRUG-REAX. University of Technology Sydney. Available online: https://search.lib.uts.edu.au/discovery/fulldisplay/alma991001040579705671/61UTS_INST:61UTS (accessed on 27 September 2023).
- Drug Interaction Checker. For Drugs, Food, and Alcohol. Available online: https://www.drugs.com/drug_interactions.html (accessed on 27 September 2023).
- Les Interactions Médicamenteuses. Available online: https://www.vidal.fr/medicaments/utilisation/prendre-traitement/interactions-medicamenteuses.html (accessed on 24 September 2023).
- Tatro David, S. Drug Interaction Facts: The Authority on Drug Interactions; Lippincott Williams & Wilkins: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2014; Available online: https://books.google.it/books?id=ScqioAEACAAJ (accessed on 24 September 2023)ISBN 978-1-57439-363-7.
- Monteiro, C.; Duarte, A.P.; Alves, G. Adverse Drug Reactions in Elderly: A Five-Year Review of Spontaneous Reports to the Portuguese Pharmacovigilance System. Expert. Opin. Drug Saf. 2021, 20, 109–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dubrall, D.; Just, K.S.; Schmid, M.; Stingl, J.C.; Sachs, B. Adverse Drug Reactions in Older Adults: A Retrospective Comparative Analysis of Spontaneous Reports to the German Federal Institute for Drugs and Medical Devices. BMC Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2020, 21, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlquist, J.F.; Knight, S.; Horne, B.D.; Huntinghouse, J.A.; Rollo, J.S.; Muhlestein, J.B.; May, H.; Anderson, J.L. Cardiovascular Risk among Patients on Clopidogrel Anti-Platelet Therapy after Placement of Drug-Eluting Stents Is Modified by Genetic Variants in Both the CYP2C19 and ABCB1 Genes. Thromb. Haemost. 2013, 109, 744–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, M.Y.; Tan, K.; Tan, H.-C.; Huan, P.-T.; Li, B.; Phua, Q.-H.; Lee, H.-K.; Lee, C.-H.; Low, A.; Becker, R.C.; et al. CYP2C19 and PON1 Polymorphisms Regulating Clopidogrel Bioactivation in Chinese, Malay and Indian Subjects. Pharmacogenomics 2012, 13, 533–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harmsze, A.M.; van Werkum, J.W.; Hackeng, C.M.; Ruven, H.J.T.; Kelder, J.C.; Bouman, H.J.; Breet, N.J.; Ten Berg, J.M.; Klungel, O.H.; de Boer, A.; et al. The Influence of CYP2C19*2 and *17 on On-Treatment Platelet Reactivity and Bleeding Events in Patients Undergoing Elective Coronary Stenting. Pharmacogenet. Genom. 2012, 22, 169–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurbel, P.A.; Shuldiner, A.R.; Bliden, K.P.; Ryan, K.; Pakyz, R.E.; Tantry, U.S. The Relation between CYP2C19 Genotype and Phenotype in Stented Patients on Maintenance Dual Antiplatelet Therapy. Am. Heart J. 2011, 161, 598–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallentin, L.; James, S.; Storey, R.F.; Armstrong, M.; Barratt, B.J.; Horrow, J.; Husted, S.; Katus, H.; Steg, P.G.; Shah, S.H.; et al. Effect of CYP2C19 and ABCB1 Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms on Outcomes of Treatment with Ticagrelor versus Clopidogrel for Acute Coronary Syndromes: A Genetic Substudy of the PLATO Trial. Lancet 2010, 376, 1320–1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andersson, M.L.; Eliasson, E.; Lindh, J.D. A Clinically Significant Interaction between Warfarin and Simvastatin Is Unique to Carriers of the CYP2C9*3 Allele. Pharmacogenomics 2012, 13, 757–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uno, T.; Shimizu, M.; Yasui-Furukori, N.; Sugawara, K.; Tateishi, T. Different Effects of Fluvoxamine on Rabeprazole Pharmacokinetics in Relation to CYP2C19 Genotype Status. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2006, 61, 309–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sangkuhl, K.; Klein, T.E.; Altman, R.B. Clopidogrel Pathway. Pharmacogenet. Genom. 2010, 20, 463–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furuta, T.; Iwaki, T.; Umemura, K. Influences of Different Proton Pump Inhibitors on the Anti-Platelet Function of Clopidogrel in Relation to CYP2C19 Genotypes. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2010, 70, 383–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harmsze, A.M.; van Werkum, J.W.; Souverein, P.C.; Breet, N.J.; Bouman, H.J.; Hackeng, C.M.; Ruven, H.J.T.; ten Berg, J.M.; Klungel, O.H.; de Boer, A.; et al. Combined Influence of Proton-Pump Inhibitors, Calcium-Channel Blockers and CYP2C19*2 on on-Treatment Platelet Reactivity and on the Occurrence of Atherothrombotic Events after Percutaneous Coronary Intervention. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2011, 9, 1892–1901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vormfelde, S.V.; Brockmöller, J.; Bauer, S.; Herchenhein, P.; Kuon, J.; Meineke, I.; Roots, I.; Kirchheiner, J. Relative Impact of Genotype and Enzyme Induction on the Metabolic Capacity of CYP2C9 in Healthy Volunteers. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2009, 86, 54–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Depta, J.P.; Lenzini, P.A.; Lanfear, D.E.; Wang, T.Y.; Spertus, J.A.; Bach, R.G.; Cresci, S. Clinical Outcomes Associated with Proton Pump Inhibitor Use among Clopidogrel-Treated Patients within CYP2C19 Genotype Groups Following Acute Myocardial Infarction. Pharmacogen. J. 2015, 15, 20–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laine, K.; Tybring, G.; Härtter, S.; Andersson, K.; Svensson, J.O.; Widén, J.; Bertilsson, L. Inhibition of Cytochrome P4502D6 Activity with Paroxetine Normalizes the Ultrarapid Metabolizer Phenotype as Measured by Nortriptyline Pharmacokinetics and the Debrisoquin Test. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2001, 70, 327–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicholls, G.; Youdim, K. Drug Transporters: Volume 1: Role and Importance in ADME and Drug Development; The Royal Society of Chemistry: London, UK, 2016; ISBN 978-1-78262-069-3. [Google Scholar]
- Dujic, T.; Zhou, K.; Donnelly, L.A.; Tavendale, R.; Palmer, C.N.A.; Pearson, E.R. Association of Organic Cation Transporter 1 With Intolerance to Metformin in Type 2 Diabetes: A GoDARTS Study. Diabetes 2015, 64, 1786–1793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahlin, G.; Chen, L.; Lazorova, L.; Chen, Y.; Ianculescu, A.G.; Davis, R.L.; Giacomini, K.M.; Artursson, P. Genotype-Dependent Effects of Inhibitors of the Organic Cation Transporter, OCT1: Predictions of Metformin Interactions. Pharmacogen. J. 2011, 11, 400–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grün, B.; Kiessling, M.K.; Burhenne, J.; Riedel, K.-D.; Weiss, J.; Rauch, G.; Haefeli, W.E.; Czock, D. Trimethoprim-Metformin Interaction and Its Genetic Modulation by OCT2 and MATE1 Transporters. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2013, 76, 787–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.-J.; Yin, O.Q.P.; Tomlinson, B.; Chow, M.S.S. OCT2 Polymorphisms and In-Vivo Renal Functional Consequence: Studies with Metformin and Cimetidine. Pharmacogenet. Genom. 2008, 18, 637–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filipski, K.K.; Mathijssen, R.H.; Mikkelsen, T.S.; Schinkel, A.H.; Sparreboom, A. Contribution of Organic Cation Transporter 2 (OCT2) to Cisplatin-Induced Nephrotoxicity. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2009, 86, 396–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spracklen, T.F.; Vorster, A.A.; Ramma, L.; Dalvie, S.; Ramesar, R.S. Promoter Region Variation in NFE2L2 Influences Susceptibility to Ototoxicity in Patients Exposed to High Cumulative Doses of Cisplatin. Pharmacogen. J. 2017, 17, 515–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, H.Y.; Bae, K.-S.; Cho, S.-H.; Ghim, J.-L.; Choe, S.; Jung, J.A.; Jin, S.-J.; Kim, H.-S.; Lim, H.-S. Impact of CYP2D6, CYP3A5, CYP2C19, CYP2A6, SLCO1B1, ABCB1, and ABCG2 Gene Polymorphisms on the Pharmacokinetics of Simvastatin and Simvastatin Acid. Pharmacogenet. Genom. 2015, 25, 595–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luzum, J.A.; Theusch, E.; Taylor, K.D.; Wang, A.; Sadee, W.; Binkley, P.F.; Krauss, R.M.; Medina, M.W.; Kitzmiller, J.P. Individual and Combined Associations of Genetic Variants in CYP3A4, CYP3A5, and SLCO1B1 With Simvastatin and Simvastatin Acid Plasma Concentrations. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. 2015, 66, 80–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsamandouras, N.; Dickinson, G.; Guo, Y.; Hall, S.; Rostami-Hodjegan, A.; Galetin, A.; Aarons, L. Development and Application of a Mechanistic Pharmacokinetic Model for Simvastatin and Its Active Metabolite Simvastatin Acid Using an Integrated Population PBPK Approach. Pharm. Res. 2015, 32, 1864–1883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishizato, Y.; Ieiri, I.; Suzuki, H.; Kimura, M.; Kawabata, K.; Hirota, T.; Takane, H.; Irie, S.; Kusuhara, H.; Urasaki, Y.; et al. Polymorphisms of OATP-C (SLC21A6) and OAT3 (SLC22A8) Genes: Consequences for Pravastatin Pharmacokinetics. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2003, 73, 554–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedrós, C.; Formiga, F.; Corbella, X.; Arnau, J.M. Adverse Drug Reactions Leading to Urgent Hospital Admission in an Elderly Population: Prevalence and Main Features. Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2016, 72, 219–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farrell, B.; Tsang, C.; Raman-Wilms, L.; Irving, H.; Conklin, J.; Pottie, K. What Are Priorities for Deprescribing for Elderly Patients? Capturing the Voice of Practitioners: A Modified Delphi Process. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0122246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reeve, E.; Gnjidic, D.; Long, J.; Hilmer, S. A Systematic Review of the Emerging Definition of “deprescribing” with Network Analysis: Implications for Future Research and Clinical Practice. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2015, 80, 1254–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, I.A.; Hilmer, S.N.; Reeve, E.; Potter, K.; Le Couteur, D.; Rigby, D.; Gnjidic, D.; Del Mar, C.B.; Roughead, E.E.; Page, A.; et al. Reducing Inappropriate Polypharmacy: The Process of Deprescribing. JAMA Intern. Med. 2015, 175, 827–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rochon, P.A.; Gurwitz, J.H. The Prescribing Cascade Revisited. Lancet 2017, 389, 1778–1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiber, S.; Zuker-Herman, R.; Drescher, M.J.; Glezerman, M. Gender Differences in the Comprehension of Care Plans in an Emergency Department Setting. Isr. J. Health Policy Res. 2018, 7, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kerse, N.; Buetow, S.; Mainous, A.G.; Young, G.; Coster, G.; Arroll, B. Physician-Patient Relationship and Medication Compliance: A Primary Care Investigation. Ann. Fam. Med. 2004, 2, 455–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neri, L.; Peris, K.; Longo, C.; Calvieri, S.; Frascione, P.; Parodi, A.; Eibenschuz, L.; Bottoni, U.; Pellacani, G.; the Actinic Keratosis—TReatment Adherence INitiative (AK-TRAIN) Study Group. Physician–Patient Communication and Patient-Reported Outcomes in the Actinic Keratosis Treatment Adherence Initiative (AK-TRAIN): A Multicenter, Prospective, Real-Life Study of Treatment Satisfaction, Quality of Life and Adherence to Topical Field-Directed Therapy for the Treatment of Actinic Keratosis in Italy. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2019, 33, 93–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, S.H. Potential for Physician Communication to Build Favorable Medication Beliefs among Older Adults with Hypertension: A Cross-Sectional Survey. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0210169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McInnes, G.T. Integrated Approaches to Management of Hypertension: Promoting Treatment Acceptance. Am. Heart J. 1999, 138, S252–S255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shariff, Z.B.; Dahmash, D.T.; Kirby, D.J.; Missaghi, S.; Rajabi-Siahboomi, A.; Maidment, I.D. Does the Formulation of Oral Solid Dosage Forms Affect Acceptance and Adherence in Older Patients? A Mixed Methods Systematic Review. J. Am. Med. Dir. Assoc. 2020, 21, 1015–1023.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, R.; Mainous Iii, A.G.; Gray, D.P.; Love, M.M. Exploration of the Relationship between Continuity, Trust in Regular Doctors and Patient Satisfaction with Consultations with Family Doctors. Scand. J. Prim. Health Care 2003, 21, 27–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ridd, M.; Shaw, A.; Lewis, G.; Salisbury, C. The Patient–Doctor Relationship: A Synthesis of the Qualitative Literature on Patients’ Perspectives. Br. J. Gen. Pract. 2009, 59, e116–e133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thom, D.H.; Kravitz, R.L.; Bell, R.A.; Krupat, E.; Azari, R. Patient Trust in the Physician: Relationship to Patient Requests. Fam. Pract. 2002, 19, 476–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- By the 2019 American Geriatrics Society Beers Criteria® Update Expert Panel. American Geriatrics Society 2019 Updated AGS Beers Criteria® for Potentially Inappropriate Medication Use in Older Adults. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2019, 67, 674–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Mahony, D.; O’Sullivan, D.; Byrne, S.; O’Connor, M.N.; Ryan, C.; Gallagher, P. STOPP/START Criteria for Potentially Inappropriate Prescribing in Older People: Version 2. Age Ageing 2015, 44, 213–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Mahony, D.; Cherubini, A.; Guiteras, A.R.; Denkinger, M.; Beuscart, J.-B.; Onder, G.; Gudmundsson, A.; Cruz-Jentoft, A.J.; Knol, W.; Bahat, G.; et al. STOPP/START Criteria for Potentially Inappropriate Prescribing in Older People: Version 3. Eur. Geriatr. Med. 2023, 14, 625–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- By the 2023 American Geriatrics Society Beers Criteria® Update Expert Panel. American Geriatrics Society 2023 Updated AGS Beers Criteria® for Potentially Inappropriate Medication Use in Older Adults. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2023, 71, 2052–2081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maher, R.L.; Hanlon, J.; Hajjar, E.R. Clinical Consequences of Polypharmacy in Elderly. Expert. Opin. Drug Saf. 2014, 13, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuhn-Thiel, A.M.; Weiß, C.; Wehling, M.; The FORTA authors/expert panel members. Consensus Validation of the FORTA (Fit fOR The Aged) List: A Clinical Tool for Increasing the Appropriateness of Pharmacotherapy in the Elderly. Drugs Aging 2014, 31, 131–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pazan, F.; Gercke, Y.; Weiss, C.; Wehling, M.; FORTA Raters. The U.S.-FORTA (Fit fOR The Aged) List: Consensus Validation of a Clinical Tool to Improve Drug Therapy in Older Adults. J. Am. Med. Dir. Assoc. 2020, 21, e9–e439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pazan, F.; Weiss, C.; Wehling, M.; FORTA. The EURO-FORTA (Fit fOR The Aged) List: International Consensus Validation of a Clinical Tool for Improved Drug Treatment in Older People. Drugs Aging 2018, 35, 61–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pazan, F.; Weiss, C.; Wehling, M.; FORTA. The FORTA (Fit fOR The Aged) List 2018: Third Version of a Validated Clinical Tool for Improved Drug Treatment in Older People. Drugs Aging 2019, 36, 481–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perpétuo, C.; Plácido, A.I.; Rodrigues, D.; Aperta, J.; Piñeiro-Lamas, M.; Figueiras, A.; Herdeiro, M.T.; Roque, F. Prescription of Potentially Inappropriate Medication in Older Inpatients of an Internal Medicine Ward: Concordance and Overlap among the EU(7)-PIM List and Beers and STOPP Criteria. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 676020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Field, T.S.; Mazor, K.M.; Briesacher, B.; Debellis, K.R.; Gurwitz, J.H. Adverse Drug Events Resulting from Patient Errors in Older Adults. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2007, 55, 271–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NICE. Overview|Guidance|Medicines Optimisation: The Safe and Effective Use of Medicines to Enable the Best Possible Outcomes. Available online: https://www.nice.org.uk/guidance/ng5 (accessed on 7 July 2023).
- Institute for Healthcare Improvement. Medication Reconciliation to Prevent Adverse Drug Events. Available online: https://www.ihi.org:443/Topics/ADEsMedicationReconciliation/Pages/default.aspx (accessed on 7 July 2023).
- Cynthia, R.; Hennen, B.S.; Jorgenson, J.A. Importance of Medication Reconciliation in the Continuum of Care. Am. J. Pharm. Benefits 2014, 6, 71–75. [Google Scholar]
- Lester, P.E.; Sahansra, S.; Shen, M.; Becker, M.; Islam, S. Medication Reconciliation: An Educational Module. MedEdPORTAL 2019, 15, 10852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cornish, P.L.; Knowles, S.R.; Marchesano, R.; Tam, V.; Shadowitz, S.; Juurlink, D.N.; Etchells, E.E. Unintended Medication Discrepancies at the Time of Hospital Admission. Arch. Intern. Med. 2005, 165, 424–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silvestre, C.C.; Santos, L.M.C.; Silva, R.d.O.S.; dos Santos, G.A., Jr.; Neves, S.J.F.; de Oliveira-Filho, A.D.; Lobo, I.M.F.; de Lyra, D.P., Jr. Risk Factors for Unintentional Medication Discrepancies at Hospital Admission: A Matched Case-Control Study. Eur. J. Intern. Med. 2017, 40, e24–e25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mueller, S.K.; Sponsler, K.C.; Kripalani, S.; Schnipper, J.L. Hospital-Based Medication Reconciliation Practices: A Systematic Review. Arch. Intern. Med. 2012, 172, 1057–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MedStopper. Available online: http://medstopper.com/ (accessed on 2 August 2023).
- Eysenbach, G. What Is E-Health? J. Med. Internet Res. 2001, 3, e833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kampmeijer, R.; Pavlova, M.; Tambor, M.; Golinowska, S.; Groot, W. The Use of E-Health and m-Health Tools in Health Promotion and Primary Prevention among Older Adults: A Systematic Literature Review. BMC Health Serv. Res. 2016, 16, 290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linn, N.; Goetzinger, C.; Regnaux, J.-P.; Schmitz, S.; Dessenne, C.; Fagherazzi, G.; Aguayo, G.A. Digital Health Interventions among People Living with Frailty: A Scoping Review. J. Am. Med. Dir. Assoc. 2021, 22, 1802–1812.e21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- INTERCheck WEB. Available online: https://intercheckweb.marionegri.it/home#/main (accessed on 2 August 2023).
- Sutton, R.T.; Pincock, D.; Baumgart, D.C.; Sadowski, D.C.; Fedorak, R.N.; Kroeker, K.I. An Overview of Clinical Decision Support Systems: Benefits, Risks, and Strategies for Success. NPJ Digit. Med. 2020, 3, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuperman, G.J.; Bobb, A.; Payne, T.H.; Avery, A.J.; Gandhi, T.K.; Burns, G.; Classen, D.C.; Bates, D.W. Medication-Related Clinical Decision Support in Computerized Provider Order Entry Systems: A Review. J. Am. Med. Inf. Assoc. 2007, 14, 29–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaushal, R.; Shojania, K.G.; Bates, D.W. Effects of Computerized Physician Order Entry and Clinical Decision Support Systems on Medication Safety: A Systematic Review. Arch. Intern. Med. 2003, 163, 1409–1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strom, B.L.; Schinnar, R.; Aberra, F.; Bilker, W.; Hennessy, S.; Leonard, C.E.; Pifer, E. Unintended Effects of a Computerized Physician Order Entry Nearly Hard-Stop Alert to Prevent a Drug Interaction: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Arch. Intern. Med. 2010, 170, 1578–1583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Thomson and Rawlins | Type A (Augmented) | Type B (Bizarre) | Type C (Continuing) | Type D (Delayed) | Type E (End-of-Use) | Type F (Failure) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Response to drugs administrated at therapeutic doses being the result of an abnormal response of an otherwise normal pharmacological effect. | Unrelated to the pharmacodynamics or the dosage of the drug and are often fatal. These are less common, and so may only be discovered for the first time after a drug has already been made available for general use. | Related to the cumulative dose of a long-term pharmacological treatment. | Consequence to the timing of a treatment and become apparent sometime after the use of a medicine. | Associated to the withdrawal of a given medicine. | Occurring when a therapy appears futile. | |
| Dose, Time and Susceptibility (DoTS) | Relation to Dose (Do) | Time Course (T) | Susceptibility Factors (S) | |||
|
|
| ||||
| EIDOS | Extrinsic chemical species (E) | Intrinsic chemical species (I) | Distribution (D) | Outcome (O) | Sequelae (S) | |
| This can be the parent compound, an excipient, a contaminant or adulterant, a degradation product or a derivative of any of these. | This is usually the endogenous molecule with which the extrinsic species interacts; this can be a nucleic acid, an enzyme, a receptor, an ion channel or transporter or some other protein. | A drug will not produce an adverse effect if it is not distributed to the same site as the target species that mediates the adverse effect. Thus, the pharmacokinetics of the extrinsic species can affect the occurrence of adverse effects. | Interactions between extrinsic and intrinsic species in the production of an adverse effect can result in physiological or pathological changes. | The sequela of the changes induced by a drug describes the clinically recognizable adverse drug reaction, of which there may be more than one. | ||
| Required Genetic Testing | Recommended Genetic Testing | Actionable Genetic Testing | Informative Genetic Testing | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| FDA | 137 | 7 | 146 | 140 |
| EMA | 85 | 5 | 45 | 71 |
| Swissmedic | 9 | 5 | 92 | 24 |
| HCSC | 69 | 6 | 67 | 40 |
| PMDA | 14 | / | 29 | 8 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bellanca, C.M.; Augello, E.; Cantone, A.F.; Di Mauro, R.; Attaguile, G.A.; Di Giovanni, V.; Condorelli, G.A.; Di Benedetto, G.; Cantarella, G.; Bernardini, R. Insight into Risk Factors, Pharmacogenetics/Genomics, and Management of Adverse Drug Reactions in Elderly: A Narrative Review. Pharmaceuticals 2023, 16, 1542. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16111542
Bellanca CM, Augello E, Cantone AF, Di Mauro R, Attaguile GA, Di Giovanni V, Condorelli GA, Di Benedetto G, Cantarella G, Bernardini R. Insight into Risk Factors, Pharmacogenetics/Genomics, and Management of Adverse Drug Reactions in Elderly: A Narrative Review. Pharmaceuticals. 2023; 16(11):1542. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16111542
Chicago/Turabian StyleBellanca, Carlo Maria, Egle Augello, Anna Flavia Cantone, Rosaria Di Mauro, Giuseppe Antonino Attaguile, Vincenza Di Giovanni, Guido Attilio Condorelli, Giulia Di Benedetto, Giuseppina Cantarella, and Renato Bernardini. 2023. "Insight into Risk Factors, Pharmacogenetics/Genomics, and Management of Adverse Drug Reactions in Elderly: A Narrative Review" Pharmaceuticals 16, no. 11: 1542. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16111542
APA StyleBellanca, C. M., Augello, E., Cantone, A. F., Di Mauro, R., Attaguile, G. A., Di Giovanni, V., Condorelli, G. A., Di Benedetto, G., Cantarella, G., & Bernardini, R. (2023). Insight into Risk Factors, Pharmacogenetics/Genomics, and Management of Adverse Drug Reactions in Elderly: A Narrative Review. Pharmaceuticals, 16(11), 1542. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16111542