Regulatory Effects and Mechanism of Action of Green Tea Polyphenols on Osteogenesis and Adipogenesis in Human Adipose Tissue-Derived Stem Cells
Abstract
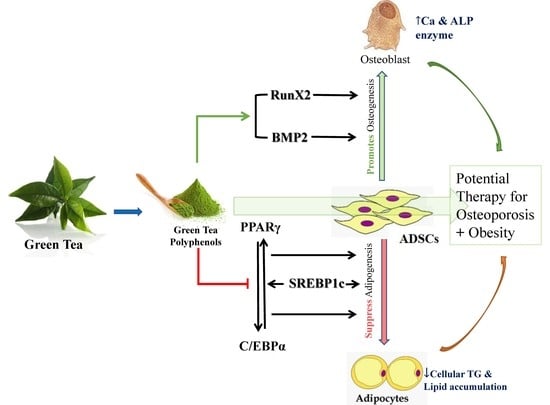
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Green Tea Polyphenols and Pioglitazone
2.2. Isolation and Culture of hADSCs
2.3. Differentiation and Treatment of hADSCs
2.4. Determination of Lipid Accumulation and Triglycerides Content
2.5. Alkaline Phosphatase Assay and Determination of Intracellular Calcium
2.6. Immunofluorescence Staining and Quantification
2.7. Total RNA Isolation and Quantitative Real-Time PCR
2.8. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. GTPs Reduces Lipid Accumulation and Triglyceride Synthesis during hADSC Differentiation into Adipocytes
3.2. GTPs Inhibits the Expression of PPARγ Protein and Genes Involved in ADSCs toward Adipogenic Differentiation
3.3. GTPs Stimulates Mineralization and ALP Activity during Osteogenic Differentiation of hADSCs
3.4. GTPs Induces the Expression of Runx2 Protein and Genes Involved in ADSC towards Osteogenic Differentiation
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rinonapoli, G.; Pace, V.; Ruggiero, C.; Ceccarini, P.; Bisaccia, M.; Meccariello, L.; Caraffa, A. Obesity and Bone: A Complex Relationship. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 13662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fassio, A.; Idolazzi, L.; Rossini, M.; Gatti, D.; Adami, G.; Giollo, A.; Viapiana, O. The obesity paradox and osteoporosis. Eat Weight Disord. 2018, 23, 293–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, L.; Tyagi, S.; Myers, D.; Duque, G. Good, Bad, or Ugly: The Biological Roles of Bone Marrow Fat. Curr. Osteoporos. Rep. 2018, 16, 130–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, L.; Yin, C.; Zhao, F.; Ali, A.; Ma, J.; Qian, A. Mesenchymal Stem Cells: Cell Fate Decision to Osteoblast or Adipocyte and Application in Osteoporosis Treatment. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Horowitz, M.C.; Lorenzo, J.A. The origins of osteoclasts. Curr. Opin. Rheumatol. 2004, 16, 464–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fazeli, P.K.; Horowitz, M.C.; MacDougald, O.A.; Scheller, E.L.; Rodeheffer, M.S.; Rosen, C.J.; Klibanski, A. Marrow fat and bone--new perspectives. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2013, 98, 935–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rayalam, S.; Della-Fera, M.A.; Baile, C.A. Synergism between resveratrol and other phytochemicals: Implications for obesity and osteoporosis. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2011, 55, 1177–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devine, A.; Hodgson, J.M.; Dick, I.M.; Prince, R.L. Tea drinking is associated with benefits on bone density in older women. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2007, 86, 1243–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, C.H.; Yang, Y.C.; Yao, W.J.; Lu, F.H.; Wu, J.S.; Chang, C.J. Epidemiological evidence of increased bone mineral density in habitual tea drinkers. Arch. Intern. Med. 2002, 162, 1001–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kanis, J.; Johnell, O.; Gullberg, B.; Allander, E.; Elffors, L.; Ranstam, J.; Dequeker, J.; Dilsen, G.; Gennari, C.; Vaz, A.L.; et al. Risk factors for hip fracture in men from southern Europe: The MEDOS study. Mediterranean Osteoporosis Study. Osteoporos. Int. 1999, 9, 45–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnell, O.; Gullberg, B.; Kanis, J.A.; Allander, E.; Elffors, L.; Dequeker, J.; Dilsen, G.; Gennari, C.; Lopes Vaz, A.; Lyritis, G.; et al. Risk factors for hip fracture in European women: The MEDOS Study. Mediterranean Osteoporosis Study. J. Bone Miner. Res. 1995, 10, 1802–1815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.N.; Xiang, J.Z.; Qi, Z.; Du, M. Plant extracts in prevention of obesity. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2022, 62, 2221–2234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonzalez Suarez, N.; Rodriguez Torres, S.; Ouanouki, A.; El Cheikh-Hussein, L.; Annabi, B. EGCG Inhibits Adipose-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells Differentiation into Adipocytes and Prevents a STAT3-Mediated Paracrine Oncogenic Control of Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Cell Invasive Phenotype. Molecules 2021, 26, 1506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, H.T.; Cheng, T.L.; Lin, S.Y.; Ho, C.J.; Chyu, J.Y.; Yang, R.S.; Chen, C.H.; Shen, C.L. Osteoprotective Roles of Green Tea Catechins. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.Y.; Kang, L.; Wang, C.Z.; Huang, H.H.; Cheng, T.L.; Huang, H.T.; Lee, M.J.; Lin, Y.S.; Ho, M.L.; Wang, G.J.; et al. (-)-Epigallocatechin-3-Gallate (EGCG) Enhances Osteogenic Differentiation of Human Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells. Molecules 2018, 23, 3221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lao, W.; Tan, Y.; Jin, X.; Xiao, L.; Kim, J.J.; Qu, X. Comparison of Cytotoxicity and the Anti-Adipogenic Effect of Green Tea Polyphenols with Epigallocatechin-3-Gallate in 3T3-L1 Preadipocytes. Am. J. Chin. Med. 2015, 43, 1177–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.; Tan, Y.; Zhou, J.; Xiao, L.; Johnson, M.; Qu, X. Green tea polyphenols ameliorate metabolic abnormalities and insulin resistance by enhancing insulin signalling in skeletal muscle of Zucker fatty rats. Clin. Sci. 2020, 134, 1167–1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derosa, G.; Maffioli, P. Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma (PPAR-gamma) agonists on glycemic control, lipid profile and cardiovascular risk. Curr. Mol. Pharmacol. 2012, 5, 272–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bunnell, B.A.; Flaat, M.; Gagliardi, C.; Patel, B.; Ripoll, C. Adipose-derived stem cells: Isolation, expansion and differentiation. Methods 2008, 45, 115–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Takada, I.; Kouzmenko, A.P.; Kato, S. Molecular switching of osteoblastogenesis versus adipogenesis: Implications for targeted therapies. Expert Opin. Ther. Targets 2009, 13, 593–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuk, P.A.; Zhu, M.; Ashjian, P.; De Ugarte, D.A.; Huang, J.I.; Mizuno, H.; Alfonso, Z.C.; Fraser, J.K.; Benhaim, P.; Hedrick, M.H. Human adipose tissue is a source of multipotent stem cells. Mol. Biol. Cell 2002, 13, 4279–4295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chani, B.; Puri, V.; Chander Sobti, R.; Puri, S. Epigallocatechin Gallate Inhibits Mouse Mesenchymal Stem Cell Differentiation to Adipogenic Lineage. J. Stem Cells Regen. Med. 2016, 12, 16–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Souza, C.J.; Eckhardt, M.; Gagen, K.; Dong, M.; Chen, W.; Laurent, D.; Burkey, B.F. Effects of pioglitazone on adipose tissue remodeling within the setting of obesity and insulin resistance. Diabetes 2001, 50, 1863–1871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shen, C.L.; Han, J.; Wang, S.; Chung, E.; Chyu, M.C.; Cao, J.J. Green tea supplementation benefits body composition and improves bone properties in obese female rats fed with high-fat diet and caloric restricted diet. Nutr. Res. 2015, 35, 1095–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, C.L.; Yeh, J.K.; Samathanam, C.; Cao, J.J.; Stoecker, B.J.; Dagda, R.Y.; Chyu, M.C.; Dunn, D.M.; Wang, J.S. Green tea polyphenols attenuate deterioration of bone microarchitecture in female rats with systemic chronic inflammation. Osteoporos. Int. 2011, 22, 327–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.W.; Klemm, D.J.; Vinson, C.; Lane, M.D. Role of CREB in transcriptional regulation of CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein beta gene during adipogenesis. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 4471–4478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wu, Z.; Rosen, E.D.; Brun, R.; Hauser, S.; Adelmant, G.; Troy, A.E.; McKeon, C.; Darlington, G.J.; Spiegelman, B.M. Cross-regulation of C/EBP alpha and PPAR gamma controls the transcriptional pathway of adipogenesis and insulin sensitivity. Mol. Cell 1999, 3, 151–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haakonsson, A.K.; Stahl Madsen, M.; Nielsen, R.; Sandelin, A.; Mandrup, S. Acute genome-wide effects of rosiglitazone on PPARgamma transcriptional networks in adipocytes. Mol. Endocrinol. 2013, 27, 1536–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruderer, M.; Richards, R.G.; Alini, M.; Stoddart, M.J. Role and regulation of RUNX2 in osteogenesis. Eur Cell Mater 2014, 28, 269–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yodthong, T.; Kedjarune-Leggat, U.; Smythe, C.; Wititsuwannakul, R.; Pitakpornpreecha, T. l-Quebrachitol Promotes the Proliferation, Differentiation, and Mineralization of MC3T3-E1 Cells: Involvement of the BMP-2/Runx2/MAPK/Wnt/beta-Catenin Signaling Pathway. Molecules 2018, 23, 3086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chava, S.; Chennakesavulu, S.; Gayatri, B.M.; Reddy, A.B.M. A novel phosphorylation by AMP-activated kinase regulates RUNX2 from ubiquitination in osteogenesis over adipogenesis. Cell Death Dis. 2018, 9, 754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]






| Primer Symbol | Forward Primer | Reverse Primer |
|---|---|---|
| Cebpa | 5′-TATAGGCTGGGCTTCCCCTT-3′ | 5′-AGCTTTCTGGTGTGACTCGG-3′ |
| Pparγ | 5′-CCGTGGCCGCAGATTTGA-3′ | 5′-AGATCCACGGAGCTGATCCC-3′ |
| Creb | 5′-TTCAAGCCCAGCCACAGATT-3′ | 5′-AGTTGAAATCTGAACTGTTTGGAC-3′ |
| Runx2 | 5′-CACCGAGACCAACAGAGTCA-3′ | 5′-TGGTGTCACTGTGCTGAAGA-3′ |
| Bmp2 | 5′-TTTCAATGGACGTGTCCCCG-3′ | 5′-AGCAGCAACGCTAGAAGACA-3′ |
| Actb | 5′-CTCACCATGGATGATGATATCGC-3′ | 5′-AGGAATCCTTCTGACCCATGC-3′ |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lao, W.; Zhao, Y.; Tan, Y.; Johnson, M.; Li, Y.; Xiao, L.; Cheng, J.; Lin, Y.; Qu, X. Regulatory Effects and Mechanism of Action of Green Tea Polyphenols on Osteogenesis and Adipogenesis in Human Adipose Tissue-Derived Stem Cells. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2022, 44, 6046-6058. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb44120412
Lao W, Zhao Y, Tan Y, Johnson M, Li Y, Xiao L, Cheng J, Lin Y, Qu X. Regulatory Effects and Mechanism of Action of Green Tea Polyphenols on Osteogenesis and Adipogenesis in Human Adipose Tissue-Derived Stem Cells. Current Issues in Molecular Biology. 2022; 44(12):6046-6058. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb44120412
Chicago/Turabian StyleLao, Weiguo, Yi Zhao, Yi Tan, Michael Johnson, Yan Li, Linda Xiao, Jing Cheng, Yiguang Lin, and Xianqin Qu. 2022. "Regulatory Effects and Mechanism of Action of Green Tea Polyphenols on Osteogenesis and Adipogenesis in Human Adipose Tissue-Derived Stem Cells" Current Issues in Molecular Biology 44, no. 12: 6046-6058. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb44120412
APA StyleLao, W., Zhao, Y., Tan, Y., Johnson, M., Li, Y., Xiao, L., Cheng, J., Lin, Y., & Qu, X. (2022). Regulatory Effects and Mechanism of Action of Green Tea Polyphenols on Osteogenesis and Adipogenesis in Human Adipose Tissue-Derived Stem Cells. Current Issues in Molecular Biology, 44(12), 6046-6058. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb44120412