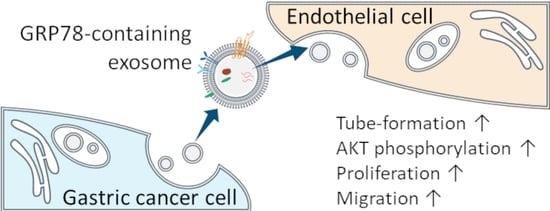
Gastric Cancer Cell-Derived Exosomal GRP78 Enhances Angiogenesis upon Stimulation of Vascular Endothelial Cells
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Culture
2.2. Preparation and Confirmation of Exosomes
2.3. Western Blotting
2.4. Ultrasensitive Thio-NAD Cycling ELISA
2.5. Tube Formation Assay
2.6. MTT Assay
2.7. Wound Healing Assay
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Exosome Characterization and GRP78 Quantification in Exosomes
3.2. Tube Formation Assay of Vascular Endothelial Cells by the Application of GRP78-Containing Exosomes
3.3. Phosphorylation of AKT in Vascular Endothelial Cells by the Application of Grp78 Containing Exosomes
3.4. MTT Assay for Vascular Endothelial Cells by the Application of GRP78-Containing Exosomes
3.5. Wound Healing Assay for Migration Potential of Vascular Endothelial Cells Following the Application of GRP78-Containing Exosomes
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, Z.; Li, Z. Glucose regulated protein 78: A critical link between tumor microenvironment and cancer hallmarks. Biochim. Biophys. Acta-Rev. Cancer 2012, 1826, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.H.; Tsai, H.Y.; Chen, C.L.; Chen, J.L.; Lu, C.C.; Fang, Y.P.; Wu, D.C.; Huang, Y.B.; Lin, M.W. Isoliquiritigenin inhibits gastric cancer stemness, modulates tumor microenvironment, and suppresses tumor growth through glucose-regulated protein 78 downregulation. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iha, K.; Tsurusawa, N.; Tsai, H.-Y.; Lin, M.-W.; Sonoda, H.; Watabe, S.; Yoshimura, T.; Ito, E. Ultrasensitive ELISA detection of proteins in separated lumen and membrane fractions of cancer cell exosomes. Anal. Biochem. 2022, 654, 114831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsurusawa, N.; Iha, K.; Sato, A.; Tsai, H.-Y.; Sonoda, H.; Watabe, S.; Yoshimura, T.; Wu, D.-C.; Lin, M.-W.; Ito, E. Ultrasensitive detection of GRP78 in exosomes and observation of migration and proliferation of cancer cells by application of GRP78-containing exosomes. Cancers 2022, 14, 3887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, D.; Stapleton, C.; Luo, B.; Xiong, S.; Ye, W.; Zhang, Y.; Jhaveri, N.; Zhu, G.; Ye, R.; Liu, Z.; et al. A critical role for GRP78/BiP in the tumor microenvironment for neovascularization during tumor growth and metastasis. Cancer Res. 2011, 71, 2848–2857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, Y.; Zhang, L.; La, X.; Li, Z.; Li, H.; Guo, S. Salvianolic acid A inhibits tumor-associated angiogenesis by blocking GRP78 secretion. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg’s Arch. Pharmacol. 2018, 392, 467–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, H.; Gong, L.; Liu, J.; Zhou, Q.; Zheng, Z. Diosgenin inhibits tumor angiogenesis through regulating GRP78-mediated HIF-1α and VEGF/VEGFR signaling pathways. Pharmazie 2019, 74, 680–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anno, K.; Hayashi, A.; Takahashi, T.; Mitsui, Y.; Ide, T.; Tahara, H. Telomerase activation induces elongation of the telomeric single-stranded overhang, but does not prevent chromosome aberrations in human vascular endothelial cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2007, 353, 926–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Théry, C.; Witwer, K.W.; Aikawa, E.; Alcaraz, M.J.; Anderson, J.D.; Andriantsitohaina, R.; Antoniou, A.; Arab, T.; Archer, F.; Atkin-Smith, G.K.; et al. Minimal Information for Studies of Extracellular Vesicles 2018 (MISEV2018): A Position Statement of the International Society for Extracellular Vesicles and Update of the MISEV2014 Guidelines. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2018, 7, 1535750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Colombo, M.; Moita, C.; van Niel, G.; Kowal, J.; Vigneron, J.; Benaroch, P.; Manel, N.; Moita, L.F.; Théry, C.; Raposo, G. Analysis of ESCRT Functions in Exosome Biogenesis, Composition and Secretion Highlights the Heterogeneity of Extracellular Vesicles. J. Cell Sci. 2013, 126, 5553–5565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerber, H.P.; McMurtrey, A.; Kowalski, J.; Yan, M.; Keyt, B.A.; Dixit, V.; Ferrara, N. Vascular endothelial growth factor regulates endothelial cell survival through the phosphatidylinositol 3′-kinase/Akt signal transduction pathway: Requirement for Flk-1/KDR activation. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 30336–30343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cheng, H.W.; Chen, Y.F.; Wong, J.M.; Weng, C.W.; Chen, H.Y.; Yu, S.L.; Chen, H.W.; Yuan, A.; Chen, J.J.W. Cancer cells increase endothelial cell tube formation and survival by activating the PI3K/Akt signalling pathway. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2017, 36, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, M.; Chen, M.; Qi, M.; Ye, G.; Pan, J.; Shi, C.; Yang, Y.; Zhao, L.; Mo, X.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Perivascular cell-derived extracellular vesicles stimulate colorectal cancer revascularization after withdrawal of antiangiogenic drugs. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2021, 10, e12096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watabe, S.; Kodama, H.; Kaneda, M.; Morikawa, M.; Nakaishi, K.; Yoshimura, T.; Iwai, A.; Miura, T.; Ito, E. Ultrasensitive enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) of proteins by combination with the THIO-NAD cycling method. Biophysics 2014, 10, 49–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Iha, K.; Kyosei, Y.; Namba, M.; Makioka, D.; Yamura, S.; Watabe, S.; Yoshimura, T.; Ito, E. Zeptomole detection of an enzyme by a simple colorimetric method. Anal. Sci. 2021, 37, 1469–1472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iha, K.; Inada, M.; Kawada, N.; Nakaishi, K.; Watabe, S.; Tan, Y.H.; Shen, C.; Ke, L.-Y.; Yoshimura, T.; Ito, E. Ultrasensitive ELISA developed for diagnosis. Diagnostics 2019, 9, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ito, E.; Iha, K.; Yoshimura, T.; Nakaishi, K.; Watabe, S. Early diagnosis with ultrasensitive ELISA. Adv. Clin. Chem. 2021, 101, 121–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyosei, Y.; Yamura, S.; Namba, M.; Yoshimura, T.; Watabe, S.; Ito, E. Antigen tests for COVID-19. Biophys. Physicobiol. 2021, 18, 28–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsurusawa, N.; Chang, J.; Namba, M.; Makioka, D.; Yamura, S.; Iha, K.; Kyosei, Y.; Watabe, S.; Yoshimura, T.; Ito, E. Modified ELISA for ultrasensitive diagnosis. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 5197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suarez-Arnedo, A.; Figueroa, F.T.; Clavijo, C.; Arbeláez, P.; Cruz, J.C.; Muñoz-Camargo, C. An image J plugin for the high throughput image analysis of in vitro scratch wound healing assays. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0232565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, Y.; Scott, E.; Lu, R.; Xu, Y.; Oh, W.K.; Yu, Q. TIMP-1 promotes accumulation of cancer associated fibroblasts and cancer progression. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e77366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tominaga, N.; Hagiwara, K.; Kosaka, N.; Honma, K.; Nakagama, H.; Ochiya, T. RPN2-mediated glycosylation of tetraspanin CD63 regulates breast cancer cell malignancy. Mol. Cancer 2014, 13, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Roucourt, B.; Meeussen, S.; Bao, J.; Zimmermann, P.; David, G. Heparanase activates the syndecan-syntenin-ALIX exosome pathway. Cell Res. 2015, 25, 412–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mathieu, M.; Névo, N.; Jouve, M.; Valenzuela, J.I.; Maurin, M.; Verweij, F.J.; Palmulli, R.; Lankar, D.; Dingli, F.; Loew, D.; et al. Specificities of exosome versus small ectosome secretion revealed by live intracellular tracking of CD63 and CD9. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 4389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhagwat, S.V.; Lahdenranta, J.; Giordano, R.; Arap, W.; Pasqualini, R.; Shapiro, L.H. CD13/APN is activated by angiogenic signals and is essential for capillary tube formation. Blood 2001, 97, 652–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dimmeler, S.; Dernbach, E.; Zeiher, A.M. Phosphorylation of the endothelial nitric oxide synthase at Ser-1177 is required for VEGF-induced endothelial cell migration. FEBS Lett. 2000, 477, 258–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kureishi, Y.; Luo, Z.; Shiojima, I.; Bialik, A.; Fulton, D.; Lefer, D.J.; Sessa, W.C.; Walsh, K. The HMG-CoA reductase inhibitor simvastatin activates the protein kinase Akt and promotes angiogenesis in normocholesterolemic animals. Nat. Med. 2000, 6, 1004–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales-Ruiz, M.; Fulton, D.; Sowa, G.; Languino, L.R.; Fujio, Y.; Walsh, K.; Sessa, W.C. Vascular endothelial growth factor-stimulated actin reorganization and migration of endothelial cells is regulated via the serine/threonine kinase Akt. Circ. Res. 2000, 86, 892–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, R.; Yang, P.; Wu, H.-L.; Li, Z.-W.; Li, Z.-Y. GRP78 secreted by colon cancer cells facilitates cell proliferation via PI3K/Akt signaling. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2014, 15, 7245–7249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, K.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, M.; Cao, X.; Qi, J.; Wang, D.; Gong, A.; Zhu, H. Role of GRP78 Inhibiting Artesunate-Induced Ferroptosis in KRAS Mutant Pancreatic Cancer Cells. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2019, 13, 2135–2144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Wang, Y.; Wu, H.; Zhang, L.; Yang, P.; Li, Z. GRP78 Enhances the Glutamine Metabolism to Support Cell Survival from Glucose Deficiency by Modulating the β-Catenin Signaling. Oncotarget 2014, 5, 5369–5380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Luo, S.; Mao, C.; Lee, B.; Lee, A.S. GRP78/BiP is required for cell proliferation and protecting the inner cell mass from apoptosis during early mouse embryonic development. Mol. Cell Biol. 2006, 26, 5688–5697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, L.; Guo, H.; Peng, Y.; Nie, D.; Mo, J.; Ye, L. Knockdown of MALAT1 Attenuates High-Glucose-Induced Angiogenesis and Inflammation via Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress in Human Retinal Vascular Endothelial Cells. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2020, 124, 109699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Yoon, Y.M.; Han, Y.-S.; Lee, J.H.; Hur, J.; Lee, S.H. Administration of Cripto in GRP78 Overexpressed Human MSCs Enhances Stem Cell Viability and Angiogenesis during Human MSC Transplantation Therapy. Cell Prolif. 2018, 51, e12463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shiojima, I.; Walsh, K. Role of Akt signaling in vascular homeostasis and angiogenesis. Circ. Res. 2002, 90, 1243–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Karar, J.; Maity, A. PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway in angiogenesis. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2011, 4, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kobialka, P.; Graupera, M. Revisiting PI3-kinase signalling in angiogenesis. Vasc. Biol. 2019, 1, H125–H134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- He, L.; Zhu, W.; Chen, Q.; Yuan, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wang, J.; Wu, X. Ovarian cancer cell-secreted exosomal miR-205 promotes metastasis by inducing angiogenesis. Theranostics 2019, 9, 8206–8220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raiter, A.; Weiss, C.; Bechor, Z.; Ben-Dor, I.; Battler, A.; Kaplan, B.; Hardy, B. Activation of GRP78 on endothelial cell membranes by an ADAM15-derived peptide induces angiogenesis. J. Vasc. Res. 2010, 47, 399–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ku, Y.H.; Cho, B.J.; Kim, M.J.; Lim, S.; Park, Y.J.; Jang, H.C.; Choi, S.H. Rosiglitazone increases endothelial cell migration and vascular permeability through Akt phosphorylation. BMC Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2017, 18, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Li, X.; Gao, W.; Zhou, Y.; Wey, S.; Mitra, S.K.; Krasnoperov, V.; Dong, D.; Liu, S.; Li, D.; et al. Monoclonal antibody against cell surface GRP78 as a novel agent in suppressing PI3K/AKT signaling, tumor growth, and metastasis. Clin. Cancer Res. 2013, 19, 6802–6811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fu, Y.; Wey, S.; Wang, M.; Ye, R.; Liao, C.P.; Roy-Burman, P.; Lee, A.S. Pten null prostate tumorigenesis and AKT activation are blocked by targeted knockout of ER chaperone GRP78/BiP in prostate epithelium. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 19444–19449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tseng, Y.Z.C.C.; Tsai, Y.L.; Fu, X.; Schiff, R.; Lee, A.S. Cancer cells resistant to therapy promote cell surface relocalization of GRP78 which complexes with PI3K and enhances PI(3,4,5)P3 production. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e80071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Iha, K.; Sato, A.; Tsai, H.-Y.; Sonoda, H.; Watabe, S.; Yoshimura, T.; Lin, M.-W.; Ito, E. Gastric Cancer Cell-Derived Exosomal GRP78 Enhances Angiogenesis upon Stimulation of Vascular Endothelial Cells. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2022, 44, 6145-6157. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb44120419
Iha K, Sato A, Tsai H-Y, Sonoda H, Watabe S, Yoshimura T, Lin M-W, Ito E. Gastric Cancer Cell-Derived Exosomal GRP78 Enhances Angiogenesis upon Stimulation of Vascular Endothelial Cells. Current Issues in Molecular Biology. 2022; 44(12):6145-6157. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb44120419
Chicago/Turabian StyleIha, Kanako, Akane Sato, Hsin-Yi Tsai, Hikaru Sonoda, Satoshi Watabe, Teruki Yoshimura, Ming-Wei Lin, and Etsuro Ito. 2022. "Gastric Cancer Cell-Derived Exosomal GRP78 Enhances Angiogenesis upon Stimulation of Vascular Endothelial Cells" Current Issues in Molecular Biology 44, no. 12: 6145-6157. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb44120419
APA StyleIha, K., Sato, A., Tsai, H. -Y., Sonoda, H., Watabe, S., Yoshimura, T., Lin, M. -W., & Ito, E. (2022). Gastric Cancer Cell-Derived Exosomal GRP78 Enhances Angiogenesis upon Stimulation of Vascular Endothelial Cells. Current Issues in Molecular Biology, 44(12), 6145-6157. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb44120419