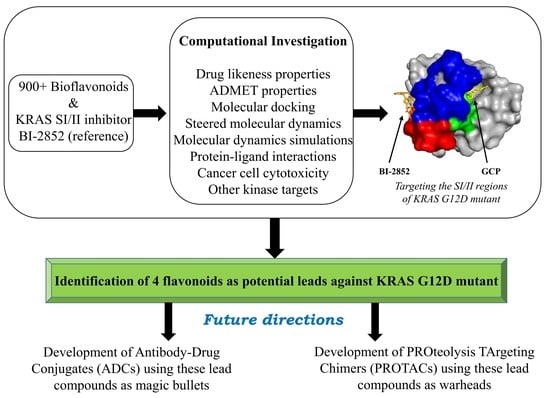
Identification of Dietary Bioflavonoids as Potential Inhibitors against KRAS G12D Mutant—Novel Insights from Computer-Aided Drug Discovery
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Protein and Ligand Preparation
2.2. Drug-Likeness and ADME Properties
2.3. Molecular Docking
2.4. Steered Molecular Dynamics
2.5. Molecular-Dynamics Simulation
2.6. SwissTargetPrediction Analysis
2.7. In Silico Cytotoxicity Prediction
3. Results
3.1. Evaluation of Lipinski’s Rule and ADME Properties
3.2. Molecular-Docking Analysis
3.3. Binding Interactions of Lead Flavonoids
3.4. Steered Molecular Dynamics
3.5. Molecular-Dynamics Simulation
3.6. Lead-Flavonoid Effect on Other Molecular Targets
3.7. Toxicity and Cell-Line Cytotoxicity of Lead Flavonoids
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- O’Bryan, J.P. Pharmacological Targeting of RAS: Recent Success with Direct Inhibitors. Pharmacol. Res. 2019, 139, 503–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hancock, J.F. Ras Proteins: Different Signals from Different Locations. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2003, 4, 373–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Q.; Fujimiya, R.; Kubo, S.; Marshall, C.B.; Ikura, M.; Shimada, I.; Nishida, N. Real-Time In-Cell NMR Reveals the Intracellular Modulation of GTP-Bound Levels of RAS. Cell Rep. 2020, 32, 108074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simanshu, D.K.; Nissley, D.V.; McCormick, F. RAS Proteins and Their Regulators in Human Disease. Cell 2017, 170, 17–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Takács, T.; Kudlik, G.; Kurilla, A.; Szeder, B.; Buday, L.; Vas, V. The Effects of Mutant Ras Proteins on the Cell Signalome. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2020, 39, 1051–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prior, I.A.; Lewis, P.D.; Mattos, C. A Comprehensive Survey of Ras Mutations in Cancer. Cancer Res. 2012, 72, 2457–2467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Malumbres, M.; Barbacid, M. RAS Oncogenes: The First 30 Years. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2003, 3, 459–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harvey, J.J. An Unidentified Virus which causes the Rapid Production of Tumours in Mice. Nature 1964, 204, 1104–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirsten, W.H.; Schauf, V.; McCoy, J. Properties of a Murine Sarcoma Virus. Bibl. Haematol. 1970, 36, 246–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burge, R.A.; Hobbs, G.A. Not All RAS Mutations Are Equal: A Detailed Review of the Functional Diversity of RAS Hot Spot Mutations. Adv. Cancer Res. 2022, 153, 29–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hobbs, G.A.; Der, C.J.; Rossman, K.L. RAS Isoforms and Mutations in Cancer at a Glance. J. Cell Sci. 2016, 129, 1287–1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, H.; Tsou, J.-H.; Leng, Q.; Jiang, F. Sensitive Detection of KRAS Mutations by Clustered Regularly Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeats. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stolze, B.; Reinhart, S.; Bulllinger, L.; Fröhling, S.; Scholl, C. Comparative Analysis of KRAS Codon 12, 13, 18, 61 and 117 Mutations Using Human MCF10A Isogenic Cell Lines. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 8535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tate, J.G.; Bamford, S.; Jubb, H.C.; Sondka, Z.; Beare, D.M.; Bindal, N.; Boutselakis, H.; Cole, C.G.; Creatore, C.; Dawson, E.; et al. COSMIC: The Catalogue Of Somatic Mutations In Cancer. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, D941–D947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lanman, B.A.; Allen, J.R.; Allen, J.G.; Amegadzie, A.K.; Ashton, K.S.; Booker, S.K.; Chen, J.J.; Chen, N.; Frohn, M.J.; Goodman, G.; et al. Discovery of a Covalent Inhibitor of KRASG12C (AMG 510) for the Treatment of Solid Tumors. J. Med. Chem. 2020, 63, 52–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kulkarni, A.M.; Kumar, V.; Parate, S.; Lee, G.; Yoon, S.; Lee, K.W. Identification of New KRAS G12D Inhibitors through Computer-Aided Drug Discovery Methods. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ou, S.-H.I.; Jänne, P.A.; Leal, T.A.; Rybkin, I.I.; Sabari, J.K.; Barve, M.A.; Bazhenova, L.; Johnson, M.L.; Velastegui, K.L.; Cilliers, C.; et al. First-in-Human Phase I/IB Dose-Finding Study of Adagrasib (MRTX849) in Patients with Advanced KRASG12C Solid Tumors (KRYSTAL-1). J. Clin. Oncol. Off. J. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 40, 2530–2538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lito, P.; Solomon, M.; Li, L.-S.; Hansen, R.; Rosen, N. Allele-Specific Inhibitors Inactivate Mutant KRAS G12C by a Trapping Mechanism. Science 2016, 351, 604–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Welsch, M.E.; Kaplan, A.; Chambers, J.M.; Stokes, M.E.; Bos, P.H.; Zask, A.; Zhang, Y.; Sanchez-Martin, M.; Badgley, M.A.; Huang, C.S.; et al. Multivalent Small-Molecule Pan-RAS Inhibitors. Cell 2017, 168, 878–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tran, T.H.; Alexander, P.; Dharmaiah, S.; Agamasu, C.; Nissley, D.V.; McCormick, F.; Esposito, D.; Simanshu, D.K.; Stephen, A.G.; Balius, T.E. The Small Molecule BI-2852 Induces a Nonfunctional Dimer of KRAS. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 3363–3364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Menyhárd, D.K.; Pálfy, G.; Orgován, Z.; Vida, I.; Keserű, G.M.; Perczel, A. Structural Impact of GTP Binding on Downstream KRAS Signaling. Chem. Sci. 2020, 11, 9272–9289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodríguez-García, C.; Sánchez-Quesada, C.; Gaforio, J.J. Dietary Flavonoids as Cancer Chemopreventive Agents: An Updated Review of Human Studies. Antioxidants 2019, 8, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kopustinskiene, D.M.; Jakstas, V.; Savickas, A.; Bernatoniene, J. Flavonoids as Anticancer Agents. Nutrients 2020, 12, 457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, T.; Chen, G.Y. Flavonoids and Colorectal Cancer Prevention. Antioxidants 2018, 7, 187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cruz-Migoni, A.; Canning, P.; Quevedo, C.E.; Bataille, C.J.R.; Bery, N.; Miller, A.; Russell, A.J.; Phillips, S.E.V.; Carr, S.B.; Rabbitts, T.H. Structure-Based Development of New RAS-Effector Inhibitors from a Combination of Active and Inactive RAS-Binding Compounds. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 2545–2550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, S.; Chen, J.; Cheng, T.; Gindulyte, A.; He, J.; He, S.; Li, Q.; Shoemaker, B.A.; Thiessen, P.A.; Yu, B.; et al. PubChem in 2021: New Data Content and Improved Web Interfaces. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, D1388–D1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Boyle, N.M.; Banck, M.; James, C.A.; Morley, C.; Vandermeersch, T.; Hutchison, G.R. Open Babel: An Open Chemical Toolbox. J. Cheminform. 2011, 3, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hanwell, M.D.; Curtis, D.E.; Lonie, D.C.; Vandermeersch, T.; Zurek, E.; Hutchison, G.R. Avogadro: An Advanced Semantic Chemical Editor, Visualization, and Analysis Platform. J. Cheminform. 2012, 4, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Daina, A.; Michielin, O.; Zoete, V. SwissADME: A Free Web Tool to Evaluate Pharmacokinetics, Drug-Likeness and Medicinal Chemistry Friendliness of Small Molecules. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 42717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lipinski, C.A.; Lombardo, F.; Dominy, B.W.; Feeney, P.J. Experimental and Computational Approaches to Estimate Solubility and Permeability in Drug Discovery and Development Settings. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2001, 46, 3–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mekala, J.R.; Ramalingam, P.S.; Mathavan, S.; Yamajala, R.B.R.D.; Moparthi, N.R.; Kurappalli, R.K.; Manyam, R.R. Synthesis, in vitro and Structural Aspects of Cap Substituted Suberoylanilide Hydroxamic Acid Analogs as Potential Inducers of Apoptosis in Glioblastoma Cancer Cells via HDAC/MicroRNA Regulation. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2022, 357, 109876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mekala, J.R.; Kurappalli, R.K.; Ramalingam, P.; Moparthi, N.R. N-Acetyl l-Aspartate and Triacetin Modulate Tumor Suppressor MicroRNA and Class I and II HDAC Gene Expression Induce Apoptosis in Glioblastoma Cancer Cells in vitro. Life Sci. 2021, 286, 120024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trott, O.; Olson, A.J. AutoDock Vina: Improving the Speed and Accuracy of Docking with a New Scoring Function, Efficient Optimization, and Multithreading. J. Comput. Chem. 2010, 31, 455–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Srinivasan, E.; Chandrasekhar, G.; Rajasekaran, R. Probing the Polyphenolic Flavonoid, Morin as a Highly Efficacious Inhibitor against Amyloid(A4V) Mutant SOD1 in Fatal Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2022, 727, 109318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wolf, R.M.; Caldwell, J.W.; Kollman, P.A.; Case, D.A. Development and Testing of a General Amber Force Field. J. Comput. Chem. 2004, 25, 1157–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Y.; Ewalt, J.; Ng, H.-L. Recent Insights from Molecular Dynamics Simulations for G Protein-Coupled Receptor Drug Discovery. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 4237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Case, D.A.; Cheatham, T.E., 3rd; Darden, T.; Gohlke, H.; Luo, R.; Merz, K.M.J.; Onufriev, A.; Simmerling, C.; Wang, B.; Woods, R.J. The Amber Biomolecular Simulation Programs. J. Comput. Chem. 2005, 26, 1668–1688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shakil, S.; Rizvi, S.M.D.; Greig, N.H. High Throughput Virtual Screening and Molecular Dynamics Simulation for Identifying a Putative Inhibitor of Bacterial CTX-M-15. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daina, A.; Michielin, O.; Zoete, V. SwissTargetPrediction: Updated Data and New Features for Efficient Prediction of Protein Targets of Small Molecules. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, W357–W364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lagunin, A.A.; Dubovskaja, V.I.; Rudik, A.V.; Pogodin, P.V.; Druzhilovskiy, D.S.; Gloriozova, T.A.; Filimonov, D.A.; Sastry, N.G.; Poroikov, V.V. CLC-Pred: A Freely Available Web-Service for in Silico Prediction of Human Cell Line Cytotoxicity for Drug-like Compounds. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0191838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xiong, G.; Wu, Z.; Yi, J.; Fu, L.; Yang, Z.; Hsieh, C.; Yin, M.; Zeng, X.; Wu, C.; Lu, A.; et al. ADMETlab 2.0: An Integrated Online Platform for Accurate and Comprehensive Predictions of ADMET Properties. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, W5–W14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cox, A.D.; Fesik, S.W.; Kimmelman, A.C.; Luo, J.; Der, C.J. Drugging the Undruggable RAS: Mission Possible? Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2014, 13, 828–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moore, A.R.; Rosenberg, S.C.; McCormick, F.; Malek, S. RAS-Targeted Therapies: Is the Undruggable Drugged? Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2020, 19, 533–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsai, Y.S.; Woodcock, M.G.; Azam, S.H.; Thorne, L.B.; Kanchi, K.L.; Parker, J.S.; Vincent, B.G.; Pecot, C.V. Rapid Idiosyncratic Mechanisms of Clinical Resistance to KRAS G12C Inhibition. J. Clin. Investig. 2022, 132, e155523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Kang, R.; Tang, D. The KRAS-G12C Inhibitor: Activity and Resistance. Cancer Gene Ther. 2022, 29, 875–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abotaleb, M.; Samuel, S.M.; Varghese, E.; Varghese, S.; Kubatka, P.; Liskova, A.; Büsselberg, D. Flavonoids in Cancer and Apoptosis. Cancers 2018, 11, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Woo, H.-H.; Jeong, B.R.; Hawes, M.C. Flavonoids: From Cell Cycle Regulation to Biotechnology. Biotechnol. Lett. 2005, 27, 365–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bondonno, N.P.; Dalgaard, F.; Kyrø, C.; Murray, K.; Bondonno, C.P.; Lewis, J.R.; Croft, K.D.; Gislason, G.; Scalbert, A.; Cassidy, A.; et al. Flavonoid Intake Is Associated with Lower Mortality in the Danish Diet Cancer and Health Cohort. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 3651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Masoodi, T.A.; Alhamdanz, A.H. Inhibitory Effect of Flavonoids on Mutant H-Rasp Protein. Bioinformation 2010, 5, 11–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Imran, M.; Rauf, A.; Abu-Izneid, T.; Nadeem, M.; Shariati, M.A.; Khan, I.A.; Imran, A.; Orhan, I.E.; Rizwan, M.; Atif, M.; et al. Luteolin, a Flavonoid, as an Anticancer Agent: A Review. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2019, 112, 108612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Wang, T.; Chen, D.; Ma, Q.; Zheng, Y.; Liao, S.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, J. Quercetin Preferentially Induces Apoptosis in KRAS-Mutant Colorectal Cancer Cells via JNK Signaling Pathways. Cell Biol. Int. 2019, 43, 117–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xavier, C.P.R.; Lima, C.F.; Preto, A.; Seruca, R.; Fernandes-Ferreira, M.; Pereira-Wilson, C. Luteolin, Quercetin and Ursolic Acid Are Potent Inhibitors of Proliferation and Inducers of Apoptosis in Both KRAS and BRAF Mutated Human Colorectal Cancer Cells. Cancer Lett. 2009, 281, 162–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jitapunkul, K.; Toochinda, P.; Lawtrakul, L. Molecular Dynamic Simulation Analysis on the Inclusion Complexation of Plumbagin with β-Cyclodextrin Derivatives in Aqueous Solution. Molecules 2021, 26, 6784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alaaeldin, R.; Abdel-Rahman, I.A.M.; Hassan, H.A.; Youssef, N.; Allam, A.E.; Abdelwahab, S.F.; Zhao, Q.-L.; Fathy, M. Carpachromene Ameliorates Insulin Resistance in HepG2 Cells via Modulating IR/IRS1/PI3k/Akt/GSK3/FoxO1 Pathway. Molecules 2021, 26, 7629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.-J.; Cui, Q.-X.; Wang, G.-L.; Li, X.-L.; Zhou, X.-L.; Zhao, H.-J.; Zhang, M.-Q.; Li, M.-J.; He, X.-J.; Zheng, Q.-S.; et al. Sanggenon C Suppresses Tumorigenesis of Gastric Cancer by Blocking ERK-Drp1-Mediated Mitochondrial Fission. J. Nat. Prod. 2022, 85, 2351–2362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tajuddeen, N.; Van Heerden, F.R. Antiplasmodial Natural Products: An Update. Malar. J. 2019, 18, 404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hu, X.; Zhang, K.; Pan, G.; Wang, Y.; Shen, Y.; Peng, C.; Deng, L.; Cui, H. Cortex Mori Extracts Induce Apoptosis and Inhibit Tumor Invasion via Blockage of the PI3K/AKT Signaling in Melanoma Cells. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 1007279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parasuraman, S. Toxicological Screening. J. Pharmacol. Pharmacother. 2011, 2, 74–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nagasaka, M.; Potugari, B.; Nguyen, A.; Sukari, A.; Azmi, A.S.; Ou, S.-H.I. KRAS Inhibitors- Yes but What next? Direct Targeting of KRAS- Vaccines, Adoptive T Cell Therapy and Beyond. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2021, 101, 102309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; Liu, Y.; Yang, S.; Wu, X.; Li, H.; Wang, Q. MEK Inhibitors for the Treatment of Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2021, 14, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bryant, K.L.; Stalnecker, C.A.; Zeitouni, D.; Klomp, J.E.; Peng, S.; Tikunov, A.P.; Gunda, V.; Pierobon, M.; Waters, A.M.; George, S.D.; et al. Combination of ERK and Autophagy Inhibition as a Treatment Approach for Pancreatic Cancer. Nat. Med. 2019, 25, 628–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]









| Flavonoid/Compound Name | Physicochemical Properties | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MF | MW | HA | AHA | HBD | HBA | RB | MR | TPSA | |
| BI-2852 (reference) | C31H28N6O2 | 516.59 | 39 | 29 | 4 | 4 | 7 | 155.12 | 99.9 |
| 5-Dehydroxy paratocarpin K (L1) | C20H18O4 | 322.35 | 24 | 12 | 1 | 4 | 1 | 91.65 | 55.76 |
| Carpachromene (L2) | C20H16O5 | 336.34 | 25 | 16 | 2 | 5 | 1 | 96.09 | 79.9 |
| Sanggenone H (L3) | C20H18O6 | 354.35 | 26 | 12 | 3 | 6 | 1 | 95.69 | 96.22 |
| Kuwanol C (L4) | C25H26O6 | 422.47 | 31 | 12 | 3 | 6 | 4 | 119.25 | 96.22 |
| Flavonoid/Compound Name | Lipophilicity | Water Solubility | Pharmacokinetics | Drug-Likeness | Medicinal Chemistry | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Consensus Log Po/w | LogS | GIA | BBBP | Lipinski | BA | SA | |
| BI-2852 (reference) | 3.2 | −4.98 | High | No | No | 0.55 | 4.25 |
| 5-Dehydroxy paratocarpin K (L1) | 3.31 | −4.33 | High | Yes | Yes | 0.55 | 3.92 |
| Carpachromene (L2) | 3.32 | −4.82 | High | No | Yes | 0.55 | 3.71 |
| Sanggenone H (L3) | 2.71 | −4.48 | High | No | Yes | 0.55 | 4.03 |
| Kuwanol C (L4) | 4.15 | −5.8 | High | No | Yes | 0.55 | 4.79 |
| Compound Name | Binding Energy (Kcal/mol) | Ki (µM) | Interacting Residues |
|---|---|---|---|
| BI-2852 | −8.59 | 3.69 | Lys5, Leu6, Val7, Glu37, Ser39, Asp54, Leu56, Cln70, Tyr71, Thr74, Gly75 |
| L1 | −8.80 | 4.19 | Lys5, Leu6, Val7, Glu37, Asp54, Leu56, Met67, Gln70, Tyr71, Thr74 |
| L2 | −8.64 | 7.95 | Lys5, Leu6, Val7, Glu37, Asp54, Leu56, Met67, Gln70, Tyr71, Thr74, Gly75 |
| L3 | −8.62 | 0.83 | Lys5, Leu6, Val7, Glu37, Ser39, Asp54, Leu56, Met67, Gln70, Tyr71, Thr74, Gly75 |
| L4 | −8.58 | 28.54 | Lys5, Leu6, Val7, Glu37, Asp54, Ile55, Leu56, Met67, Gln70, Tyr71, Thr74, Gly75 |
| Flavonoid Name | Interaction | Distance (Å) |
|---|---|---|
| BI-2852 (reference) | OG atom in Ser39 with N2 atom in BI-2852 | 3.11 |
| OD1 atom in Asp54 with N1 atom in BI-2852 | 2.84 | |
| 5-Dehydroxyparatocarpin K (L1) | O atom in Leu6 with O4 atom in L1 | 2.79 |
| O atom in Asp54 with O4 atom in L1 | 3.00 | |
| Carpachromene (L2) | O atom in Leu6 with O4 atom in L2 | 2.78 |
| O atom in Asp54 with O4 atom in L2 | 2.97 | |
| Sanggenone H (L3) | O atom in Asp54 with O4 atom in L3 | 3.19 |
| Kuwanol C (L4) | O atom in Leu6 with O5 atom in L4 | 2.70 |
| O atom in Asp54 with O5 atom in L4 | 2.48 | |
| O atom in Tyr71 with O4 atom in L4 | 2.70 |
| Interactions | BI-2852 | L1 | L2 | L3 | L4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Electrostatic | |||||
| Charge | Asp54 | - | - | - | - |
| Hydrophobic | |||||
| Alkyl | - | Met67 | Met67 | Leu56 | Met67 |
| Mixed Pi-Alkyl | Leu56 | Lys5, Leu56 | Lys5, Leu56 | Lys5, Leu56 | Lys5, Leu56 |
| Flavonoid | Time Taken to Dissociate the Ligand (ps) |
|---|---|
| BI-2852 (reference) | 51.162 |
| L1 | 32.067 |
| L2 | 41.805 |
| L3 | 89.435 |
| L4 | 44.557 |
| Flavonoids/Compounds | Pa | Pi | Cell Line | Type | Region |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BI-2852 | 0.356 | 0.218 | DMS-114 | Lung carcinoma | Lung |
| 0.326 | 0.041 | SW-620 | Colon adenocarcinoma | Colon | |
| L1 | 0.457 | 0.029 | NCI-H187 | Small-cell lung carcinoma | Lung |
| 0.421 | 0.024 | HOP-18 | Non-small-cell lung carcinoma | Lung | |
| 0.365 | 0.053 | PC-6 | Small-cell lung carcinoma | Lung | |
| L2 | 0.430 | 0.022 | HOP-18 | Non-small-cell lung carcinoma | Lung |
| 0.395 | 0.075 | NCI-H187 | Small-cell lung carcinoma | Lung | |
| L3 | 0.476 | 0.020 | NCI-H187 | Small-cell lung carcinoma | Lung |
| 0.459 | 0.017 | HOP-18 | Non-small-cell lung carcinoma | Lung | |
| L4 | 0.604 | 0.004 | HOP-18 | Non-small-cell lung carcinoma | Lung |
| 0.470 | 0.023 | NCI-H187 | Small-cell lung carcinoma | Lung | |
| 0.369 | 0.056 | NCI-H322M | Non-small-cell lung carcinoma | Lung | |
| 0.360 | 0.042 | NCI-H522 | Non-small-cell lung carcinoma | Lung | |
| 0.314 | 0.077 | NCI-H226 | Non-small-cell lung carcinoma | Lung |
| Toxicity | BI-2852 | L1 | L2 | L3 | L4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| H-HT | 0.846 | 0.847 | 0.372 | 0.275 | 0.851 |
| DILI | 0.953 | 0.484 | 0.941 | 0.905 | 0.806 |
| AMES | 0.256 | 0.409 | 0.195 | 0.108 | 0.086 |
| ROAT | 0.75 | 0.189 | 0.193 | 0.883 | 0.749 |
| FDAMMD | 0.978 | 0.671 | 0.848 | 0.907 | 0.905 |
| NR-AR | 0.016 | 0.041 | 0.005 | 0.005 | 0.006 |
| NR-ER | 0.215 | 0.804 | 0.938 | 0.625 | 0.666 |
| NR-PPAR-γ | 0.13 | 0.807 | 0.984 | 0.974 | 0.972 |
| SR-ARE | 0.73 | 0.915 | 0.939 | 0.941 | 0.951 |
| Carcinogenicity | 0.088 | 0.875 | 0.79 | 0.71 | 0.76 |
| Toxicophores | 4 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Golden Triangle | Rejected | Accepted | Accepted | Accepted | Accepted |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ramalingam, P.S.; Balakrishnan, P.; Rajendran, S.; Jothi, A.; Ramalingam, R.; Arumugam, S. Identification of Dietary Bioflavonoids as Potential Inhibitors against KRAS G12D Mutant—Novel Insights from Computer-Aided Drug Discovery. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2023, 45, 2136-2156. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb45030137
Ramalingam PS, Balakrishnan P, Rajendran S, Jothi A, Ramalingam R, Arumugam S. Identification of Dietary Bioflavonoids as Potential Inhibitors against KRAS G12D Mutant—Novel Insights from Computer-Aided Drug Discovery. Current Issues in Molecular Biology. 2023; 45(3):2136-2156. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb45030137
Chicago/Turabian StyleRamalingam, Prasanna Srinivasan, Purushothaman Balakrishnan, Senthilnathan Rajendran, Arunachalam Jothi, Rajasekaran Ramalingam, and Sivakumar Arumugam. 2023. "Identification of Dietary Bioflavonoids as Potential Inhibitors against KRAS G12D Mutant—Novel Insights from Computer-Aided Drug Discovery" Current Issues in Molecular Biology 45, no. 3: 2136-2156. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb45030137
APA StyleRamalingam, P. S., Balakrishnan, P., Rajendran, S., Jothi, A., Ramalingam, R., & Arumugam, S. (2023). Identification of Dietary Bioflavonoids as Potential Inhibitors against KRAS G12D Mutant—Novel Insights from Computer-Aided Drug Discovery. Current Issues in Molecular Biology, 45(3), 2136-2156. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb45030137