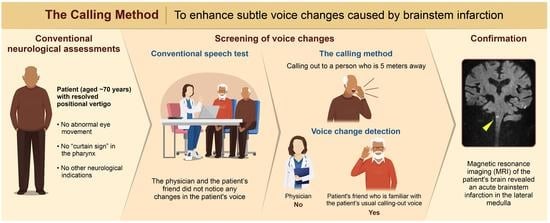
A New Neurological Screening Approach for Diagnosing Brainstem Infarction Using the Calling Method and Familiar Voices
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Case Presentation
3. The “Calling Method” and Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Saleh Velez, F.G.; Alvarado-Dyer, R.; Pinto, C.B.; Ortiz García, J.G.; Mchugh, D.; Lu, J.; Otlivanchik, O.; Flusty, B.L.; Liberman, A.L.; Prabhakaran, S. Safer Stroke-Dx Instrument: Identifying stroke misdiagnosis in the emergency department. Circ. Cardiovasc. Qual. Outcomes 2021, 14, e007758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Q.; Tong, X.; Schieb, L.; Vaughan, A.; Gillespie, C.; Wiltz, J.L.; King, S.C.; Odom, E.; Merritt, R.; Hong, Y.; et al. Vital signs: Recent trends in stroke death rates—United States, 2000–2015. MMWR Morb. Mortal. Wkly Rep. 2017, 66, 933–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Singh, H.; Giardina, T.D.; Meyer, A.N.D.; Forjuoh, S.N.; Reis, M.D.; Thomas, E.J. Types and origins of diagnostic errors in primary care settings. JAMA Intern. Med. 2013, 173, 418–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liberman, A.L.; Skillings, J.; Greenberg, P.; Newman-Toker, D.E.; Siegal, D. Breakdowns in the initial patient-provider encounter are a frequent source of diagnostic error among ischemic stroke cases included in a large medical malpractice claims database. Diagnosis 2020, 7, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gowda, S.N.; De Jesus, O. Brainstem Infarction; StatPearls Publishing: Petersburg, FL, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Ortiz de Mendivil, A.; Alcala-Galiano, A.; Ochoa, M.; Salvador, E.; Milian, J.M. Brainstem Stroke: Anatomy, Clinical and Radiological Findings. Smin. Ultrasound CT MR 2013, 34, 131–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burger, K.M.; Tuhrim, S.; Naidich, T.P. Brainstem vascular stroke anatomy. Neuroimaging Clin. N. Am. 2005, 15, 297–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nogueira, R.G.; Jadhav, A.P.; Haussen, D.C.; Bonafe, A.; Budzik, R.F.; Bhuva, P.; Yavagal, D.R.; Ribo, M.; Cognard, C.; Hanel, R.A.; et al. Thrombectomy 6 to 24 hours after stroke with a mismatch between deficit and infarct. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fanning, J.P.; Wesley, A.J.; Wong, A.A.; Fraser, J.F. Emerging spectra of silent brain infarction. Stroke 2014, 45, 3461–3471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Enderby, P.; Crow, E. Frenchay Aphasia Screening Test: Validity and comparability. Disabil. Rehabil. 1996, 18, 238–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azuar, C.; Leger, A.; Arbizu, C.; Henry-Amar, F.; Chomel-Guillaume, S.; Samson, Y. The aphasia rapid test: An NIHSS-like aphasia test. J. Neurol. 2013, 260, 2110–2117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Flamand-Roze, C.; Falissard, B.; Roze, E.; Maintigneux, L.; Beziz, J.; Chacon, A.; Join-Lambert, C.; Adams, D.; Denier, C. Validation of a new language screening tool for patients with acute stroke: The Language screening test (LAST). Stroke 2011, 42, 1224–1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Arch, A.E.; Weisman, D.C.; Coca, S.; Nystrom, K.V.; Wira, C.R., 3rd; Schindler, J.L. Missed ischemic stroke diagnosis in the emergency department by emergency medicine and neurology services. Stroke 2016, 47, 668–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hurford, R.; Sekhar, A.; Hughes, T.A.T.; Muir, K.W. Diagnosis and management of acute ischaemic stroke. Pract. Neurol. 2020, 20, 304–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, D.; Smith, M. The intensive care management of acute ischaemic stroke. Curr. Opin. Crit. Care 2022, 28, 157–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Cock, E.; Batens, K.; Hemelsoet, D.; Boon, P.; Oostra, K.; De Herdt, V. Dysphagia, dysarthria and aphasia following a first acute ischaemic stroke: Incidence and associated factors. Eur. J. Neurol. 2020, 27, 2014–2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuruvilla, A.; Bhattacharya, P.; Rajamani, K.; Chaturvedi, S. Factors associated with misdiagnosis of acute stroke in young adults. J. Stroke Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2011, 20, 523–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joshy, A.A.; Rajan, R. Automated dysarthria severity classification: A study on acoustic features and deep learning techniques. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2022, 30, 1147–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, J.; Lee, J.H.; Choi, J.; Suh, M.K.; Chung, M.J.; Kim, Y.H.; Park, J.; Choo, S.H.; Son, J.H.; Lee, D.Y.; et al. Detection and differentiation of ataxic and hypokinetic dysarthria in cerebellar ataxia and parkinsonian disorders via wave splitting and integrating neural networks. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0268337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brady, M.C.; Clark, A.M.; Dickson, S.; Paton, G.; Barbour, R.S. The impact of stroke-related dysarthria on social participation and implications for rehabilitation. Disabil. Rehabil. 2011, 33, 178–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calic, Z.; Cappelen-Smith, C.; Anderson, C.S.; Xuan, W.; Cordato, D.J. Cerebellar infarction and factors associated with delayed presentation and misdiagnosis. Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2016, 42, 476–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ohshiro, Y. A New Neurological Screening Approach for Diagnosing Brainstem Infarction Using the Calling Method and Familiar Voices. Medicina 2023, 59, 1344. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina59071344
Ohshiro Y. A New Neurological Screening Approach for Diagnosing Brainstem Infarction Using the Calling Method and Familiar Voices. Medicina. 2023; 59(7):1344. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina59071344
Chicago/Turabian StyleOhshiro, Yuzuru. 2023. "A New Neurological Screening Approach for Diagnosing Brainstem Infarction Using the Calling Method and Familiar Voices" Medicina 59, no. 7: 1344. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina59071344
APA StyleOhshiro, Y. (2023). A New Neurological Screening Approach for Diagnosing Brainstem Infarction Using the Calling Method and Familiar Voices. Medicina, 59(7), 1344. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina59071344