Antibacterial Bisabolane-Type Sesquiterpenoids from the Sponge-Derived Fungus Aspergillus sp.
Abstract
:1. Introduction
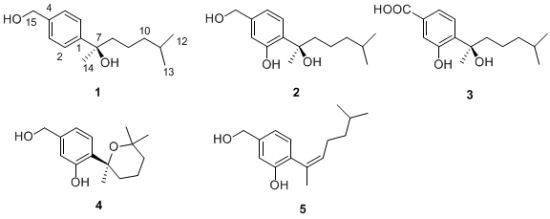
2. Results and Discussion
| Position | δC, mult | δH (J in Hz) |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 147.8, C | – |
| 2 | 125.1, CH | 7.43, dd (8.4, 1.8) |
| 3 | 127.0, CH | 7.34, dd (8.4, 1.8) |
| 4 | 139.1, C | – |
| 5 | 127.0, CH | 7.34, dd (8.4, 1.8) |
| 6 | 125.1, CH | 7.43, dd (8.4, 1.8) |
| 7 | 74.8, C | – |
| 8 | 44.4, CH2 | 1.77, m |
| 9 | 21.8, CH2 | 1.26, m; 1.12, overlapped |
| 10 | 39.3, CH2 | 1.12, overlapped |
| 11 | 27.9, CH | 1.47, m |
| 12 | 22.6, CH3 | 0.81, d (6.6) |
| 13 | 22.7, CH3 | 0.81,d (6.6) |
| 14 | 30.3, CH3 | 1.55, s |
| 15 | 65.2, CH2 | 4.69, d (3.0) |
| 7–OH | 1.71, s | |
| 15–OH | 1.66, brs |

| Strains | Compounds | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | Ciprofloxacin | |
| Staphylococcus albus | >20.0 | 5.00 | >20.0 | 5.00 | 20.0 | 0.312 |
| Bacillus subtilis | >20.0 | >20.0 | 2.50 | 2.50 | 10.0 | 1.25 |
| Bacillus cereus | >20.0 | >20.0 | >20.0 | >20.0 | 10.0 | 0.625 |
| Sarcina lutea | >20.0 | >20.0 | 2.50 | >20.0 | >20.0 | 2.50 |
| Escherichia coli | 20.0 | 20.0 | 5.00 | >20.0 | 10.0 | 0.625 |
| Micrococcus tetragenus | 10.0 | 1.25 | 20.0 | >20.0 | 10.0 | 0.312 |
| Vibrio Parahaemolyticus | >20.0 | >20.0 | 10.0 | >20.0 | >20.0 | 0.160 |
| Vibrio anguillarum | >20.0 | >20.0 | 5.00 | >20.0 | >20.0 | 0.160 |
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. General Experimental Procedures
3.2. Fungal Material
3.3. Identification of Fungus
3.4. Extraction and Isolation
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgements
- Samples Availability: Available from the authors.
Supplementary Files
References
- D’Armas, H.T.; Mootoo, B.S.; Reynolds, W.F. An unusual sesquiterpene derivative from the caribbean gorgonian Pseudopterogorgia rigida. J. Nat. Prod. 2000, 63, 1593–1595. [Google Scholar]
- Sugahara, T.; Ogasawara, K. A new stereocontrolled route to (+)-curcuphenol, a phenolic sesquiterpene from the marine sponge Didiscus flavus. Tetrahedron 1998, 9, 2215–2217. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, J.N.; Franzblau, S.G.; Zhang, F.Q.; Hamann, M.T. Novel sesquiterpenes and a lactone from the Jamaican sponge Myrmekioderma styx. Tetrahedron Lett. 2002, 43, 9699–9702. [Google Scholar]
- Celso, A.; Somaia, E.; Stefan, K.; Koenig, G.M. Novel bisabolane sesquiterpenes from the marine-derived fungus Verticillium tenerum. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2010, 5, 507–510. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, M.Y.; Wang, C.Y.; Liu, Q.A.; Shao, C.L.; She, Z.G.; Lin, Y.C. Five sesquiterpenoids from a marine-derived fungus Aspergillus sp. isolated from a gorgonian Dichotella gemmacea. Mar. Drugs 2010, 8, 941–949. [Google Scholar]
- Trisuwan, K.; Rukachaisikikul, V.; Kaewpet, M.; Phongpaichit, S.; Hutadilok-Towatana, N.; Preedanon, S.; Sakayaroj, J. Sesquiterpene and xanthone derivatives from the sea fan-derived fungus Aspergillus sydowii PSU-F154. J. Nat. Prod. 2011, 74, 1663–1667. [Google Scholar]
- Fujiwara, M.; Yagi, N.; Miyazawa, M. Acetylcholinesterase inhibitory activity of volatile oil from Peltophorum dasyrachis Kurz ex Bakar (yellow batai) and bisabolane-type sesquiterpenoids. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2010, 58, 2824–2829. [Google Scholar]
- Takamatsu, S.; Hodges, T.W.; Rajbhandari, I.; Gerwick, W.H.; Hamann, M.T.; Nagle, D.G. Marine natural products as novel antioxidant prototypes. J. Nat. Prod. 2003, 66, 605–608. [Google Scholar]
- Huo, J.; Yang, S.P.; Xie, B.J.; Liao, S.G.; Lin, L.P.; Ding, J.; Yue, J.M. Cytotoxic sesquiterpenoids from Vernonia bockiana. J. Asian Nat. Prod. Res. 2008, 10, 571–575. [Google Scholar]
- Mcenroe, F.J.; Fenical, W. Structures and synthesis of some new antibacterial sesquiterpenoids from the gorgonian coral Pseudopterogorgia rigida. Tetrahedron 1978, 34, 1661–1164. [Google Scholar]
- Shao, C.L.; Wang, C.Y.; Gu, Y.C.; Wei, M.Y.; Pan, J.H.; Deng, D.S.; She, Z.G.; Lin, Y.C. Penicinoline, a new pyrrolyl 4-quinolinone alkaloid with an unprecedented ring system from an endophytic fungus Penicillium sp. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2010, 20, 3284–3286. [Google Scholar]
- Shao, C.L.; Wang, C.Y.; Wei, M.Y.; Gu, Y.C.; She, Z.G.; Qian, P.Y.; Lin, Y.C. Aspergilones A and B, two benzylazaphilones with an unprecedented carbon skeleton from the gorgonian-derived fungus Aspergillus sp. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2011, 21, 690–693. [Google Scholar]
- Shao, C.L.; Wu, H.X.; Wang, C.Y.; Liu, Q.A.; Xu, Y.; Wei, M.Y.; Qian, P.Y.; Gu, Y.C.; Zheng, C.J.; She, Z.G.; et al. Potent antifouling resorcylic acid lactones from the gorgonian-derived fungus Cochliobolus lunatus. J. Nat. Prod. 2011, 74, 629–633. [Google Scholar]
- Sumarah, M.W.; Kesting, J.R.; Sørensen, D.; Miller, J.D. Antifungal metabolites from fungal endophytes of Pinus strobus. Phytochemistry 2011, 72, 1833–1837. [Google Scholar]
- Nukina, M.; Sato, Y.; Ikeda, M.; Sassa, T. Sydonol, a new fungal morphogenic substance produced by an unidentified Aspergillus sp. Agric. Biol. Chem. 1981, 45, 789–790. [Google Scholar]
- Hamasaki, T.; Nagayama, K.; Hatsuda, Y. Two new metabolites, sydonic acid and hydroxysydonic acid, from Aspergillus sydowi. Agric. Biol. Chem. 1978, 42, 37–40. [Google Scholar]
- Kudo, S.; Murakami, T.; Miyanishi, J.; Tanaka, K.; Takada, N.; Hashimoto, M. Isolation and absolute stereochemistry of optically active sydonic acid from Glonium sp., (Hysteriales, Ascomycota). Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2009, 73, 203–204. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Serra, S. Bisabolane sesquiterpenes: Synthesis of (R)-(+)-sydowic acid and (R)-(+)-curcumene ether. Syn. Lett. 2000, 6, 890–892. [Google Scholar]
- Pierce, C.G.; Uppuluri, P.; Teistan, A.R.; Wormley, F.L., Jr.; Mowat, E.; Ramage, G.; Lopez-ribot, J.L. A simple and reproducible 96-well plate-based method for the formation of fungal biofilms and its application to antifungal susceptibility testing. Nat. Protoc. 2008, 3, 1494–1500. [Google Scholar]
- Qi, S.H.; Zhang, S.; Qian, P.Y.; Xiao, Z.H.; Li, M.Y. Ten new antifouling briarane diterpenoids from the South China Sea gorgonian Junceella juncea. Tetrahedron 2006, 62, 9123–9130. [Google Scholar]
© 2012 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland This article is an open-access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, D.; Xu, Y.; Shao, C.-L.; Yang, R.-Y.; Zheng, C.-J.; Chen, Y.-Y.; Fu, X.-M.; Qian, P.-Y.; She, Z.-G.; Voogd, N.J.d.; et al. Antibacterial Bisabolane-Type Sesquiterpenoids from the Sponge-Derived Fungus Aspergillus sp. Mar. Drugs 2012, 10, 234-241. https://doi.org/10.3390/md10010234
Li D, Xu Y, Shao C-L, Yang R-Y, Zheng C-J, Chen Y-Y, Fu X-M, Qian P-Y, She Z-G, Voogd NJd, et al. Antibacterial Bisabolane-Type Sesquiterpenoids from the Sponge-Derived Fungus Aspergillus sp. Marine Drugs. 2012; 10(1):234-241. https://doi.org/10.3390/md10010234
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Dan, Ying Xu, Chang-Lun Shao, Rui-Yun Yang, Cai-Juan Zheng, Yi-Yan Chen, Xiu-Mei Fu, Pei-Yuan Qian, Zhi-Gang She, Nicole J. de Voogd, and et al. 2012. "Antibacterial Bisabolane-Type Sesquiterpenoids from the Sponge-Derived Fungus Aspergillus sp." Marine Drugs 10, no. 1: 234-241. https://doi.org/10.3390/md10010234
APA StyleLi, D., Xu, Y., Shao, C. -L., Yang, R. -Y., Zheng, C. -J., Chen, Y. -Y., Fu, X. -M., Qian, P. -Y., She, Z. -G., Voogd, N. J. d., & Wang, C. -Y. (2012). Antibacterial Bisabolane-Type Sesquiterpenoids from the Sponge-Derived Fungus Aspergillus sp. Marine Drugs, 10(1), 234-241. https://doi.org/10.3390/md10010234