Paralytic Toxins Accumulation and Tissue Expression of α-Amylase and Lipase Genes in the Pacific Oyster Crassostrea gigas Fed with the Neurotoxic Dinoflagellate Alexandrium catenella
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Feeding Activity Parameters
Clearance Rate and Cell Filtration


2.2. Composition of Fecal Ribbons

2.3. Toxin Profile and Concentration in the Algae and Fed Oysters

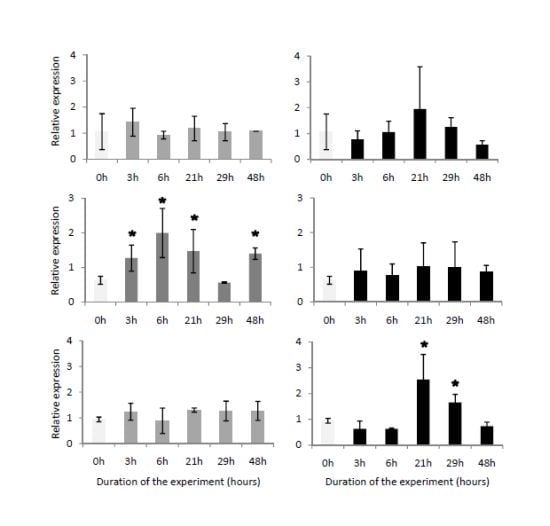
2.4. Temporal Expression of the Three Genes Related to Digestive Processes

3. Experimental Section
3.1. Biological Material
3.1.1. Oysters
3.1.2. Microalgae
3.2. Feeding Experiments
3.3. Measurement of the Feeding Parameters
3.3.1. Clearance Rate
3.3.2. Cell Filtration
3.4. Fecal Material Examination
3.5. Tissue Sampling
3.6. Chemical Analysis by Liquid Chromatography/Fluorescence Detection (LC/FD)
3.7. Semi-Quantitative Analyses of the Transcription of Digestive-Related Genes
| Gene | Primers sequences 5′→3′ | Tm | Product size (bp) | Genbank ID |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| α-Amylase A | CAACGGGGACATGAGCATT | 62 | 116 | AF320688 |
| CGTTACGGAAGGCAACCA | ||||
| α-Amylase B | CGCGTCACGGACTTCATT | 62 | 115 | AF321515 |
| CAGCGTCATTGGAGTTAGGC | ||||
| Triacylglycerol lipase precursor | TCAAGGCCTGTGATTCTACC | 60 | 96 | CB617387 |
| CTCGGACGTCCATATCATCG | ||||
| Ribosomal protein F40 (RPL40) | AATCTTGCACCGTCATGCAG | 60 | 149 | FP004478 |
| AATCAATCTCTGCTGATCTGG |
3.8. Statistics
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
References
- Zingone, A.; Enevoldsen, H.O. The diversity of harmful algal blooms: A challenge for science and management. Ocean Coast. Manag. 2000, 43, 725–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masselin, P.; Amzil, Z.; Abadie, E.; Nézan, E.; Le Bec, C.; Chiantella, C.; Truquet, P. Paralytic Shellfish Poisoning on the French Mediterranean Coast in the Autumn 1988: Alexandrium tamarense Complex (Dinophycea) as Causative Agent. In Proceeding of the Ninth International Conference on Harmful Algae Blooms, Hobart, Australia, 7–11 February 2000; Hallegraeff, G.M., Blackburn, S.I., Bolch, C.J., Lewis, R.J, Eds.; JOC of UNESCO: Paris, France, 2001; pp. 407–410. [Google Scholar]
- Shumway, S.E. A review of the effects of algal blooms on shellfish and aquaculture. J. World Aquacul. Soc. 1990, 21, 65–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, D.; Haberkorn, H.; Soudant, P.; Ciret, P.; Massabuau, J.C. Behavioral responses of Crassostrea gigas exposed to the harmful algae Alexandrium minutum. Aquaculture 2010, 298, 338–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bardouil, M.; Bohec, M.; Bougrier, S.; Lassus, P.; Truquet, P. Feeding responses of Crassostrea gigas (Thunberg) to inclusion of different proportions of toxic dinoflagellates in their diet. Oceanol. Acta 1996, 19, 177–182. [Google Scholar]
- Laabir, M.; Gentien, P. Survival of toxic dinoflagellates after gut passage in the Pacific oyster Crassostrea gigas Thunburg. J. Shellfish. Res. 1999, 18, 217–222. [Google Scholar]
- Laabir, M.; Amzil, Z.; Lassus, P.; Masseret, E.; Tapilatu, Y.; De Vargas, R.; Grzebyk, D. Viability, growth and toxicity of Alexandrium catenella and Alexandrium minutum (Dinophyceae) following ingestion and gut passage in the oyster Crassostrea gigas. Aquat. Living Resour. 2007, 20, 51–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gueguen, M.; Bardouil, M.; Baron, R.; Lassus, P.; Truquet, P.; Massardier, J.; Amzil, Z. Detoxification of Pacific oyster Crassostrea gigas fed on diets of Skeletonema costatum with and without silt, following PSP contamination by Alexandrium minutum. Aquat. Living Resour. 2008, 21, 13–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibarrola, I.; Larretxea, X.; Iglesias, J.I.P.; Urrutia, M.B.; Navarro, E. Seasonal variation of digestive enzyme activities in the digestive gland and the crystalline style of the common cockle Cerastoderma edule. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part A 1998, 121, 25–34. [Google Scholar]
- Ibarrola, I.; Navarro, E.; Iglesias, J.I.P. Short-term adaptation of digestive processes in the cockle Cerastoderma edule exposed to different food quantity and quality. J. Comp. Physiol. Part B 1998, 168, 32–40. [Google Scholar]
- Huvet, A.; Daniel, J.Y.; Quere, C.; Dubois, S.; Prudence, M.; van Wormhoudt, A.; Sellos, D.; Samain, J.F.; Moal, J. Tissue expression of two alpha-amylase genes in the Pacific oyster Crassostrea gigas. Effects of two different food rations. Aquaculture 2003, 228, 321–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sellos, D.; Moal, J.; Degremont, L.; Huvet, A.; Daniel, J.Y.; Nicoulaud, S.; Boudry, P.; van Wormhoudt, A.; Samain, J.F. Structure of the amylase genes in populations of the Pacific cupped oyster Crassostrea gigas: Tissue expression and allelic polymorphism. Mar. Biotechnol. 2003, 5, 360–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huvet, A.; Jeffroy, F.; Fabioux, C.; Daniel, J.Y.; Quillien, V.; Wormhoudt, A.; Moal, J.; Samain, J.F.; Boudry, P.; Pouvreau, S. Association among growth, food consumption-related traits and amylase gene polymorphism in the Pacific oyster Crassostrea gigas. Anim. Genet. 2008, 39, 662–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moal, J.; Daniel, J.Y.; Sellos, D.; Van Wormhoudt, A.; Samain, J.F. Amylase mRNA expression in Crassostrea gigas during feeding cycles. J. Comp. Physiol. Part B 2000, 170, 21–26. [Google Scholar]
- Boutet, I.; Tanguy, A.; Moraga, D. Response of the Pacific oyster Crassostrea gigas to hydrocarbon contamination under experimental conditions. Gene 2004, 329, 147–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bardouil, M.; Bohec, M.; Cormerais, M.; Bougrier, S.; Lassus, P. Experimental study of the effects of a toxic microalgal diet on feeding of the oyster Crassostrea gigas Thunberg. J. Shellfish. Res. 1993, 12, 417–422. [Google Scholar]
- Lassus, P.; Wildish, D.J.; Bardouil, M.; Martin, J.L.; Bohec, M.; Bougrier, S. Ecophysiological study of toxic Alexandrium spp. Effects on the oyster Crassostrea gigas. In Harmful and Toxic Algal Blooms; Yasumoto, T., Oshima, Y., Fukuyo, Y., Eds.; IOC of UNESCO: Paris, France, 1996; pp. 409–412. [Google Scholar]
- Genovesi, B.; Shin-Grzebyk, M.S.; Grzebyk, D.; Laabir, M.; Gagnaire, P.A.; Vaquer, A.; Pastoureaud, A.; Lasserre, B.; Collos, Y.; Berrebi, P.; et al. Assessment of cryptic species diversity within blooms and cyst bank of the Alexandrium tamarense complex (Dinophyceae) in a Mediterranean lagoon facilitated by semi-multiplex PCR. J. Plankton Res. 2011, 33, 405–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lassus, P.; Amzil, Z.; Baron, R.; Sechet, V.; Barille, L.; Abadie, E.; Bardouil, M.; Sibat, M.; Truquet, P.; Berard, J.B.; et al. Modelling the accumulation of PSP toxins in Thau Lagoon oysters (Crassostrea gigas) from trials using mixed cultures of Alexandrium catenella and Thalassiosira weissflogii. Aquat. Living Resour. 2007, 20, 59–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vila, M.; Garces, E.; Maso, M.; Camp, J. Is the distribution of the toxic dinoflagellate Alexandrium catenella expanding along the NW Mediterranean coast. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2001, 222, 73–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asakawa, M.; Beppu, R.; Tsubota, M.; Ito, K.; Takayama, H.; Miyazawa, K. Paralytic shellfish poison (PSP) profiles and toxification of short-necked clams fed with the toxic dinoflagellate Alexandrium tamarense. J. Food. Hygienic. Soc. Jpn. 2005, 46, 251–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bougrier, S.; Lassus, P.; Bardouil, M.; Masselin, P.; Truquet, P. Paralytic shellfish poison accumulation yields and feeding time activity in the Pacific oyster (Crassostrea gigas) and king scallop (Pecten maximus). Aquat. Living. Resour. 2003, 16, 347–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oshima, Y. Chemical and enzymatic transformation of paralytic shellfish toxins in marine organisms. In Harmful Marine Algal Blooms; Lassus, P., Arzul, G., Erard, E., Gentien, P., Marcaillou, C., Eds.; Lavoisier/Intercept: Paris, France, 1995; pp. 475–480. [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki, T.; Ichimi, K.; Oshima, Y.; Kamiyama, T. Paralytic shellfish poisoning (PSP) toxin profiles and short-term detoxification kinetics in mussels Mytilus galloprovincialis fed with the toxic dinoflagellate Alexandrium tamarense. Harmful Algae 2003, 2, 201–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cembella, A.D.; Shumway, S.E.; Larocque, R. Sequestering and putative biotransformation of paralytic shellfish toxins by the sea scallop Placopecten magellanicus: Seasonal and special scales in natural populations. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 1994, 180, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanco, J.; Reyero, M.I.; Franco, J. Kinetics of accumulation and transformation of paralytic shellfish toxins in the blue mussel Mytilus galloprovincialis. Toxicon 2003, 42, 777–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, A.M.Y.; Yu, P.K.N.; Hsieh, D.P.H.; Wang, W.X.; Wu, R.S.S.; Lam, P.K.S. Uptake and depuration of paralytic shellfish toxins in the green lipped mussel, Perna viridis: A dynamic model. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2005, 24, 129–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurr, M.; Harwood, J.; Frayn, K. Lipid Biochemistry: An Introduction; John Wiley & Sons: Chichester, UK, 2008; ISBN 1405172703, 9781405172707. [Google Scholar]
- Labbir, M. University of Montpellier II, Montpellier, France. 2007; Unpublished work. [Google Scholar]
- Harrison, P.J.; Waters, R.E.; Taylor, F.J.R. A Broad-spectrum artificial seawater medium for coastal and open ocean phytoplankton. J. Phycol. 1980, 16, 28–35. [Google Scholar]
- Laabir, M.; Jauzein, C.; Genovesi, B.; Masseret, E.; Grzebyk, D.; Cecchi, P.; Vaquer, A.; Perrin, Y.; Colos, Y. Influence of temperature, salinity and irradiance on the growth and cell yield of the harmful red tide dinoflagellate Alexandrium catenella colonizing Mediterranean waters. J. Plankton Res. 2011, 33, 1550–1563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coughlan, J. The estimation of filtering rate from the clearance of suspensions. Mar. Biol. 1969, 2, 356–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oshima, Y. Post-column derivatization HPLC methods for paralytic shellfish poisons. In Manual on Harmful Marine Microalgae; United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization: Paris, France, 1995; pp. 81–94. [Google Scholar]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samples Availability: Available from the authors.
© 2012 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open-access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Rolland, J.-L.; Pelletier, K.; Masseret, E.; Rieuvilleneuve, F.; Savar, V.; Santini, A.; Amzil, Z.; Laabir, M. Paralytic Toxins Accumulation and Tissue Expression of α-Amylase and Lipase Genes in the Pacific Oyster Crassostrea gigas Fed with the Neurotoxic Dinoflagellate Alexandrium catenella. Mar. Drugs 2012, 10, 2519-2534. https://doi.org/10.3390/md10112519
Rolland J-L, Pelletier K, Masseret E, Rieuvilleneuve F, Savar V, Santini A, Amzil Z, Laabir M. Paralytic Toxins Accumulation and Tissue Expression of α-Amylase and Lipase Genes in the Pacific Oyster Crassostrea gigas Fed with the Neurotoxic Dinoflagellate Alexandrium catenella. Marine Drugs. 2012; 10(11):2519-2534. https://doi.org/10.3390/md10112519
Chicago/Turabian StyleRolland, Jean-Luc, Kevin Pelletier, Estelle Masseret, Fabien Rieuvilleneuve, Veronique Savar, Adrien Santini, Zouher Amzil, and Mohamed Laabir. 2012. "Paralytic Toxins Accumulation and Tissue Expression of α-Amylase and Lipase Genes in the Pacific Oyster Crassostrea gigas Fed with the Neurotoxic Dinoflagellate Alexandrium catenella" Marine Drugs 10, no. 11: 2519-2534. https://doi.org/10.3390/md10112519
APA StyleRolland, J. -L., Pelletier, K., Masseret, E., Rieuvilleneuve, F., Savar, V., Santini, A., Amzil, Z., & Laabir, M. (2012). Paralytic Toxins Accumulation and Tissue Expression of α-Amylase and Lipase Genes in the Pacific Oyster Crassostrea gigas Fed with the Neurotoxic Dinoflagellate Alexandrium catenella. Marine Drugs, 10(11), 2519-2534. https://doi.org/10.3390/md10112519