Lipid Peroxidation Is another Potential Mechanism besides Pore-Formation Underlying Hemolysis of Tentacle Extract from the Jellyfish Cyanea capillata
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
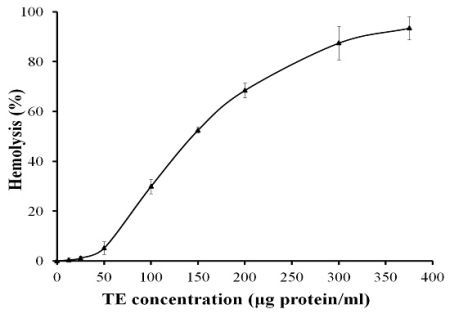
2.1. Hemolytic Activity

2.2. Effects of Ca2+ and Ca2+ Channel Blockers on the Hemolysis of TE


2.3. Changes of Ca2+ in Erythrocytes

2.4. Effect of Osmotic Protectants


2.5. Effects of Antioxidants on the Hemolysis of TE in Vitro
2.6. Lipid Peroxidation

2.7. Effect of Vc on the Hemolysis of TE in Vivo

| Na+ (mM) | K+ (mM) | Ca2+ (mM) | Cl− (mM) | Lac (mM) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | 139.8 ± 1.33 | 7.23 ± 0.44 | 2.34 ± 0.08 | 99.8 ± 1.70 | 3.18 ± 0.40 |
| TE (1.25 mg/kg) | 137.5 ± 1.05 Δ | 10.65 ± 1.31 Δ | 2.20 ± 0.05 Δ | 94.7 ± 0.82 Δ | 8.02 ± 0.43 Δ |
| Vc (250 mg/kg) + TE (1.25 mg/kg) | 136.0 ± 1.10 Δ | 8.42 ± 0.72 Δ▲ | 2.26 ± 0.04 Δ | 93.7 ± 0.52 Δ | 4.98 ± 0.85 Δ▲ |
3. Discussion
4. Experimental Section
4.1. TE Preparation from the Jellyfish C. capillata
4.2. Hemolytic Activity Assay
4.3. Effects of Ca2+ and Ca2+ Channel Blockers on the Hemolysis of TE
4.4. Measurement of Cytosolic Free Ca2+ Using CLSM
4.5. Osmotic Protection Assay
4.6. Effects of Antioxidants on the Hemolysis of TE in Vitro
4.7. Measurement of Malondialdehyde
4.8. Effect of Vc on the Hemolysis of TE in Vivo
4.9. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
References
- Helmholz, H.; Ruhnau, C.; Schutt, C.; Prange, A. Comparative study on the cell toxicity and enzymatic activity of two northern scyphozoan species Cyanea capillata (L.) and Cyanea lamarckii (Peron & Leslieur). Toxicon 2007, 50, 53–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brinkman, D.L.; Burnell, J.N. Biochemical and molecular characterisation of cubozoan protein toxins. Toxicon 2009, 54, 1162–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suput, D. In vivo effects of cnidarian toxins and venoms. Toxicon 2009, 54, 1190–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagai, H.; Takuwa, K.; Nakao, M.; Ito, E.; Miyake, M.; Noda, M.; Nakajima, T. Novel proteinaceous toxins from the box jellyfish (sea wasp) Carybdea rastoni. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2000, 275, 582–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagai, H.; Takuwa, K.; Nakao, M.; Sakamoto, B.; Crow, G.L.; Nakajima, T. Isolation and characterization of a novel protein toxin from the Hawaiian box jellyfish (sea wasp) Carybdea alata. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2000, 275, 589–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagai, H.; Takuwa-Kuroda, K.; Nakao, M.; Oshiro, N.; Iwanaga, S.; Nakajima, T. A novel protein toxin from the deadly box jellyfish (sea wasp, Habu-kurage) Chiropsalmus quadrigatus. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2002, 66, 97–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brinkman, D.; Burnell, J. Identification, cloning and sequencing of two major venom proteins from the box jellyfish, Chironex fleckeri. Toxicon 2007, 50, 850–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lassen, S.; Helmholz, H.; Ruhnau, C.; Prange, A. A novel proteinaceous cytotoxin from the northern Scyphozoa Cyanea capillata (L.) with structural homology to cubozoan hemolysins. Toxicon 2011, 57, 721–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, C.L.; Gao, J.D.; Ren, Y.K.; Xiao, L.; Wang, Q.Q.; Guo, Y.F.; Cai, B.X.; Zhang, L.M. Bioinformatic analysis on jellyfish hematoxin. Chin. J. Nat. Med. 2009, 7, 145–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marino, A.; Morabito, R.; Pizzata, T.; La Spada, G. Effect of various factors on Pelagia noctiluca (Cnidaria, Scyphozoa) crude venom-induced hemolysis. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part A 2008, 151, 144–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Xiao, L.; He, Q.; Liu, S.; Zhang, J.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Nie, F.; Guo, Y.; Zhang, L. Comparison of hemolytic activity of tentacle-only extract from jellyfish Cyanea capillata in diluted whole blood and erythrocyte suspension: Diluted whole blood is a valid test system for haemolysis study. Exp. Toxicol. Pathol. 2012, 64, 831–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwards, L.; Luo, E.; Hall, R.; Gonzalez, R.R., Jr.; Hessinger, D.A. The effect of Portuguese Man-of-war (Physalia physalis) venom on calcium, sodium and potassium fluxes of cultured embryonic chick heart cells. Toxicon 2000, 38, 323–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwards, L.P.; Whitter, E.; Hessinger, D.A. Apparent membrane pore-formation by Portuguese Man-of-war (Physalia physalis) venom in intact cultured cells. Toxicon 2002, 40, 1299–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailey, P.M.; Bakker, A.J.; Seymour, J.E.; Wilce, J.A. A functional comparison of the venom of three Australian jellyfish—Chironex fleckeri, Chiropsalmus sp., and Carybdea xaymacana—On cytosolic Ca2+, hemolysis and Artemia sp. lethality. Toxicon 2005, 45, 233–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, C.; Munawir, A.; Cha, M.; Sohn, E.T.; Lee, H.; Kim, J.S.; Yoon, W.D.; Lim, D.; Kim, E. Cytotoxicity and hemolytic activity of jellyfish Nemopilema nomurai (Scyphozoa: Rhizostomeae) venom. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part C 2009, 150, 85–90. [Google Scholar]
- Stark, G. Functional consequences of oxidative membrane damage. J. Membr. Biol. 2005, 205, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rice-Evans, C.A. Formation of Free Radicals and Mechanisms of Action in Normal Biochemical Processes and Pathological States. In Free Radical Damage and Its Control, 1st; Rice-Evans, C.A., Burdon, R.H., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1994; Volume 1, pp. 131–153. [Google Scholar]
- Bartosz, G.; Finkelshtein, A.; Przygodzki, T.; Bsor, T.; Nesher, N.; Sher, D.; Zlotkin, E. A pharmacological solution for a conspecific conflict: ROS-mediated territorial aggression in sea anemones. Toxicon 2008, 51, 1038–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santamaria, A.; Sanchez-Rodriguez, J.; Zugasti, A.; Martinez, A.; Galvan-Arzate, S.; Segura-Puertas, L. A venom extract from the sea anemone Bartholomea annulata produces hemolysis and lipid peroxidation in mouse erythrocytes. Toxicology 2002, 173, 221–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butzke, D.; Luch, A. High-molecular weight protein toxins of marine invertebrates and their elaborate modes of action. Mol. Clin. Environ. Toxicol. 2010, 100, 213–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, L.; Wang, B.L.; Li, Y.; Wang, Q.Q.; Liu, S.H.; Wang, Y.; Liu, G.Y.; Lu, J.; Ye, X.T.; Zhang, L.M. Cardiovascular effect is independent of hemolytic toxicity of tentacle-only extract from the jellyfish Cyanea capillata. PloS One 2012, 7, e43096. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, L.; Zhang, J.; Wang, Q.Q.; He, Q.; Liu, S.H.; Li, Y.; Zhang, L.M. In vitro and in vivo hemolytic studies of tentacle-only extract from jellyfish Cyanea capillata. Toxicol. In Vitro 2010, 24, 1203–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, L.; Liu, S.; He, Q.; Wang, Q.; Ye, X.; Liu, G.; Nie, F.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, L. The acute toxicity and hematological characterization of the effects of tentacle-only extract from the jellyfish Cyanea capillata. Mar. Drugs 2011, 9, 526–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, L.; Liu, G.S.; Wang, Q.Q.; He, Q.; Liu, S.H.; Li, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, L.M. The lethality of tentacle-only extract from jellyfish Cyanea capillata is primarily attributed to cardiotoxicity in anaesthetized SD rats. Toxicon 2010, 55, 838–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, L.; He, Q.; Guo, Y.; Zhang, J.; Nie, F.; Li, Y.; Ye, X.; Zhang, L. Cyanea capillata tentacle-only extract as a potential alternative of nematocyst venom: Its cardiovascular toxicity and tolerance to isolation and purification procedures. Toxicon 2009, 53, 146–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Wang, Q.Q.; Zhang, W.; Wang, B.L.; Wang, T.; Zhang, L.; Wen, X.J.; Liu, G.Y.; Zhao, J.; Xiao, L.; et al. Effect of various cations on the hemolytic activity of tentacle-only extract from the jellyfish Cyanea capillata. Acad. J. Second Mil. Med. Univ. 2012, 33, 240–246. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, J.; Yu, H.; Xing, R.; Liu, S.; Wang, L.; Cai, S.; Li, P. Partial characterization of the hemolytic activity of the nematocyst venom from the jellyfish Cyanea nozakii Kishinouye. Toxicol. In Vitro 2010, 24, 1750–1756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noguchi, K.; Sakanashi, M.; Matsuzaki, T.; Nakasone, J.; Koyama, T.; Hamadate, N. Cardiovascular effects and lethality of venom from nematocysts of the box-jellyfish Chiropsalmus quadrigatus (Habu-kurage) in anaesthetized rats. Toxicon 2005, 45, 519–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.L.; Zhang, L.; He, Q.; Wang, Q.Q.; Wang, T.; Lu, J.; Wen, X.J.; Ye, X.T.; Xiao, L.; Zhang, L.M. Direct cardiac toxicity of the tentacle-only extract from the jellyfish Cyanea capillata demonstrated in isolated rat heart. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. 2012, 59, 331–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.P.; Li, P.C.; Feng, J.H.; Li, R.F.; Yu, H.H. Cytotoxicity of the venom from the nematocysts of jellyfish Cyanea nozakii Kishinouye. Toxicol. Ind. Health 2012, 28, 186–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marino, A.; Crupi, R.; Rizzo, G.; Morabito, R.; Musci, G.; La Spada, G. The unusual toxicity and stability properties of crude venom from isolated nematocysts of Pelagia noctiluca (Cnidaria, Scyphozoa). Cell. Mol. Biol. 2007, 53 Suppl., OL994–OL1002. [Google Scholar]
- Gutteridge, J.M.; Halliwell, B. The measurement and mechanism of lipid peroxidation in biological systems. Trends Biochem. Sci. 1990, 15, 129–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiu, D.; Lubin, B.; Shohet, S. Peroxidative Reactions in Red Cell Biology. In FreeRadicalsinBiology, 1st; Pryor, W.A., Ed.; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1982; Volume 4, pp. 115–160. [Google Scholar]
- Jacob, H.S.; Lux, S.E. Degradation of membrane phospholipids and thiols in peroxide hemolysis: Studies in vitamin E deficiency. Blood 1968, 32, 549–568. [Google Scholar]
- Bloom, D.A.; Burnett, J.W.; Alderslade, P. Partial purification of box jellyfish (Chironex fleckeri) nematocyst venom isolated at the beachside. Toxicon 1998, 36, 1075–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradford, M.M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal. Biochem. 1976, 72, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2013 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open-access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, T.; Wen, X.-J.; Mei, X.-B.; Wang, Q.-Q.; He, Q.; Zheng, J.-M.; Zhao, J.; Xiao, L.; Zhang, L.-M. Lipid Peroxidation Is another Potential Mechanism besides Pore-Formation Underlying Hemolysis of Tentacle Extract from the Jellyfish Cyanea capillata. Mar. Drugs 2013, 11, 67-80. https://doi.org/10.3390/md11010067
Wang T, Wen X-J, Mei X-B, Wang Q-Q, He Q, Zheng J-M, Zhao J, Xiao L, Zhang L-M. Lipid Peroxidation Is another Potential Mechanism besides Pore-Formation Underlying Hemolysis of Tentacle Extract from the Jellyfish Cyanea capillata. Marine Drugs. 2013; 11(1):67-80. https://doi.org/10.3390/md11010067
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Tao, Xiao-Juan Wen, Xiao-Bin Mei, Qian-Qian Wang, Qian He, Jie-Min Zheng, Jie Zhao, Liang Xiao, and Li-Ming Zhang. 2013. "Lipid Peroxidation Is another Potential Mechanism besides Pore-Formation Underlying Hemolysis of Tentacle Extract from the Jellyfish Cyanea capillata" Marine Drugs 11, no. 1: 67-80. https://doi.org/10.3390/md11010067
APA StyleWang, T., Wen, X. -J., Mei, X. -B., Wang, Q. -Q., He, Q., Zheng, J. -M., Zhao, J., Xiao, L., & Zhang, L. -M. (2013). Lipid Peroxidation Is another Potential Mechanism besides Pore-Formation Underlying Hemolysis of Tentacle Extract from the Jellyfish Cyanea capillata. Marine Drugs, 11(1), 67-80. https://doi.org/10.3390/md11010067