Improved Detection of Domoic Acid Using Covalently Immobilised Antibody Fragments
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Cloning and Sequencing of Cysteine-Functionalised scFvs

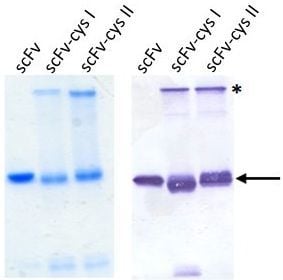
2.2. ScFv Expression and Purification


2.3. ScFv Immobilisation and Domoic Acid Binding



3. Experimental Section
3.1. Materials, Strains and Plasmids
3.2. Genetic Construction
3.3. ScFv Modelling
3.4. ScFv Expression and Purification
3.5. Binding Studies
3.5.1. Immobilisation of scFvs on Maleimide-Activated Plates
3.5.2. Competitive EIA in Polystyrene Plates
3.5.3. Competitive EIA in Maleimide-Activated Plates
3.6. Immobilisation Studies
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgements
References
- Morgan, K.L.; Larkin, S.L.; Adams, C.M. Firm-Level economic effects of HABS: A tool for business loss assessment. Harmful Algae 2009, 8, 212–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoagland, P.; Scatasta, S. The Economic Effect of Harmful Algal Blooms. In Ecology on Harmful Algae; Graneli, E.T.T., Ed.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2006; Volume 189, pp. 391–402. [Google Scholar]
- Van Dolah, F.M.; Ramsdell, J.S. Review and assessment of in vitro detection methods for algal toxins. J. AOAC Int. 2001, 84, 1617–1625. [Google Scholar]
- Mos, L. Domoic acid: A fascinating marine toxin. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2001, 9, 79–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debonnel, G.; Beauchesne, L.; de Montigny, C. Domoic acid, the alleged “mussel toxin,” might produce its neurotoxic effect through kainate receptor activation: An electrophysiological study in the dorsal hippocampus. Can. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 1989, 67, 29–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grant, K.S.; Burbacher, T.M.; Faustman, E.M.; Gratttan, L. Domoic acid: Neurobehavioral consequences of exposure to a prevalent marine biotoxin. Neurotoxicol. Teratol. 2010, 32, 132–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quilliam, M.A.; Wright, J.L. The amnesic shellfish poisoning mystery. Anal. Chem. 1989, 61, 1053A–1106A. [Google Scholar]
- Campbell, K.; Vilariño, N.; Botana, L.M.; Elliott, C.T. A European perspective on progress in moving away from the mouse bioassay for marine-toxin analysis. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2011, 30, 239–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerssen, A.; Pol-Hofstad, I.E.; Poelman, M.; Mulder, P.P.; van den Top, H.J.; de Boer, J. Marine toxins: Chemistry, toxicity, occurrence and detection, with special reference to the Dutch situation. Toxins 2010, 2, 878–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EFSA Panel on Contaminants in the Food Chain. Scientific Opinion of the Panel on Contaminants in the Food Chain on a request from the European Commission on marine biotoxins in shellfish–domoic acid. EFSA J. 2009, 1181, 1–61.
- He, Y.; Fekete, A.; Chen, G.; Harir, M.; Zhang, L.; Tong, P.; Schmitt-Kopplin, P. Analytical approaches for an important shellfish poisoning agent: Domoic Acid. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2010, 58, 11525–11533. [Google Scholar]
- Vilariño, N.; Louzao, M.C.; Vieytes, M.; Botana, L. Biological methods for marine toxin detection. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2010, 397, 1673–1681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holland, P. Analysis of Marine Toxins—Techniques, Method Validation, Calibration Standards and Screening Methods. In Seafood and Freshwater Toxins: Pharmacology, Physiology and Detection, 2nd; Botana, L.M., Ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2008; pp. 21–49. [Google Scholar]
- Traynor, I.M.; Plumpton, L.; Fodey, T.L.; Higgins, C.; Elliott, C.T. Immunobiosensor detection of domoic acid as a screening test in bivalve molluscs: Comparison with liquid chromatography-based analysis. J. AOAC Int. 2006, 89, 868–872. [Google Scholar]
- MacKenzie, L.A. In situ passive solid-phase adsorption of micro-algal biotoxins as a monitoring tool. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2010, 21, 326–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doucette, G.J.; Mikulski, C.M.; Jones, K.L.; King, K.L.; Greenfield, D.I.; Marin Iii, R.; Jensen, S.; Roman, B.; Elliott, C.T.; Scholin, C.A. Remote, subsurface detection of the algal toxin domoic acid onboard the Environmental Sample Processor: Assay development and field trials. Harmful Algae 2009, 8, 880–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; O’Connor, I.B.; Wall, J.G. Antibody Immobilization on Solid Surfaces: Methods and Applications. In Biological Interactions with Surface Charge in Biomaterials; The Royal Society of Chemistry: Cambridge, UK, 2012; pp. 90–104. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, X.; O’Dwyer, R.; Wall, J.G. Cloning, expression and characterisation of a single-chain Fv antibody fragment against domoic acid in Escherichia coli. J. Biotechnol. 2005, 120, 38–45. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, X.; O’Hara, L.; White, S.; Magner, E.; Kane, M.; Wall, J.G. Optimisation of production of a domoic acid-binding scFv antibody fragment in Escherichia coli using molecular chaperones and functional immobilisation on a mesoporous silicate support. Protein Expr. Purif. 2007, 52, 194–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Spada, S.; White, S.; Hudson, S.; Magner, E.; Wall, J.G. Adsorption and activity of a domoic acid binding antibody fragment on mesoporous silicates. J. Phys. Chem. B 2006, 110, 18703–18709. [Google Scholar]
- Kabat, E.A. Sequences of Proteins of Immunological Interest; U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, Public Health Service, National Institutes of Health: Bethesda, MD, USA, 1983. [Google Scholar]
- Studier, F.W. Protein production by auto-induction in high-density shaking cultures. Protein Expr. Purif. 2005, 41, 207–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bessette, P.H.; Qiu, J.; Bardwell, J.C.; Swartz, J.R.; Georgiou, G. Effect of sequences of the active-site dipeptides of DsbA and DsbC on in vivo folding of multidisulfide proteins in Escherichia coli. J. Bacteriol. 2001, 183, 980–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.T.; Shi, J.; Zhao, J.; Qi, Y.F.; Guo, A.G. Expression of soluble and functional snake venom fibrinolytic enzyme fibrolase via the co-expression of DsbC in Escherichia coli. Protein Peptide Lett. 2006, 13, 559–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maskos, K.; Huber-Wunderlich, M.; Glockshuber, R. DsbA and DsbC-catalyzed oxidative folding of proteins with complex disulfide bridge patterns in vitro and in vivo. J. Mol. Biol. 2003, 325, 495–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subedi, G.P.; Satoh, T.; Hanashima, S.; Ikeda, A.; Nakada, H.; Sato, R.; Mizuno, M.; Yuasa, N.; Fujita-Yamaguchi, Y.; Yamaguchi, Y. Overproduction of anti-Tn antibody MLS128 single-chain Fv fragment in Escherichia coli cytoplasm using a novel pCold-PDI vector. Protein Expr. Purif. 2012, 82, 197–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhao, T.-J.; Yan, Y.-B.; Zhou, H.-M. Increase of soluble expression in Escherichia coli cytoplasm by a protein disulfide isomerase gene fusion system. Protein Expr. Purif. 2005, 44, 155–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolaj, O.; Spada, S.; Robin, S.; Wall, J.G. Use of folding modulators to improve heterologous protein production in Escherichia coli. Microb. Cell Fact. 2009, 8, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albrecht, H.; Burke, P.A.; Natarajan, A.; Xiong, C.-Y.; Kalicinsky, M.; DeNardo, G.L.; DeNardo, S.J. Production of soluble ScFvs with C-terminal-free thiol for site-specific conjugation or stable dimeric ScFvs on demand. Bioconjug. Chem. 2003, 15, 16–26. [Google Scholar]
- O’Dwyer, R.; Razzaque, R.; Hu, X.; Hollingshead, S.K.; Wall, J.G. Engineering of cysteine residues leads to improved production of a human dipeptidase enzyme in E. coli. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2009, 159, 178–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiedzierska, A.; Czepczynska, H.; Smietana, K.; Otlewski, J. Expression, purification and crystallization of cysteine-rich human protein muskelin in Escherichia coli. Protein Expr. Purif. 2008, 60, 82–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ackerson, C.J.; Jadzinsky, P.D.; Jensen, G.J.; Kornberg, R.D. Rigid, specific, and discrete gold nanoparticle/antibody conjugates. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 2635–2640. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, D.; Berven, E.; Li, Q.; Uckun, F.; Kersey, J.H. Optimization of Conditions for formation and analysis of Anti-CD19 FVS191 single-chain Fv homodimer (scFv’)2. Bioconjug. Chem. 1997, 8, 64–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaw, I.; O’Reilly, A.; Charleton, M.; Kane, M. Development of a high-affinity anti-domoic acid sheep scFv and its use in detection of the toxin in shellfish. Anal. Chem. 2008, 80, 3205–3212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Pan, F.; Garcia-Gancedo, L.; Flewitt, A.J.; Ashley, G.M.; Luo, J.; Lu, J.R. Interfacial recognition of human prostate-specific antigen by immobilized monoclonal antibody: Effects of solution conditions and surface chemistry. J. R. Soc. Interface 2012, 9, 2457–2467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchner, J.; Rudolph, R.; Lilie, H. Intradomain disulfide bonds impede formation of the alternatively folded state of antibody chains. J. Mol. Biol. 2002, 318, 829–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Addai-Mensah, J.; Losic, D. Key factors influencing the optical detection of biomolecules by their evaporative assembly on diatom frustules. J. Mater. Sci. 2012, 47, 6315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fowler, C.E.; Buchber, C.; Lebeau, B.; Patarin, J.; Delacôte, C.; Walcarius, A. An aqueous route to organically functionalized silica diatom skeletons. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2007, 253, 5485–5493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, A.; Kucukural, A.; Zhang, Y. I-TASSER: A unified platform for automated protein structure and function prediction. Nat. Protoc. 2010, 5, 725–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y. I-TASSER server for protein 3D structure prediction. BMC Bioinforma. 2008, 9, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guex, N.; Peitsch, M.C. SWISS-MODEL and the Swiss-PdbViewer: An environment for comparative protein modeling. Electrophoresis 1997, 18, 2714–2723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samples Availability: Available from the authors.
© 2013 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Hortigüela, M.J.; Wall, J.G. Improved Detection of Domoic Acid Using Covalently Immobilised Antibody Fragments. Mar. Drugs 2013, 11, 881-895. https://doi.org/10.3390/md11030881
Hortigüela MJ, Wall JG. Improved Detection of Domoic Acid Using Covalently Immobilised Antibody Fragments. Marine Drugs. 2013; 11(3):881-895. https://doi.org/10.3390/md11030881
Chicago/Turabian StyleHortigüela, María J., and J. Gerard Wall. 2013. "Improved Detection of Domoic Acid Using Covalently Immobilised Antibody Fragments" Marine Drugs 11, no. 3: 881-895. https://doi.org/10.3390/md11030881
APA StyleHortigüela, M. J., & Wall, J. G. (2013). Improved Detection of Domoic Acid Using Covalently Immobilised Antibody Fragments. Marine Drugs, 11(3), 881-895. https://doi.org/10.3390/md11030881