Structural and Immunochemical Studies of the Lipopolysaccharide from the Fish Pathogen, Aeromonas bestiarum Strain K296, Serotype O18
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Isolation of LPS and SDS-PAGE

2.2. Chemical and ESI FT-ICR Mass Spectrometric Analyses of LPS Preparations

| Species | Mmeasured | Mcalculated | Composition |
|---|---|---|---|
| LPStriI | 2910.129 | 2910.128 | Hep6HexHexN3KdoP3[14:0(3-OH)]212:0 |
| LPStetraI | 3136.324 | 3136.318 | Hep6HexHexN3KdoP3[14:0(3-OH)]312:0 |
| 3136.347 | 3136.318 | ||
| LPStetraII | 3298.378 | 3298.370 | Hep6Hex2HexN3KdoP3[14:0(3-OH)]312:0 |
| 3298.404 | 3298.370 | ||
| LPShexaI | 3544.677 | 3544.668 | Hep6HexHexN3KdoP3[14:0(3-OH)]412:02 |
| 3544.708 | 3544.668 | ||
| LPShexaI | 3675.742 | 3675.713 | Hep6HexHexN3PenNKdoP3[14:0(3-OH)]412:02 |
| 3675.771 | 3675.713 | ||
| LPShexaII | 3706.766 | 3706.720 | Hep6Hex2HexN3KdoP3[14:0(3-OH)]412:02 |
| 3706.792 | 3706.720 | ||
| LPShexaI | 3806.816 | 3806.758 | Hep6HexHexN3PenN2KdoP3[14:0(3-OH)]412:02 |
| LPShexaII | 3837.778 | 3837.765 | Hep6Hex2HexN3PenNKdoP3[14:0(3-OH)]412:02 |
| LPShexaII | 3967.862 | 3968.810 | Hep6Hex2HexN3PenN2KdoP3[14:0(3-OH)]412:02 |
| SR-LPStetraII | 4082.635 | 4081.648 | 6dHex2Hep6Hex3HexN4KdoP3Ac4[14:0(3-OH)]312:0 |

| Species | Mmeasured | Mcalculated | Composition |
|---|---|---|---|
| YI | 1134.625 | 1134.621 | HexN2P2[14:0(3-OH)]212:0 |
| YII | 1360.813 | 1360.811 | HexN2P2[14:0(3-OH)]312:0 |
| 1360.821 | |||
| BI | 1583.451 | 1583.447 | Hep5HexHexNKdoP |
| 1583.455 | |||
| YIII | 1769.174 | 1769.161 | HexN2P2[14:0(3-OH)]4(12:0)2 |
| BII | 1775.510 | 1775.507 | Hep6HexHexNKdoP |
| 1775.522 | |||
| BIII | 1937.556 | 1937.559 | Hep6Hex2HexNKdoP |
| 1937.568 | |||
| BIV | 2720.830 | 2720.837 | 6dHex2Hep6Hex3HexN2KdoPAc4 |
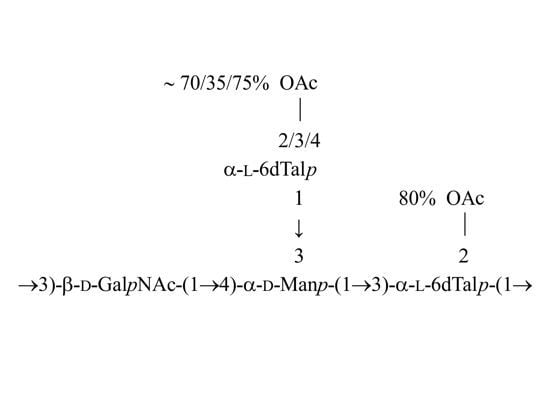
2.3. Structural Studies of the O-Deacetylated OPS
| Sugar residue | Chemical shifts (ppm) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| H-1 C-1 | H-2 C-2 | H-3 C-3 | H-4 C-4 | H-5 C-5 | H-6 C-6 | ||
| →3,4)-α-d-Manp-(1→ | A | 5.10 | 4.23 | 4.09 | 3.84 | 3.99 | 3.73–3.84 |
| 98.6 | 67.4 | 73.4 | 73.5 | 71.9 | 61.2 | ||
| α-l-6dTalp-(1→ | B | 5.06 | 3.87 | 4.10 | 3.78 | 4.71 | 1.29 |
| 97.6 | 70.9 | 66.3 | 73.4 | 68.2 | 16.3 | ||
| →3)-α-l-6dTalp-(1→ | C | 5.01 | 3.90 | 4.03 | 3.87 | 4.15 | 1.24 |
| 104.0 | 68.0 | 71.6 | 72.2 | 68.8 | 16.3 | ||
| →3)-β-d-GalpNAc-(1→ | D | 4.49 | 4.02 | 3.75 | 3.95 | 3.60 | 3.72–3.77 |
| 101.6 | 52.5 | 79.9 | 68.4 | 75.8 | 62.3 | ||


2.4. Identification of O-Acetylation Sites in the Initial OPS

| Sugar residue | Chemical shifts (ppm) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| H-1 C-1 | H-2 C-2 | H-3 C-3 | H-4 C-4 | H-5 C-5 | H-6 C-6 | ||
| α-l-6dTalp3Ac-(1→ | B′″ | 5.23 | 4.25 | 5.01 | 3.84 | 3.98 | 1.23 |
| ND | 65.6 | 66.0 | 70.6 | 67.3 | 16.2 | ||
| α-l-6dTalp2Ac4Ac-(1→ | B″ | 5.16 | 5.25 | 4.42 | 5.05 | 3.99 | 1.23 |
| 96.7 | 71.4 | 64.6 | 70.5 | 67.3 | 16.2 | ||
| α-l-6dTalp2Ac4Ac-(1→ | B′ | 5.08 | 5.21 | 4.35 | 5.07 | 4.03 | 1.23 |
| 96.5 | 69.0 | 64.7 | 68.2 | 67.4 | 16.2 | ||
| →3,4)-α-d-Manp-(1→ | A′ | 5.06 | 4.19 | 4.00 | 3.75 | 4.02 | 3.76 |
| 98.7 | 68.3 | 73.3 | 73.7 | 71.4 | 61.8 | ||
| →3)-α-l-6dTalp2Ac-(1→ | C′ | 4.98 | 5.10 | 4.21 | 3.85 | 4.16 | 1.23 |
| 101.3 | 68.2 | 71.4 | 70.6 | 68.4 | 16.2 | ||
| →3)-β-D-GalpNAc-(1→ | D′ | 4.49 | 4.04 | 3.72 | 3.92 | 3.58 | 3.74 |
| 101.4 | 52.6 | 79.9 | 68.4 | 76.0 | 62.4 | ||

2.5. Immunoblotting Studies

3. Experimental Section
3.1. Bacterial Strain, Cultivation Conditions and Isolation of the LPS
3.2. Isolation and O-Deacetylation of the OPS and O-Deacylation of the R-Type LPS and LPSs for Serological Studies
3.3. Chemical Analyses
3.4. NMR Spectroscopy
3.5. Mass Spectrometry Analysis
3.6. SDS-PAGE
3.7. Immunization Procedures and Immunoblotting
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Conflict of Interest
References
- Janda, J.M.; Duffy, P.S. Mesophilic aeromonads in human diseases: Current taxonomy, laboratory infection and infectious diseases spectrum. Rev. Infect. Dis. 1988, 10, 980–997. [Google Scholar]
- Janda, J.M. Recent advances in the study of the taxonomy, pathogenicity and infectious syndromes with the genus Aeromonas. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 1991, 4, 397–410. [Google Scholar]
- Nawaz, M.; Khan, S.A.; Khan, A.A.; Sung, K.; Tran, Q.; Kerdahi, K.; Steele, R. Detection and characterization of virulence genes and integrons in Aeromonas veronii isolated from catfish. Food Microbiol. 2010, 27, 327–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araujo, R.M.; Arribas, R.M.; Pares, R. Distributionof Aeromonas species in waterswith different levels of pollution. J. Appl. Bacteriol. 1991, 71, 182–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janda, J.M.; Abbott, S. The genus Aeromonas: Taxonomy, pathogenicity, and infection. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2010, 23, 35–73. [Google Scholar]
- Holmberg, S.D.; Schell, W.L.; Fanning, G.R.; Wachsmuth, I.K.; Blake, P.A.; Brenner, D.J.; Farmer, J.J. Aeromonas intestinal infections in the United States. Ann. Int. Med. 1986, 105, 683–689. [Google Scholar]
- Ali, A.; Carnahan, A.M.; Altwegg, M.; Luthy-Hottenstein, J.; Joseph, S.W. Aeromonas bestiarum sp. nov. (formerly genomospecies DNA group 2 A. hydrophila), a new species isolated from non human sources. Med. Microbiol. Lett. 1996, 5, 156–165. [Google Scholar]
- Kahajanchi, B.K.; Fadl, A.A.; Borchardt, M.A.; Berg, R.L.; Horneman, A.J.; Stemper, M.E.; Joseph, S.W.; Moyer, N.P.; Sha, J.; Chopra, A.K. Distribution of virulence factors and molecular fingerprinting of Aeromonas species isolates from water and clinical samples: Suggestive evidence of water-to-human transmission. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2010, 76, 2313–2325. [Google Scholar]
- Figueras, M.J. Clinical relevance of Aeromonas spp. Rev. Clin. Microbiol. 2005, 16, 145–153. [Google Scholar]
- Dooley, J.S.G.; Lallier, R.; Shaw, D.H.; Trust, T.J. Electrophoretic and immunochemical analyses of the lipopolysaccharides from various strains of Aeromonas hydrophila. J. Bacteriol. 1985, 164, 263–269. [Google Scholar]
- Merino, S.; Rubires, X.; Aguillar, A.; Guillot, J.F.; Tomas, J.M. The role of the O-antigen lipopolysaccharide on the colonization in vivo of the germfree chicken gut by Aeromonas hydrophila serogroup O:34. Microb. Pathog. 1996, 20, 325–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguilar, A.; Merino, S.; Rubires, X.; Tomas, J. Influence of osmolarity on lipopolysaccharides and virulence of Aeromonas hydrophila serotype O:34 strains grown at 37 degrees C. Infect. Immun. 1997, 65, 1245–1250. [Google Scholar]
- Rabaan, A.A.; Gryllos, I.; Tomas, J.M.; Shaw, J.G. Motility and polar flagellum are required for Aeromonas caviae adherence to HEp-2 cells. Infect. Immun. 2001, 69, 4257–4267. [Google Scholar]
- Garduno, R.A.; Moore, A.R.; Oliver, G.; Lizama, A.L.; Garduno, E.; Kay, W.W. Host cell invasion and intracellular resistance by Aeromonas salmonicida: Role of the S-layer. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2000, 46, 660–668. [Google Scholar]
- Asha, A.; Nayak, D.K.; Shankar, K.M.; Mohan, C.V. Antigen expression in biofilm cells of Aeromonas hydrophila employed in oral vaccination of fish. Fish Shellfish Immun. 2004, 16, 429–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nandapalan, N.; Chang, B.J. Production and characterization of monoclonal antibodies to Aeromonas sobria surface antigens. FEMS Microbiol. Immunol. 1989, 47, 515–524. [Google Scholar]
- Francki, K.T.; Chang, B.J.; Mee, B.J.; Collignon, P.J.; Susai, V.; Keese, P.K. Identification of genes associated with copper tolerance in an adhesion-defective mutant of Aeromonas veronii biovar sobria. FEMS Immunol. Med. Microbiol. 2000, 29, 115–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazarenko, E.L.; Crawford, R.J.; Iwanowa, E.P. The structural diversity of carbohydrate antigens of selected Gram-negative marine bacteria. Mar. Drugs 2011, 9, 1914–1954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Liu, X.; Dacanay, A.; Harrison, B.A.; Fast, M.; Colquhoun, D.J.; Lund, V.; Brown, L.L.; Li, J.; Altman, E. Carbohydrate analysis and serological classification of typical and atypical isolates of Aeromonas salmonicida: A rationale for the lipopolysaccharide-based classification of A. salmonicida. Fish Shellfish Immun. 2007, 23, 1095–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knirel, Y.A.; Shashkov, A.S.; Senchenkova, S.N.; Merino, S.; Tomas, J.M. Structure of the O-specific polysaccharide of Aeromonas hydrophila O:34; a case of random O-acetylation of 6-deoxy-l-talose. Carbohydr. Res. 2002, 337, 1381–1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozinska, A.; Pekala, A. Serotyping of Aeromonas species isolated from Polish fish farms in relation to species and virulence phenotype of the bacteria. Bull. Vet. Inst. Pulawy 2010, 54, 315–320. [Google Scholar]
- Turska-Szewczuk, A.; Kozinska, A.; Russa, R.; Holst, O. The structure of the O-specific polysaccharide from the lipopolysaccharide of Aeromonas bestiarum strain 207. Carbohydr. Res. 2010, 345, 680–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turska-Szewczuk, A.; Guz, L.; Lindner, B.; Pietras, H.; Russa, R.; Holst, O. Structural characterization of the O-specific polysaccharide from the lipopolysaccharide of fish pathogen Aeromonas bestiarum strain P1S. Carbohydr. Res. 2011, 346, 815–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozinska, A.; Figueras, M.J.; Chacon, M.R.; Soler, L. Phenotypic characteristics of Aeromonas genomospecies isolated from common carp (Cyprinus carpio L.). J. Appl. Microbiol. 2002, 93, 1034–1041. [Google Scholar]
- Westphal, O.; Jann, K. Bacterial lipopolysaccharide. Extraction with phenol-water and further applications of the procedure. Meth. Carbohydr. Chem. 1965, 5, 83–91. [Google Scholar]
- Domon, B.; Costello, C.E. A systamatic nomenclature for carbohydrate fragmentations in FAB MS/MS spectra of glycoconjugates. Glycoconj. J. 1988, 5, 397–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turska-Szewczuk, A.; Russa, R. Structural studies of the O-specific polysaccharide from the lipopolysaccharide of Mesorhizobium huakuii strain S-52, the symbiotic partner of Astragalus sinicus. Carbohydr. Res. 2011, 346, 1065–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leontein, K.; Lindberg, B.; Lönngren, J. Assignment of absolute configuration of sugars by GLC of their acetylated glycosides formed from chiral alcohols. Carbohydr. Res. 1978, 62, 359–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipkind, G.M.; Shashkov, A.S.; Knirel, Y.A.; Vinogradov, E.V.; Kochetkov, N.K. A computer-assisted structural analysis of regular polysaccharides on the basis of 13C-n.m.r. data. Carbohydr. Res. 1988, 175, 59–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jansson, P.E.; Kenne, L.; Widmalm, G. Computer-assisted structural analysis of polysaccharides with an extended version of CASPER using 1H- and 13C-NMR data. Carbohydr. Res. 1989, 188, 169–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kocharowa, N.A.; Zatonsky, G.V.; Bystrova, O.V.; Shashkov, A.S.; Knirel, Y.A.; Kholodkova, E.V.; Stanislavsky, E.S. Structure of the O-specific polysaccharide of Citrobacter braakii O7a,3b,1c. Carbohydr. Res. 2001, 333, 335–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knirel, Y.A.; Paramonov, N.A.; Shashkov, A.S.; Kochetkov, N.K.; Yarullin, R.G.; Farber, S.M.; Efremenko, V.I. Structure of the polysaccharide chains of Pseudomonas pseudomallei lipopolysaccharides. Carbohydr. Res. 1992, 233, 185–193. [Google Scholar]
- Russa, R.; Urbanik-Sypniewska, T.; Shashkov, A.S.; Kochanowski, H.; Mayer, H. The structure of the homopolymeric O-specific chain from the phenol soluble LPS of the Rhizobium loti type strain NZP2213. Carbohydr. Polym. 1995, 27, 299–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Percy, A.; Ono, H.; Watt, D.; Hayashi, K. Synthesis of β-d-glucopyranosyl-(1-4)-d-arabinose, β-d-glucopyranosyl-(1-4)-l-fucose, and β-d-glucopyranosyl-(1-4)-d-altrose catalysed by cellobiose phosphorylase from Cellvibrio gilvus. Carbohydr. Res. 1998, 305, 543–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turska-Szewczuk, A.; Palusinska-Szysz, M.; Russa, R. Structural studies of O-polysaccharide chain from the lipopolysaccharide of symbiotically enhanced mutant Mlo-13 of Mesorhizobium loti NZP2213. Carbohydr. Res. 2008, 343, 477–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubler-Kielb, J.; Vinogradov, E.; Chu, C.; Schneerson, R. O-Acetylation in the O-specific polysaccharide isolated from Shigella flexneri serotype 2a. Carbohydr. Res. 2007, 342, 643–647. [Google Scholar]
- Perepelov, A.V.; L’vov, V.L.; Liu, B.; Senchenkova, S.N.; Shekht, M.E.; Shashkov, A.S.; Feng, L.; Aparin, P.G.; Wang, L.; Knirel, Y.A. A similarity in the O-acetylation pattern of the O-antigens of Shigella flexneri types 1a, 1b, and 2a. Carbohydr. Res. 2009, 344, 687–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slauch, J.M.; Mahan, M.J.; Michetti, P.; Neutra, M.R.; Mekalanos, J.J. Acetylation (O-factor 5) affects the structural and immunological properties of Salmonella typhimurium lipopolysaccharide O antigen. Infect. Immun. 1995, 63, 437–441. [Google Scholar]
- Kahler, C.M.; Lyons-Schindler, S.; Choundhury, B.; Glushka, J.; Carlson, R.W.; Stephens, D.S. O-Acetylation of the terminal N-acetylglucosamine of the lipooligosaccharide inner core in Neisseria meningitidis. Influence on inner core structure and assembly. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 19939–19948. [Google Scholar]
- Sakazaki, R.; Shimada, T. O-Serogrouping for mesophilic Aeromonas strains. Jpn. J. Med. Sci. 1984, 37, 247–255. [Google Scholar]
- Haishima, Y.; Holst, O.; Brade, H. Structural investigation on the lipopolysaccharide of Escherichia coli rough mutant F653 representing the R3 core type. Eur. J. Biochem. 1992, 203, 127–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russa, R.; Urbanik-Sypniewska, T.; Lindstrom, K.; Mayer, H. Chemical characterization of two lipopolysaccharide species isolated from Rhizobium loti NZP2213. Arch. Microbiol. 1995, 163, 345–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hakomori, S. A rapid permethylation of glycolipid and polysaccharide catalyzed by methylsulfinyl carbanion in dimethyl sulfoxide. J. Biochem. (Tokyo) 1964, 55, 205–208. [Google Scholar]
- Pieretti, G.; Corsaro, M.M.; Lanzetta, R.; Parrilli, M.; Vilches, S.; Merino, S.; Tomas, J.M. Structure of the core region from the lipopolysaccharide of Plesiomonas shigelloides strain 302-73 (serotype O1). Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2009, 2009, 1365–1371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komaniecka, I.; Choma, A.; Lindner, B.; Holst, O. The structure of a novel lipid A from the lipopolysaccharide of Bradyrhizobium elkanii containing three mannose units in the backbone. Chem. Eur. J. 2010, 16, 2922–2929. [Google Scholar]
- Kondakova, A.; Lindner, B. Structural characterization of complex bacterial glycolipids by Fourier transform ion cyclotron mass spectrometry. Eur. J. Mass Spectrom. 2005, 11, 535–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, G.; Lindner, B.; Brabetz, W.; Brade, H.; Raina, S. Escherichia coli K-12 suppressor-free mutants lacking early glycosyltransferases and late acyltransferases: Minimal lipopolysaccharide structure and induction of envelope stress response. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 15369–15389. [Google Scholar]
- Turska-Szewczuk, A.; Pietras, H.; Borucki, W.; Russa, R. Alteration of O-specific polysaccharide structure of symbiotically defective Mesorhizobium loti mutant 2213.1 derived from strain NZP2213. Acta Biochim. Pol. 2008, 55, 191–199. [Google Scholar]
- Raetz, C.R.H.; Whitfield, C. Lipopolysaccharide endotoxins. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2002, 71, 635–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knirel, Y.A.; Vinogradov, E.; Jimenez, N.; Merino, S.; Tomas, J.M. Structural studies on the R-type lipopolysaccharide of Aeromonas hydrophila. Carbohydr. Res. 2004, 339, 787–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2013 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Turska-Szewczuk, A.; Lindner, B.; Komaniecka, I.; Kozinska, A.; Pekala, A.; Choma, A.; Holst, O. Structural and Immunochemical Studies of the Lipopolysaccharide from the Fish Pathogen, Aeromonas bestiarum Strain K296, Serotype O18. Mar. Drugs 2013, 11, 1235-1255. https://doi.org/10.3390/md11041235
Turska-Szewczuk A, Lindner B, Komaniecka I, Kozinska A, Pekala A, Choma A, Holst O. Structural and Immunochemical Studies of the Lipopolysaccharide from the Fish Pathogen, Aeromonas bestiarum Strain K296, Serotype O18. Marine Drugs. 2013; 11(4):1235-1255. https://doi.org/10.3390/md11041235
Chicago/Turabian StyleTurska-Szewczuk, Anna, Buko Lindner, Iwona Komaniecka, Alicja Kozinska, Agnieszka Pekala, Adam Choma, and Otto Holst. 2013. "Structural and Immunochemical Studies of the Lipopolysaccharide from the Fish Pathogen, Aeromonas bestiarum Strain K296, Serotype O18" Marine Drugs 11, no. 4: 1235-1255. https://doi.org/10.3390/md11041235
APA StyleTurska-Szewczuk, A., Lindner, B., Komaniecka, I., Kozinska, A., Pekala, A., Choma, A., & Holst, O. (2013). Structural and Immunochemical Studies of the Lipopolysaccharide from the Fish Pathogen, Aeromonas bestiarum Strain K296, Serotype O18. Marine Drugs, 11(4), 1235-1255. https://doi.org/10.3390/md11041235