Okadaic Acid Meet and Greet: An Insight into Detection Methods, Response Strategies and Genotoxic Effects in Marine Invertebrates
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods Used for the Detection of Okadaic Acid

2.1. Biological Methods
2.2. Chemical Methods
2.3. Biochemical Methods
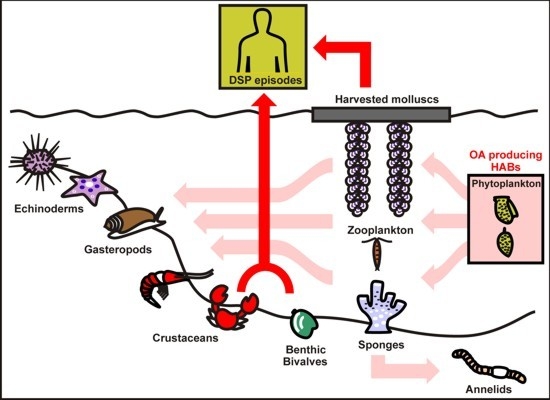
3. Response Strategies to Okadaic Acid in Marine Invertebrates

3.1. Bivalve Molluscs
3.2. Crabs and Annelids
3.3. Zooplankton and Phytoplankton
3.4. Role of OA as Defense Mechanism in Marine Organisms
4. Genotoxic Effects of Okadaic Acid: Lessons from Bivalve Molluscs

4.1. Study of OA Effects on Genome Integrity: The Comet Assay
4.2. Study of OA Effects on Chromosome Integrity: The Micronucleus Assay
4.3. Study of OA Effects on Damage Control Mechanisms: Assessment by Flow Cytometry
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Conflict of Interest
References
- Landsberg, J.H. The effects of harmful algal blooms on aquatic organisms. Rev. Fish. Sci. 2002, 10, 113–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasumoto, T.; Murata, M.; Oshima, Y.; Matsumoto, G.K.; Clardy, J. Diarrhetic Shellfish Poisoning. In Seafood Toxins; Ragelis, E.P., Ed.; AOAC: Washington, DC, USA, 1984; pp. 214–217. [Google Scholar]
- Yasumoto, T.; Oshima, Y.; Yamaguchi, M. Occurrence of a new type of shellfish poisoning in Tohoku district. Bull. Jpn. Soc. Sci. Fish. 1978, 44, 1249–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Dolah, F.M. Marine algal toxins: Origins, health effects, and their increased occurrence. Environ. Health Perspect. 2000, 108, 133–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sellner, K.G.; Doucette, G.J.; Kirkpatrick, G.J. Harmful algal blooms: Causes, impacts and detection. J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2003, 30, 383–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tachibana, K.; Scheuer, P.J.; Tsukitani, Y.; Kikuchi, H.; van Engen, D.; Clardy, J.; Gopichand, Y.; Schmitz, F.J. Okadaic acid, a cytotoxic poliether from two marine sponges of the genus Halichondria. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1981, 103, 2469–2471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.-S.; Igarashi, T.; Fraga, S.; Dahl, E.; Hovgaard, P.; Yasumoto, T. Determination of diarrhetic shellfish toxins in various dinoflagellate species. J. Appl. Phycol. 1989, 1, 147–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reguera, B.; Velo-Suárez, L.; Raine, R.; Park, M.G. Harmful Dinophysis species: A review. Harmful Algae 2012, 14, 87–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujiki, H.; Suganuma, M. Unique features of the okadaic acid activity class of tumor promoters. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 1999, 125, 150–155. [Google Scholar]
- Suganuma, M.; Fujiki, H.; Suguri, H.; Yoshizawa, S.; Hirota, M.; Nakayasu, M.; Ojika, M.; Wakamatsu, K.; Yamada, K.; Sugimura, T. Okadaic acid: An additional non-phorbol-12-tetradecanoate-13-acetate-type tumor promoter. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1988, 85, 1768–1771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shumway, S.E. Phycotoxin-related shellfish poisoning: Bivalve molluscs are not the only vectors. Rev. Fish. Sci. 1995, 3, 1–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilariño, N.; Louzao, M.C.; Vieytes, M.R.; Botana, L.M. Biological methods for marine toxin detection. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2010, 397, 1673–1681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vernoux, J.P.; Le Baut, C.; Masselin, P.; Marais, C.; Baron, B.; Choumiloff, R.; Proniewski, F.; Nizard, G.; Bohec, M. The use of Daphnia magna for detection of okadaic acid in mussel extracts. Food Addit. Contam. 1993, 10, 603–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garthwaite, I. Keeping shellfish fresh to eat: A brief review on shellfish toxins, and methods for their detection. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2000, 11, 235–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Croci, L.; Cozzi, L.; Stacchini, A.; de Medici, D.; Toti, L. A rapid tissue culture assay for the detection of okadaic acid and related compounds in mussels. Toxicon 1997, 35, 223–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amzil, Z.; Pouchus, Y.F.; Le Boterff, J.; Roussakis, C.; Verbist, J.F.; Marcaillou-Lebaut, C.; Masselin, P. Short-time cytotoxicity of mussel extracts: A new bioassay for okadaic acid detection. Toxicon 1992, 30, 1419–1425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tubaro, A.; Florio, C.; Luxich, E.; Vertua, R.; Della Loggia, R.; Yasumoto, T. Suitability of the MTT-based cytotoxicity assay to detect okadaic acid contamination of mussels. Toxicon 1996, 34, 965–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerssen, A.; Pol-Hofstad, I.E.; Poelman, M.; Mulder, P.P.; van den Top, H.J.; de Boer, J. Marine toxins: Chemistry, toxicity, occurrence and detection, with special reference to the Dutch situation. Toxins (Basel) 2010, 2, 878–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerssen, A.; Mulder, P.P.; de Boer, J. Screening of lipophilic marine toxins in shellfish and algae: Development of a library using liquid chromatography coupled to orbitrap mass spectrometry. Anal. Chim. Acta 2011, 685, 176–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christian, B.; Luckas, B. Determination of marine biotoxins relevant for regulations: From the mouse bioassay to coupled LC-MS methods. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2008, 391, 117–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.S.; Yanagi, T.; Kenma, R.; Yasumoto, T. Fluorometric determination of diarrhetic shellfish toxins by high-perfomance liquid chromatography. Agric. Biol. Chem. 1987, 51, 877–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hungerford, J.M.; Wekell, M.M. Analytical Methods for Marine Toxins. In Handbook of Natural Toxins; Tu, A., Ed.; Marcel Dekker Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1992; Volume 7, pp. 415–473. [Google Scholar]
- Bouaicha, N.; Hennion, M.C.; Sandra, P. Determination of okadaic acid by micellar electrokinetic chromatography with ultraviolet detection. Toxicon 1997, 35, 273–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aune, T.; Yndestad, M. Diarrhetic Shellfish Poisoning. In Algal Toxins in Seafood and Drinking Water; Falconer, I.R., Ed.; Academic Press: London, UK, 1993; pp. 87–104. [Google Scholar]
- Nincevic Gladan, Z.; Ujevic, I.; Milandri, A.; Marasovic, I.; Ceredi, A.; Pigozzi, S.; Arapov, J.; Skejic, S. Lipophilic toxin profile in Mytilus galloprovincialis during episodes of diarrhetic shellfish poisoning (DSP) in the N.E. Adriatic Sea in 2006. Molecules 2011, 16, 888–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armi, Z.; Turki, S.; Trabelsi, E.; Ceredi, A.; Riccardi, E.; Milandri, A. Occurrence of diarrhetic shellfish poisoning (DSP) toxins in clams (Ruditapes decussatus) from Tunis north lagoon. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2012, 184, 5085–5095. [Google Scholar]
- Vieytes, M.R.; Fontal, O.I.; Leira, F.; Baptista de Sousa, J.M.; Botana, L.M. A fluorescent microplate assay for diarrheic shellfish toxins. Anal. Biochem. 1997, 248, 258–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tubaro, A.; Florio, C.; Luxich, E.; Sosa, S.; Della Loggia, R.; Yasumoto, T. A protein phosphatase 2A inhibition assay for a fast and sensitive assessment of okadaic acid contamination in mussels. Toxicon 1996, 34, 743–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morton, S.L.; Tindall, D.R. Determination of okadaic acid content of dinoflagellate cells: A comparison of the HPLC-fluorescent method and two monoclonal antibody ELISA test kits. Toxicon 1996, 34, 947–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vale, P.; Sampayo, M.A. Comparison between HPLC and a commercial immunoassay kit for detection of okadaic acid and esters in Portuguese bivalves. Toxicon 1999, 37, 1565–1577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcaillou-Le Baut, C.; Amzil, Z.; Vernoux, J.P.; Pouchus, Y.F.; Bohec, M.; Simon, J.F. Studies on the detection of okadaic acid in mussels: preliminary comparison of bioassays. Nat. Toxins 1994, 2, 312–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vieites, J.M.; Leira, F.; Botana, L.M.; Vieytes, M.R. Determination of DSP toxins: Comparative study of HPLC and bioassay to reduce the observation time of the mouse bioassay. Arch. Toxicol. 1996, 70, 440–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González, J.C.; Leira, F.; Fontal, O.I.; Vieytes, M.R.; Arévalo, F.F.; Vieites, J.M.; Bermúdez-Puente, M.; Muñiz, S.; Salgado, C.; Yasumoto, T.; Botana, L.M. Inter-laboratory validation of the fluorescent protein phosphatase inhibition assay to determine diarrhetic shellfish toxins: Intercomparison with liquid chromatography and mouse bioassay. Anal. Chim. Acta 2002, 466, 233–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Louppis, A.P.; Badeka, A.V.; Katikou, P.; Paleologos, E.K.; Kontominas, M.G. Determination of okadaic acid, dinophysistoxin-1 and related esters in Greek mussels using HPLC with fluorometric detection, LC-MS/MS and mouse bioassay. Toxicon 2009, 55, 724–733. [Google Scholar]
- Mouratidou, T.; Kaniou-Grigoriadou, I.; Samara, C.; Kouimtzis, T. Detection of the marine toxin okadaic acid in mussels during a diarrhetic shellfish poisoning (DSP) episode in Thermaikos Gulf, Greece, using biological, chemical and immunological methods. Sci. Total Environ. 2006, 366, 894–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turrell, E.A.; Stobo, L. A comparison of the mouse bioassay with liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry for the detection of lipophilic toxins in shellfish from Scottish waters. Toxicon 2007, 50, 442–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sassolas, A.; Catanante, G.; Hayat, A.; Stewart, L.D.; Elliott, C.T.; Marty, J.L. Improvement of the efficiency and simplification of ELISA tests for rapid and ultrasensitive detection of okadaic acid in shellfish. Food Control 2013, 30, 144–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, T.; Winshell, J.; Scorzetti, G.; Fell, J.W.; Rein, K.S. Identification of okadaic acid production in the marine dinoflagellate Prorocentrum rhathymum from Florida Bay. Toxicon 2009, 55, 653–657. [Google Scholar]
- Rossignoli, A.E.; Blanco, J. Cellular distribution of okadaic acid in the digestive gland of Mytilus galloprovincialis (Lamarck, 1819). Toxicon 2008, 52, 957–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanco, J.; Marino, C.; Martin, H.; Acosta, C.P. Anatomical distribution of diarrhetic shellfish poisoning (DSP) toxins in the mussel Mytilus galloprovincialis. Toxicon 2007, 50, 1011–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svensson, S. Effects, Dynamics and Management of Okadaic Acid in Blue Mussels, Mytilus edulis. Ph.D. Thesis, Göteborg University, Göteborg, Sweden, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Svensson, S.; Forlin, L. Analysis of the importance of lipid breakdown for elimination of okadaic acid (diarrhetic shellfish toxin) in mussels, Mytilus edulis: Results from a field study and a laboratory experiment. Aquat. Toxicol. 2004, 66, 405–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duinker, A.; Bergslien, M.; Strand, Ø.; Olseng, C.D.; Svardal, A. The effect of size and age on depuration rates of diarrhetic shellfish toxins (DST) in mussels (Mytilus edulis L.). Harmful Algae 2007, 6, 288–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossignoli, A.E.; Blanco, J. Subcellular distribution of okadaic acid in the digestive gland of Mytilus galloprovincialis: First evidences of lipoprotein binding to okadaic acid. Toxicon 2010, 55, 221–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, T.; Igarashi, T.; Ichimi, K.; Watai, M.; Suzuki, M.; Ogiso, E.; Yasumoto, T. Kinetics of diarrhetic shellfish poisoning toxins, okadaic acid, dinophysistoxin-1, pectenotoxin-6 and yessotoxin in scallops Patinopecten yessoensis. Fish. Sci. 2005, 71, 948–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vale, P. Profiles of fatty acids and 7-O-acyl okadaic acid esters in bivalves: Can bacteria be involved in acyl esterification of okadaic acid? Comp. Biochem. Physiol. C 2010, 151, 18–24. [Google Scholar]
- Rossignoli, A.E.; Fernandez, D.; Regueiro, J.; Marino, C.; Blanco, J. Esterification of okadaic acid in the mussel Mytilus galloprovincialis. Toxicon 2011, 57, 712–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torgersen, T.; Miles, C.O.; Rundberget, T.; Wilkins, A.L. New esters of okadaic acid in seawater and blue mussels (Mytilus edulis). J. Agric. Food Chem. 2008, 56, 9628–9635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitching, J.A.; Sloane, J.F.; Ebling, F.J. The ecology of lough ine VIII. Mussels and their predators. J. Anim. Ecol. 1959, 28, 331–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vale, P.; de M. Sampayo, M.A. First confirmation of human diarrhoeic poisonings by okadaic acid esters after ingestion of razor clams (Solen marginatus) and green crabs (Carcinus maenas) in Aveiro lagoon, Portugal and detection of okadaic acid esters in phytoplankton. Toxicon 2002, 40, 989–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torgersen, T.; Aasen, J.; Aune, T. Diarrhetic shellfish poisoning by okadaic acid esters from Brown crabs (Cancer pagurus) in Norway. Toxicon 2005, 46, 572–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castberg, T.; Torgersen, T.; Aasen, J.; Aune, T.; Naustvoll, L.-J. Diarrhoetic shellfish poisoning toxins in Cancer pagurus Linnaeus, 1758 (Brachyura, Cancridae) in Norwegian waters. Sarsia 2004, 89, 311–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jorgensen, K.; Cold, U.; Fischer, K. Accumulation and depuration of okadaic acid esters in the European green crab (Carcinus maenas) during a feeding study. Toxicon 2008, 51, 468–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro-Ferreira, M.P.; Roelofs, D.; van Gestel, C.A.; Verweij, R.A.; Soares, A.M.; Amorim, M.J. Enchytraeus crypticus as model species in soil ecotoxicology. Chemosphere 2012, 87, 1222–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franchini, A.; Marchetti, M. The effects of okadaic acid on Enchytraeus crypticus (Annelida: Oligochaeta). Invertebr. Surviv. J. 2006, 3, 111–117. [Google Scholar]
- Franchini, A.; Ottaviani, E. Age-related toxic effects and recovery from okadaic acid treatment in Enchytraeus crypticus (Annelida: Oligochaeta). Toxicon 2008, 52, 115–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, J.T.; Tester, P.A. Toxic marine phytoplankton, zooplankton grazers, and pelagic food webs. Limmnol. Oceanogr. 1997, 42, 1203–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maneiro, I.; Frangópoulos, M.; Guisande, C.; Fernández, M.; Reguera, B.; Riveiro, I. Zooplankton as a potential vector of diarrhetic shellfish poisoning toxins through the food web. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2000, 201, 155–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, J.T.; Tester, P.A.; Hansen, P.J. Interactions between Toxic Marine Phytoplankton and Metazoan and Protistan Grazers. In The Physiological Ecology of Harmful Algal Blooms; Anderson, D.M., Cembella, A.D., Hallegraeff, G.M., Eds.; Springer-Verlag: Berlin, Germany, 1998; Volume G41, pp. 453–474. [Google Scholar]
- Maneiro, I.; D’Aleo, O.; Guisande, C.; Reguera, B. Interactions between the DSP Agent Dinophysis acuminata and the Microzooplankton Community. In Harmful algae; Reguera, B., Blanco, J., Fernández, M.L., Wyatt, T., Eds.; Xunta de Galicia and IOC of UNESCO: Santiago de Compostela, Spain, 1998; pp. 386–389. [Google Scholar]
- Windust, A.J.; Quilliam, M.A.; Wright, J.L.; McLachlan, J.L. Comparative toxicity of the diarrhetic shellfish poisons, okadaic acid, okadaic acid diol-ester and dinophysistoxin-4, to the diatom Thalassiosira weissflogii. Toxicon 1997, 35, 1591–1603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugg, L.; VanDolah, F.M. No evidence for an allelopathic role of okadaic acid among ciguatera-associated dinoflagellates. J. Phycol. 1999, 35, 93–103. [Google Scholar]
- Perreault, F.; Matias, M.S.; Oukarroum, A.; Matias, W.G.; Popovic, R. Okadaic acid inhibits cell growth and photosynthetic electron transport in the alga Dunaliella tertiolecta. Sci. Total Environ. 2012, 414, 198–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silvestre, F.; Tosti, E. Impact of marine drugs on animal reproductive processes. Mar. Drugs 2009, 7, 539–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiens, M.; Luckas, B.; Brümmer, F.; Shokry, M.; Ammar, A.; Steffen, R.; Batel, R.; Diehl-Seifert, B.; Schröder, H.C.; Müller, W.E.G. Okadaic acid: A potential defense molecule for the sponge Suberites domuncula. Mar. Biol. 2003, 142, 213–223. [Google Scholar]
- Schroder, H.C.; Breter, H.J.; Fattorusso, E.; Ushijima, H.; Wiens, M.; Steffen, R.; Batel, R.; Muller, W.E. Okadaic acid, an apoptogenic toxin for symbiotic/parasitic annelids in the demosponge Suberites domuncula. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2006, 72, 4907–4916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konoki, K.; Saito, K.; Matsuura, H.; Sugiyama, N.; Cho, Y.; Yotsu-Yamashita, M.; Tachibana, K. Binding of diarrheic shellfish poisoning toxins to okadaic acid binding proteins purified from the sponge Halichondria okadai. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2010, 18, 7607–7610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugiyama, N.; Konoki, K.; Tachibana, K. Isolation and characterization of okadaic acid binding proteins from the marine sponge Halichondria okadai. Biochemistry 2007, 46, 11410–11420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muller, W.E.; Belikov, S.I.; Kaluzhnaya, O.V.; Perovic-Ottstadt, S.; Fattorusso, E.; Ushijima, H.; Krasko, A.; Schroder, H.C. Cold stress defense in the freshwater sponge Lubomirskia baicalensis. Role of okadaic acid produced by symbiotic dinoflagellates. FEBS J. 2007, 274, 23–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prado-Alvarez, M.; Florez-Barros, F.; Sexto-Iglesias, A.; Mendez, J.; Fernandez-Tajes, J. Effects of okadaic acid on haemocytes from Mytilus galloprovincialis: A comparison between field and laboratory studies. Mar. Environ. Res. 2012, 81, 90–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prado-Alvarez, M.; Florez-Barros, F.; Mendez, J.; Fernandez-Tajes, J. Effect of okadaic acid on carpet shell clam (Ruditapes decussatus) haemocytes by in vitro exposure and harmful algal bloom simulation assays. Cell Biol. Toxicol. 2013, 29, 189–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svensson, S.; Sarngren, A.; Forlin, L. Mussel blood cells, resistant to the cytotoxic effects of okadaic acid, do not express cell membrane p-glycoprotein activity (multixenobiotic resistance). Aquat. Toxicol. 2003, 65, 27–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fladmark, K.E.; Serres, M.H.; Larsen, N.L.; Yasumoto, T.; Aune, T.; Doskeland, S.O. Sensitive detection of apoptogenic toxins in suspension cultures of rat and salmon hepatocytes. Toxicon 1998, 36, 1101–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laidley, C.W.; Cohen, E.; Casida, J.E. Protein phosphatase in neuroblastoma cells: [3H]cantharidin binding site in relation to cytotoxicity. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1997, 280, 1152–1158. [Google Scholar]
- Ritz, V.; Marwitz, J.; Richter, E.; Ziemann, C.; Quentin, I.; Steinfelder, H.J. Characterization of two pituitary GH3 cell sublines partially resistant to apoptosis induction by okadaic acid. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1997, 54, 967–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tohda, H.; Yasui, A.; Yasumoto, T.; Nakayasu, M.; Shima, H.; Nagao, M.; Sugimura, T. Chinese hamster ovary cells resistant to okadaic acid express a multidrug resistant phenotype. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1994, 203, 1210–1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Creppy, E.E.; Traore, A.; Baudrimont, I.; Cascante, M.; Carratu, M.R. Recent advances in the study of epigenetic effects induced by the phycotoxin okadaic acid. Toxicology 2002, 181-182, 433–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Traore, A.; Baudrimont, I.; Ambaliou, S.; Dano, S.D.; Creppy, E.E. DNA breaks and cell cycle arrest induced by okadaic acid in Caco-2 cells, a human colonic epithelial cell line. Arch. Toxicol. 2001, 75, 110–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Dolah, F.M.; Ramsdell, J.S. Okadaic acid inhibits a protein phosphatase activity involved in formation of the mitotic spindle of GH4 rat pituitary cells. J. Cell. Physiol. 1992, 151, 190–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho Pinto-Silva, C.R.; Catian, R.; Moukha, S.; Matias, W.G.; Creppy, E.E. Comparative study of Domoic Acid and Okadaic Acid induced-chromosomal abnormalities in the Caco-2 cell line. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2006, 3, 4–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gehringer, M.M. Microcystin-LR and okadaic acid-induced cellular effects: A dualistic response. FEBS Lett. 2004, 557, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Florez-Barros, F.; Prado-Alvarez, M.; Mendez, J.; Fernandez-Tajes, J. Evaluation of genotoxicity in gills and hemolymph of clam Ruditapes decussatus fed with the toxic dinoflagellate Prorocentrum lima. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health A 2011, 74, 971–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho Pinto-Silva, C.R.; Ferreira, J.F.; Costa, R.H.; Belli Filho, P.; Creppy, E.E.; Matias, W.G. Micronucleus induction in mussels exposed to okadaic acid. Toxicon 2003, 41, 93–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho Pinto-Silva, C.R.; Creppy, E.E.; Matias, W.G. Micronucleus test in mussels Perna perna fed with the toxic dinoflagellate Prorocentrum lima. Arch. Toxicol. 2005, 79, 422–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malagoli, D.; Casarini, L.; Ottaviani, E. Effects of the marine toxins okadaic acid and palytoxin on mussel phagocytosis. Fish. Shellfish Immunol. 2008, 24, 180–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manfrin, C.; Dreos, R.; Battistella, S.; Beran, A.; Gerdol, M.; Varotto, L.; Lanfranchi, G.; Venier, P.; Pallavicini, A. Mediterranean mussel gene expression profile induced by okadaic acid exposure. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 8276–8283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suarez-Ulloa, V.; Fernandez-Tajes, J.; Aguiar-Pulido, V.; Rivera-Casas, C.; Gonzalez-Romero, R.; Ausio, J.; Mendez, J.; Dorado, J.; Eirin-Lopez, J.M. The CHROMEVALOA Database: A Resource for the Evaluation of Okadaic Acid Contamination in the Marine Environment Based on the Chromatin-Associated Transcriptome of the Mussel Mytilus galloprovincialis. Mar. Drugs 2013, 11, 830–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valdiglesias, V.; Mendez, J.; Pasaro, E.; Cemeli, E.; Anderson, D.; Laffon, B. Assessment of okadaic acid effects on cytotoxicity, DNA damage and DNA repair in human cells. Mutat. Res. 2010, 689, 74–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, J.T.; Pascoe, P.L.; Parry, J.M.; Dixon, D.R. Evaluation of the comet assay as a method for the detection of DNA damage in the cells of a marine invertebrate, Mytilus edulis L. (Mollusca: Pelecypoda). Mutat. Res. 1998, 399, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, R.F.; Steinert, S. Use of the single cell gel electrophoresis/comet assay for detecting DNA damage in aquatic (marine and freshwater) animals. Mutat. Res. 2003, 544, 43–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valdiglesias, V.; Laffon, B.; Pasaro, E.; Mendez, J. Evaluation of okadaic acid-induced genotoxicity in human cells using the micronucleus test and gammaH2AX analysis. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health A 2011, 74, 980–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Hegarat, L.; Puech, L.; Fessard, V.; Poul, J.M.; Dragacci, S. Aneugenic potential of okadaic acid revealed by the micronucleus assay combined with the FISH technique in CHO-K1 cells. Mutagenesis 2003, 18, 293–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Hegarat, L.; Fessard, V.; Poul, J.M.; Dragacci, S.; Sanders, P. Marine toxin okadaic acid induces aneuploidy in CHO-K1 cells in presence of rat liver postmitochondrial fraction, revealed by cytokinesis-block micronucleus assay coupled to FISH. Environ. Toxicol. 2004, 19, 123–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hegaret, H.; da Silva, P.M.; Wikfors, G.H.; Haberkorn, H.; Shumway, S.E.; Soudant, P. In vitro interactions between several species of harmful algae and haemocytes of bivalve molluscs. Cell Biol. Toxicol. 2011, 27, 249–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, A.; Cayla, X.; Guergnon, J.; Dessauge, F.; Hospital, V.; Rebollo, M.P.; Fleischer, A.; Rebollo, A. Serine/threonine protein phosphatases PP1 and PP2A are key players in apoptosis. Biochimie 2003, 85, 721–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2013 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Prego-Faraldo, M.V.; Valdiglesias, V.; Méndez, J.; Eirín-López, J.M. Okadaic Acid Meet and Greet: An Insight into Detection Methods, Response Strategies and Genotoxic Effects in Marine Invertebrates. Mar. Drugs 2013, 11, 2829-2845. https://doi.org/10.3390/md11082829
Prego-Faraldo MV, Valdiglesias V, Méndez J, Eirín-López JM. Okadaic Acid Meet and Greet: An Insight into Detection Methods, Response Strategies and Genotoxic Effects in Marine Invertebrates. Marine Drugs. 2013; 11(8):2829-2845. https://doi.org/10.3390/md11082829
Chicago/Turabian StylePrego-Faraldo, María Verónica, Vanessa Valdiglesias, Josefina Méndez, and José M. Eirín-López. 2013. "Okadaic Acid Meet and Greet: An Insight into Detection Methods, Response Strategies and Genotoxic Effects in Marine Invertebrates" Marine Drugs 11, no. 8: 2829-2845. https://doi.org/10.3390/md11082829
APA StylePrego-Faraldo, M. V., Valdiglesias, V., Méndez, J., & Eirín-López, J. M. (2013). Okadaic Acid Meet and Greet: An Insight into Detection Methods, Response Strategies and Genotoxic Effects in Marine Invertebrates. Marine Drugs, 11(8), 2829-2845. https://doi.org/10.3390/md11082829