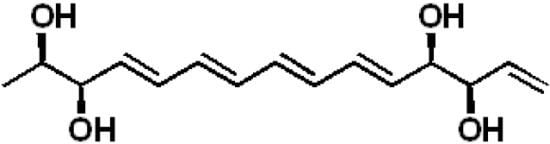
Separacenes A–D, Novel Polyene Polyols from the Marine Actinomycete, Streptomyces sp.
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Structural Elucidation

| C/H | 1 | 2 | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| δH a | mult (J in Hz) | δC b | δHc | mult (J in Hz) | δC d | |||||
| 1 | 1.43 | d (6.5) | 19.6 | CH3 | 1.54 | d (5.5) | 20.7 | CH3 | ||
| 2 | 4.11 | m | 71.2 | CH | 4.24 | dd (11.0, 5.5) | 72.6 | CH | ||
| 3 | 4.43 | dd (10.0, 6.0) | 77.3 | CH | 4.56 | m | 77.8 | CH | ||
| 4 | 6.21 | dd (15.5, 6.0) | 135.9 | CH | 6.35 | dd (15.5, 6.5) | 137.8 | CH | ||
| 5 | 6.75 | dd (15.5, 10.5) | 131.6 | CH | 6.76 | dd (15.5, 9.5) | 132.3 | CH | ||
| 6 | 6.42 | dd (15.0, 10.5) | 133.3 | CH | 6.44 | dd (14.5, 9.5) | 133.3 | CH | ||
| 7 | 6.40 | m | 132.9 | CH | 6.38 | m | 133.7 | CH | ||
| 8 | 6.38 | m | 132.8 | CH | 6.40 | m | 134.0 | CH | ||
| 9 | 6.44 | dd (15.0, 10.5) | 133.3 | CH | 6.42 | dd (15.5, 10.0) | 134.3 | CH | ||
| 10 | 6.79 | dd (15.5, 10.5) | 131.5 | CH | 6.80 | dd (15.5, 10.0) | 132.8 | CH | ||
| 11 | 6.26 | dd (15.5, 6.0) | 135.7 | CH | 6.26 | dd (15.5, 6.0) | 136.8 | CH | ||
| 12 | 4.58 | dd (9.5, 6.0) | 76.0 | CH | 4.63 | dd (11.0, 6.0) | 77.3 | CH | ||
| 13 | 4.54 | dd (9.5, 5.5) | 76.5 | CH | 4.58 | m | 78.2 | CH | ||
| 14 | 6.35 | ddd (17.5, 10.5, 5.5) | 139.8 | CH | 6.36 | ddd (17.5, 10.5, 5.5) | 142.4 | CH | ||
| 15 | 5.66 | dd (17.5, 1.0) | 115.4 | CH2 | 5.70 | dd (17.5, 1.0) | 115.4 | CH2 | ||
| 5.30 | dd (10.5, 1.0) | 5.31 | dd (10.5, 1.0) | |||||||

| 3 | 4 | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| δH a | mult (J in Hz) | δC b | δHc | mult (J in Hz) | δC d | ||||||
| 1 | 1.67 | d (5.0) | 18.7 | CH3 | 1.66 | d (5.0) | 18.7 | CH3 | |||
| 2 | 5.98 | m | 133.2 | CH | 5.98 | m | 133.6 | CH | |||
| 3 | 5.96 | dd (15.5, 5.0) | 127.4 | CH | 5.95 | dd (15.5, 5.5) | 127.8 | CH | |||
| 4 | 4.48 | dd (10.5, 5.0) | 77.3 | CH | 4.48 | dd (10.5, 5.5) | 77.0 | CH | |||
| 5 | 4.58 | dd (10.5, 6.0) | 76.6 | CH | 4.58 | dd (10.5, 6.0) | 76.5 | CH | |||
| 6 | 6.23 | dd (15.5, 6.0) | 135.8 | CH | 6.23 | dd (15.0, 6.0) | 132.0 | CH | |||
| 7 | 6.75 | dd (15.5, 10.5) | 131.7 | CH | 6.76 | dd (15.0, 11.5) | 136.0 | CH | |||
| 8 | 6.42 | dd (15.0, 10.5) | 133.1 | CH | 6.42 | dd (15.0, 11.5) | 133.2 | CH | |||
| 9 | 6.44 | dd (15.0, 10.0) | 133.0 | CH | 6.40 | dd (15.0, 11.0) | 133.0 | CH | |||
| 10 | 6.79 | dd (15.5, 10.0) | 131.7 | CH | 6.78 | dd (15.5, 11.0) | 131.7 | CH | |||
| 11 | 6.35 | dd (15.5, 6.0) | 136.3 | CH | 6.26 | dd (15.5, 6.0) | 136.3 | CH | |||
| 12 | 4.67 | dd (11.0, 6.0) | 76.5 | CH | 4.60 | dd (10.0, 6.0) | 76.6 | CH | |||
| 13 | 4.62 | dd (11.0, 5.5) | 76.9 | CH | 4.56 | dd (10.0, 5.5) | 77.1 | CH | |||
| 14 | 6.48 | ddd (17.0, 10.5, 5.5) | 140.8 | CH | 6.36 | ddd (17.5, 10.0, 5.5) | 140.3 | CH | |||
| 15 | 5.68 | dd (17.0, 1.0) | 115.6 | CH2 | 5.70 | dd (17.5, 1.5) | 115.9 | CH2 | |||
| 5.30 | dd (10.5, 1.0) | 5.30 | dd (10.5, 1.5) | ||||||||
2.2. Bioactivities of Separacenes
3. Experimental Section
3.1. General Experimental Procedures
3.2. Isolation of Bacteria, Cultivation, and Extraction
3.3. Isolation of Separacenes A–D
3.3.1. Separacene A (1)
3.3.2. Separacene B (2)
3.3.3. Separacene C (3)
3.3.4. Separacene D (4)
3.4. MTPA Esterification of Separacenes A–D
3.4.1. Tetra S-MTPA Ester (5) of Separacene A (1)
3.4.2. Tetra-R-MTPA Ester (6) of Separacene A (1)
3.4.3. Tetra-S-MTPA ester (7) of separacene B (2)
3.4.4. Tetra-R-MTPA Ester (8) of Separacene B (2)
3.4.5. Tetra-S-MTPA Ester (9) of Separacene C (3)
3.4.6. Tetra-R-MTPA Ester (10) of Separacene C (3)
3.4.7. Tetra-S-MTPA Ester (11) of Separacene D (4)
3.4.8. Tetra-R-MTPA Ester (12) of Separacene D (4)
3.5. Antibacterial Activity Assay
3.6. Antifungal Activity Assay
3.7. Isocitrate Lyase (ICL) Activity Assay
3.8. Evaluation of Anti-Proliferative Activity
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
References
- Li, J.W.-H.; Vederas, J.C. Drug discovery and natural products: End of an era or an endless frontier. Science 2009, 325, 161–165. [Google Scholar]
- Weissman, K.J.; Leadlay, P.F. Combinatorial biosynthesis of reduced polyketides. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2005, 3, 925–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clardy, J.; Walsh, C. Lessons from natural molecules. Nature 2004, 432, 829–837. [Google Scholar]
- Bérdy, J. Bioactive microbial metabolites. J. Antibiot. 2005, 58, 1–26. [Google Scholar]
- Fenical, W.; Jensen, P.R. Developing a new resource for drug discovery: Marine actinomycete bacteria. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2006, 2, 666–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molinski, T.F.; Dalisay, D.S.; Lievens, S.L.; Saludes, J.P. Drug development from marine natural products. Nat. Drug. Discov. 2009, 8, 69–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fenical, W.; Jensen, P.R.; Palladino, M.A.; Lam, K.S.; Lloyd, G.K.; Potts, B.C. Discovery and development of the anticancer agent salinosporamide A(NPI-0052). Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2009, 17, 2175–2180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.; Sharma, M.; Joshi, P.; Rawat, D.S. Clinical status of anti-cancer agents derived from marine sources. Anti-Cancer Agents Med. Chem. 2008, 8, 603–617. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, D.-G.; Moon, K.; Kim, S.-H.; Park, S.-H.; Park, S.; Lee, S.K.; Oh, K.-B.; Shin, J.; Oh, D.-C. Bahamaolides A and B, antifungal polyene polyol macrolides from the marine actinomycete, Streptomyces sp. J. Nat. Prod. 2012, 75, 959–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Um, S.; Kim, Y.-J.; Kwon, H.; Wen, H.; Kim, S.-H.; Kwon, H.C.; Park, S.; Shin, J.; Oh, D.-C. Sungsanpin, a lasso peptide from a deep-sea streptomycete. J. Nat. Prod. 2013, 76, 873–879. [Google Scholar]
- Félix, F.; Seco, J.M.; Quiñoá, E.; Riguera, R. Determining the absolute stereochemistry of secondary/secondary diols by 1H NMR: Basis and applications. J. Org. Chem. 2005, 70, 3778–3790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.D. Isolation of Antifungal Agents from Pine Roots. WO 9800091 A2, 8 January 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Dunn, M.F.; Ramirez-Trujillo, J.A.; Hernandez-Lucas, I. Major roles of isocitrate lyase and malate synthase in bacterial and fungal pathogenesis. Microbiology 2009, 155, 3166–3175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sample Availability: Available from the authors.
© 2013 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Bae, M.; Kim, H.; Shin, Y.; Kim, B.Y.; Lee, S.K.; Oh, K.-B.; Shin, J.; Oh, D.-C. Separacenes A–D, Novel Polyene Polyols from the Marine Actinomycete, Streptomyces sp. Mar. Drugs 2013, 11, 2882-2893. https://doi.org/10.3390/md11082882
Bae M, Kim H, Shin Y, Kim BY, Lee SK, Oh K-B, Shin J, Oh D-C. Separacenes A–D, Novel Polyene Polyols from the Marine Actinomycete, Streptomyces sp. Marine Drugs. 2013; 11(8):2882-2893. https://doi.org/10.3390/md11082882
Chicago/Turabian StyleBae, Munhyung, Heegyu Kim, Yoonho Shin, Byung Yong Kim, Sang Kook Lee, Ki-Bong Oh, Jongheon Shin, and Dong-Chan Oh. 2013. "Separacenes A–D, Novel Polyene Polyols from the Marine Actinomycete, Streptomyces sp." Marine Drugs 11, no. 8: 2882-2893. https://doi.org/10.3390/md11082882
APA StyleBae, M., Kim, H., Shin, Y., Kim, B. Y., Lee, S. K., Oh, K. -B., Shin, J., & Oh, D. -C. (2013). Separacenes A–D, Novel Polyene Polyols from the Marine Actinomycete, Streptomyces sp. Marine Drugs, 11(8), 2882-2893. https://doi.org/10.3390/md11082882