Solomonsterol A, a Marine Pregnane-X-Receptor Agonist, Attenuates Inflammation and Immune Dysfunction in a Mouse Model of Arthritis
Abstract
:1. Introduction

2. Results
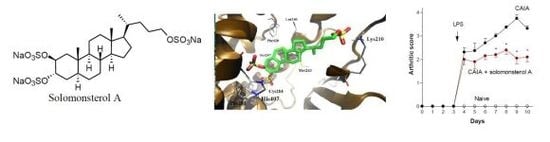
2.1. Sulfated Sterol Solomonsterol A Is a Selective Human PXR Agonist

2.2. Solomonterol A Administration Reduces Clinical and Local Signs of Arthritis


2.3. Solomonsterol A Administration Reduces Systemic Signs of Arthritis

2.4. PXR Agonism Abrogates Arthritic Profile of DLN Cells Induced by CAIA Treatment


2.5. Solomonsterol A Modulates PXR Target Genes in the Liver

3. Experimental Section
3.1. Animals
3.2. Induction of Arthritis: CAIA Mouse Model
3.3. Biochemical Analyses and Histopathologic Assessment
3.4. Cell Preparation and Activation
3.5. Isolation and Culture of Murine Primary Hepatocytes
3.6. HepG2 Cell Culture
3.7. RNA Extraction and Real-Time PCR
3.8. Transactivation Assay
3.9. Synthesis of Solomonsterol A
3.10. Statistical Analysis
4. Discussion and Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CDCA | chenodeoxycholic acid |
| cyp3a11 | mouse cytochrome P450 |
| FXR | Farnesoid-X-Receptor |
| GR | Glucocorticoid Receptor |
| IL-6 | interleukin-6 |
| IL-17 | interleukin-17 |
| IL-10 | interleukin-10 |
| INFγ | interferon gamma |
| LXRα | Liver-X-receptor alpha |
| MCP-1 | monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 |
| mdr1 | multi-drug resistance 1 |
| mrp2 | multidrug resistance-associated protein 2 |
| PPARγ | Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptor gamma |
| PXR-LBD | Pregnane-X-Receptor-Ligand Binding Domain |
| TGF-β1 | transforming growth factor beta |
| TNFα | tumor necrosis factor alpha |
References
- Fiorucci, S.; Distrutti, E.; Bifulco, G.; D’Auria, M.V.; Zampella, A. Marine sponge steroids as nuclear receptor ligands. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2012, 33, 591–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kliewer, S.A.; Moore, J.T.; Wade, L.; Staudinger, J.L.; Watson, M.A.; Jones, S.A.; McKee, D.D.; Oliver, B.B.; Wilson, T.M.; Zetterström, R.H.; et al. An orphan nuclear receptor activated by pregnanes defines a novel steroid signaling pathway. Cell 1998, 92, 73–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staudinger, J.L.; Goodwin, B.; Jones, S.A.; Hawkins-Brown, D.; MacKenzie, K.I.; LaTour, A.; Liu, Y.; Klaassen, C.D.; Brown, K.K.; Reinhard, J.; et al. The nuclear receptor PXR is a lithocholic acid sensor that protects against liver toxicity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 3369–3374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, W.; Uppal, H.; Saini, S.P.; Mu, Y.; Little, J.M.; Radominska-Pandya, A.; Zemaiti, M.A. Orphan nuclear receptor-mediated xenobiotic regulation in drug metabolism. Drug Discov. Today 2004, 9, 442–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubrac, S.; Elentner, A.; Ebner, S.; Horejs-Hoeck, J.; Schmuth, M. Modulation of T lymphocyte function by the pregnane X receptor. J. Immunol. 2010, 184, 2949–2957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renga, B.; Francisci, D.; D’Amore, C.; Schiaroli, E.; Carino, A.; Baldelli, F.; Fiorucci, S. HIV-1 infection is associated with changes in nuclear receptor transcriptome, pro-inflammatory and lipid profile of monocytes. BMC Infect. Dis. 2012, 12, 274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schote, A.B.; Turner, J.D.; Schiltz, J.; Muller, C.P. Nuclear receptors in human immune cells: Expression and correlations. Mol. Immunol. 2007, 44, 1436–1445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siest, G.; Jeannesson, E.; Marteau, J.B.; Samara, A.; Marie, B.; Pfister, M.; Pfister, M.; Visvikis-Siest, S. Transcription factor and drug-metabolizing enzyme gene expression in lymphocytes from healthy human subjects. Drug. Metab. Dispos. 2008, 36, 182–189. [Google Scholar]
- Mencarelli, A.; Migliorati, M.; Barbanti, M.; Cipriani, S.; Palladino, G.; Distrutti, E.; Renga, B.; Fiorucci, S. Pregnane-X-receptor mediates the anti-inflammatory activities of rifaximin on detoxification pathways in intestinal epithelial cells. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2010, 80, 1700–1707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mencarelli, A.; Renga, B.; Palladino, G.; D’Amore, C.; Ricci, P.; Distrutti, E.; Barbanti, M.; Baldelli, F.; Fiorucci, S. Inhibition of NF-κB by a PXR-dependent pathway mediates counter-regulatory activities of rifaximin on innate immunity in intestinal epithelial cells. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2011, 668, 317–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, X.; Ke, S.; Liu, D.; Sheng, T.; Thomas, P.E.; Rabson, A.B.; Gallo, M.A.; Xie, W.; Tian, Y. Role of NF-kappaB in regulation of PXR-mediated gene expression: a mechanism for the suppression of cytochrome P-450 3A4 by proinflammatory agents. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 17882–17889. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, C.; Tabb, M.M.; Nelson, E.L.; Grün, F.; Verma, S.; Sadatrafiei, A.; Lin, M.; Mallich, S.; Forman, B.M.; Thummel, K.E.; et al. Mutual repression between steroid and xenobiotic receptor and NF-kappaB signaling pathways links xenobiotic metabolism and inflammation. J. Clin. Invest. 2006, 116, 2280–2289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chini, M.G.; Jones, C.R.; Zampella, A.; D’Auria, M.V.; Renga, B.; Fiorucci, S.; Butts, C.P.; Bifulco, G. Quantitative NMR-derived interproton distances combined with quantum mechanical calculations of 13C chemical shifts in the stereochemical determination of conicasterol F, a nuclear receptor ligand from Theonella swinhoei. J. Org. Chem. 2012, 77, 1489–1496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Marino, S.; Sepe, V.; D’Auria, M.V.; Bifulco, G.; Renga, B.; Petek, S.; Fiorucci, S.; Zampella, A. Towards new ligands of nuclear receptors. Discovery of malaitasterol A, an unique bis-secosterol from marine sponge Theonella swinhoei. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2011, 9, 4856–4862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Marino, S.; Ummarino, R.; D’Auria, M.V.; Chini, M.G.; Bifulco, G.; Renga, B.; D’Amore, C.; Fiorucci, S.; Debitus, C.; Zampella, A. Theonellasterols and conicasterols from Theonella swinhoei. Novel marine natural ligands for human nuclear receptors. J. Med. Chem. 2011, 54, 3065–3075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Marino, S.; Ummarino, R.; D’Auria, M.V.; Chini, M.G.; Bifulco, G.; D’Amore, C.; Renga, B.; Mencarelli, A.; Petek, S.; Fiorucci, S. 4-Methylenesterols from Theonella swinhoei sponge are natural pregnane-X-receptor agonists and farnesoid-X-receptor antagonists that modulate innate immunity. Steroids 2012, 77, 484–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Festa, C.; D’Amore, C.; Renga, B.; Lauro, G.; De Marino, S.; D’Auria, M.V.; Bifulco, G.; Zampella, A.; Fiorucci, S. Oxygenated polyketides from Plakinastrella mamillaris as a new chemotype of PXR agonists. Mar. Drugs 2013, 11, 2314–2327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sepe, V.; Ummarino, R.; D’Auria, M.V.; Chini, M.G.; Bifulco, G.; Renga, B.; D’Amore, C.; Debitus, C.; Fiorucci, S.; Zampella, A. Conicasterol E, a small heterodimer partner sparing farnesoid X receptor modulator endowed with a pregnane X receptor agonistic activity, from the marine sponge Theonella swinhoe. J. Med. Chem. 2012, 55, 84–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Festa, C.; De Marino, S.; D’Auria, M.V.; Bifulco, G.; Renga, B.; Fiorucci, S.; Petek, S.; Zampella, A. Solomonsterols A and B from Theonella swinhoei. The first example of C-24 and C-23 sulfated sterols from a marine source endowed with a PXR agonistic activity. J. Med. Chem. 2011, 54, 401–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sepe, V.; Ummarino, R.; D’Auria, M.V.; Lauro, G.; Bifulco, G.; D’Amore, C.; Renga, B.; Fiorucci, S.; Zampella, A. Modification in the side chain of solomonsterol A: discovery of cholestan disulfate as a potent pregnane-X-receptor agonist. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2012, 10, 6350–6362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sepe, V.; Ummarino, R.; D’Auria, M.V.; Mencarelli, A.; D’Amore, C.; Renga, B.; Zampella, A.; Fiorucci, S. Total synthesis and pharmacological characterization of solomonsterol A, a potent marine pregnane-X-receptor agonist endowed with anti-inflammatory activity. J. Med. Chem. 2011, 54, 4590–4599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Firestein, G.S.; Zvaifler, N.J. How important are T cells in chronic rheumatoid synovitis? Arthritis Rheum. 1990, 33, 768–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Firestein, G.S. Evolving concepts of rheumatoid arthritis. Nature 2003, 423, 356–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Z.; Boyle, D.L.; Manning, A.M.; Firestein, G.S. AP-1 and NF-kappaB regulation in rheumatoid arthritis and murine collagen-induced arthritis. Autoimmunity 1998, 28, 197–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitamura, M.; Nakano, N.; Yonekawa, T.; Shan, L.; Kaise, T.; Kobayashi, T.; Yamashita, K.; Kikkawa, H.; Kinoshita, M. T cells are involved in the development of arthritis induced by anti-type II collagen antibody. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2007, 7, 1360–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins-Racie, L.A.; Yang, Z.; Arai, M.; Li, N.; Majumdar, M.K.; Nagpal, S.; Mounts, M.W.; Dorner, A.J.; Morris, E.; LaVallie, E.R. Global analysis of nuclear receptor expression and dysregulation in human osteoarthritic articular cartilage: Reduced LXR signaling contributes to catabolic metabolism typical of osteoarthritis. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2009, 17, 832–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olszewski, W.L.; Pazdur, J.; Kubasiewicz, E.; Zaleska, M.; Cooke, C.J.; Miller, N.E. Lymph draining from foot joints in rheumatoid arthritis provides insight into local cytokine and chemokine production and transport to lymph nodes. Arthritis Rheum. 2001, 44, 541–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.; Shah, Y.M.; Ma, X.; Pang, X.; Tanaka, T.; Kodama, T.; Krausz, K.W.; Gonzalez, F.J. Therapeutic role of rifaximin in inflammatory bowel disease: Clinical implication of human pregnane X receptor activation. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2010, 335, 32–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bender, A.T.; Spyvee, M.; Satoh, T.; Gershman, B.; Teceno, T.; Burgess, L.; Kumar, V.; Wu, Y.; Yang, H.; Ding, Y.; et al. Evaluation of a candidate anti-arthritic drug using the mouse collagen antibody induced arthritis model and clinically relevant biomarkers. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2013, 5, 92–102. [Google Scholar]
- Bevaart, L.; Vervoordeldonk, M.J.; Tak, P.P. Evaluation of therapeutic targets in animal models of arthritis: how does it relate to rheumatoid arthritis? Arthritis Rheum. 2010, 62, 2192–2205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, Y.G.; Cho, M.L.; Min, S.Y.; Kim, H.Y. Type II collagen autoimmunity in a mouse model of human rheumatoid arthritis. Autoimmun. Rev. 2007, 7, 65–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Primer3. Available online: http://frodo.wi.mit.edu/primer3/ (accessed on 16 November 2011).
- Chen, Y.; Tang, Y.; Guo, C.; Wang, J.; Boral, D.; Nie, D. Nuclear receptors in the multidrug resistance through the regulation of drug-metabolizing enzymes and drug transporters. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2012, 83, 1112–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dring, M.M.; Goulding, C.A.; Trimble, V.I.; Keegan, D.; Ryan, A.W.; Brophy, K.M.; Smyth, C.M.; Keeling, P.W.; O’Donoghue, D.; O’Suliivan, M.; et al. The pregnane X receptor locus is associated with susceptibility to inflammatory bowel disease. Gastroenterology 2006, 130, 341–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, F.; Apetoh, L.; Ghiringhelli, F. Controversies on the role of Th17 in cancer: a TGF-β-dependent immunosuppressive activity? Trends Mol. Med. 2012, 18, 742–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2013 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Mencarelli, A.; D'Amore, C.; Renga, B.; Cipriani, S.; Carino, A.; Sepe, V.; Perissutti, E.; D'Auria, M.V.; Zampella, A.; Distrutti, E.; et al. Solomonsterol A, a Marine Pregnane-X-Receptor Agonist, Attenuates Inflammation and Immune Dysfunction in a Mouse Model of Arthritis. Mar. Drugs 2014, 12, 36-53. https://doi.org/10.3390/md12010036
Mencarelli A, D'Amore C, Renga B, Cipriani S, Carino A, Sepe V, Perissutti E, D'Auria MV, Zampella A, Distrutti E, et al. Solomonsterol A, a Marine Pregnane-X-Receptor Agonist, Attenuates Inflammation and Immune Dysfunction in a Mouse Model of Arthritis. Marine Drugs. 2014; 12(1):36-53. https://doi.org/10.3390/md12010036
Chicago/Turabian StyleMencarelli, Andrea, Claudio D'Amore, Barbara Renga, Sabrina Cipriani, Adriana Carino, Valentina Sepe, Elisa Perissutti, Maria Valeria D'Auria, Angela Zampella, Eleonora Distrutti, and et al. 2014. "Solomonsterol A, a Marine Pregnane-X-Receptor Agonist, Attenuates Inflammation and Immune Dysfunction in a Mouse Model of Arthritis" Marine Drugs 12, no. 1: 36-53. https://doi.org/10.3390/md12010036
APA StyleMencarelli, A., D'Amore, C., Renga, B., Cipriani, S., Carino, A., Sepe, V., Perissutti, E., D'Auria, M. V., Zampella, A., Distrutti, E., & Fiorucci, S. (2014). Solomonsterol A, a Marine Pregnane-X-Receptor Agonist, Attenuates Inflammation and Immune Dysfunction in a Mouse Model of Arthritis. Marine Drugs, 12(1), 36-53. https://doi.org/10.3390/md12010036